Deck 4: Cell Membranes and Signaling
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Cell Membranes and Signaling
1
Which of the following is a function of the sterols that are found in animal cell membranes?
A) They maintain membrane fluidity.
B) They facilitate ion transport.
C) They store cellular energy.
D) They increase the rate of diffusion.
A) They maintain membrane fluidity.
B) They facilitate ion transport.
C) They store cellular energy.
D) They increase the rate of diffusion.
A
2
What are the major structural components of a cell membrane?
A) glycolipids and cellulose
B) glycolipids and proteins
C) phospholipids and cellulose
D) phospholipids and proteins
A) glycolipids and cellulose
B) glycolipids and proteins
C) phospholipids and cellulose
D) phospholipids and proteins
D
3
Which type of lipid is most important in the structure of biological membranes?
A) wax
B) cholesterol
C) phospholipid
D) fat
A) wax
B) cholesterol
C) phospholipid
D) fat
C
4
In the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, what does the "fluid" part of the model refer to?
A) the constant movement of the hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane
B) the phospholipid and protein molecules, which move and exchange places within the two layers of phospholipids
C) the free movement of cholesterol molecules within the membrane
D) a thin layer of water found sandwiched between the two layers of phospholipids
A) the constant movement of the hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane
B) the phospholipid and protein molecules, which move and exchange places within the two layers of phospholipids
C) the free movement of cholesterol molecules within the membrane
D) a thin layer of water found sandwiched between the two layers of phospholipids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In an aqueous environment, how are the phospholipids of a membrane arranged?
A) in a single layer
B) in a bilayer, with the fatty acid tails located at the surface
C) in a bilayer, but the phospholipids have no specific orientation
D) in a bilayer, with the polar heads of each layer located at the surface
A) in a single layer
B) in a bilayer, with the fatty acid tails located at the surface
C) in a bilayer, but the phospholipids have no specific orientation
D) in a bilayer, with the polar heads of each layer located at the surface

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following strongly suggests that the membrane is exposed to low temperature?
A) Ions such as K+, Na+, and Ca+ begin to freely leak across the membrane.
B) Molecular motion may increase.
C) Molecular motion may decrease.
D) The membrane may become too fluid.
A) Ions such as K+, Na+, and Ca+ begin to freely leak across the membrane.
B) Molecular motion may increase.
C) Molecular motion may decrease.
D) The membrane may become too fluid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
One component of the cell membrane functions as a selective barrier, and one component has specific functions such as transport, recognizing other cells, and binding to other cells. Which pair of terms refers to these two components, respectively?
A) carbohydrate and nucleic acid
B) lipid and carbohydrate
C) protein and carbohydrate
D) lipid and protein
A) carbohydrate and nucleic acid
B) lipid and carbohydrate
C) protein and carbohydrate
D) lipid and protein

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What does the "mosaic" part of the fluid mosaic model refer to?
A) the membrane cholesterol
B) the membrane functions
C) the membrane proteins
D) the membrane phospholipids
A) the membrane cholesterol
B) the membrane functions
C) the membrane proteins
D) the membrane phospholipids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Why do the cells die when the ambient temperature drops to freezing?
A) because of the increased cellular signalling inside the cell
B) because of the inhibition of cell division
C) because of the inhibition of molecule transport across the cell membrane
D) because of the increased metabolic reactions inside the cell
A) because of the increased cellular signalling inside the cell
B) because of the inhibition of cell division
C) because of the inhibition of molecule transport across the cell membrane
D) because of the increased metabolic reactions inside the cell

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Unsaturated fatty acids cause a membrane to be fluid at lower temperatures. What is a reasonable explanation for this?
A) Unsaturated fatty acids permit more water into the interior of the membrane.
B) The double bonds form a kink in the fatty acid tail, forcing adjacent lipids to be spaced farther apart.
C) The double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acids block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
D) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content.
A) Unsaturated fatty acids permit more water into the interior of the membrane.
B) The double bonds form a kink in the fatty acid tail, forcing adjacent lipids to be spaced farther apart.
C) The double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acids block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
D) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which phrase describes the selective permeability of a membrane?
A) the ability of only certain molecules to pass across a membrane
B) the ability of a molecule to pass through a membrane
C) the need for carrier proteins to transport certain molecules
D) the movement of a molecule from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration
A) the ability of only certain molecules to pass across a membrane
B) the ability of a molecule to pass through a membrane
C) the need for carrier proteins to transport certain molecules
D) the movement of a molecule from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
What is the primary function of a cell membrane?
A) recognizing other cells as being "like"
B) controlling the transport of substances into and out of cells
C) recognizing chemical signals from other cells
D) cell-cell binding
A) recognizing other cells as being "like"
B) controlling the transport of substances into and out of cells
C) recognizing chemical signals from other cells
D) cell-cell binding

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Suppose that you fuse a mouse cell and a human cell, and then treats the cell with specific antibodies covalently linked to fluorescent dyes (antibodies linked to mouse proteins are green; antibodies linked to human proteins are red). What will the cell look like immediately after labelling?
A) The red and green fluorescent labels will be uniformly distributed across the entire membrane of the cell.
B) The cell will be half red and half green.
C) The red and green labels will be distributed in the cell in intermingled patches.
D) The red and green labels will flash in the cell intermittently.
A) The red and green fluorescent labels will be uniformly distributed across the entire membrane of the cell.
B) The cell will be half red and half green.
C) The red and green labels will be distributed in the cell in intermingled patches.
D) The red and green labels will flash in the cell intermittently.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Suppose that you are comparing the outside and inside halves of a cell membrane's phospholipid bilayer. Which of the following describes the composition of the lipids on the two surfaces?
A) asymmetrical composition
B) symmetrical but not identical composition
C) highly random and varied composition
D) identical composition
A) asymmetrical composition
B) symmetrical but not identical composition
C) highly random and varied composition
D) identical composition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Cells must constantly bring in certain molecules and ions while keeping others out. What part of the cell accomplishes this function?
A) the plasma membrane
B) the vesicles
C) the nucleus
D) the lysosomes
A) the plasma membrane
B) the vesicles
C) the nucleus
D) the lysosomes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
How are the membranes of animal cells in winter able to remain fluid when the weather becomes extremely cold?
A) The percentage of both unsaturated phospholipids and cholesterol increases.
B) The percentage of saturated phospholipids in the membrane decreases.
C) The percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane decreases.
D) The percentage of cholesterol molecules in the membrane increases.
A) The percentage of both unsaturated phospholipids and cholesterol increases.
B) The percentage of saturated phospholipids in the membrane decreases.
C) The percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane decreases.
D) The percentage of cholesterol molecules in the membrane increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
When referring to membrane glycolipids and glycoproteins, what does the prefix "glyco-" indicate?
A) polar carbohydrate groups that are attached to the molecules
B) nonpolar carbohydrate groups that are attached to the molecules
C) the molecules that are attached to the membrane by ionic bonds
D) the molecules that are attached to the membrane by covalent bonds
A) polar carbohydrate groups that are attached to the molecules
B) nonpolar carbohydrate groups that are attached to the molecules
C) the molecules that are attached to the membrane by ionic bonds
D) the molecules that are attached to the membrane by covalent bonds

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Patients with cystic fibrosis are very susceptible to bacterial infections. Which of the following best describes why this is the case?
A) Water cannot be pumped into the cells from the mucus lining.
B) Water cannot be pumped out of the cells and into the mucus lining.
C) Transport protein cannot pump sodium ions out of the lung cells and into the mucus lining; the water then remains in the cells.
D) Transport protein cannot pump chloride ions out of the lung cells and into the mucus lining; the water then remains in the cells.
A) Water cannot be pumped into the cells from the mucus lining.
B) Water cannot be pumped out of the cells and into the mucus lining.
C) Transport protein cannot pump sodium ions out of the lung cells and into the mucus lining; the water then remains in the cells.
D) Transport protein cannot pump chloride ions out of the lung cells and into the mucus lining; the water then remains in the cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
How do insects alter membrane fluidity?
A) by adjusting the relative proportions of cholesterol and proteins
B) by adjusting the relative proportions of cholesterol and fatty acids
C) by adjusting the relative proportions of proteins and fatty acids
D) by adjusting the relative proportions of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
A) by adjusting the relative proportions of cholesterol and proteins
B) by adjusting the relative proportions of cholesterol and fatty acids
C) by adjusting the relative proportions of proteins and fatty acids
D) by adjusting the relative proportions of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Suppose that you fuse a mouse cell and a human cell, and then treat the cell with specific antibodies covalently linked to fluorescent dyes (antibodies linked to mouse proteins are green; antibodies linked to human proteins are red). Forty minutes later, you look at the fused cell. Which of the following will you observe?
A) The red and green labels will be distributed in intermingled patches.
B) The red and green labels will flash intermittently.
C) The red and green labels will be uniformly distributed across the entire membrane.
D) The cell will be half red and half green.
A) The red and green labels will be distributed in intermingled patches.
B) The red and green labels will flash intermittently.
C) The red and green labels will be uniformly distributed across the entire membrane.
D) The cell will be half red and half green.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What are aquaporins?
A) spaces that transport water molecules
B) pores made of water molecules
C) protein channels for water transport
D) pores found only in bacterial cells
A) spaces that transport water molecules
B) pores made of water molecules
C) protein channels for water transport
D) pores found only in bacterial cells

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which molecules will pass most easily through a cell membrane by diffusion?
A) large, hydrophilic molecules
B) large, polar molecules
C) small, hydrophobic molecules
D) ionic molecules
A) large, hydrophilic molecules
B) large, polar molecules
C) small, hydrophobic molecules
D) ionic molecules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which statement applies to facilitated diffusion?
A) It requires ATP.
B) It can involve either carrier proteins or channel proteins.
C) It is nonspecific with respect to the nature of the molecules being transported.
D) It is not dependent on a concentration gradient.
A) It requires ATP.
B) It can involve either carrier proteins or channel proteins.
C) It is nonspecific with respect to the nature of the molecules being transported.
D) It is not dependent on a concentration gradient.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
How are integral and peripheral proteins similar to each other?
A) They both interact with the hydrophobic core of the membrane.
B) They both function at the membrane.
C) They both consist of a mixture of polar and nonpolar amino acids.
D) They are both found on the membrane surface.
A) They both interact with the hydrophobic core of the membrane.
B) They both function at the membrane.
C) They both consist of a mixture of polar and nonpolar amino acids.
D) They are both found on the membrane surface.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which terms refer to the movement of water across a membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration?
A) both endocytosis and active transport
B) both diffusion and endocytosis
C) both active transport and osmosis
D) both diffusion and osmosis
A) both endocytosis and active transport
B) both diffusion and endocytosis
C) both active transport and osmosis
D) both diffusion and osmosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
How are simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion different?
A) Facilitated diffusion is passive transport, while simple diffusion is not.
B) Facilitated diffusion requires a transport protein, while simple diffusion does not.
C) Simple diffusion requires a transport protein, while facilitated diffusion does not.
D) Simple diffusion is passive transport, while facilitated diffusion is not.
A) Facilitated diffusion is passive transport, while simple diffusion is not.
B) Facilitated diffusion requires a transport protein, while simple diffusion does not.
C) Simple diffusion requires a transport protein, while facilitated diffusion does not.
D) Simple diffusion is passive transport, while facilitated diffusion is not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
What is responsible for the selective permeability of a cell membrane?
A) the position of cholesterol in the membrane bilayer
B) the integral proteins of the membrane
C) the hydrophobic core formed by the phospholipid tails
D) the hydrophilic end facing the cell exterior
A) the position of cholesterol in the membrane bilayer
B) the integral proteins of the membrane
C) the hydrophobic core formed by the phospholipid tails
D) the hydrophilic end facing the cell exterior

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
How do small polar and charged molecules typically cross the cell membrane?
A) by facilitated diffusion
B) by osmosis
C) by active transport
D) by filtration
A) by facilitated diffusion
B) by osmosis
C) by active transport
D) by filtration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Suppose water moves across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. What is this an example of?
A) both diffusion and osmosis
B) both osmosis and active transport
C) both diffusion and endocytosis
D) both endocytosis and active transport
A) both diffusion and osmosis
B) both osmosis and active transport
C) both diffusion and endocytosis
D) both endocytosis and active transport

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
How do the various membranes of a cell differ?
A) Only certain membranes are constructed of a selectively permeable membrane.
B) Certain proteins are unique to each membrane.
C) Phospholipids are found only in certain membranes.
D) Only certain membranes are constructed from molecules with dual solubility.
A) Only certain membranes are constructed of a selectively permeable membrane.
B) Certain proteins are unique to each membrane.
C) Phospholipids are found only in certain membranes.
D) Only certain membranes are constructed from molecules with dual solubility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Suppose a drop of food colouring is placed in a container of clear water. What happens to the coloured dye molecules?
A) They undergo osmosis at the top of the container.
B) They diffuse to the top of the container.
C) They undergo osmosis equally throughout the container.
D) They diffuse equally throughout the container.
A) They undergo osmosis at the top of the container.
B) They diffuse to the top of the container.
C) They undergo osmosis equally throughout the container.
D) They diffuse equally throughout the container.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following is absolutely necessary for diffusion to occur?
A) a phospholipid bilayer
B) a living cell
C) a selectively permeable membrane
D) a concentration gradient
A) a phospholipid bilayer
B) a living cell
C) a selectively permeable membrane
D) a concentration gradient

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
How are simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion similar to each other?
A) They both belong to passive transport.
B) They both transport through the aid of a transport molecule.
C) They both require energy.
D) They both belong to active transport.
A) They both belong to passive transport.
B) They both transport through the aid of a transport molecule.
C) They both require energy.
D) They both belong to active transport.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What should the tonicity of the distilled water be compared to body cells?
A) It should be isotonic to the cells.
B) It should be hypotonic to the cells.
C) It should be protonic to the cells.
D) It should be hypertonic to the cells.
A) It should be isotonic to the cells.
B) It should be hypotonic to the cells.
C) It should be protonic to the cells.
D) It should be hypertonic to the cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following will diffuse most rapidly across membranes?
A) O2
B) glucose
C) ions
D) macromolecules
A) O2
B) glucose
C) ions
D) macromolecules

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What do we mean when we say that facilitated diffusion is specific?
A) A protein will transport specific molecules.
B) One specific integral protein per membrane is involved in facilitated diffusion.
C) Only specific hydrophobic molecules can be transported.
D) The energy molecule ATP is specifically required for transport.
A) A protein will transport specific molecules.
B) One specific integral protein per membrane is involved in facilitated diffusion.
C) Only specific hydrophobic molecules can be transported.
D) The energy molecule ATP is specifically required for transport.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following do carrier proteins often transport?
A) proteins
B) steroid hormones
C) H2O
D) glucose and amino acids
A) proteins
B) steroid hormones
C) H2O
D) glucose and amino acids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What does the cell wall do when a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution?
A) It prevents diffusion.
B) It prevents plasmolysis.
C) It prevents the cell from bursting.
D) It prevents active transport.
A) It prevents diffusion.
B) It prevents plasmolysis.
C) It prevents the cell from bursting.
D) It prevents active transport.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An unknown cell contains cholesterol. What type of cell is it most likely to be?
A) a bacterial cell
B) a fungal cell
C) a plant cell
D) an animal cell
A) a bacterial cell
B) a fungal cell
C) a plant cell
D) an animal cell

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What type of channel opens in response to changes in ionic charge across a membrane?
A) an electric-gated channel
B) a charge-gated channel
C) a ligand-gated channel
D) a voltage-gated channel
A) an electric-gated channel
B) a charge-gated channel
C) a ligand-gated channel
D) a voltage-gated channel

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which term refers to the movement of a substance from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration using energy obtained from ATP?
A) passive transport
B) facilitated transport
C) active transport
D) osmosis
A) passive transport
B) facilitated transport
C) active transport
D) osmosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What is the sequence of signal transduction?
A) transduction
B) reception
C) response
D) transduction
A) transduction
B) reception
C) response
D) transduction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
How are exocytosis and endocytosis different?
A) Endocytosis transports small molecules into cells, and exocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
B) Endocytosis transports large molecules into cells, and exocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
C) Endocytosis transports small molecules out of cells, and exocytosis transports small molecules into cells.
D) Endocytosis transports large molecules into cells, and exocytosis transports small molecules out of cells.
A) Endocytosis transports small molecules into cells, and exocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
B) Endocytosis transports large molecules into cells, and exocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
C) Endocytosis transports small molecules out of cells, and exocytosis transports small molecules into cells.
D) Endocytosis transports large molecules into cells, and exocytosis transports small molecules out of cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which environment is ideal for plant cells, and which is best for animal cells?
A) isotonic for plant cells, and hypertonic for animal cells
B) isotonic for plant cells, and hypotonic for animal cells
C) hypotonic for plant cells, and isotonic for animal cells
D) hypotonic for plant cells, and hypertonic for animal cells
A) isotonic for plant cells, and hypertonic for animal cells
B) isotonic for plant cells, and hypotonic for animal cells
C) hypotonic for plant cells, and isotonic for animal cells
D) hypotonic for plant cells, and hypertonic for animal cells

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
How are receptor-mediated endocytosis and pinocytosis different?
A) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports small molecules into cells, and pinocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
B) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports all molecules out of cells, and pinocytosis transports small molecules into cells.
C) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports large molecules into cells, and pinocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
D) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports specific molecules into cells, and pinocytosis transports nonspecific molecules found in liquids into cells.
A) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports small molecules into cells, and pinocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
B) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports all molecules out of cells, and pinocytosis transports small molecules into cells.
C) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports large molecules into cells, and pinocytosis transports large molecules out of cells.
D) Receptor-mediated endocytosis transports specific molecules into cells, and pinocytosis transports nonspecific molecules found in liquids into cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following is created as ions diffuse across membranes?
A) an electrical gradient
B) a chemical gradient
C) an electrochemical gradient
D) a biochemical gradient
A) an electrical gradient
B) a chemical gradient
C) an electrochemical gradient
D) a biochemical gradient

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which of the following is responsible for maintaining the membrane potential?
A) the Na+/K+ pump
B) the diffusion gradient
C) the Ca2+ pump
D) the H+ pump
A) the Na+/K+ pump
B) the diffusion gradient
C) the Ca2+ pump
D) the H+ pump

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following molecules could be secreted from a eukaryotic cell?
A) ions
B) metals
C) water
D) carbohydrates
A) ions
B) metals
C) water
D) carbohydrates

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A water concentration gradient is influenced by the number of solute molecules present on both sides of the membrane.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
When do cells undergo exocytosis?
A) when secreting protein and wastes from the cell
B) when replicating
C) when ingesting nutrients
D) when pumping protons down a concentration gradient
A) when secreting protein and wastes from the cell
B) when replicating
C) when ingesting nutrients
D) when pumping protons down a concentration gradient

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What two processes are involved when eukaryotic cells import and secrete large molecules?
A) exocytosis when importing and diffusion when secreting
B) exocytosis when importing and endocytosis when secreting
C) endocytosis when importing and exocytosis when secreting
D) diffusion when importing and exocytosis when secreting
A) exocytosis when importing and diffusion when secreting
B) exocytosis when importing and endocytosis when secreting
C) endocytosis when importing and exocytosis when secreting
D) diffusion when importing and exocytosis when secreting

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which pair of activities are carrier molecules involved in?
A) passive transport and osmosis
B) active and passive transport
C) active transport and osmosis
D) osmosis and diffusion
A) passive transport and osmosis
B) active and passive transport
C) active transport and osmosis
D) osmosis and diffusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which process leads to a net movement of uncharged molecules from a low concentration to a higher concentration?
A) active transport
B) osmosis
C) facilitated diffusion
D) exocytosis
A) active transport
B) osmosis
C) facilitated diffusion
D) exocytosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which term refers to the voltage across a membrane?
A) membrane electrochemical gradient
B) membrane chemical gradient
C) membrane potential
D) membrane turgor pressure
A) membrane electrochemical gradient
B) membrane chemical gradient
C) membrane potential
D) membrane turgor pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which statement applies to both simple diffusion and active transport?
A) Transport proteins are not specific for the molecules being transported.
B) A concentration gradient is not present.
C) A concentration gradient is present.
D) Transport proteins are specific for the molecules being transported.
A) Transport proteins are not specific for the molecules being transported.
B) A concentration gradient is not present.
C) A concentration gradient is present.
D) Transport proteins are specific for the molecules being transported.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
How are facilitated diffusion and active transport different from each other?
A) Active transport requires a transport protein, while facilitated diffusion does not.
B) Facilitated diffusion requires a transport protein, while active transport does not.
C) Facilitated diffusion occurs against the gradient, while active transport does not.
D) Active transport occurs against the gradient, while facilitated diffusion does not.
A) Active transport requires a transport protein, while facilitated diffusion does not.
B) Facilitated diffusion requires a transport protein, while active transport does not.
C) Facilitated diffusion occurs against the gradient, while active transport does not.
D) Active transport occurs against the gradient, while facilitated diffusion does not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
How are exocytosis and endocytosis similar to each other?
A) They both transport large molecules.
B) They both transport materials into cells.
C) They both transport materials out of cells.
D) They both transport small molecules.
A) They both transport large molecules.
B) They both transport materials into cells.
C) They both transport materials out of cells.
D) They both transport small molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which cell organelle helps pinocytosis and phagocytosis to occur?
A) the endoplasmic reticulum
B) the lysosome
C) the plasma membrane
D) the nucleus
A) the endoplasmic reticulum
B) the lysosome
C) the plasma membrane
D) the nucleus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
How do the charges inside and outside of the cell compare?
A) There is negative charge inside and positive charge outside of the cell.
B) There is positive charge inside and positive charge outside of the cell.
C) There is positive charge inside and negative charge outside of the cell.
D) There is negative charge inside and negative charge outside of the cell.
A) There is negative charge inside and positive charge outside of the cell.
B) There is positive charge inside and positive charge outside of the cell.
C) There is positive charge inside and negative charge outside of the cell.
D) There is negative charge inside and negative charge outside of the cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
How are receptor-mediated endocytosis and pinocytosis similar to each other?
A) They both transport liquids into cells.
B) They both transport particles into cells.
C) They both transport particles out of cells.
D) They both transport liquids out of cells.
A) They both transport liquids into cells.
B) They both transport particles into cells.
C) They both transport particles out of cells.
D) They both transport liquids out of cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
These micrographs of animal cells depict the effects of various aqueous environments on red blood cells placed in a hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic environment. Match each term to a micrograph. 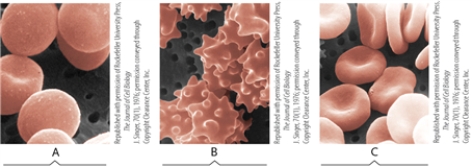 ©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1
©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1
hypertonic
 ©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1
©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1hypertonic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Identify the structures indicated in this drawing of a typical plasma membrane. 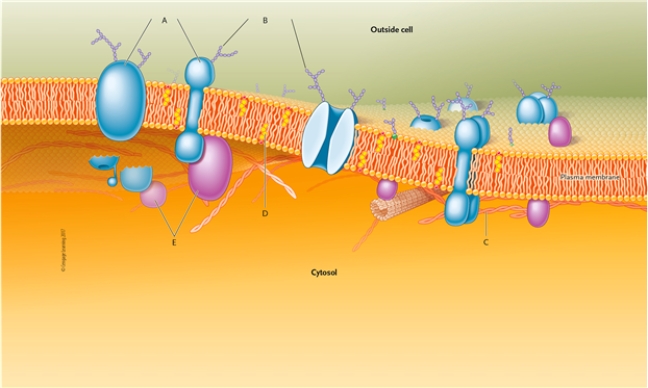
peripheral proteins

peripheral proteins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Carrier proteins share several characteristics with enzymes used to catalyze metabolic reactions. In what ways are carrier proteins and enzymes similar?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
A hypertonic environment would be ideal for a healthy plant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Match each mechanism of cellular transport with its correct definition.
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
facilitated diffusion
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
facilitated diffusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Water is a strongly polar molecule, so how does it cross the plasma membrane?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
These micrographs of animal cells depict the effects of various aqueous environments on red blood cells placed in a hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic environment. Match each term to a micrograph.  ©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1
©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1
isotonic
 ©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1
©1976 The Rockefeller University Press. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1976, 70:193-203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.1isotonic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution will swell and perhaps burst.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A solution of 65% water, 35% solute is more concentrated with respect to solute than a solution of 70% water, 30% solute.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Physiological saline is 0.9% NaCl. Red blood cells placed in such a solution will NOT gain or lose water; therefore, one could state that the fluid in red blood cells is hypertonic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Match each mechanism of cellular transport with its correct definition.
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
diffusion
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
diffusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Match each mechanism of cellular transport with its correct definition.
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
receptor-mediated endocytosis
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
receptor-mediated endocytosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Match each mechanism of cellular transport with its correct definition.
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
phagocytosis
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
phagocytosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Identify the structures indicated in this drawing of a typical plasma membrane. 
cholesterol

cholesterol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Explain why the transport of molecules across the cell membrane is considered to be both specific and directional.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Identify the structures indicated in this drawing of a typical plasma membrane. 
carbohydrate groups

carbohydrate groups

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Identify the structures indicated in this drawing of a typical plasma membrane. 
microfilament

microfilament

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Match each mechanism of cellular transport with its correct definition.
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
pinocytosis
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
pinocytosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Identify the structures indicated in this drawing of a typical plasma membrane. 
integral proteins

integral proteins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Match each mechanism of cellular transport with its correct definition.
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
osmosis
a.movement of a molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
b.cells internalize molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles possessing receptors specific to the molecule being transported
c.movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a hypertonic solution across a selectively permeable membrane
d.large particles are enveloped by the cell membrane and internalized
e.a process in which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells
f.diffusion of molecules across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transport proteins
osmosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 81 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








