Deck 5: E Asticity and Its Application
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: E Asticity and Its Application
1
For each of the following pairs of goods, which good would you expect to have more elastic demand and why?
a. required textbooks or mystery novels
b. Beethoven recordings or classical music recordings in general
c. subway rides during the next six months or subway rides during the next five years
d. root beer or water
a. required textbooks or mystery novels
b. Beethoven recordings or classical music recordings in general
c. subway rides during the next six months or subway rides during the next five years
d. root beer or water
Elasticity of demand is defined as the increase or decrease on the demand of a good due to the change in the price of the good.
Demand is said to be elastic if demand changes a lot when the prices changes.
(a)Required textbooks are a necessity and have no close substitutes. Thus, the demand for textbooks is inelastic.
Mystery novels have close substitutes. Thus, their demand is elastic.
Therefore, Mystery Novels have more elastic demand.
(b)Beethoven recordings have more elastic demand than classical music recordings in general. Beethoven recordings are a narrower market than classical music recordings, so it is easy to find close substitutes for them.
Therefore, Beethoven recordings have more elastic demand.
(c)Subway rides during the next five years have more elastic demand than subway rides during the next six months. This is because goods tend to have more elastic demand over longer time horizons and inelastic demand over shorter time horizons.
Therefore, Subway rides have more elastic demand.
(d)Root beer has more elastic demand than water. Root beer is a luxury with close
substitutes, while water is a necessity with no close substitutes.
Therefore, root beer have more elastic demand.
Demand is said to be elastic if demand changes a lot when the prices changes.
(a)Required textbooks are a necessity and have no close substitutes. Thus, the demand for textbooks is inelastic.
Mystery novels have close substitutes. Thus, their demand is elastic.
Therefore, Mystery Novels have more elastic demand.
(b)Beethoven recordings have more elastic demand than classical music recordings in general. Beethoven recordings are a narrower market than classical music recordings, so it is easy to find close substitutes for them.
Therefore, Beethoven recordings have more elastic demand.
(c)Subway rides during the next five years have more elastic demand than subway rides during the next six months. This is because goods tend to have more elastic demand over longer time horizons and inelastic demand over shorter time horizons.
Therefore, Subway rides have more elastic demand.
(d)Root beer has more elastic demand than water. Root beer is a luxury with close
substitutes, while water is a necessity with no close substitutes.
Therefore, root beer have more elastic demand.
2
Define the price elasticity of demand and the income elasticity of demand.
Price Elasticity of Demand
The price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds to a change in price.
The price elasticity of demand for any good measures how willing consumers are to move away from the good as its price rises. Thus, the elasticity shows the many economic, social and psychological forces that shape consumer tastes.
The price elasticity of demand is computed as follows.
Price elasticity of demand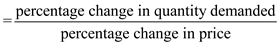 Demand for a good is said to be elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price. Demand is said to be inelastic if the quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price.
Demand for a good is said to be elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price. Demand is said to be inelastic if the quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price.
Income Elasticity of Demand
The income elasticity of demand measures how the quantity demand changes as consumer income changes. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. That is,
Income elasticity of demand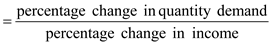
The price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds to a change in price.
The price elasticity of demand for any good measures how willing consumers are to move away from the good as its price rises. Thus, the elasticity shows the many economic, social and psychological forces that shape consumer tastes.
The price elasticity of demand is computed as follows.
Price elasticity of demand
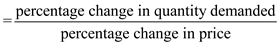 Demand for a good is said to be elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price. Demand is said to be inelastic if the quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price.
Demand for a good is said to be elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price. Demand is said to be inelastic if the quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price.Income Elasticity of Demand
The income elasticity of demand measures how the quantity demand changes as consumer income changes. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. That is,
Income elasticity of demand
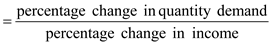
3
Suppose that business travelers and vacationers have the following demand for airline tickets from New York to Boston:
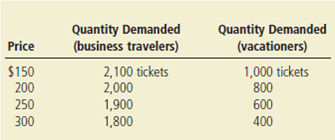
a. As the price of tickets rises from $200 to $250, what is the price elasticity of demand for (i) business travelers and (ii) vacationers? (Use the midpoint method in your calculations.)
b. Why might vacationers have a different elasticity from business travelers?

a. As the price of tickets rises from $200 to $250, what is the price elasticity of demand for (i) business travelers and (ii) vacationers? (Use the midpoint method in your calculations.)
b. Why might vacationers have a different elasticity from business travelers?
(a) Price elasticity of demand (midpoint method) 
 For business travelers,
For business travelers,
When When
When  Price elasticity of demand for business travelers
Price elasticity of demand for business travelers 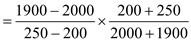
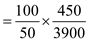 = 0.23
= 0.23
*Ignore the minus.
For vacationers ,
When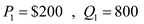 When
When 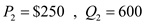 Price elasticity of demand for vacationers
Price elasticity of demand for vacationers 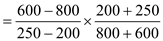
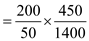 = 1.28
= 1.28
Elasticity is greater than one.
(b)The price elasticity of demand for vacationers is higher than the elasticity for business travelers because vacationers can choose a different mode of transportation (like driving or taking the train) more easily. Business travelers are less likely to do so because time is more important to them and their schedules are less flexible.

 For business travelers,
For business travelers, When
 When
When  Price elasticity of demand for business travelers
Price elasticity of demand for business travelers 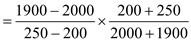
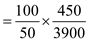 = 0.23
= 0.23*Ignore the minus.
For vacationers ,
When
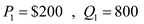 When
When 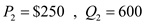 Price elasticity of demand for vacationers
Price elasticity of demand for vacationers 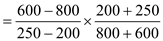
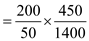 = 1.28
= 1.28Elasticity is greater than one.
(b)The price elasticity of demand for vacationers is higher than the elasticity for business travelers because vacationers can choose a different mode of transportation (like driving or taking the train) more easily. Business travelers are less likely to do so because time is more important to them and their schedules are less flexible.
4
List and explain the four determinants of the price elasticity of demand discussed in the chapter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Suppose the price elasticity of demand for heating oil is 0.2 in the short run and 0.7 in the long run.
a. if the price of heating oil rises from $1.80 to $2.20 per gallon, what happens to the quantity of heating oil demanded in the short run? In the long run? (Use the midpoint method in your calculations.)
b. Why might this elasticity depend on the time horizon?
a. if the price of heating oil rises from $1.80 to $2.20 per gallon, what happens to the quantity of heating oil demanded in the short run? In the long run? (Use the midpoint method in your calculations.)
b. Why might this elasticity depend on the time horizon?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What is the main advantage of using the midpoint method for calculating elasticity?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A price change causes the quantity demanded of a good to decrease by 30 percent, while the total revenue of that good increases by 15 percent. Is the demand curve elastic or inelastic? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If the elasticity is greater than 1, is demand elastic or inelastic? If the elasticity equals 0, is demand perfectly elastic or perfectly inelastic?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The equilibrium price of coffee mugs rose sharply last month, but the equilibrium quantity was the same as ever. Three people tried to explain the situation. Which explanations could be right? Explain your logic.
Billy : Demand increased, but supply was totally inelastic.
Marian : Supply increased, but so did demand.
Valerie : Supply decreased, but demand was totally inelastic.
Billy : Demand increased, but supply was totally inelastic.
Marian : Supply increased, but so did demand.
Valerie : Supply decreased, but demand was totally inelastic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
On a supply-and-demand diagram, show equilibrium price, equilibrium quantity, and the total revenue received by producers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Suppose that your demand schedule for DVDs is as follows:
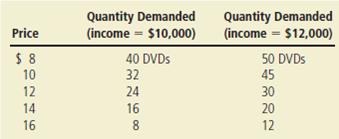
a. Use the midpoint method to calculate your price elasticity of demand as the price of DVDs increases from $8 to $10 if (i) your income is $10,000 and (ii) your income is $12,000.
b. Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10,000 to $12,000 if (i) the price is $12 and (ii) the price is $16.
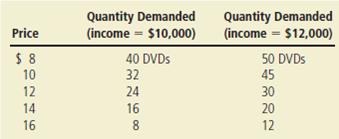
a. Use the midpoint method to calculate your price elasticity of demand as the price of DVDs increases from $8 to $10 if (i) your income is $10,000 and (ii) your income is $12,000.
b. Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10,000 to $12,000 if (i) the price is $12 and (ii) the price is $16.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If demand is elastic, how will an increase in price change total revenue? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
You have the following information about good X and good Y:
• Income elasticity of demand for good X: ?3
• Cross-price elasticity of demand for good X with respect to the price of good Y: 2
Would an increase in income and a decrease in the price of good Y unambiguously decrease the demand for good X? Why or why not?
• Income elasticity of demand for good X: ?3
• Cross-price elasticity of demand for good X with respect to the price of good Y: 2
Would an increase in income and a decrease in the price of good Y unambiguously decrease the demand for good X? Why or why not?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What do we call a good whose income elasticity is less than 0?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Maria has decided always to spend one-third of her income on clothing.
a. What is her income elasticity of clothing demand?
b. What is her price elasticity of clothing demand?
c. If Maria's tastes change and she decides to spend only one-fourth of her income on clothing, how does her demand curve change? What is her income elasticity and price elasticity now?
a. What is her income elasticity of clothing demand?
b. What is her price elasticity of clothing demand?
c. If Maria's tastes change and she decides to spend only one-fourth of her income on clothing, how does her demand curve change? What is her income elasticity and price elasticity now?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
How is the price elasticity of supply calculated? Explain what it measures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The New York Times reported (Feb. 17, 1996) that subway ridership declined after a fare increase: "There were nearly four million fewer riders in December 1995, the first full month after the price of a token increased 25 cents to $1.50, than in the previous December, a 4.3 percent decline."
a. Use these data to estimate the price elasticity of demand for subway rides.
b. According to your estimate, what happens to the Transit Authority's revenue when the fare rises?
c. Why might your estimate of the elasticity be unreliable?
a. Use these data to estimate the price elasticity of demand for subway rides.
b. According to your estimate, what happens to the Transit Authority's revenue when the fare rises?
c. Why might your estimate of the elasticity be unreliable?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
What is the price elasticity of supply of Picasso paintings?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Two drivers-Tom and Jerry-each drive up to a gas station. Before looking at the price, each places an order. Tom says, "I'd like 10 gallons of gas." Jerry says, "I'd like $10 worth of gas." What is each driver's price elasticity of demand?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Is the price elasticity of supply usually larger in the short run or in the long run? Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider public policy aimed at smoking.
a. Studies indicate that the price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is about 0.4. If a pack of cigarettes currently costs $2 and the government wants to reduce smoking by 20 percent, by how much should it increase the price?
b. If the government permanently increases the price of cigarettes, will the policy have a larger effect on smoking one year from now or five years from now?
c. Studies also find that teenagers have a higher price elasticity than do adults. Why might this be true?
a. Studies indicate that the price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is about 0.4. If a pack of cigarettes currently costs $2 and the government wants to reduce smoking by 20 percent, by how much should it increase the price?
b. If the government permanently increases the price of cigarettes, will the policy have a larger effect on smoking one year from now or five years from now?
c. Studies also find that teenagers have a higher price elasticity than do adults. Why might this be true?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
How can elasticity help explain why drug interdiction could reduce the supply of drugs, yet possibly increase drug-related crime?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
You are the curator of a museum. The museum is running short of funds, so you decide to increase revenue. Should you increase or decrease the price of admission? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Pharmaceutical drugs have an inelastic demand, and computers have an elastic demand. Suppose that technological advance doubles the supply of both products (that is, the quantity supplied at each price is twice what it was).
a. What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity in each market?
b. Which product experiences a larger change in price?
c. Which product experiences a larger change in quantity?
d. What happens to total consumer spending on each product?
a. What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity in each market?
b. Which product experiences a larger change in price?
c. Which product experiences a larger change in quantity?
d. What happens to total consumer spending on each product?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Several years ago, flooding along the Missouri and the Mississippi rivers destroyed thousands of acres of wheat.
a. Farmers whose crops were destroyed by the floods were much worse off, but farmers whose crops were not destroyed benefited from the floods. Why?
b. What information would you need about the market for wheat to assess whether farmers as a group were hurt or helped by the floods?
a. Farmers whose crops were destroyed by the floods were much worse off, but farmers whose crops were not destroyed benefited from the floods. Why?
b. What information would you need about the market for wheat to assess whether farmers as a group were hurt or helped by the floods?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Explain why the following might be true: A drought around the world raises the total revenue that farmers receive from the sale of grain, but a drought only in Kansas reduces the total revenue that Kansas farmers receive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 26 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








