Deck 23: Performance Evaluation Using Variances From Standard Costs
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 23: Performance Evaluation Using Variances From Standard Costs
1
Ethics and professional conduct in business using nonmanufacturing standards
Dash Riprock is a cost analyst with Safe Insurance Company. Safe is applying standards to its claims payment operation. Claims payment is a repetitive operation that could be evaluated with standards. Dash used time and motion studies to identify an ideal standard of 36 claims processed per hour. The Claims Processing Department manager, Henry Tudor, has rejected this standard and has argued that the standard should be 30 claims processed per hour. Henry and Dash were unable to agree, so they decided to discuss this matter openly at a joint meeting with the vice president of operations, who would arbitrate a final decision. Prior to the meeting, Dash wrote the following memo to the VP:

As you know, Henry and I are scheduled to meet with you to discuss our disagreement with respect to the appropriate standards for the Claims Processing Department. I have conducted time and motion studies and have determined that the ideal standard is 36 claims processed per hour. Henry argues that 30 claims processed per hour would be more appropriate. I believe he is trying to "pad" the budget with some slack. I'm not sure what he is trying to get away with, but I believe a tight standard will drive efficiency up in his area. I hope you will agree when we meet with you next week.
Discuss the ethical and professional issues in this situation.
Dash Riprock is a cost analyst with Safe Insurance Company. Safe is applying standards to its claims payment operation. Claims payment is a repetitive operation that could be evaluated with standards. Dash used time and motion studies to identify an ideal standard of 36 claims processed per hour. The Claims Processing Department manager, Henry Tudor, has rejected this standard and has argued that the standard should be 30 claims processed per hour. Henry and Dash were unable to agree, so they decided to discuss this matter openly at a joint meeting with the vice president of operations, who would arbitrate a final decision. Prior to the meeting, Dash wrote the following memo to the VP:

As you know, Henry and I are scheduled to meet with you to discuss our disagreement with respect to the appropriate standards for the Claims Processing Department. I have conducted time and motion studies and have determined that the ideal standard is 36 claims processed per hour. Henry argues that 30 claims processed per hour would be more appropriate. I believe he is trying to "pad" the budget with some slack. I'm not sure what he is trying to get away with, but I believe a tight standard will drive efficiency up in his area. I hope you will agree when we meet with you next week.
Discuss the ethical and professional issues in this situation.
Ethics and Professional conduct of business:
Analysis: Dash being a cost analyst determined 36 insurance claims can be processed in an hour, after time and motion study. But the claims processing manager, Henry argued that only 30 claims can be processed per hour. Because of their disagreement on the standard number of claims that can be processed per hour, they agreed to put the matter before the Mr. Anne Boleyn, Vice-president, Operations, who will take a final decision.
Before their meeting with the Vice-president, writing a letter to Anne by Mr. Dash is unethical. He should not have written letter to Anne. It is nothing but influencing the decision of Mr. Anne. Dash is preparing a ground to get the support of the Vice-president, operations.
It is not the professional way of fixing the standards. Time and motion study may be applicable to physical labour work. But settling of claims is not fully a physical work. Partly physical and partly mental work. So, we should not entirely depend upon time and motion study for this type of work. Dash himself is saying " a tight standard will drive efficiency". It denotes that he fixed a tight standard.
Analysis: Dash being a cost analyst determined 36 insurance claims can be processed in an hour, after time and motion study. But the claims processing manager, Henry argued that only 30 claims can be processed per hour. Because of their disagreement on the standard number of claims that can be processed per hour, they agreed to put the matter before the Mr. Anne Boleyn, Vice-president, Operations, who will take a final decision.
Before their meeting with the Vice-president, writing a letter to Anne by Mr. Dash is unethical. He should not have written letter to Anne. It is nothing but influencing the decision of Mr. Anne. Dash is preparing a ground to get the support of the Vice-president, operations.
It is not the professional way of fixing the standards. Time and motion study may be applicable to physical labour work. But settling of claims is not fully a physical work. Partly physical and partly mental work. So, we should not entirely depend upon time and motion study for this type of work. Dash himself is saying " a tight standard will drive efficiency". It denotes that he fixed a tight standard.
2
What are the basic objectives in the use of standard costs?
Standard costs assist management in controlling costs and in motivating employees to focus on costs.
3
Standard direct materials cost per unit
Choco La Ti-Da Company produces chocolate bars. The primary materials used in producing chocolate bars are cocoa, sugar, and milk. The standard costs for a batch of chocolate (4,500 bars) are as follows:

Determine the standard direct materials cost per bar of chocolate.
Choco La Ti-Da Company produces chocolate bars. The primary materials used in producing chocolate bars are cocoa, sugar, and milk. The standard costs for a batch of chocolate (4,500 bars) are as follows:

Determine the standard direct materials cost per bar of chocolate.
Standard direct material Cost per Chocolate Bar is calculated as under:
Company produces chocolate bars. The ingredients to produce chocolate bars are cocoa, sugar, and milk.
The standard costs for a batch of chocolates (4,500 bars) are as follows:
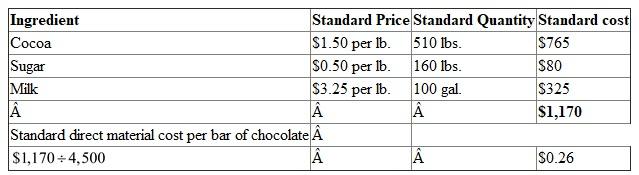 Therefore, standard direct materials cost per bar of chocolate is $0.26.
Therefore, standard direct materials cost per bar of chocolate is $0.26.
Company produces chocolate bars. The ingredients to produce chocolate bars are cocoa, sugar, and milk.
The standard costs for a batch of chocolates (4,500 bars) are as follows:
 Therefore, standard direct materials cost per bar of chocolate is $0.26.
Therefore, standard direct materials cost per bar of chocolate is $0.26. 4
Direct materials variances
Lo-bed Company produces a product that requires two standard gallons per unit. The standard price is $20.00 per gallon. If 4,000 units required 8,200 gallons, which were purchased at $1975 per gallon, what is the direct materials (a) price variance, (b) quantity variance, and (c) cost variance?
Dvorak Company produces a product that requires five standard pounds per unit. The standard price is $2.50 per pound. If 1,000 units required 4,500 pounds, which were purchased at $3.00 per pound, what is the direct materials (a) price variance, (b) quantity variance, and (c) cost variance?
Lo-bed Company produces a product that requires two standard gallons per unit. The standard price is $20.00 per gallon. If 4,000 units required 8,200 gallons, which were purchased at $1975 per gallon, what is the direct materials (a) price variance, (b) quantity variance, and (c) cost variance?
Dvorak Company produces a product that requires five standard pounds per unit. The standard price is $2.50 per pound. If 1,000 units required 4,500 pounds, which were purchased at $3.00 per pound, what is the direct materials (a) price variance, (b) quantity variance, and (c) cost variance?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
direct materials and direct labor variance analysis
Fancy Fixture Company manufactures faucets in a small manufacturing facility. The faucets are made from brass. Manufacturing has 100 employees. Each employee presently provides 40 hours of labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows:

Instructions
Determine (a) the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor; (b) the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; and (c) the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.
Fancy Fixture Company manufactures faucets in a small manufacturing facility. The faucets are made from brass. Manufacturing has 100 employees. Each employee presently provides 40 hours of labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows:

Instructions
Determine (a) the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor; (b) the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; and (c) the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
direct materials and direct labor variance analysis
Lenni Clothing Co. manufactures clothing in a small manufacturing facility. Manufacturing has 25 employees. Each employee presently provides 40 hours of productive labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows:

Instructions
Determine (a) the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor; (b) the price variance, quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; and (c) the rate variance, time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.
Lenni Clothing Co. manufactures clothing in a small manufacturing facility. Manufacturing has 25 employees. Each employee presently provides 40 hours of productive labor per week. Information about a production week is as follows:

Instructions
Determine (a) the standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor; (b) the price variance, quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; and (c) the rate variance, time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Nonfinancial performance measures
The senior management of Tungston Company has proposed the following three performance measures for the company:
1. Net income as a percent of stockholders' equity
2. Revenue growth
3. Employee satisfaction
Management believes these three measures combine both financial and nonfinancial measures and are thus superior to using just financial measures.
What advice would you give Tungston Company for improving its performance measurement system?
The senior management of Tungston Company has proposed the following three performance measures for the company:
1. Net income as a percent of stockholders' equity
2. Revenue growth
3. Employee satisfaction
Management believes these three measures combine both financial and nonfinancial measures and are thus superior to using just financial measures.
What advice would you give Tungston Company for improving its performance measurement system?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What is meant by reporting by the "principle of exceptions," as the term is used in reference to cost control?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Standard product cost
Wood You Lie To Me Furniture Company manufactures designer home furniture. Wood You Lie To Me uses a standard cost system. The direct labor, direct materials, and factory overhead standards for an unfinished dining room table are as follows:

a. Determine the standard cost per dining room table.
b. Why would Wood You Lie To Me Furniture Company use a standard cost system?
Wood You Lie To Me Furniture Company manufactures designer home furniture. Wood You Lie To Me uses a standard cost system. The direct labor, direct materials, and factory overhead standards for an unfinished dining room table are as follows:

a. Determine the standard cost per dining room table.
b. Why would Wood You Lie To Me Furniture Company use a standard cost system?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Direct labor variances
Lo-bed Company produces a product that requires four standard hours per unit at a standard hourly rate of $28.00 per hour. If 4,000 units required 16,750 hours at an hourly rate of $28.40 per hour, what is the direct labor (a) rate variance, (b) time variance, and (c) cost variance?
Dvorak Company produces a product that requires three standard hours per unit at a standard hourly rate of $17 per hour. If 1,000 units required 2,800 hours at an hourly rate of $16.50 per hour, what is the direct labor (a) rate variance, (b) time variance, and (c) cost variance?
Lo-bed Company produces a product that requires four standard hours per unit at a standard hourly rate of $28.00 per hour. If 4,000 units required 16,750 hours at an hourly rate of $28.40 per hour, what is the direct labor (a) rate variance, (b) time variance, and (c) cost variance?
Dvorak Company produces a product that requires three standard hours per unit at a standard hourly rate of $17 per hour. If 1,000 units required 2,800 hours at an hourly rate of $16.50 per hour, what is the direct labor (a) rate variance, (b) time variance, and (c) cost variance?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
flexible budgeting and variance analysis
I Love My Chocolate Company makes dark chocolate and light chocolate. Both products require cocoa and sugar. The following planning information has been made available:
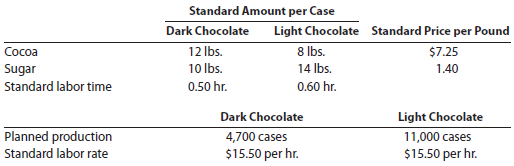
I Love My Chocolate Company does not expect there to be any beginning or ending inventories of cocoa or sugar. At the end of the budget year, I Love My Chocolate Company had the following actual results:
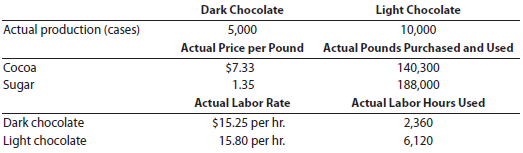
Instructions
1. Prepare the following variance analyses for both chocolates and the total, based on the actual results and production levels at the end of the budget year:
a. Direct materials price, quantity, and total variance.
b. Direct labor rate, time, and total variance.
2. Why are the standard amounts in part (1) based on the actual production for the year instead of the planned production for the year?
I Love My Chocolate Company makes dark chocolate and light chocolate. Both products require cocoa and sugar. The following planning information has been made available:

I Love My Chocolate Company does not expect there to be any beginning or ending inventories of cocoa or sugar. At the end of the budget year, I Love My Chocolate Company had the following actual results:

Instructions
1. Prepare the following variance analyses for both chocolates and the total, based on the actual results and production levels at the end of the budget year:
a. Direct materials price, quantity, and total variance.
b. Direct labor rate, time, and total variance.
2. Why are the standard amounts in part (1) based on the actual production for the year instead of the planned production for the year?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
flexible budgeting and variance analysis
I'm Really Cold Coat Company makes women's and men's coats. Both products require filler and lining material. The following planning information has been made available:
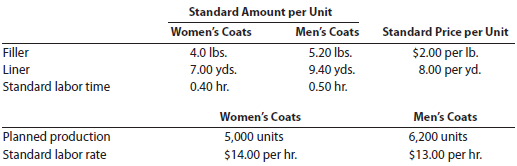
I'm Really Cold Coat Company does not expect there to be any beginning or ending inventories of filler and lining material. At the end of the budget year, I'm Really Cold Coat Company experienced the following actual results:
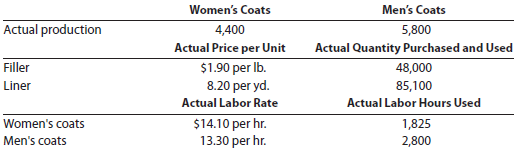
The expected beginning inventory and desired ending inventory were realized.
Instructions
1. Prepare the following variance analyses for both coats and the total, based on the actual results and production levels at the end of the budget year:
a. Direct materials price, quantity, and total variance.
b. Direct labor rate, time, and total variance.
2. Why are the standard amounts in part (1) based on the actual production at the end of the year instead of the planned production at the beginning of the year?
I'm Really Cold Coat Company makes women's and men's coats. Both products require filler and lining material. The following planning information has been made available:

I'm Really Cold Coat Company does not expect there to be any beginning or ending inventories of filler and lining material. At the end of the budget year, I'm Really Cold Coat Company experienced the following actual results:

The expected beginning inventory and desired ending inventory were realized.
Instructions
1. Prepare the following variance analyses for both coats and the total, based on the actual results and production levels at the end of the budget year:
a. Direct materials price, quantity, and total variance.
b. Direct labor rate, time, and total variance.
2. Why are the standard amounts in part (1) based on the actual production at the end of the year instead of the planned production at the beginning of the year?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
variance interpretation
You have been asked to investigate some cost problems in the Assembly Department of Ruthenium Electronics Co., a consumer electronics company. To begin your investigation, you have obtained the following budget performance report for the department for the last quarter:
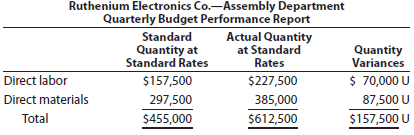
The following reports were also obtained:
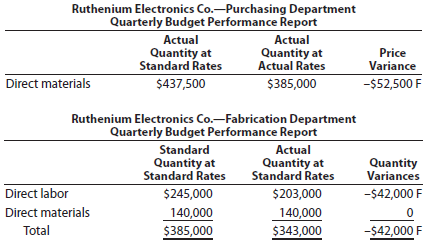
You also interviewed the Assembly Department supervisor. Excerpts from the interview follow: Q: What explains the poor performance in your department?
A: Listen, you've got to understand what it's been like in this department recently. Lately, it seems no matter how hard we try, we can't seem to make the standards. I'm not sure what is going on, but we've been having a lot of problems lately.
Q: What kind of problems?
A: Well, for instance, all this quarter we've been requisitioning purchased parts from the material storeroom, and the parts just didn't fit together very well. I'm not sure what is going on, but during most of this quarter we've had to scrap and sort purchased parts-just to get our assemblies put together. Naturally, all this takes time and material. And that's not all.
Q: Go on.
A: All this quarter, the work that we've been receiving from the Fabrication Department has been shoddy. I mean, maybe around 20% of the stuff that comes in from Fabrication just can't be assembled. The fabrication is all wrong. As a result, we've had to scrap and rework a lot of the stuff. Naturally, this has just shot our quantity variances.
Interpret the variance reports in light of the comments by the Assembly Department supervisor.
You have been asked to investigate some cost problems in the Assembly Department of Ruthenium Electronics Co., a consumer electronics company. To begin your investigation, you have obtained the following budget performance report for the department for the last quarter:

The following reports were also obtained:

You also interviewed the Assembly Department supervisor. Excerpts from the interview follow: Q: What explains the poor performance in your department?
A: Listen, you've got to understand what it's been like in this department recently. Lately, it seems no matter how hard we try, we can't seem to make the standards. I'm not sure what is going on, but we've been having a lot of problems lately.
Q: What kind of problems?
A: Well, for instance, all this quarter we've been requisitioning purchased parts from the material storeroom, and the parts just didn't fit together very well. I'm not sure what is going on, but during most of this quarter we've had to scrap and sort purchased parts-just to get our assemblies put together. Naturally, all this takes time and material. And that's not all.
Q: Go on.
A: All this quarter, the work that we've been receiving from the Fabrication Department has been shoddy. I mean, maybe around 20% of the stuff that comes in from Fabrication just can't be assembled. The fabrication is all wrong. As a result, we've had to scrap and rework a lot of the stuff. Naturally, this has just shot our quantity variances.
Interpret the variance reports in light of the comments by the Assembly Department supervisor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What are the two variances between the actual cost and the standard cost for direct materials?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Budget performance report
Genie in a Bottle Company (GBC) manufactures plastic two-liter bottles for the beverage industry. The cost standards per 100 two-liter bottles are as follows:

At the beginning of July, GBC management planned to produce 400,000 bottles. The actual number of bottles produced for July was 406,000 bottles. The actual costs for July of the current year were as follows:

a. Prepare the July manufacturing standard cost budget (direct labor, direct materials, and factory overhead) for GBC, assuming planned production.
b. Prepare a budget performance report for manufacturing costs, showing the total cost variances for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead for July.
c. Interpret the budget performance report.
Genie in a Bottle Company (GBC) manufactures plastic two-liter bottles for the beverage industry. The cost standards per 100 two-liter bottles are as follows:

At the beginning of July, GBC management planned to produce 400,000 bottles. The actual number of bottles produced for July was 406,000 bottles. The actual costs for July of the current year were as follows:

a. Prepare the July manufacturing standard cost budget (direct labor, direct materials, and factory overhead) for GBC, assuming planned production.
b. Prepare a budget performance report for manufacturing costs, showing the total cost variances for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead for July.
c. Interpret the budget performance report.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Factory overhead controllable variance
Lo-bed Company produced 4,000 units of product that required four standard hours per unit. The standard variable overhead cost per unit is $3.00 per hour. The actual variable factory overhead was $51,240. Determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance.
Dvorak Company produced 1,000 units of product that required three standard hours per unit. The standard variable overhead cost per unit is $1.40 per hour. The actual variable factory overhead was $4,000. Determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance.
Lo-bed Company produced 4,000 units of product that required four standard hours per unit. The standard variable overhead cost per unit is $3.00 per hour. The actual variable factory overhead was $51,240. Determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance.
Dvorak Company produced 1,000 units of product that required three standard hours per unit. The standard variable overhead cost per unit is $1.40 per hour. The actual variable factory overhead was $4,000. Determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead cost variance analysis
Adamantane Inc. processes a base chemical into plastic. Standard costs and actual costs for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead incurred for the manufacture of 15,000 units of product were as follows:
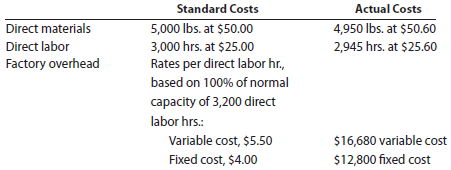
Each unit requires 0.2 hour of direct labor.
Instructions
Determine (a) the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; (b) the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance; and (c) the variable factory overhead controllable variance, fixed factory overhead volume variance, and total factory overhead cost variance.
Adamantane Inc. processes a base chemical into plastic. Standard costs and actual costs for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead incurred for the manufacture of 15,000 units of product were as follows:

Each unit requires 0.2 hour of direct labor.
Instructions
Determine (a) the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; (b) the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance; and (c) the variable factory overhead controllable variance, fixed factory overhead volume variance, and total factory overhead cost variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead cost variance analysis
Road Gripper Tire Co. manufactures automobile tires. Standard costs and actual costs for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead incurred for the manufacture of 4,160 tires were as follows:
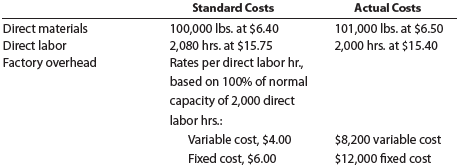
Each tire requires 0.5 hour of direct labor.
Instructions
Determine (a) the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; (b) the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance; and (c) the variable factory overhead controllable variance, fixed factory overhead volume variance, and total factory overhead cost variance.
Road Gripper Tire Co. manufactures automobile tires. Standard costs and actual costs for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead incurred for the manufacture of 4,160 tires were as follows:

Each tire requires 0.5 hour of direct labor.
Instructions
Determine (a) the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance; (b) the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance; and (c) the variable factory overhead controllable variance, fixed factory overhead volume variance, and total factory overhead cost variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Variance interpretation
Vanadium Audio Inc. is a small manufacturer of electronic musical instruments. The plant manager received the following variable factory overhead report for the period:
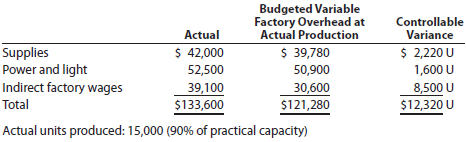
The plant manager is not pleased with the $12,320 unfavorable variable factory overhead controllable variance and has come to discuss the matter with the controller. The following discussion occurred:
Plant Manager: I just received this factory report for the latest month of operation. I'm not very pleased with these figures. Before these numbers go to headquarters, you and I will need to reach an understanding.
Controller: Go ahead, what's the problem?
Plant Manager: What's the problem? Well, everything. Look at the variance. It's too large. If I understand the accounting approach being used here, you are assuming that my costs are variable to the units produced. Thus, as the production volume declines, so should these costs. Well, I don't believe that these costs are variable at all. I think they are fixed costs. As a result, when we operate below capacity, the costs really don't go down at all. I'm being penalized for costs I have no control over at all. I need this report to be redone to reflect this fact. If anything, the difference between actual and budget is essentially a volume variance. Listen, I know that you're a team player. You really need to reconsider your assumptions on this one.
If you were in the controller's position, how would you respond to the plant manager?
Vanadium Audio Inc. is a small manufacturer of electronic musical instruments. The plant manager received the following variable factory overhead report for the period:

The plant manager is not pleased with the $12,320 unfavorable variable factory overhead controllable variance and has come to discuss the matter with the controller. The following discussion occurred:
Plant Manager: I just received this factory report for the latest month of operation. I'm not very pleased with these figures. Before these numbers go to headquarters, you and I will need to reach an understanding.
Controller: Go ahead, what's the problem?
Plant Manager: What's the problem? Well, everything. Look at the variance. It's too large. If I understand the accounting approach being used here, you are assuming that my costs are variable to the units produced. Thus, as the production volume declines, so should these costs. Well, I don't believe that these costs are variable at all. I think they are fixed costs. As a result, when we operate below capacity, the costs really don't go down at all. I'm being penalized for costs I have no control over at all. I need this report to be redone to reflect this fact. If anything, the difference between actual and budget is essentially a volume variance. Listen, I know that you're a team player. You really need to reconsider your assumptions on this one.
If you were in the controller's position, how would you respond to the plant manager?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The materials cost variance report for Nickols Inc. indicates a large favorable materials price variance and a significant unfavorable materials quantity variance. What might have caused these offsetting variances?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Direct materials variances
The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 4,000 automobile tires:

a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance.
b. To whom should the variances be reported for analysis and control?
The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 4,000 automobile tires:

a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance.
b. To whom should the variances be reported for analysis and control?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Factory overhead volume variance
Lo-bed Company produced 4,000 units of product that required four standard hours per unit. The standard fixed overhead cost per unit is $1.20 per hour at 16,400 hours, which is 100% of normal capacity. Determine the fixed factory overhead volume variance.
Dvorak Company produced 1,000 units of product that required three standard hours per unit. The standard fixed overhead cost per unit is $0.60 per hour at 3,500 hours, which is 100% of normal capacity. Determine the fixed factory overhead volume variance.
Lo-bed Company produced 4,000 units of product that required four standard hours per unit. The standard fixed overhead cost per unit is $1.20 per hour at 16,400 hours, which is 100% of normal capacity. Determine the fixed factory overhead volume variance.
Dvorak Company produced 1,000 units of product that required three standard hours per unit. The standard fixed overhead cost per unit is $0.60 per hour at 3,500 hours, which is 100% of normal capacity. Determine the fixed factory overhead volume variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Factory overhead cost variance report
Tiger Equipment Inc., a manufacturer of construction equipment, prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Welding Department for May of the current year. The company expected to operate the department at 100% of normal capacity of 8,400 hours.
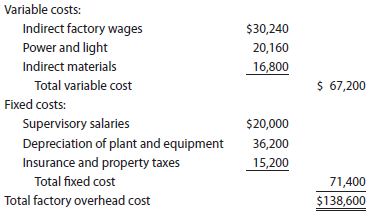
During May, the department operated at 8,860 standard hours, and the factory overhead costs incurred were indirect factory wages, $32,400; power and light, $21,000; indirect materials, $18,250; supervisory salaries, $20,000; depreciation of plant and equipment, $36,200; and insurance and property taxes, $15,200.
Instructions
Prepare a factory overhead cost variance report for May. To be useful for cost control, the budgeted amounts should be based on 8,860 hours.
Tiger Equipment Inc., a manufacturer of construction equipment, prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Welding Department for May of the current year. The company expected to operate the department at 100% of normal capacity of 8,400 hours.

During May, the department operated at 8,860 standard hours, and the factory overhead costs incurred were indirect factory wages, $32,400; power and light, $21,000; indirect materials, $18,250; supervisory salaries, $20,000; depreciation of plant and equipment, $36,200; and insurance and property taxes, $15,200.
Instructions
Prepare a factory overhead cost variance report for May. To be useful for cost control, the budgeted amounts should be based on 8,860 hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Factory overhead cost variance report
Feeling Better Medical Inc., a manufacturer of disposable medical supplies, prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Assembly Department for October of the current year. The company expected to operate the department at 100% of normal capacity of 30,000 hours.
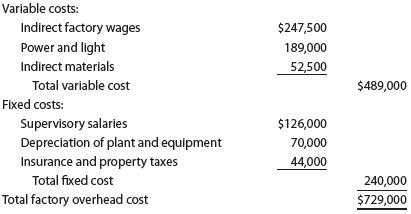
During October, the department operated at 28,500 hours, and the factory overhead costs incurred were indirect factory wages, $234,000; power and light, $178,500; indirect materials, $50,600; supervisory salaries, $126,000; depreciation of plant and equipment, $70,000; and insurance and property taxes, $44,000.
Instructions
Prepare a factory overhead cost variance report for October. To be useful for cost control, the budgeted amounts should be based on 28,500 hours.
Feeling Better Medical Inc., a manufacturer of disposable medical supplies, prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Assembly Department for October of the current year. The company expected to operate the department at 100% of normal capacity of 30,000 hours.

During October, the department operated at 28,500 hours, and the factory overhead costs incurred were indirect factory wages, $234,000; power and light, $178,500; indirect materials, $50,600; supervisory salaries, $126,000; depreciation of plant and equipment, $70,000; and insurance and property taxes, $44,000.
Instructions
Prepare a factory overhead cost variance report for October. To be useful for cost control, the budgeted amounts should be based on 28,500 hours.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Nonmanufacturing performance measures-government
Group project
Municipal governments are discovering that you can control only what you measure. As a result, many municipal governments are introducing nonfinancial performance measures to help improve municipal services. In a group, use the Google search engine to perform a search for "municipal government performance measurement." Google will provide a list of Internet sites that outline various city efforts in using nonfinancial performance measures. As a group, report on the types of measures used by one of the cities from the search.
Group project
Municipal governments are discovering that you can control only what you measure. As a result, many municipal governments are introducing nonfinancial performance measures to help improve municipal services. In a group, use the Google search engine to perform a search for "municipal government performance measurement." Google will provide a list of Internet sites that outline various city efforts in using nonfinancial performance measures. As a group, report on the types of measures used by one of the cities from the search.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1, 2016. The company produces eight-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Eternal Beauty. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12-bottle cases for $100 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The January direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead costs are as follows:
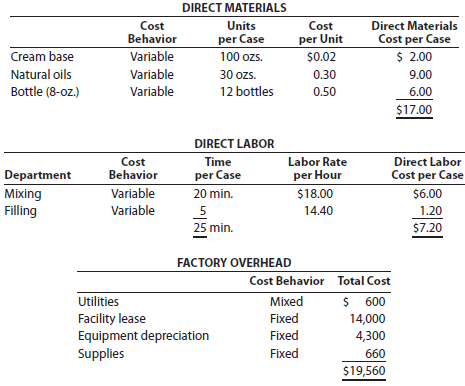
part A-Break-Even Analysis
The management of Genuine Spice Inc. wishes to determine the number of cases required to break even per month. The utilities cost, which is part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. The following information was gathered from the first six months of operation regarding this cost:
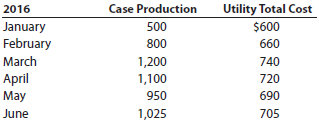
Instructions
1. Determine the fixed and variable portion of the utility cost using the high-low method.
2. Determine the contribution margin per case.
3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part (1).
4. Determine the break-even number of cases per month.
part B-august Budgets
During July of the current year, the management of Genuine Spice Inc. asked the controller to prepare August manufacturing and income statement budgets. Demand was expected to be 1,500 cases at $100 per case for August. Inventory planning information is provided as follows:
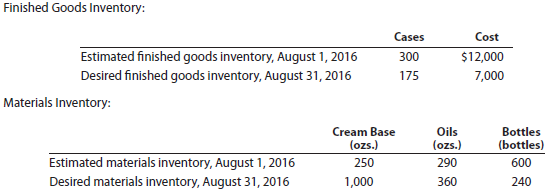
There was negligible work in process inventory assumed for either the beginning or end of the month; thus, none was assumed. In addition, there was no change in the cost per unit or estimated units per case operating data from January.
Instructions
5. Prepare the August production budget.
6. Prepare the August direct materials purchases budget.
7. Prepare the August direct labor budget. Round the hours required for production to the nearest hour.
8. Prepare the August factory overhead budget.
9. Prepare the August budgeted income statement, including selling expenses.
part C-august Variance analysis
During September of the current year, the controller was asked to perform variance analyses for August. The January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1,500 actual cases produced during August, which was 250 more cases than planned at the beginning of the month. Actual data for August were as follows:
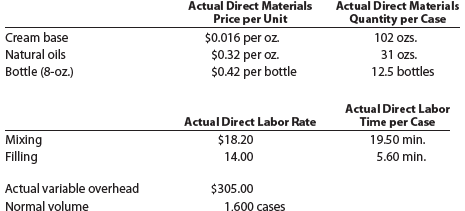
The prices of the materials were different than standard due to fluctuations in market prices. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. The Mixing Department used a higher grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual labor rate to exceed standard. The Filling Department used a lower grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual labor rate to be less than standard.
Instructions
10. Determine and interpret the direct materials price and quantity variances for the three materials.
11. Determine and interpret the direct labor rate and time variances for the two departments. Round hours to the nearest hour.
12. Determine and interpret the factory overhead controllable variance.
13. Determine and interpret the factory overhead volume variance.
14. Why are the standard direct labor and direct materials costs in the calculations for parts (10) and (11) based on the actual 1,500-case production volume rather than the planned 1,250 cases of production used in the budgets for parts (6) and (7)?

part A-Break-Even Analysis
The management of Genuine Spice Inc. wishes to determine the number of cases required to break even per month. The utilities cost, which is part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. The following information was gathered from the first six months of operation regarding this cost:

Instructions
1. Determine the fixed and variable portion of the utility cost using the high-low method.
2. Determine the contribution margin per case.
3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part (1).
4. Determine the break-even number of cases per month.
part B-august Budgets
During July of the current year, the management of Genuine Spice Inc. asked the controller to prepare August manufacturing and income statement budgets. Demand was expected to be 1,500 cases at $100 per case for August. Inventory planning information is provided as follows:

There was negligible work in process inventory assumed for either the beginning or end of the month; thus, none was assumed. In addition, there was no change in the cost per unit or estimated units per case operating data from January.
Instructions
5. Prepare the August production budget.
6. Prepare the August direct materials purchases budget.
7. Prepare the August direct labor budget. Round the hours required for production to the nearest hour.
8. Prepare the August factory overhead budget.
9. Prepare the August budgeted income statement, including selling expenses.
part C-august Variance analysis
During September of the current year, the controller was asked to perform variance analyses for August. The January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1,500 actual cases produced during August, which was 250 more cases than planned at the beginning of the month. Actual data for August were as follows:

The prices of the materials were different than standard due to fluctuations in market prices. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an ideal standard. The Mixing Department used a higher grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual labor rate to exceed standard. The Filling Department used a lower grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual labor rate to be less than standard.
Instructions
10. Determine and interpret the direct materials price and quantity variances for the three materials.
11. Determine and interpret the direct labor rate and time variances for the two departments. Round hours to the nearest hour.
12. Determine and interpret the factory overhead controllable variance.
13. Determine and interpret the factory overhead volume variance.
14. Why are the standard direct labor and direct materials costs in the calculations for parts (10) and (11) based on the actual 1,500-case production volume rather than the planned 1,250 cases of production used in the budgets for parts (6) and (7)?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
a. What are the two variances between the actual cost and the standard cost for direct labor?
b. Who generally has control over the direct labor cost variances
b. Who generally has control over the direct labor cost variances

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Direct materials variances
The Silicone Engine Inc. produces wrist-worn tablet computers. The company uses Thin Film Crystal (TFC) LCD displays for its products. Each tablet uses one display. The company produced 580 tablets during December. However, due to LCD defects, the company actually used 600 LCD displays during December. Each display has a standard cost of $15.00. Six hundred LCD displays were purchased for December production at a cost of $8,550.
Determine the price variance, quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance for December.
The Silicone Engine Inc. produces wrist-worn tablet computers. The company uses Thin Film Crystal (TFC) LCD displays for its products. Each tablet uses one display. The company produced 580 tablets during December. However, due to LCD defects, the company actually used 600 LCD displays during December. Each display has a standard cost of $15.00. Six hundred LCD displays were purchased for December production at a cost of $8,550.
Determine the price variance, quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance for December.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Standard cost journal entries
Lo-bed Company produced 4,000 units that require two standard gallons per unit at $20.00 standard price per gallon. The company actually used 8,200 gallons in production. Journalize the entry to record the standard direct materials used in production.
Dvorak Company produced 1,000 units that require five standard pounds per unit at $2.50 standard price per pound. The company actually used 4,500 pounds in production. Journalize the entry to record the standard direct materials used in production.
Lo-bed Company produced 4,000 units that require two standard gallons per unit at $20.00 standard price per gallon. The company actually used 8,200 gallons in production. Journalize the entry to record the standard direct materials used in production.
Dvorak Company produced 1,000 units that require five standard pounds per unit at $2.50 standard price per pound. The company actually used 4,500 pounds in production. Journalize the entry to record the standard direct materials used in production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Standards for nonmanufacturing expenses
CodeHead Software Inc. does software development. One important activity in software development is writing software code. The manager of the WordPro Development Team determined that the average software programmer could write 25 lines of code in an hour. The plan for the first week in May called for 4,650 lines of code to be written on the WordPro product. The WordPro Team has five programmers. Each programmer is hired from an employment firm that requires temporary employees to be hired for a minimum of a 40-hour week. Programmers are paid $32.00 per hour. The manager offered a bonus if the team could generate more lines for the week, without overtime. Due to a project emergency, the programmers wrote more code in the first week of May than planned. The actual amount of code written in the first week of May was 5,650 lines, without overtime. As a result, the bonus caused the average programmer's hourly rate to increase to $40.00 per hour during the first week in May.
Instructions
1. If the team generated 4,650 lines of code according to the original plan, what would have been the labor time variance?
2. What was the actual labor time variance as a result of generating 5,650 lines of code?
3. What was the labor rate variance as a result of the bonus?
4. Are there any performance-related issues that the labor time and rate variances fail to consider? Explain.
5. The manager is trying to determine if a better decision would have been to hire a temporary programmer to meet the higher programming demand in the first week of May, rather than paying out the bonus. If another employee was hired from the employment firm, what would have been the labor time variance in the first week?
6. Which decision is better, paying the bonus or hiring another programmer?
CodeHead Software Inc. does software development. One important activity in software development is writing software code. The manager of the WordPro Development Team determined that the average software programmer could write 25 lines of code in an hour. The plan for the first week in May called for 4,650 lines of code to be written on the WordPro product. The WordPro Team has five programmers. Each programmer is hired from an employment firm that requires temporary employees to be hired for a minimum of a 40-hour week. Programmers are paid $32.00 per hour. The manager offered a bonus if the team could generate more lines for the week, without overtime. Due to a project emergency, the programmers wrote more code in the first week of May than planned. The actual amount of code written in the first week of May was 5,650 lines, without overtime. As a result, the bonus caused the average programmer's hourly rate to increase to $40.00 per hour during the first week in May.
Instructions
1. If the team generated 4,650 lines of code according to the original plan, what would have been the labor time variance?
2. What was the actual labor time variance as a result of generating 5,650 lines of code?
3. What was the labor rate variance as a result of the bonus?
4. Are there any performance-related issues that the labor time and rate variances fail to consider? Explain.
5. The manager is trying to determine if a better decision would have been to hire a temporary programmer to meet the higher programming demand in the first week of May, rather than paying out the bonus. If another employee was hired from the employment firm, what would have been the labor time variance in the first week?
6. Which decision is better, paying the bonus or hiring another programmer?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Standards for nonmanufacturing expenses for a service company
The Radiology Department provides imaging services for Emergency Medical Center. One important activity in the Radiology Department is transcribing digitally recorded analyses of images into a written report. The manager of the Radiology Department determined that the average transcriptionist could type 700 lines of a report in an hour. The plan for the first week in May called for 81,900 typed lines to be written. The Radiology Department has three transcriptionists. Each transcriptionist is hired from an employment firm that requires temporary employees to be hired for a minimum of a 40-hour week. Transcriptionists are paid $23.00 per hour. The manager offered a bonus if the department could type more lines for the week, without overtime. Due to high service demands, the transcriptionists typed more lines in the first week of May than planned. The actual amount of lines typed in the first week of May was 88,900 lines, without overtime. As a result, the bonus caused the average transcriptionist hourly rate to increase to $30.00 per hour during the first week in May.
Instructions
1. If the department typed 81,900 lines according to the original plan, what would have been the labor time variance?
2. What was the labor time variance as a result of typing 88,900 lines?
3. What was the labor rate variance as a result of the bonus?
4. The manager is trying to determine if a better decision would have been to hire a temporary transcriptionist to meet the higher typing demands in the first week of May, rather than paying out the bonus. If another employee was hired from the employment firm, what would have been the labor time variance in the first week?
5. Which decision is better, paying the bonus or hiring another transcriptionist?
6. Are there any performance-related issues that the labor time and rate variances fail to consider? Explain.
The Radiology Department provides imaging services for Emergency Medical Center. One important activity in the Radiology Department is transcribing digitally recorded analyses of images into a written report. The manager of the Radiology Department determined that the average transcriptionist could type 700 lines of a report in an hour. The plan for the first week in May called for 81,900 typed lines to be written. The Radiology Department has three transcriptionists. Each transcriptionist is hired from an employment firm that requires temporary employees to be hired for a minimum of a 40-hour week. Transcriptionists are paid $23.00 per hour. The manager offered a bonus if the department could type more lines for the week, without overtime. Due to high service demands, the transcriptionists typed more lines in the first week of May than planned. The actual amount of lines typed in the first week of May was 88,900 lines, without overtime. As a result, the bonus caused the average transcriptionist hourly rate to increase to $30.00 per hour during the first week in May.
Instructions
1. If the department typed 81,900 lines according to the original plan, what would have been the labor time variance?
2. What was the labor time variance as a result of typing 88,900 lines?
3. What was the labor rate variance as a result of the bonus?
4. The manager is trying to determine if a better decision would have been to hire a temporary transcriptionist to meet the higher typing demands in the first week of May, rather than paying out the bonus. If another employee was hired from the employment firm, what would have been the labor time variance in the first week?
5. Which decision is better, paying the bonus or hiring another transcriptionist?
6. Are there any performance-related issues that the labor time and rate variances fail to consider? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A new assistant controller recently was heard to remark: "All the assembly workers in this plant are covered by union contracts, so there should be no labor variances." Was the controller's remark correct? Discuss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Standard direct materials cost per unit from variance data
The following data relating to direct materials cost for October of the current year are taken from the records of Good Clean Fun Inc., a manufacturer of organic toys:

Determine the standard direct materials cost per unit of finished product, assuming that there was no inventory of work in process at either the beginning or the end of the month.
The following data relating to direct materials cost for October of the current year are taken from the records of Good Clean Fun Inc., a manufacturer of organic toys:

Determine the standard direct materials cost per unit of finished product, assuming that there was no inventory of work in process at either the beginning or the end of the month.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Income statement with variances
Prepare a 2016 income statement through gross profit for Lo-bed Company, using the variance data in Practice Exercises 22-1A, 22-2A, 22-3A, and 22-4A. Assume Lo-bed sold 4.000 units at $250 per unit.
Prepare a 2016 income statement through gross profit for Dvorak Company, using the variance data in Practice Exercises 22-1B, 22-2B, 22-3B, and 22-4B. Assume Dvorak sold 1.000 units at $90 per unit.
Prepare a 2016 income statement through gross profit for Lo-bed Company, using the variance data in Practice Exercises 22-1A, 22-2A, 22-3A, and 22-4A. Assume Lo-bed sold 4.000 units at $250 per unit.
Prepare a 2016 income statement through gross profit for Dvorak Company, using the variance data in Practice Exercises 22-1B, 22-2B, 22-3B, and 22-4B. Assume Dvorak sold 1.000 units at $90 per unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Would the use of standards be appropriate in a nonmanufacturing setting, such as a fast-food restaurant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Standard product cost, direct material variance
H.J. Heinz Company uses standards to control its materials costs. Assume that a batch of ketchup (3,128 pounds) has the following standards:
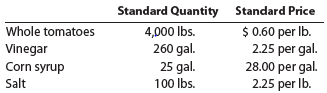
The actual materials in a batch may vary from the standard due to tomato characteristics. Assume that the actual quantities of materials for batch K-111 were as follows:
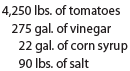
a. Determine the standard unit materials cost per pound for a standard batch.
b. Determine the direct materials quantity variance for batch K-111. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
H.J. Heinz Company uses standards to control its materials costs. Assume that a batch of ketchup (3,128 pounds) has the following standards:

The actual materials in a batch may vary from the standard due to tomato characteristics. Assume that the actual quantities of materials for batch K-111 were as follows:
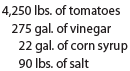
a. Determine the standard unit materials cost per pound for a standard batch.
b. Determine the direct materials quantity variance for batch K-111. Round your answer to the nearest cent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Activity inputs and outputs
The following are inputs and outputs to the copying process of a copy shop:
Number of employee errors
Number of times paper supply runs out
Copy machine downtime (broken)
Number of pages copied per hour
Number of customer complaints
Percent jobs done on time
Identify whether each is an input or output to the copying process.
The following are inputs and outputs to the cooking process of a restaurant:
Number of times ingredients are missing
Number of customer complaints
Number of hours kitchen equipment is down for repairs
Number of server order mistakes
Percent of meals prepared on time
Number of unexpected cook absences
Identify whether each is an input or output to the cooking process.
The following are inputs and outputs to the copying process of a copy shop:
Number of employee errors
Number of times paper supply runs out
Copy machine downtime (broken)
Number of pages copied per hour
Number of customer complaints
Percent jobs done on time
Identify whether each is an input or output to the copying process.
The following are inputs and outputs to the cooking process of a restaurant:
Number of times ingredients are missing
Number of customer complaints
Number of hours kitchen equipment is down for repairs
Number of server order mistakes
Percent of meals prepared on time
Number of unexpected cook absences
Identify whether each is an input or output to the cooking process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
a. Describe the two variances between the actual costs and the standard costs for factory overhead.
b. What is a factory overhead cost variance report?
b. What is a factory overhead cost variance report?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Direct labor variances
The following data relate to labor cost for production of 20,000 cellular telephones:
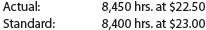
a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.
b. Discuss what might have caused these variances.
The following data relate to labor cost for production of 20,000 cellular telephones:
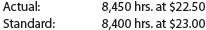
a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.
b. Discuss what might have caused these variances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
If variances are recorded in the accounts at the time the manufacturing costs are incurred, what does a debit balance in Direct Materials Price Variance represent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Direct labor variances
Reincarnation Bicycle Company manufactures commuter bicycles from recycled materials. The following data for April of the current year are available:

a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.
b. How much direct labor should be debited to Work in Process?
Reincarnation Bicycle Company manufactures commuter bicycles from recycled materials. The following data for April of the current year are available:

a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, time variance, and total direct labor cost variance.
b. How much direct labor should be debited to Work in Process?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Briefly explain why firms might use nonfinancial performance measures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Direct labor variances
The Greeson Clothes Company produced 25,000 units during June of the current year. The Cutting Department used 6,380 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $10.90 per hour. The Sewing Department used 9,875 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $11.12 per hour. Assume there were no work in process inventories in either department at the beginning or end of the month. The standard labor rate is $11.00. The standard labor time for the Cutting and Sewing departments is 0.25 hour and 0.4 hour per unit, respectively.
a. Determine the direct labor rate, direct labor time, and total direct labor cost variance for the (1) Cutting Department and (2) Sewing Department.
b. Interpret your results.
The Greeson Clothes Company produced 25,000 units during June of the current year. The Cutting Department used 6,380 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $10.90 per hour. The Sewing Department used 9,875 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $11.12 per hour. Assume there were no work in process inventories in either department at the beginning or end of the month. The standard labor rate is $11.00. The standard labor time for the Cutting and Sewing departments is 0.25 hour and 0.4 hour per unit, respectively.
a. Determine the direct labor rate, direct labor time, and total direct labor cost variance for the (1) Cutting Department and (2) Sewing Department.
b. Interpret your results.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Direct labor standards for non manufacturing expenses
Englert Hospital began using standards to evaluate its Admissions Department. The standard was broken into two types of admissions as follows:

The unscheduled admission took longer because name, address, and insurance information needed to be determined and verified at the time of admission. Information was collected on scheduled admissions prior to the admissions, which was less time consuming.
The Admissions Department employs four full-time people (40 productive hours per week, with no overtime) at $15 per hour. For the most recent week, the department handled 140 unscheduled and 350 scheduled admissions.
a. How much was actually spent on labor for the week?
b. What are the standard hours for the actual volume for the week?
c. Calculate a time variance, and report how well the department performed for the week.
Englert Hospital began using standards to evaluate its Admissions Department. The standard was broken into two types of admissions as follows:

The unscheduled admission took longer because name, address, and insurance information needed to be determined and verified at the time of admission. Information was collected on scheduled admissions prior to the admissions, which was less time consuming.
The Admissions Department employs four full-time people (40 productive hours per week, with no overtime) at $15 per hour. For the most recent week, the department handled 140 unscheduled and 350 scheduled admissions.
a. How much was actually spent on labor for the week?
b. What are the standard hours for the actual volume for the week?
c. Calculate a time variance, and report how well the department performed for the week.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Direct labor standards for a service company
One of the operations in the United States Postal Service is a mechanical mail sorting operation. In this operation, letter mail is sorted at a rate of 1.5 letters per second. The letter is mechanically sorted from a three-digit code input by an operator sitting at a keyboard. The manager of the mechanical sorting operation wishes to determine the number of temporary employees to hire for December. The manager estimates that there will be an additional 24,192,000 pieces of mail in December, due to the upcoming holiday season.
Assume that the sorting operators are temporary employees. The union contract requires that temporary employees be hired for one month at a time. Each temporary employee is hired to work 160 hours in the month.
a. How many temporary employees should the manager hire for December?
b. If each temporary employee earns a standard $16.40 per hour, what would be the labor time variance if the actual number of additional letters sorted in December was 23,895,000?
One of the operations in the United States Postal Service is a mechanical mail sorting operation. In this operation, letter mail is sorted at a rate of 1.5 letters per second. The letter is mechanically sorted from a three-digit code input by an operator sitting at a keyboard. The manager of the mechanical sorting operation wishes to determine the number of temporary employees to hire for December. The manager estimates that there will be an additional 24,192,000 pieces of mail in December, due to the upcoming holiday season.
Assume that the sorting operators are temporary employees. The union contract requires that temporary employees be hired for one month at a time. Each temporary employee is hired to work 160 hours in the month.
a. How many temporary employees should the manager hire for December?
b. If each temporary employee earns a standard $16.40 per hour, what would be the labor time variance if the actual number of additional letters sorted in December was 23,895,000?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Direct labor variances for a service company
Hit-n-Run Food Trucks, Inc. owns and operates food trucks (mobile kitchens) throughout the west coast. The company's employees have varying wage levels depending on their experience and length of time with the company. Employees work eight hour shifts and are assigned to a truck each day based on labor needs to support the daily menu. One of their trucks, Jose O'Brien's Mobile Fiesta, specializes in Irish-Mexican fusion cuisine. The truck offers a single menu item which changes daily. On November 11, the truck prepared 200 of its most popular item, the Irish Breakfast Enchiladas. The following data are available for that day:

a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and the total direct labor cost variance.
b. Discuss what might have caused these variances.
Hit-n-Run Food Trucks, Inc. owns and operates food trucks (mobile kitchens) throughout the west coast. The company's employees have varying wage levels depending on their experience and length of time with the company. Employees work eight hour shifts and are assigned to a truck each day based on labor needs to support the daily menu. One of their trucks, Jose O'Brien's Mobile Fiesta, specializes in Irish-Mexican fusion cuisine. The truck offers a single menu item which changes daily. On November 11, the truck prepared 200 of its most popular item, the Irish Breakfast Enchiladas. The following data are available for that day:

a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and the total direct labor cost variance.
b. Discuss what might have caused these variances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Direct materials and direct labour variances
At the beginning of June, Bezco Toy Company budgeted 5,000 toy action figures to be manufactured in June at standard direct materials and direct labor costs as follows:

The standard materials price is $4.00 per pound. The standard direct labor rate is $18.00 per hour. At the end of June, the actual direct materials and direct labor costs were as follows:

There were no direct materials price or direct labor rate variances for June. In addition, assume no changes in the direct materials inventory balances in June. Bezco Toy Company actually produced 4,850 units during June.
Determine the direct materials quantity and direct labor time variances.
At the beginning of June, Bezco Toy Company budgeted 5,000 toy action figures to be manufactured in June at standard direct materials and direct labor costs as follows:

The standard materials price is $4.00 per pound. The standard direct labor rate is $18.00 per hour. At the end of June, the actual direct materials and direct labor costs were as follows:

There were no direct materials price or direct labor rate variances for June. In addition, assume no changes in the direct materials inventory balances in June. Bezco Toy Company actually produced 4,850 units during June.
Determine the direct materials quantity and direct labor time variances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Flexible overhead budget
Leno Manufacturing Company prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Press Department for October of the current year, during which it expected to require 20,000 hours of productive capacity in the department:
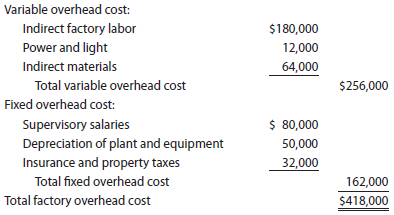
Assuming that the estimated costs for November are the same as for October, prepare a flexible factory overhead cost budget for the Press Department for November for 18,000, 20,000, and 22,000 hours of production.
Leno Manufacturing Company prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Press Department for October of the current year, during which it expected to require 20,000 hours of productive capacity in the department:

Assuming that the estimated costs for November are the same as for October, prepare a flexible factory overhead cost budget for the Press Department for November for 18,000, 20,000, and 22,000 hours of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Flexible overhead budget
Wiki Wiki Company has determined that the variable overhead rate is $4.50 per direct labor hour in the Fabrication Department. The normal production capacity for the Fabrication Department is 10,000 hours for the month. Fixed costs are budgeted at $60,000 for the month.
a. Prepare a monthly factory overhead flexible budget for 9,000, 10,000, and 11,000 hours of production.
b. How much overhead would be applied to production if 9,000 hours were used in the department during the month?
Wiki Wiki Company has determined that the variable overhead rate is $4.50 per direct labor hour in the Fabrication Department. The normal production capacity for the Fabrication Department is 10,000 hours for the month. Fixed costs are budgeted at $60,000 for the month.
a. Prepare a monthly factory overhead flexible budget for 9,000, 10,000, and 11,000 hours of production.
b. How much overhead would be applied to production if 9,000 hours were used in the department during the month?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Factory overhead cost variances
The following data relate to factor overhead cost for the production of 10,000 computer:
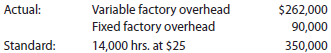
If productive capacity of 100% was 15,000 hours and the total factory overhead cost budgeted at the level of 14,000 standard hours was $356,000, determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance, fixed factory overhead volume variance, and total factory overhead cost variance. The fixed factory overhead rate was $6.00 per hour.
The following data relate to factor overhead cost for the production of 10,000 computer:
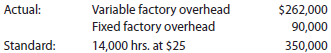
If productive capacity of 100% was 15,000 hours and the total factory overhead cost budgeted at the level of 14,000 standard hours was $356,000, determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance, fixed factory overhead volume variance, and total factory overhead cost variance. The fixed factory overhead rate was $6.00 per hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Factory overhead cost variances
Blumen Textiles Corporation began April with a budget for 90,000 hours of production in the Weaving Department. The department has a full capacity of 100,000 hours under normal business conditions. The budgeted overhead at the planned volumes at the beginning of April was as follows:

The actual factory overhead was $782,000 for April. The actual fixed factory overhead was as budgeted. During April, the Weaving Department had standard hours at actual production volume of 92,500 hours.
a. Determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance.
b. Determine the fixed factory overhead volume variance.
Blumen Textiles Corporation began April with a budget for 90,000 hours of production in the Weaving Department. The department has a full capacity of 100,000 hours under normal business conditions. The budgeted overhead at the planned volumes at the beginning of April was as follows:

The actual factory overhead was $782,000 for April. The actual fixed factory overhead was as budgeted. During April, the Weaving Department had standard hours at actual production volume of 92,500 hours.
a. Determine the variable factory overhead controllable variance.
b. Determine the fixed factory overhead volume variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Factory overhead variance corrections
The data related to Shunda Enterprises Inc.'s factory overhead cost for the production of
100,000 units of product are as follows:

Productive capacity at 100% of normal was 130,000 hours, and the factory overhead cost budgeted at the level of 132,000 standard hours was $956,000. Based on these data, the chief cost accountant prepared the following variance analysis:

Identify the errors in the factory overhead cost variance analysis.
The data related to Shunda Enterprises Inc.'s factory overhead cost for the production of
100,000 units of product are as follows:

Productive capacity at 100% of normal was 130,000 hours, and the factory overhead cost budgeted at the level of 132,000 standard hours was $956,000. Based on these data, the chief cost accountant prepared the following variance analysis:

Identify the errors in the factory overhead cost variance analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Factory overhead cost variance report
Tannin Products Inc. prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Trim Department for July of the current year, during which it expected to use 20,000 hours for production:
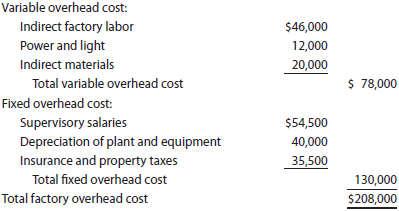
Tannin has available 25,000 hours of monthly productive capacity in the Trim Department under normal business conditions. During July, the Trim Department actually used 22,000 hours for production. The actual fixed costs were as budgeted. The actual variable overhead for July was as follows:

Construct a factory overhead cost variance report for the Trim Department for July.
Tannin Products Inc. prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Trim Department for July of the current year, during which it expected to use 20,000 hours for production:

Tannin has available 25,000 hours of monthly productive capacity in the Trim Department under normal business conditions. During July, the Trim Department actually used 22,000 hours for production. The actual fixed costs were as budgeted. The actual variable overhead for July was as follows:

Construct a factory overhead cost variance report for the Trim Department for July.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Recording standards in accounts
Cioffi Manufacturing Company incorporates standards in its accounts and identifies variances at the time the manufacturing costs are incurred. Journalize the entries to record the following transactions:
a. Purchased 2,450 units of copper tubing on account at $52.00 per unit. The standard price is $48.50 per unit.
b. Used 1,900 units of copper tubing in the process of manufacturing 200 air conditioners. Ten units of copper tubing are required, at standard, to produce one air conditioner.
Cioffi Manufacturing Company incorporates standards in its accounts and identifies variances at the time the manufacturing costs are incurred. Journalize the entries to record the following transactions:
a. Purchased 2,450 units of copper tubing on account at $52.00 per unit. The standard price is $48.50 per unit.
b. Used 1,900 units of copper tubing in the process of manufacturing 200 air conditioners. Ten units of copper tubing are required, at standard, to produce one air conditioner.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Recording standards in accounts
The Assembly Department produced 5,000 units of product during March. Each unit required 2.20 standard direct labor hours. There were 11,500 actual hours used in the Assembly Department during March at an actual rate of $17.60 per hour. The standard direct labor rate is $18.00 per hour. Assuming direct labor for a month is paid on the fifth day of the following month, journalize the direct labor in the Assembly Department on March 31.
The Assembly Department produced 5,000 units of product during March. Each unit required 2.20 standard direct labor hours. There were 11,500 actual hours used in the Assembly Department during March at an actual rate of $17.60 per hour. The standard direct labor rate is $18.00 per hour. Assuming direct labor for a month is paid on the fifth day of the following month, journalize the direct labor in the Assembly Department on March 31.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Income statement indicating standard cost variances
The following data were taken from the records of Griggs Company for December 2016:

Prepare an income statement for presentation to management.
The following data were taken from the records of Griggs Company for December 2016:

Prepare an income statement for presentation to management.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Nonfinancial performance measures
Diamond Inc. is an Internet retailer of woodworking equipment. Customers order woodworking equipment from the company, using an online catalog. The company processes these orders and delivers the requested product from its warehouse. The company wants to provide customers with an excellent purchase experience in order to expand the business through favorable word-of-mouth advertising and to drive repeat business. To help monitor performance, the company developed a set of performance measures for its order placement and delivery process:
Average computer response time to customer "clicks"
Dollar amount of returned goods
Elapsed time between customer order and product delivery
Maintenance dollars divided by hardware investment
Number of customer complaints divided by the number of order
Number of misfilled orders divided by the number of orders
Number of orders per warehouse employee
Number of page faults or errors due to software programming errors
Number of software fixes per week
Server (computer) downtime
Training dollars per programmer
a. For each performance measure, identify it as either an input or output measure related to the "order placement and delivery" process.
b. Provide an explanation for each performance measure.
Diamond Inc. is an Internet retailer of woodworking equipment. Customers order woodworking equipment from the company, using an online catalog. The company processes these orders and delivers the requested product from its warehouse. The company wants to provide customers with an excellent purchase experience in order to expand the business through favorable word-of-mouth advertising and to drive repeat business. To help monitor performance, the company developed a set of performance measures for its order placement and delivery process:
Average computer response time to customer "clicks"
Dollar amount of returned goods
Elapsed time between customer order and product delivery
Maintenance dollars divided by hardware investment
Number of customer complaints divided by the number of order
Number of misfilled orders divided by the number of orders
Number of orders per warehouse employee
Number of page faults or errors due to software programming errors
Number of software fixes per week
Server (computer) downtime
Training dollars per programmer
a. For each performance measure, identify it as either an input or output measure related to the "order placement and delivery" process.
b. Provide an explanation for each performance measure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Nonfinancial performance measures
Alpha University wishes to monitor the efficiency and quality of its course registration process.
a. Identify three input and three output measures for this process.
b. Why would Alpha University use nonfinancial measures for monitoring this process?
Alpha University wishes to monitor the efficiency and quality of its course registration process.
a. Identify three input and three output measures for this process.
b. Why would Alpha University use nonfinancial measures for monitoring this process?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 58 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








