Deck 22: Money Growth and Inflation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 22: Money Growth and Inflation
1
Explain how an increase in the price level affects the real value of money.
From the quantity theory of money, an increase in the quantity of money causes a proportional decrease in the real value of money.
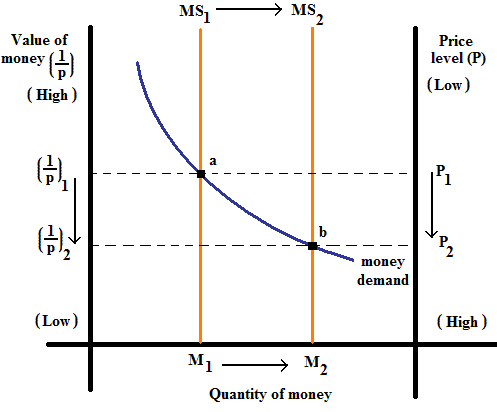 From the graph, we could observe that when the Money supply is increased from MS 1 to MS 2 , the equilibrium shifts from 'a' to 'b' as the increase in the quantity of money reduces its demand.
From the graph, we could observe that when the Money supply is increased from MS 1 to MS 2 , the equilibrium shifts from 'a' to 'b' as the increase in the quantity of money reduces its demand.
Thus the increase in the money supply from MS 1 to MS 2 decreases the value of money from
 .
.
 From the graph, we could observe that when the Money supply is increased from MS 1 to MS 2 , the equilibrium shifts from 'a' to 'b' as the increase in the quantity of money reduces its demand.
From the graph, we could observe that when the Money supply is increased from MS 1 to MS 2 , the equilibrium shifts from 'a' to 'b' as the increase in the quantity of money reduces its demand.Thus the increase in the money supply from MS 1 to MS 2 decreases the value of money from
 .
. 2
If nominal GDP is $400, real GDP is $200, and the money supply is $100, then
A) the price level is ½, and velocity is 2.
B) the price level is ½, and velocity is 4.
C) the price level is 2, and velocity is 2.
D) the price level is 2, and velocity is 4.
A) the price level is ½, and velocity is 2.
B) the price level is ½, and velocity is 4.
C) the price level is 2, and velocity is 2.
D) the price level is 2, and velocity is 4.
Velocity of money:
In an economy, nominal GDP is $400, real GDP is $200, and money supply is $100.
Price level is ratio of real GDP to nominal GDP. Hence, the price level is

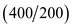 .
.
Velocity of money can be obtained as follows:
 …… (1)
…… (1)
Where,
V= velocity of money
M= supply of money
P= price level
Y= output
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to obtain the velocity of money.
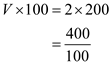 Hence, the velocity of money is
Hence, the velocity of money is
 .
.
Thus, the option 'd' is correct.
In an economy, nominal GDP is $400, real GDP is $200, and money supply is $100.
Price level is ratio of real GDP to nominal GDP. Hence, the price level is

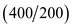 .
.Velocity of money can be obtained as follows:
 …… (1)
…… (1)Where,
V= velocity of money
M= supply of money
P= price level
Y= output
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to obtain the velocity of money.
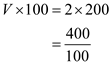 Hence, the velocity of money is
Hence, the velocity of money is  .
.Thus, the option 'd' is correct.
3
Suppose that changes in bank regulations expand the availability of credit cards so that people need to hold less cash.
a. How does this event affect the demand for money?
b. If the Fed does not respond to this event, what will happen to the price level?
c. If the Fed wants to keep the price level stable, what should it do?
a. How does this event affect the demand for money?
b. If the Fed does not respond to this event, what will happen to the price level?
c. If the Fed wants to keep the price level stable, what should it do?
(a) If the bank regulations expand the availability of credit cards so that people need to hold less cash, it will decrease the demand for money because both people and businesses need to keep less cash with them selves so as to meet their transaction as well as precautionary requirements.
(b) If Fed does not respond to this event then an excess supply of money would emerge in the money market which in turn would increase the prices of goods and services. In other words if Fed continues with the same level of supply of money then inflation would emerge.
(c) If Fed wants to keep price level stable then it should decrease the money supply in the economy so as to keep it in line with its lower demand for money, and hence the price level would remain stable.
(b) If Fed does not respond to this event then an excess supply of money would emerge in the money market which in turn would increase the prices of goods and services. In other words if Fed continues with the same level of supply of money then inflation would emerge.
(c) If Fed wants to keep price level stable then it should decrease the money supply in the economy so as to keep it in line with its lower demand for money, and hence the price level would remain stable.
4
According to the quantity theory of money, what is the effect of an increase in the quantity of money?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
According to the quantity theory of money, which variable in the quantity equation is most stable over long periods of time?
A) money
B) velocity
C) price level
D) output
A) money
B) velocity
C) price level
D) output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
It is sometimes suggested that the Fed should try to achieve zero inflation. If we assume that velocity is constant, does this zero-inflation goal require that the rate of money growth equal zero? If yes, explain why. If no, explain what the rate of money growth should equal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Explain the difference between nominal and real variables and give two examples of each. According to the principle of monetary neutrality, which variables are affected by changes in the quantity of money?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Suppose that a country's inflation rate increases sharply. What happens to the inflation tax on the holders of money? Why is wealth that is held in savings accounts not subject to a change in the inflation tax? Can you think of any way holders of savings accounts are hurt by the increase in the inflation rate?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In what sense is inflation like a tax? How does thinking about inflation as a tax help explain hyperinflation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
According to the quantity theory of money and the Fisher effect, if the central bank increases the rate of money growth,
A) inflation and the nominal interest rate both increase.
B) inflation and the real interest rate both increase.
C) the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate both increase.
D) inflation, the real interest rate, and the nominal interest rate all increase.
A) inflation and the nominal interest rate both increase.
B) inflation and the real interest rate both increase.
C) the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate both increase.
D) inflation, the real interest rate, and the nominal interest rate all increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Let's consider the effects of inflation in an economy composed of only two people: Bob, a bean farmer, and Rita, a rice farmer. Bob and Rita both always consume equal amounts of rice and beans. In 2013, the price of beans was $1 and the price of rice was $3.
a. Suppose that in 2014 the price of beans was $2 and the price of rice was $6. What was inflation? Was Bob better off, worse off, or unaffected by the changes in prices? What about Rita?
b. Now suppose that in 2014 the price of beans was $2 and the price of rice was $4. What was inflation? Was Bob better off, worse off, or unaffected by the changes in prices? What about Rita?
c. Finally, suppose that in 2014 the price of beans was $2 and the price of rice was $1.50. What was inflation? Was Bob better off, worse off, or unaffected by the changes in prices? What about Rita?
d. What matters more to Bob and Rita-the overall inflation rate or the relative price of rice and beans?
a. Suppose that in 2014 the price of beans was $2 and the price of rice was $6. What was inflation? Was Bob better off, worse off, or unaffected by the changes in prices? What about Rita?
b. Now suppose that in 2014 the price of beans was $2 and the price of rice was $4. What was inflation? Was Bob better off, worse off, or unaffected by the changes in prices? What about Rita?
c. Finally, suppose that in 2014 the price of beans was $2 and the price of rice was $1.50. What was inflation? Was Bob better off, worse off, or unaffected by the changes in prices? What about Rita?
d. What matters more to Bob and Rita-the overall inflation rate or the relative price of rice and beans?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
According to the Fisher effect, how does an increase in the inflation rate affect the real interest rate and the nominal interest rate?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If an economy always has inflation of 10 percent per year, which of the following costs of inflation will it NOT suffer?
A) shoeleather costs from reduced holdings of money
B) menu costs from more frequent price adjustment
C) distortions from the taxation of nominal capital gains
D) arbitrary redistributions between debtors and creditors
A) shoeleather costs from reduced holdings of money
B) menu costs from more frequent price adjustment
C) distortions from the taxation of nominal capital gains
D) arbitrary redistributions between debtors and creditors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If the tax rate is 40 percent, compute the before-tax real interest rate and the after-tax real interest rate in each of the following cases.
a. The nominal interest rate is 10 percent, and the inflation rate is 5 percent.
b. The nominal interest rate is 6 percent, and the inflation rate is 2 percent.
c. The nominal interest rate is 4 percent, and the inflation rate is 1 percent.
a. The nominal interest rate is 10 percent, and the inflation rate is 5 percent.
b. The nominal interest rate is 6 percent, and the inflation rate is 2 percent.
c. The nominal interest rate is 4 percent, and the inflation rate is 1 percent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The classical principle of monetary neutrality states that changes in the money supply do not influence _________ variables and is thought most applicable in the _________ run.
A) nominal, short
B) nominal, long
C) real, short
D) real, long
A) nominal, short
B) nominal, long
C) real, short
D) real, long

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What are the costs of inflation? Which of these costs do you think are most important for the U.S. economy?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Suppose that this year's money supply is $500 billion, nominal GDP is $10 trillion, and real GDP is $5 trillion.
a. What is the price level? What is the velocity of money?
b. Suppose that velocity is constant and the economy's output of goods and services rises by 5 percent each year. What will happen to nominal GDP and the price level next year if the Fed keeps the money supply constant?
c. What money supply should the Fed set next year if it wants to keep the price level stable?
d. What money supply should the Fed set next year if it wants an inflation of 10 percent?
a. What is the price level? What is the velocity of money?
b. Suppose that velocity is constant and the economy's output of goods and services rises by 5 percent each year. What will happen to nominal GDP and the price level next year if the Fed keeps the money supply constant?
c. What money supply should the Fed set next year if it wants to keep the price level stable?
d. What money supply should the Fed set next year if it wants an inflation of 10 percent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Recall that money serves three functions in the economy. What are those functions? How does inflation affect the ability of money to serve each of these functions?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 18 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








