Deck 8: Economic Growth I: Capital Accumulation and Population Growth
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Economic Growth I: Capital Accumulation and Population Growth
1
The Solow growth model describes:
A)how output is determined at a fixed point in time.
B)how output is determined with fixed amounts of capital and labour.
C)how saving, population growth, and technological change affect output over time.
D)the static allocation, production, and distribution of the economy's output.
A)how output is determined at a fixed point in time.
B)how output is determined with fixed amounts of capital and labour.
C)how saving, population growth, and technological change affect output over time.
D)the static allocation, production, and distribution of the economy's output.
how saving, population growth, and technological change affect output over time.
2
In the Solow growth model, the steady-state occurs when:
A)capital per worker is constant.
B)the saving rate equals the depreciation rate.
C)output per worker equals consumption per worker.
D)consumption per worker is maximized.
A)capital per worker is constant.
B)the saving rate equals the depreciation rate.
C)output per worker equals consumption per worker.
D)consumption per worker is maximized.
capital per worker is constant.
3
In the Solow growth model, investment equals:
A)output.
B)consumption.
C)the marginal product of capital.
D)saving.
A)output.
B)consumption.
C)the marginal product of capital.
D)saving.
saving.
4
Exhibit: Capital per Worker and the Steady State 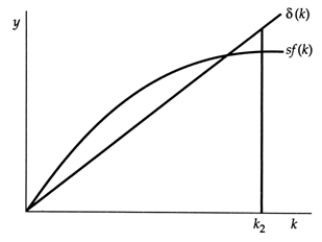 In this graph, capital-labour ratio k2 is not the steady-state because:
In this graph, capital-labour ratio k2 is not the steady-state because:
A)the saving rate is too high.
B)the investment ratio is too high.
C)gross investment is greater than depreciation.
D)depreciation is greater than gross investment.
 In this graph, capital-labour ratio k2 is not the steady-state because:
In this graph, capital-labour ratio k2 is not the steady-state because:A)the saving rate is too high.
B)the investment ratio is too high.
C)gross investment is greater than depreciation.
D)depreciation is greater than gross investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In the Solow growth model, where s is the saving rate, y is output per worker, and i is investment per worker, consumption per worker (c) equals:
A)sy
B)(1 - s) y
C)(1 + s) y
D)(1 - s) y - i
A)sy
B)(1 - s) y
C)(1 + s) y
D)(1 - s) y - i

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the Solow growth model, for any given capital stock, the _____ determines how much output the economy produces, and the _____ determines the allocation of output between consumption and investment.
A)saving rate; production function
B)depreciation rate; population growth rate
C)production function; saving rate
D)population growth rate; saving rate
A)saving rate; production function
B)depreciation rate; population growth rate
C)production function; saving rate
D)population growth rate; saving rate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Exhibit: Output, Consumption, and Investment 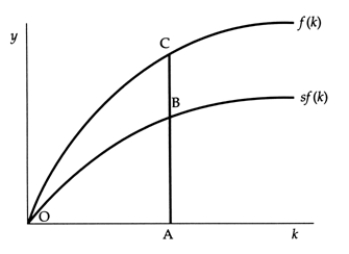 In this graph, when the capital stock per worker is OA, AB represents:
In this graph, when the capital stock per worker is OA, AB represents:
A)investment per worker, and AC represents consumption per worker.
B)consumption per worker, and AC represents investment per worker.
C)investment per worker, and BC represents consumption per worker.
D)consumption per worker, and BC represents investment per worker.
 In this graph, when the capital stock per worker is OA, AB represents:
In this graph, when the capital stock per worker is OA, AB represents:A)investment per worker, and AC represents consumption per worker.
B)consumption per worker, and AC represents investment per worker.
C)investment per worker, and BC represents consumption per worker.
D)consumption per worker, and BC represents investment per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Exhibit: Steady-State Capital-Labour Ratio  In this graph, the steady-state capital-labour ratio is:
In this graph, the steady-state capital-labour ratio is:
A)k0.
B)k1.
C)k2.
D)k3.
 In this graph, the steady-state capital-labour ratio is:
In this graph, the steady-state capital-labour ratio is:A)k0.
B)k1.
C)k2.
D)k3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In the Solow growth model the demand for goods equals investment:
A)minus depreciation.
B)plus saving.
C)plus consumption.
D)plus depreciation.
A)minus depreciation.
B)plus saving.
C)plus consumption.
D)plus depreciation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
In the Solow model, it is assumed that a(n) _____ fraction of capital wears out as the capital-labour ratio increases.
A)smaller
B)larger
C)constant
D)increasing
A)smaller
B)larger
C)constant
D)increasing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If the capital stock equals 200 units in year 1 and the depreciation rate is 5 percent per year, then in year 2, assuming no new or replacement investment, the capital stock would equal _____ units.
A)210
B)200
C)195
D)190
A)210
B)200
C)195
D)190

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In the Solow growth model of Chapter 8, the economy ends up with a steady-state level of capital:
A)only if it starts from a level of capital below the steady-state level.
B)only if it starts from a level of capital above the steady-state level.
C)only if it starts from a steady-state level of capital.
D)regardless of the starting level of capital.
A)only if it starts from a level of capital below the steady-state level.
B)only if it starts from a level of capital above the steady-state level.
C)only if it starts from a steady-state level of capital.
D)regardless of the starting level of capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
_____ cause(s) the capital stock to rise, while _____ cause(s) the capital stock to fall.
A)Inflation; deflation
B)Interest rates; the discount rate
C)Investment; depreciation
D)International trade; depressions
A)Inflation; deflation
B)Interest rates; the discount rate
C)Investment; depreciation
D)International trade; depressions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The consumption function in the Solow model assumes that society saves a:
A)constant proportion of income.
B)smaller proportion of income as it becomes richer.
C)larger proportion of income as it becomes richer.
D)larger proportion of income when the interest rate is higher.
A)constant proportion of income.
B)smaller proportion of income as it becomes richer.
C)larger proportion of income as it becomes richer.
D)larger proportion of income when the interest rate is higher.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The production function y = f (k) means:
A)labour is not a factor of production.
B)output per worker is a function of labour productivity.
C)output per worker is a function of capital per worker.
D)the production function exhibits increasing returns to scale.
A)labour is not a factor of production.
B)output per worker is a function of labour productivity.
C)output per worker is a function of capital per worker.
D)the production function exhibits increasing returns to scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The steady-state level of capital occurs when the change in the capital stock per worker (Δk) equals:
A)0.
B)the saving rate.
C)the depreciation rate.
D)the population growth rate.
A)0.
B)the saving rate.
C)the depreciation rate.
D)the population growth rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
When f (k) is drawn on a graph with increases in k noted along the horizontal axis, the slope of the curve denotes:
A)output per worker.
B)output per unit of capital.
C)the marginal product of labour.
D)the marginal product of capital.
A)output per worker.
B)output per unit of capital.
C)the marginal product of labour.
D)the marginal product of capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In the Solow growth model, the assumption of constant returns to scale means that:
A)all economies have the same amount of capital per worker.
B)the steady-state level of output is constant, regardless of the number of workers.
C)the saving rate equals the constant rate of depreciation.
D)the number of workers in an economy does not affect the relationship between output per worker and capital per worker.
A)all economies have the same amount of capital per worker.
B)the steady-state level of output is constant, regardless of the number of workers.
C)the saving rate equals the constant rate of depreciation.
D)the number of workers in an economy does not affect the relationship between output per worker and capital per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Two economies are identical except that the level of capital per worker is higher in Highland than in Lowland. The production functions in both economies exhibit diminishing marginal product of capital. An extra unit of capital per worker increases output per worker:
A)more in Highland.
B)more in Lowland.
C)by the same amount in Highland and Lowland.
D)in Highland but not in Lowland.
A)more in Highland.
B)more in Lowland.
C)by the same amount in Highland and Lowland.
D)in Highland but not in Lowland.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Investment per worker (i) as a function of the saving ratio (s) and output per worker (f (k)) may be expressed as:
A)s + f (k).
B)s - f (k).
C)sf (k).
D)s / f (k).
A)s + f (k).
B)s - f (k).
C)sf (k).
D)s / f (k).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Assume that two economies are identical in every way except that one has a higher saving rate. According to the Solow growth model, in the steady state the country with the higher saving rate will have _____ level of output per person and _____ rate of growth of output per worker compared to the country with the lower saving rate.
A)the same; the same
B)the same; a higher
C)a higher; the same
D)a higher; a higher
A)the same; the same
B)the same; a higher
C)a higher; the same
D)a higher; a higher

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Exhibit: The Capital-Labour Ratio 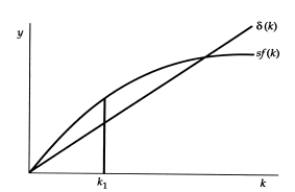 In this graph, starting from capital-labour ratio k1, the capital-labour ratio will:
In this graph, starting from capital-labour ratio k1, the capital-labour ratio will:
A)decrease.
B)remain constant.
C)increase.
D)first decrease and then remain constant.
 In this graph, starting from capital-labour ratio k1, the capital-labour ratio will:
In this graph, starting from capital-labour ratio k1, the capital-labour ratio will:A)decrease.
B)remain constant.
C)increase.
D)first decrease and then remain constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If the per-worker production function is given by y = k1/2, the saving rate (s) is 0.2, and the depreciation rate is 0.1, then the steady-state ratio of capital to labour is:
A)1.
B)2.
C)4.
D)9.
A)1.
B)2.
C)4.
D)9.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Exhibit: Steady-State Consumption II 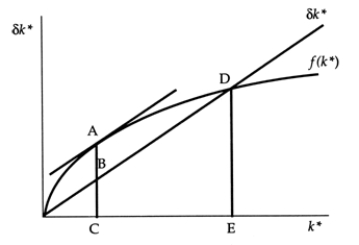 The Golden Rule level of steady-state investment per worker is:
The Golden Rule level of steady-state investment per worker is:
A)AC.
B)AB.
C)BC.
D)DE.
 The Golden Rule level of steady-state investment per worker is:
The Golden Rule level of steady-state investment per worker is:A)AC.
B)AB.
C)BC.
D)DE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If the per-worker production function is given by y = k1/2, the saving ratio is 0.3, and the depreciation rate is 0.1, then the steady-state ratio of capital to labour is:
A)1.
B)2.
C)4.
D)9.
A)1.
B)2.
C)4.
D)9.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If a war destroys a large portion of a country's capital stock but the saving rate is unchanged, the Solow model predicts that output will grow and that the new steady state will approach:
A)a higher level of output per person than before.
B)the same level of output per person as before.
C)a lower level of output per person than before.
D)the Golden Rule level of output per person.
A)a higher level of output per person than before.
B)the same level of output per person as before.
C)a lower level of output per person than before.
D)the Golden Rule level of output per person.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A higher saving rate leads to a:
A)higher rate of economic growth in both the short run and the long run.
B)higher rate of economic growth only in the long run.
C)higher rate of economic growth in the short run but a decline in the long run.
D)larger capital stock and a higher level of output in the long run.
A)higher rate of economic growth in both the short run and the long run.
B)higher rate of economic growth only in the long run.
C)higher rate of economic growth in the short run but a decline in the long run.
D)larger capital stock and a higher level of output in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
In an economy with no population growth and no technological change, steady-state consumption is at its greatest possible level when the marginal product of:
A)labour equals the marginal product of capital.
B)labour equals the depreciation rate.
C)capital equals the depreciation rate.
D)capital equals zero.
A)labour equals the marginal product of capital.
B)labour equals the depreciation rate.
C)capital equals the depreciation rate.
D)capital equals zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Exhibit: Steady-State Consumption II 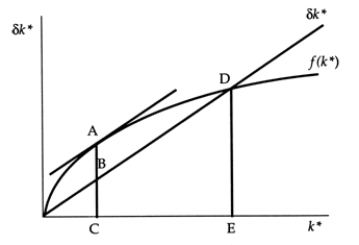 The Golden Rule level of steady-state consumption per worker is:
The Golden Rule level of steady-state consumption per worker is:
A)AC.
B)AB.
C)BC.
D)DE.
 The Golden Rule level of steady-state consumption per worker is:
The Golden Rule level of steady-state consumption per worker is:A)AC.
B)AB.
C)BC.
D)DE.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
If the saving rate increases, the:
A)economy will grow at a faster rate forever.
B)capital-labour ratio will increase forever.
C)economy will grow at a faster rate until a new, higher, steady-state capital-labour ratio is reached.
D)capital-labour ratio will eventually decline.
A)economy will grow at a faster rate forever.
B)capital-labour ratio will increase forever.
C)economy will grow at a faster rate until a new, higher, steady-state capital-labour ratio is reached.
D)capital-labour ratio will eventually decline.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The formula for steady-state consumption per worker (c*) as a function of output per worker and investment per worker is:
A)c* = f (k*) - δk*.
B)c* = f (k*) + δk*.
C)c* = f (k*) ÷ δk*.
D)c* = k* - δf (k)*.
A)c* = f (k*) - δk*.
B)c* = f (k*) + δk*.
C)c* = f (k*) ÷ δk*.
D)c* = k* - δf (k)*.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The Golden Rule level of capital accumulation is the steady state with the highest level of:
A)output per worker.
B)capital per worker.
C)savings per worker.
D)consumption per worker.
A)output per worker.
B)capital per worker.
C)savings per worker.
D)consumption per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If an economy with no population growth or technological change has a steady-state MPK of 0.125, a depreciation rate of 0.1, and a saving rate of 0.225, then the steady-state capital stock:
A)is greater than the Golden Rule level.
B)is less than the Golden Rule level.
C)equals the Golden Rule level.
D)could be either above or below the Golden Rule level.
A)is greater than the Golden Rule level.
B)is less than the Golden Rule level.
C)equals the Golden Rule level.
D)could be either above or below the Golden Rule level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Exhibit: Steady-State Consumption I 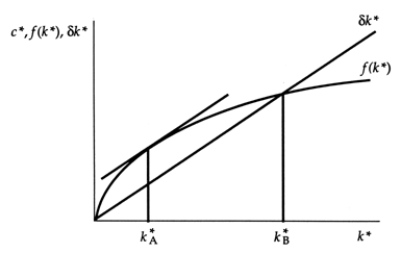 The Golden Rule level of the capital-labour ratio is:
The Golden Rule level of the capital-labour ratio is:
A)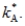
B)above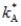 but below
but below 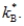
C)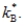
D)above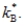
 The Golden Rule level of the capital-labour ratio is:
The Golden Rule level of the capital-labour ratio is:A)
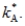
B)above
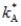 but below
but below 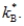
C)
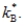
D)above
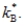

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
In the Solow growth model, if investment exceeds depreciation, the capital stock will ______, and output will ______ until the steady state is attained.
A)increase; increase
B)increase; decrease
C)decrease; decrease
D)decrease; increase
A)increase; increase
B)increase; decrease
C)decrease; decrease
D)decrease; increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Examination of recent data for many countries shows that countries with high saving rates generally have high levels of output per person because:
A)high saving rates mean permanently higher growth rates of output.
B)high saving rates lead to high levels of capital per worker.
C)countries with high levels of output per worker can afford to save a lot.
D)countries with large amounts of natural resources have both high output levels and high saving rates.
A)high saving rates mean permanently higher growth rates of output.
B)high saving rates lead to high levels of capital per worker.
C)countries with high levels of output per worker can afford to save a lot.
D)countries with large amounts of natural resources have both high output levels and high saving rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Starting from a steady-state situation, if the saving rate increases, capital per worker will:
A)increase and continue to increase unabated.
B)increase until the new steady state is reached.
C)decrease until the new steady state is reached.
D)decrease and continue to decrease unabated.
A)increase and continue to increase unabated.
B)increase until the new steady state is reached.
C)decrease until the new steady state is reached.
D)decrease and continue to decrease unabated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The Solow model shows that a key determinant of the steady-state ratio of capital to labour is the:
A)level of output.
B)labour force.
C)saving rate.
D)capital elasticity in the production function.
A)level of output.
B)labour force.
C)saving rate.
D)capital elasticity in the production function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If an economy is in a steady state with no population growth or technological change and the marginal product of capital is less than the depreciation rate:
A)the economy is following the Golden Rule.
B)steady-state consumption per worker would be higher in a steady state with a lower saving rate.
C)steady-state consumption per worker would be higher in a steady state with a higher saving rate.
D)the depreciation rate should be decreased to achieve the Golden Rule level of consumption per worker.
A)the economy is following the Golden Rule.
B)steady-state consumption per worker would be higher in a steady state with a lower saving rate.
C)steady-state consumption per worker would be higher in a steady state with a higher saving rate.
D)the depreciation rate should be decreased to achieve the Golden Rule level of consumption per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In the Solow growth model, increases in capital _____ output and _____ the amount of output used to replace depreciating capital.
A)increase; increase
B)increase; decrease
C)decrease; increase
D)decrease; decrease
A)increase; increase
B)increase; decrease
C)decrease; increase
D)decrease; decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In an economy with population growth at rate n, the change in capital stock per worker is given by the equation:
A)Δk = sf (k) + δk.
B)Δk = sf (k) - δk.
C)Δk = sf (k) + (δ + n) k.
D)Δk = sf (k) - (δ + n) k.
A)Δk = sf (k) + δk.
B)Δk = sf (k) - δk.
C)Δk = sf (k) + (δ + n) k.
D)Δk = sf (k) - (δ + n) k.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Suppose an economy is initially in a steady state with capital per worker below the Golden Rule level. If the saving rate increases to a rate consistent with the Golden Rule, then in the transition to the new steady state consumption per worker will:
A)always exceed the initial level.
B)first fall below and then rise above the initial level.
C)first rise above and then fall below the initial level.
D)always be lower than the initial level.
A)always exceed the initial level.
B)first fall below and then rise above the initial level.
C)first rise above and then fall below the initial level.
D)always be lower than the initial level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
With a per-worker production function y = k1/2, the steady-state capital stock per worker (k*) as a function of the saving rate (s) is given by:
A)k* = (s / δ)2.
B)k* = (δ / s)2.
C)k* = s / δ.
D)k* = δ / s.
A)k* = (s / δ)2.
B)k* = (δ / s)2.
C)k* = s / δ.
D)k* = δ / s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
When an economy begins above the Golden Rule level, reaching the Golden Rule level:
A)results in lower consumption at all times in the future.
B)results in higher consumption at all times in the future.
C)requires initially reducing consumption to increase consumption in the future.
D)requires initially increasing consumption to decrease consumption in the future.
A)results in lower consumption at all times in the future.
B)results in higher consumption at all times in the future.
C)requires initially reducing consumption to increase consumption in the future.
D)requires initially increasing consumption to decrease consumption in the future.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In the Solow growth model with population growth but no technological progress, the steady-state amount of investment can be thought of as a break-even amount of investment because the quantity of investment just equals the amount of:
A)output needed to achieve the maximum level of consumption per worker.
B)capital needed to replace depreciated capital and to equip new workers.
C)saving needed to achieve the maximum level of output per worker.
D)output needed to make the capital per worker ratio equal to the marginal product of capital.
A)output needed to achieve the maximum level of consumption per worker.
B)capital needed to replace depreciated capital and to equip new workers.
C)saving needed to achieve the maximum level of output per worker.
D)output needed to make the capital per worker ratio equal to the marginal product of capital.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
In the Solow growth model, an economy in the steady state with a population growth rate of n but no technological growth will exhibit a growth rate of output per worker at rate:
A)0.
B)n.
C)δ.
D)(n + δ).
A)0.
B)n.
C)δ.
D)(n + δ).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
When an economy's capital is below the Golden Rule level, reaching the Golden Rule level:
A)produces lower consumption at all times in the future.
B)requires higher consumption levels at all times.
C)requires initially reducing consumption to increase consumption in the future.
D)requires initially increasing consumption to decrease consumption in the future.
A)produces lower consumption at all times in the future.
B)requires higher consumption levels at all times.
C)requires initially reducing consumption to increase consumption in the future.
D)requires initially increasing consumption to decrease consumption in the future.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In the Solow growth model of an economy with population growth but no technological change, the break-even level of investment must do all of the following except:
A)offset the depreciation of existing capital.
B)provide capital for new workers.
C)equal the marginal productivity of capital (MPK).
D)keep the level of capital per worker constant.
A)offset the depreciation of existing capital.
B)provide capital for new workers.
C)equal the marginal productivity of capital (MPK).
D)keep the level of capital per worker constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Suppose an economy is initially in a steady state with capital per worker exceeding the Golden Rule level. If the saving rate falls to a rate consistent with the Golden Rule, then in the transition to the new steady state, consumption per worker will:
A)always exceed the initial level.
B)first fall below then rise above the initial level.
C)first rise above then fall below the initial level.
D)always be lower than the initial level.
A)always exceed the initial level.
B)first fall below then rise above the initial level.
C)first rise above then fall below the initial level.
D)always be lower than the initial level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
To determine whether an economy is operating at its Golden Rule level of capital stock, a policymaker must determine the steady-state saving rate that produces the:
A)largest MPK.
B)smallest depreciation rate.
C)largest consumption per worker.
D)largest output per worker.
A)largest MPK.
B)smallest depreciation rate.
C)largest consumption per worker.
D)largest output per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In the Solow growth model, an economy in the steady state with a population growth rate of n but no technological growth will exhibit a growth rate of total output at rate:
A)0.
B)n.
C)δ.
D)(n + δ).
A)0.
B)n.
C)δ.
D)(n + δ).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In the Solow growth model of an economy with population growth but no technological change, if population grows at rate n, then capital in the steady state grows at rate _____, and output grows at rate _____ in the steady state.
A)n; n
B)n; 0
C)0; 0
D)0; n
A)n; n
B)n; 0
C)0; 0
D)0; n

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Suppose that an economy is in its steady state and the capital stock is above the Golden Rule level. Assuming that there are no population growth or technological change, if the saving rate falls:
A)output, consumption, investment, and depreciation will all decrease.
B)output and investment will decrease, and consumption and depreciation will increase.
C)output and investment will decrease, and consumption and depreciation will increase and then decrease but finally approach levels above their initial state.
D)output, investment, and depreciation will decrease, and consumption will increase and then decrease but finally approach a level above its initial state.
A)output, consumption, investment, and depreciation will all decrease.
B)output and investment will decrease, and consumption and depreciation will increase.
C)output and investment will decrease, and consumption and depreciation will increase and then decrease but finally approach levels above their initial state.
D)output, investment, and depreciation will decrease, and consumption will increase and then decrease but finally approach a level above its initial state.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
In the Solow growth model, if two countries are otherwise identical (with the same production function, same saving rate, same depreciation rate, and same rate of population growth) except that Country Large has a population of 1 billion workers and Country Small has a population of 10 million workers, the steady-state level of output per worker will be _____, and the steady-state growth rate of output per worker will be _____.
A)the same in both countries; the same in both countries
B)higher in Country Large; higher in Country Large
C)higher in Country Small; higher in Country Small
D)higher in Country Large; higher in Country Small
A)the same in both countries; the same in both countries
B)higher in Country Large; higher in Country Large
C)higher in Country Small; higher in Country Small
D)higher in Country Large; higher in Country Small

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A reduction in the saving rate starting from a steady state with more capital than the Golden Rule causes investment to _____ in the transition to the new steady state.
A)increase
B)decrease
C)first increase and then decrease
D)first decrease and then increase
A)increase
B)decrease
C)first increase and then decrease
D)first decrease and then increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Assume that two economies are identical in every way except that one has a higher population growth rate. According to the Solow growth model, in the steady state, the country with the higher population growth rate will have a _____ level of output per person and _____ rate of growth of output per worker compared to the country with the lower population growth rate.
A)higher; the same
B)higher; a higher
C)lower; the same
D)lower; a lower
A)higher; the same
B)higher; a higher
C)lower; the same
D)lower; a lower

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
If an economy is in a steady state with a saving rate below the Golden Rule level, efforts to increase the saving rate result in:
A)both higher per-capita output and higher per-capita depreciation, but the increase in per-capita output would be greater.
B)both higher per-capita output and higher per-capita depreciation, but the increase in per-capita depreciation would be greater.
C)higher per-capita output and lower per-capita depreciation.
D)lower per-capita output and higher per-capita depreciation.
A)both higher per-capita output and higher per-capita depreciation, but the increase in per-capita output would be greater.
B)both higher per-capita output and higher per-capita depreciation, but the increase in per-capita depreciation would be greater.
C)higher per-capita output and lower per-capita depreciation.
D)lower per-capita output and higher per-capita depreciation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The formula for the steady-state ratio of capital to labour (k*) with population growth at rate n but no technological change, where s is the saving rate, is s:
A)divided by the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
B)multiplied by the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
C)divided by the product of f (k*) and the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
D)multiplied by f (k*) divided by the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
A)divided by the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
B)multiplied by the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
C)divided by the product of f (k*) and the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.
D)multiplied by f (k*) divided by the sum of the depreciation rate plus n.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
In the Solow growth model of an economy with population growth but no technological change, if population grows at rate n, total output in the steady state grows at rate _____, and output per worker grows at rate _____ in the steady state.
A)n; n
B)n; 0
C)0; 0
D)0; n
A)n; n
B)n; 0
C)0; 0
D)0; n

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
An increase in the saving rate starting from a steady state with less capital than the Golden Rule causes investment to _____ in the transition to the new steady state.
A)increase
B)decrease
C)first increase and then decrease
D)first decrease and then increase
A)increase
B)decrease
C)first increase and then decrease
D)first decrease and then increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In the Solow growth model with population growth but no technological progress, if in the steady state the marginal product of capital equals 0.10, the depreciation rate equals 0.05, and the rate of population growth equals 0.03, then the capital per worker ratio _____ the Golden Rule level.
A)is above
B)is below
C)is equal to
D)will move to
A)is above
B)is below
C)is equal to
D)will move to

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If Y = K0.3L0.7, then the per-worker production function is:
A)Y = F(K / L).
B)Y / L = (K / L)0.3.
C)Y / L = (K / L)0.5.
D)Y / L = (K / L)0.7.
A)Y = F(K / L).
B)Y / L = (K / L)0.3.
C)Y / L = (K / L)0.5.
D)Y / L = (K / L)0.7.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
According to the Kremerian model, large populations improve living standards because:
A)crowded conditions put more pressure on people to work hard.
B)there are more people who can make discoveries and contribute to innovation.
C)more people have the opportunity for leisure and recreation.
D)most people prefer to live with many other people.
A)crowded conditions put more pressure on people to work hard.
B)there are more people who can make discoveries and contribute to innovation.
C)more people have the opportunity for leisure and recreation.
D)most people prefer to live with many other people.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Analysis of population growth around the world concludes that countries with high population growth tend to:
A)have high income per worker.
B)have a lower level of income per worker than countries with low population growth.
C)have the same standard of living as other parts of the world.
D)tend to be the high-income-producing nations of the world.
A)have high income per worker.
B)have a lower level of income per worker than countries with low population growth.
C)have the same standard of living as other parts of the world.
D)tend to be the high-income-producing nations of the world.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
If the Canadian production function is Cobb-Douglas with capital share 0.3, output growth is 3 percent per year, depreciation is 4 percent per year, and the Golden Rule steady-state capital-output ratio is 4.29, to reach the Golden Rule steady state, the saving rate must be:
A)17.5 percent.
B)25 percent.
C)30 percent.
D)42.9 percent.
A)17.5 percent.
B)25 percent.
C)30 percent.
D)42.9 percent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Assume that a war reduces a country's labour force but does not directly affect its capital stock. Then the immediate impact will be that:
A)total output will fall, but output per worker will rise.
B)total output will rise, but output per worker will fall.
C)both total output and output per worker will fall.
D)both total output and output per worker will rise.
A)total output will fall, but output per worker will rise.
B)total output will rise, but output per worker will fall.
C)both total output and output per worker will fall.
D)both total output and output per worker will rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
If y = k1/2, there is no population growth or technological progress, 5 percent of capital depreciates each year, and a country saves 20 percent of output each year, then the steady-state level of capital per worker is:
A)2.
B)4.
C)8.
D)16.
A)2.
B)4.
C)8.
D)16.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Assume that a country's production function is Y = K1/2L1/2 and there is no population growth or technological change.
a.What is the per-worker production function y = f(k)?
b.Assume that the country possesses 40,000 units of capital and 10,000 units of labour. What is Y? What is labour productivity computed from the per-worker production function? Is this value the same as labour productivity computed from the original production function?
c.Assume that 10 percent of capital depreciates each year. What gross saving rate is necessary to make the given capital-labour ratio the steady-state capital-labour ratio?
a.What is the per-worker production function y = f(k)?
b.Assume that the country possesses 40,000 units of capital and 10,000 units of labour. What is Y? What is labour productivity computed from the per-worker production function? Is this value the same as labour productivity computed from the original production function?
c.Assume that 10 percent of capital depreciates each year. What gross saving rate is necessary to make the given capital-labour ratio the steady-state capital-labour ratio?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
In the Solow growth model, with a given production function, depreciation rate, saving rate, and no technological change, higher rates of population growth produce:
A)higher steady-state ratios of capital per worker.
B)higher steady-state growth rates of output per worker.
C)higher steady-state growth rates of total output.
D)higher steady-state levels of output per worker.
A)higher steady-state ratios of capital per worker.
B)higher steady-state growth rates of output per worker.
C)higher steady-state growth rates of total output.
D)higher steady-state levels of output per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
If an economy moves from a steady state with positive population growth to a zero population growth rate, then in the new steady state, total output growth will be _____, and growth of output per person will be _____.
A)lower; lower
B)lower; the same as it was before
C)higher; higher than it was before
D)higher; lower
A)lower; lower
B)lower; the same as it was before
C)higher; higher than it was before
D)higher; lower

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
In the Solow growth model, the steady state level of output per worker would be higher if the _____ increased or the _____ decreased.
A)saving rate; depreciation rate
B)population growth rate; depreciation rate
C)depreciation rate; population growth rate
D)population growth rate; saving rate
A)saving rate; depreciation rate
B)population growth rate; depreciation rate
C)depreciation rate; population growth rate
D)population growth rate; saving rate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
An increase in the rate of population growth with no change in the saving rate:
A)increases the steady-state level of capital per worker.
B)decreases the steady-state level of capital per worker.
C)does not affect the steady-state level of capital per worker.
D)decreases the rate of output growth in the short run.
A)increases the steady-state level of capital per worker.
B)decreases the steady-state level of capital per worker.
C)does not affect the steady-state level of capital per worker.
D)decreases the rate of output growth in the short run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
According to Michael Kremer, large populations:
A)require the capital stock to be spread thinly, thereby reducing living standards.
B)place great strains on an economy's productive resources, resulting in perpetual poverty.
C)are a prerequisite for technological advances and higher living standards.
D)are not a factor in determining living standards.
A)require the capital stock to be spread thinly, thereby reducing living standards.
B)place great strains on an economy's productive resources, resulting in perpetual poverty.
C)are a prerequisite for technological advances and higher living standards.
D)are not a factor in determining living standards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
In the Solow growth model with population growth but no technological progress, when the economy finds itself at the Golden Rule steady state, the marginal product of capital minus the rate of depreciation will equal:
A)0.
B)the population growth rate.
C)the saving rate.
D)output per worker.
A)0.
B)the population growth rate.
C)the saving rate.
D)output per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Assume that two countries both have the per-worker production function y = k1/2, neither has population growth or technological progress, depreciation is 5 percent of capital in both countries, and country A saves 10 percent of output whereas country B saves 20 percent. If country A starts out with a capital-labour ratio of 4 and country B starts out with a capital-labour ratio of 2, in the long run:
A)both country A and country B will have capital-labour ratios of 4.
B)both country A and country B will have capital-labour ratios of 16.
C)country A's capital-labour ratio will be 4, whereas country B's will be 16.
D)country A's capital-labour ratio will be 16, whereas country B's will be 4.
A)both country A and country B will have capital-labour ratios of 4.
B)both country A and country B will have capital-labour ratios of 16.
C)country A's capital-labour ratio will be 4, whereas country B's will be 16.
D)country A's capital-labour ratio will be 16, whereas country B's will be 4.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
In the Solow growth model with population growth but no technological change, which of the following will generate a higher steady-state growth rate of total output?
A)a higher saving rate
B)a lower depreciation rate
C)a higher population growth rate
D)a higher capital per worker ratio
A)a higher saving rate
B)a lower depreciation rate
C)a higher population growth rate
D)a higher capital per worker ratio

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Assume that a war reduces a country's labour force but does not directly affect its capital stock. If the economy was in a steady state before the war and the saving rate does not change after the war, then, over time, capital per worker will _____, and output per worker will _____ as it returns to the steady state.
A)decline; increase
B)increase; increase
C)decline; decrease
D)increase; decrease
A)decline; increase
B)increase; increase
C)decline; decrease
D)increase; decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
If the production function exhibits increasing returns to scale in the steady state, an increase in the rate of growth of population would lead to:
A)growth in total output and growth in output per worker.
B)growth in total output but no growth in output per worker.
C)growth in total output but a decrease in output per worker.
D)no growth in total output or in output per worker.
A)growth in total output and growth in output per worker.
B)growth in total output but no growth in output per worker.
C)growth in total output but a decrease in output per worker.
D)no growth in total output or in output per worker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
If y = k1/2, the country saves 10 percent of its output each year, and the steady-state level of capital per worker is 4, then the steady-state levels of output per worker and consumption per worker are:
A)2 and 1.6, respectively.
B)2 and 1.8, respectively.
C)4 and 3.2, respectively.
D)4 and 3.6, respectively.
A)2 and 1.6, respectively.
B)2 and 1.8, respectively.
C)4 and 3.2, respectively.
D)4 and 3.6, respectively.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
According to Thomas Malthus, large populations:
A)require the capital stock to be spread thinly, thereby reducing living standards.
B)place great strains on an economy's productive resources, resulting in perpetual poverty.
C)are a prerequisite for technological advances and higher living standards.
D)are not a factor in determining living standards.
A)require the capital stock to be spread thinly, thereby reducing living standards.
B)place great strains on an economy's productive resources, resulting in perpetual poverty.
C)are a prerequisite for technological advances and higher living standards.
D)are not a factor in determining living standards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 99 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








