Deck 8: Cost Analysis
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Cost Analysis
1
Profit Margins on the Amazon Kindle8
Amazon's new tablet computer, the Kindle Fire, has slim margins at its $199 retail price. Admittedly, this product is trying to change the way we read books. It is therefore positioned so as to penetrate a revolutionary new target market, the twentysomethings who are comfortable never actually holding hard copies of their textbooks, novels, newspapers, or magazines.
Listed here is data on hardware components, software licensing, and other costs: display screen $35, touchscreen $25, assembly labor $11, battery $12, processor chip $18, advertising campaign $7, DRAM memory chip $5, software licenses $37, 8 GB memory module $8, wireless WiFi/Bluetooth $6, hardcase and other materials $34, R D expense $12, overhead $14.
Would you expect the Kindle tablet contribution margin percentage to exceed handset margins of 13 percent to 17 percent at Samsung, RIM, and Nokia Why or why not
Amazon's new tablet computer, the Kindle Fire, has slim margins at its $199 retail price. Admittedly, this product is trying to change the way we read books. It is therefore positioned so as to penetrate a revolutionary new target market, the twentysomethings who are comfortable never actually holding hard copies of their textbooks, novels, newspapers, or magazines.
Listed here is data on hardware components, software licensing, and other costs: display screen $35, touchscreen $25, assembly labor $11, battery $12, processor chip $18, advertising campaign $7, DRAM memory chip $5, software licenses $37, 8 GB memory module $8, wireless WiFi/Bluetooth $6, hardcase and other materials $34, R D expense $12, overhead $14.
Would you expect the Kindle tablet contribution margin percentage to exceed handset margins of 13 percent to 17 percent at Samsung, RIM, and Nokia Why or why not
Solution obtained from the above calculation shows that contribution margin percentage is 22.6% of retail price. This clearly shows that k tablet contribution margin percentage exceeds the handset margin.
Handset market is full of competition and demand. The unit's sales of handset and k tablet would make a large difference.
For example: 13% margin on 100 units of handsets and 22% margin on k tablet is what makes the difference in revenue. As kindle don't have a tough competitor, competitive prices is not required unlike handsets. Further, low margin on medium number of unit sales does not help as to meet the total costs.
Handset market is full of competition and demand. The unit's sales of handset and k tablet would make a large difference.
For example: 13% margin on 100 units of handsets and 22% margin on k tablet is what makes the difference in revenue. As kindle don't have a tough competitor, competitive prices is not required unlike handsets. Further, low margin on medium number of unit sales does not help as to meet the total costs.
2
Howard Bowen is a large-scale cotton farmer. The land and machinery he owns has a current market value of $4 million. Bowen owes his local bank $3 million. Last year Bowen sold $5 million worth of cotton. His variable operating costs were $4.5 million; accounting depreciation was $40,000, although the actual decline in value of Bowen's machinery was $60,000 last year. Bowen paid himself a salary of $50,000, which is not considered part of his variable operating costs. Interest on his bank loan was $400,000. If Bowen worked for another farmer or a local manufacturer, his annual income would be about $30,000. Bowen can invest any funds that would be derived, if the farm were sold, to earn 10 percent annually.(Ignore taxes.)
a. Compute Bowen's accounting profits.
b. Compute Bowen's economic profits.
a. Compute Bowen's accounting profits.
b. Compute Bowen's economic profits.
Following information is available about Howard Bowen's assets, liabilities, revenue and cost.
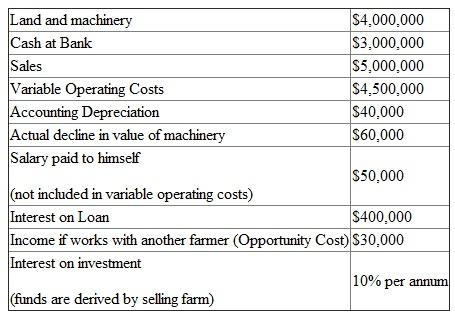 a) Accounting profits are the difference between the total revenue and explicit costs, where explicit are the direct payments made in the course of a business.
a) Accounting profits are the difference between the total revenue and explicit costs, where explicit are the direct payments made in the course of a business.
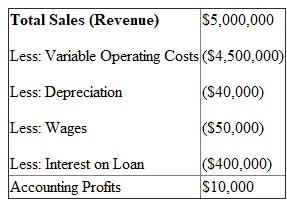 Thus, Bowen's accounting profits from large-scale cotton farm are
Thus, Bowen's accounting profits from large-scale cotton farm are
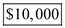 .
.
(Note: Amount in parenthesis are negative.)
b) Economic profits are the difference between the total revenue and the total of explicit and implicit costs. Implicit costs are costs of opportunity lost by using company's own resources instead of putting these to some different use.
 Thus, Bowen actually incurs economic losses of
Thus, Bowen actually incurs economic losses of
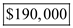 from large-scale cotton farm.
from large-scale cotton farm.
 a) Accounting profits are the difference between the total revenue and explicit costs, where explicit are the direct payments made in the course of a business.
a) Accounting profits are the difference between the total revenue and explicit costs, where explicit are the direct payments made in the course of a business. Thus, Bowen's accounting profits from large-scale cotton farm are
Thus, Bowen's accounting profits from large-scale cotton farm are 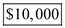 .
.(Note: Amount in parenthesis are negative.)
b) Economic profits are the difference between the total revenue and the total of explicit and implicit costs. Implicit costs are costs of opportunity lost by using company's own resources instead of putting these to some different use.
 Thus, Bowen actually incurs economic losses of
Thus, Bowen actually incurs economic losses of 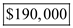 from large-scale cotton farm.
from large-scale cotton farm. 3
Based on your answers to Questions, should LP accept the Southeast order
Question
Calculate the incremental, or marginal, cost per chair to LP of accepting the order from Southeast.
Question
What assumptions did you make in calculating the incremental cost in Question 1 What additional information would be helpful in making these calculations
Question
Calculate the incremental, or marginal, cost per chair to LP of accepting the order from Southeast.
Question
What assumptions did you make in calculating the incremental cost in Question 1 What additional information would be helpful in making these calculations
The incremental cost per chair is calculated to be
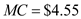 . Further, Southeast Department Stores are willing to pay a price not more than
. Further, Southeast Department Stores are willing to pay a price not more than
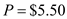 per chair.
per chair.
On the basis of our incremental analysis, since price exceeds the variable cost, it is recommended that LP should accept the Southeast order.
LP's profit
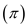 is the difference between the price and variable cost for 30,000 chairs.
is the difference between the price and variable cost for 30,000 chairs.
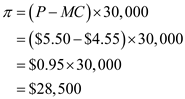 Thus, the total profit earned by LP from Southeast order is
Thus, the total profit earned by LP from Southeast order is
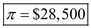 .
.
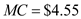 . Further, Southeast Department Stores are willing to pay a price not more than
. Further, Southeast Department Stores are willing to pay a price not more than 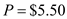 per chair.
per chair.On the basis of our incremental analysis, since price exceeds the variable cost, it is recommended that LP should accept the Southeast order.
LP's profit
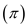 is the difference between the price and variable cost for 30,000 chairs.
is the difference between the price and variable cost for 30,000 chairs.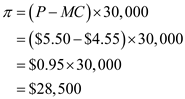 Thus, the total profit earned by LP from Southeast order is
Thus, the total profit earned by LP from Southeast order is 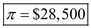 .
. 4
Profit Margins on the Amazon Kindle8
Amazon's new tablet computer, the Kindle Fire, has slim margins at its $199 retail price. Admittedly, this product is trying to change the way we read books. It is therefore positioned so as to penetrate a revolutionary new target market, the twentysomethings who are comfortable never actually holding hard copies of their textbooks, novels, newspapers, or magazines.
Listed here is data on hardware components, software licensing, and other costs: display screen $35, touchscreen $25, assembly labor $11, battery $12, processor chip $18, advertising campaign $7, DRAM memory chip $5, software licenses $37, 8 GB memory module $8, wireless WiFi/Bluetooth $6, hardcase and other materials $34, R D expense $12, overhead $14.
What about Apple iPads Why would their margins be higher Be specific.
Amazon's new tablet computer, the Kindle Fire, has slim margins at its $199 retail price. Admittedly, this product is trying to change the way we read books. It is therefore positioned so as to penetrate a revolutionary new target market, the twentysomethings who are comfortable never actually holding hard copies of their textbooks, novels, newspapers, or magazines.
Listed here is data on hardware components, software licensing, and other costs: display screen $35, touchscreen $25, assembly labor $11, battery $12, processor chip $18, advertising campaign $7, DRAM memory chip $5, software licenses $37, 8 GB memory module $8, wireless WiFi/Bluetooth $6, hardcase and other materials $34, R D expense $12, overhead $14.
What about Apple iPads Why would their margins be higher Be specific.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Mary Graham worked as a real estate agent for Piedmont Properties for 15 years. Her annual income is proximately $100,000 per year. Mary is considering establishing her own real estate agency. She expects to generate revenues during the first year of $2 million. Salaries paid to her employees are expected to total $1.5 million. Operating expenses (i.e., rent, supplies, utility services) are expected to total $250,000. To begin the business, Mary must borrow $500,000 from her bank at an interest rate of 15 percent. Equipment will cost Mary $50,000. At the end of one year, the value of this equipment will be $30,000, even though the depreciation expense for tax purposes is only $5,000 during the first year.
a. Determine the (pre-tax) accounting profit for this venture.
b. Determine the (pre-tax) economic profit for this venture.
c. Which of the costs for this firm are explicit and which are implicit
a. Determine the (pre-tax) accounting profit for this venture.
b. Determine the (pre-tax) economic profit for this venture.
c. Which of the costs for this firm are explicit and which are implicit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What additional considerations might lead LP to reject the order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
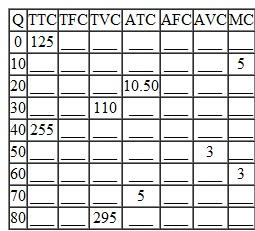
From your knowledge of the relationships among the various cost functions, complete the following table.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
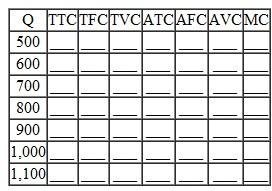
A manufacturing plant has a potential production capacity of 1,000 units per month (capacity can be increased by 10 percent if subcontractors are employed). The plant is normally operated at about 80 percent of capacity. Operating the plant above this level significantly increases variable costs per unit because of the need to pay the skilled workers higher overtime wage rates. For output levels up to 80 percent of capacity, variable cost per unit is $100. Above 80 percent and up to 90 percent, variable costs on this additional output increase by 10 percent. When output is above 90 percent and up to 100 percent of capacity, the additional units cost an additional 25 percent over the unit variable costs for outputs up to 80 percent of capacity. For production above 100 percent and up to 110 percent of capacity, extensive subcontracting work is used and the unit variable costs of these additional units are 50 percent above those at output levels up to 80 percent of capacity. At 80 percent of capacity, the plant's fixed costs per unit are $50. Total fixed costs are not expected to change within the production range under consideration. Based on the preceding information, complete the following table.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The Blair Company's three assembly plants are located in California, Georgia, and New Jersey. Previously, the company purchased a major subassembly, which becomes part of the final product, from an outside firm. Blair has decided to manufacture the subassemblies within the company and must now consider whether to rent one centrally located facility (e.g., in Missouri, where all the subassemblies would be manufactured) or to rent three separate acilities, each located near one of the assembly plants, where each facility would manufacture only the bassemblies needed for the nearby assembly plant. A single, centrally located facility, with a production capacity of 18,000 units per year, would have fixed costs of $900,000 per year and a variable cost of $250 per unit. Three separate entralized facilities, with production capacities of 8,000, 6,000, and 4,000 units per year, would have fixed costs of $475,000, $425,000, and $400,000, respectively, and variable costs per unit of only $225 per unit, owing primarily to the reduction in shipping costs. The current production rates at the three assembly plants are 6,000, 4,500, and 3,000 units, respectively.
a. Assuming that the current production rates are maintained at the three assembly plants, which alternative should management select
b. If demand for the final product were to increase to production capacity, which alternative would be more attractive
c. What additional information would be useful before making a decision
a. Assuming that the current production rates are maintained at the three assembly plants, which alternative should management select
b. If demand for the final product were to increase to production capacity, which alternative would be more attractive
c. What additional information would be useful before making a decision

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Kitchen Helper Company decides to produce and sell food blenders and is considering three different types of production facilities ("plants"). Plant A is a laborintensive facility, employing relatively little specialized capital equipment. Plant B is a semiautomated facility that would employ less labor than A but would also have higher capital equipment costs. Plant C is a completely automated facility using much more high-cost, high-technology capital equipment and even less labor than B. Information about the operating costs and production capacities of these three different types of plants is shown in the following table.
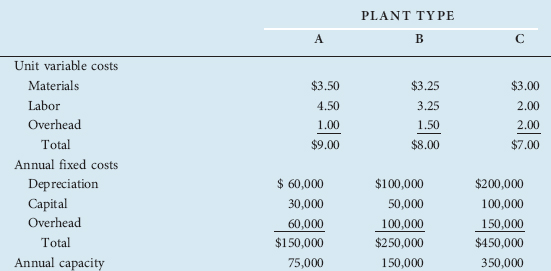
a. Determine the average total cost schedules for each plant type for annual outputs of 25,000, 50,000, 75,000, …, 350,000. For output levels beyond the capacity of a given plant, assume that multiple plants of the same type are built. For example, to produce 200,000 units with Plant A, three of these plants would be built.
b. Based on the cost schedules calculated in part (a), construct the long-run average total cost schedule for the production of blenders.

a. Determine the average total cost schedules for each plant type for annual outputs of 25,000, 50,000, 75,000, …, 350,000. For output levels beyond the capacity of a given plant, assume that multiple plants of the same type are built. For example, to produce 200,000 units with Plant A, three of these plants would be built.
b. Based on the cost schedules calculated in part (a), construct the long-run average total cost schedule for the production of blenders.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The ARA Railroad owns a piece of land along one of its right-of-ways. The land originally cost ARA $100,000. ARA is considering building a new maintenance facility on this land. ARA determined that the proposal to build the new facility is acceptable if the original cost of the land is used in the analysis, but the proposal does not meet the railroad's project acceptance criteria if the land cost is above $500,000. An investor has recently offered ARA $1 million for the land. Should ARA build the maintenance facility at this location

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The Emerson Corporation, a manufacturer of airplane landing gear equipment, is trying to develop a learning curve model to help forecast labor costs for successive units of one of its products. From past data, the firm knows that labor costs of the 25th, 75th, and 125th units were $800, $600, and $500, respectively. Using the learning curve equation for these labor costs, log C = 3.30755 0.28724 log Q, calculate the estimated cost of the 200th unit of output. What is the percentage of learning at Emerson

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Calculate the incremental, or marginal, cost per chair to LP of accepting the order from Southeast.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Profit Margins on the Amazon Kindle8
Amazon's new tablet computer, the Kindle Fire, has slim margins at its $199 retail price. Admittedly, this product is trying to change the way we read books. It is therefore positioned so as to penetrate a revolutionary new target market, the twentysomethings who are comfortable never actually holding hard copies of their textbooks, novels, newspapers, or magazines.
Listed here is data on hardware components, software licensing, and other costs: display screen $35, touchscreen $25, assembly labor $11, battery $12, processor chip $18, advertising campaign $7, DRAM memory chip $5, software licenses $37, 8 GB memory module $8, wireless WiFi/Bluetooth $6, hardcase and other materials $34, R D expense $12, overhead $14.
Categorize the listed costs as variable or fixed and calculate a contribution margin percentage defined as the net price minus variable costs as a proportion of the net sales price.
Amazon's new tablet computer, the Kindle Fire, has slim margins at its $199 retail price. Admittedly, this product is trying to change the way we read books. It is therefore positioned so as to penetrate a revolutionary new target market, the twentysomethings who are comfortable never actually holding hard copies of their textbooks, novels, newspapers, or magazines.
Listed here is data on hardware components, software licensing, and other costs: display screen $35, touchscreen $25, assembly labor $11, battery $12, processor chip $18, advertising campaign $7, DRAM memory chip $5, software licenses $37, 8 GB memory module $8, wireless WiFi/Bluetooth $6, hardcase and other materials $34, R D expense $12, overhead $14.
Categorize the listed costs as variable or fixed and calculate a contribution margin percentage defined as the net price minus variable costs as a proportion of the net sales price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
US Airways owns a piece of land near the Pittsburgh International Airport. The land originally cost US Airways $375,000. The airline is considering building a new training center on this land. US Airways determined that the roposal tobuild the new facility is acceptable if the original cost of the land is used in the analysis, but the proposal does not meet the airline's project acceptance criteria if the land cost is above $850,000. A developer recently offered US Airways $2.5 million for the land. Should US Airways build the training facility at this location

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What assumptions did you make in calculating the incremental cost in Question What additional information would be helpful in making these calculations
Question
Calculate the incremental, or marginal, cost per chair to LP of accepting the order from Southeast.
Question
Calculate the incremental, or marginal, cost per chair to LP of accepting the order from Southeast.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 16 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








