Deck 38: Animal Ecology
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 38: Animal Ecology
1
How would you distinguish between ecosystem, community, and population
When organisms of the same species exist together it is called a population.
When two or more populations of different species exist together it is called a community.
When different communities come together it is known as ecosystem.
When two or more populations of different species exist together it is called a community.
When different communities come together it is known as ecosystem.
2
The pyramid of energy has been offered as an example of the second law of thermodynamics (p. 10). Why
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that physical systems tend to move towards a state of greater disorder or entropy. This law states that whenever energy is changed from one form to another, there is always a "loss" of energy in the form of heat. This heat is responsible for the disorder or entropy seen.
The pyramid of energy is seen as an example of this law of thermodynamics as we see the loss of energy from each trophic level from producers to consumers. This loss of energy fulfills the second law of thermodynamics.
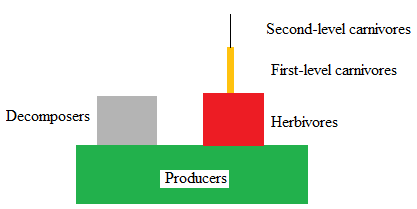 The producers produced
The producers produced
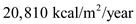 out of which herbivores used
out of which herbivores used
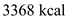 . The first-level carnivores used
. The first-level carnivores used
 out of
out of
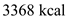 and the second level used
and the second level used
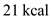 out of 383 kcal.
out of 383 kcal.
The pyramid of energy is seen as an example of this law of thermodynamics as we see the loss of energy from each trophic level from producers to consumers. This loss of energy fulfills the second law of thermodynamics.
 The producers produced
The producers produced 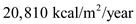 out of which herbivores used
out of which herbivores used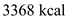 . The first-level carnivores used
. The first-level carnivores used  out of
out of 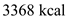 and the second level used
and the second level used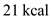 out of 383 kcal.
out of 383 kcal. 3
What is the distinction between habitat and environment
A habitat is the specific space inhabited by a particular species which includes the environment. Many habitats make up the environment.
4
Animal communities surrounding deep-sea thermal vents apparently exist in total independence of solar energy. How is this existence possible

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Define the niche concept. How does the "realized niche" of a population differ from its "fundamental niche" How does the concept of niche differ from the concept of guild

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What do paleontological studies show about the relationship between the geographic range of a species and its probability of undergoing speciation or extinction How does this present a paradox for biodiversity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Populations of independently living (unitary) animals have a characteristic age structure, sex ratio, and growth rate. However, these properties are difficult to determine for modular animals. Why

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Explain which of the three survivorship curves in Figure 38.2 best fits the following: (a) a population in which mortality as a proportion of survivors is constant; (b) a population in which there is little early death and most individuals live to old age; (c) a population that experiences heavy mortality of the very young but with the survivors living to old age. Offer an example from the real world of each survivorship pattern.
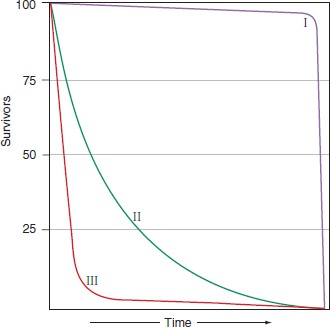
Figure 38.2 Three principal types of theoretical survivorship curves. See text for explanation.

Figure 38.2 Three principal types of theoretical survivorship curves. See text for explanation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Contrast exponential and logistic growth of a population. Under what conditions might you expect a population to exhibit exponential growth Why cannot exponential growth be perpetuated indefinitely

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Growth of a population may be hindered by either density-dependent or density-independent mechanisms. Define and contrast these two mechanisms. Offer examples of how growth of the human population might be curbed by either agent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Herbivory is an example of an interspecific interaction that is beneficial for the animal (+) but harmful to the plant it eats ( ). What are some + interactions among animal populations What is the difference between commensalism and mutualism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Explain how character displacement can ease competition between coexisting species.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Define predation. How does the predator-prey relationship differ from the parasite-host relationship Why is the evolutionary race between predator and prey one that the predator cannot afford to win

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Mimicry of monarch butterflies by viceroys is an example of a palatable species resembling a toxic one. What is the advantage to the viceroy of this form of mimicry What is the advantage to a toxic species of mimicking another toxic species

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A keystone species is defined as one whose removal from a community causes the extinction of other species. How does this extinction happen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What is a trophic level, and how does it relate to a food web

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Define productivity as the word is used in ecology. What is a primary producer What is the distinction between gross productivity, net productivity, and respiration What is the relation of net productivity to biomass (or standing crop)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
What is a food chain How does a food chain differ from a food web

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The term ecology is derived from the Greek meaning "house" or "place to live." However, as used by scientists, the term "ecology" is not the same as "environment." How do these terms differ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What conditions produce an inverted pyramid of biomass in which the consumers have a greater biomass than the producers Can you think of an example of an inverted pyramid of numbers in which there are, for example, more herbivores than plants on which they feed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 20 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








