Deck 8: Consumption, Saving, and Investment
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Consumption, Saving, and Investment
1
Real income is:
A)wL + i(B+K)
B)(w/P)L + i((B/P)+ K)
C)(w/P)L + i((B/P)+(K/P))
D)(w/P)L + i(B+ K)
A)wL + i(B+K)
B)(w/P)L + i((B/P)+ K)
C)(w/P)L + i((B/P)+(K/P))
D)(w/P)L + i(B+ K)
(w/P)L + i((B/P)+ K)
2
Figure 7.1 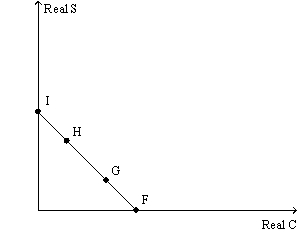
In Figure 7.1 if the household opts to consume all its income it will be at point:
A)F
B)G
C)H
D)I

In Figure 7.1 if the household opts to consume all its income it will be at point:
A)F
B)G
C)H
D)I
F
3
Real household saving is:
A) B +
B +  K
K
B) B + (
B + ( 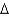 K/P)
K/P)
C)(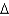 B/P) +
B/P) + 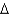 K
K
D)(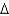 B/P) + (
B/P) + ( 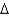 K/P)
K/P)
A)
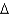 B +
B + 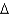 K
KB)
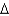 B + (
B + ( 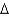 K/P)
K/P)C)(
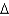 B/P) +
B/P) + 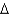 K
KD)(
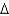 B/P) + (
B/P) + ( 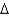 K/P)
K/P)( 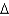 B/P) +
B/P) + 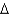 K
K
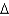 B/P) +
B/P) + 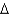 K
K 4
Real profit is zero when:
A)the interest rate is zero.
B)the depreciation rate is high.
C)the labour and capital markets clear.
D)the labour and capital markets do not clear.
A)the interest rate is zero.
B)the depreciation rate is high.
C)the labour and capital markets clear.
D)the labour and capital markets do not clear.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The household's year one budget constraint is:
A)real assets at the end of year zero plus real income in year one less consumption in year one equals real assets at the end of year one.
B)real income in year one less real assets at the end of year zero less consumption in year one equals real assets at the end of year one.
C)real assets at the end of year zero plus real income in year one plus consumption in year one equals real assets at the end of year one.
D)real income in year one plus consumption in year one less real assets at the end of year zero equals real assets at the end of year one.
A)real assets at the end of year zero plus real income in year one less consumption in year one equals real assets at the end of year one.
B)real income in year one less real assets at the end of year zero less consumption in year one equals real assets at the end of year one.
C)real assets at the end of year zero plus real income in year one plus consumption in year one equals real assets at the end of year one.
D)real income in year one plus consumption in year one less real assets at the end of year zero equals real assets at the end of year one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the one period budget constraint sources of funds include:
A)labour income.
B)income from capital.
C)income from bonds.
D)all of the above.
A)labour income.
B)income from capital.
C)income from bonds.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Figure 7.1 
In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point F to point H on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point F to point H on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
If wages rise by €10 per worker just this period, we would expect to see consumption rise by much less than €10 this period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In the one period budget constraint sources of funds include:
A)capital gains.
B)income from capital.
C)income from rising prices.
D)all of the above.
A)capital gains.
B)income from capital.
C)income from rising prices.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Figure 7.1 
In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point H to point G on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point H to point G on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Figure 7.1 
In Figure 7.1 if the household decides to save all of its income, it would be at point:
A)F
B)G
C)H
D)I

In Figure 7.1 if the household decides to save all of its income, it would be at point:
A)F
B)G
C)H
D)I

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Figure 7.1 
In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point I to point H on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point I to point H on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
€100 a year from now is equal in worth to €100 today.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
When the labour and capital markets clear:
A)depreciation is zero.
B)real profit is zero.
C)a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future.
D)all of the above.
A)depreciation is zero.
B)real profit is zero.
C)a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In the one period budget constraint sources of funds include:
A)labour income.
B)interests bearing money.
C)capital gains.
D)all of the above.
A)labour income.
B)interests bearing money.
C)capital gains.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Figure 7.1 
In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point G to point H on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

In Figure 7.1 if the household moves from point G to point H on its budget, it would be:
A)saving and consuming more.
B)saving less and consuming more.
C)saving more and consuming less.
D)saving and consuming less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A discount factor is used to deflate nominal consumption to real consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
If the value of initial assets increases, then a household will change consumption or present value of asset at the end of period 2 due to an income effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The aggregate household budget constraint is consumption plus net investment is real GDP less depreciation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Real saving in year one is:
A)real bonds plus capital in year 1 minus real bonds and capital in year 0.
B)bonds plus capital plus money period 1.
C)bonds plus capital in period 1.
D)interest times the sum of bonds plus capital in period 1.
A)real bonds plus capital in year 1 minus real bonds and capital in year 0.
B)bonds plus capital plus money period 1.
C)bonds plus capital in period 1.
D)interest times the sum of bonds plus capital in period 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An income effect is the response of households to changes in the present value of:
A)relative prices.
B)sources of funds.
C)uses of funds.
D)assets at the end of year two.
A)relative prices.
B)sources of funds.
C)uses of funds.
D)assets at the end of year two.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
An increase in the interest rate:
A)makes future consumption cheaper.
B)decreases future income.
C)makes present consumption cheaper.
D)all of the above.
A)makes future consumption cheaper.
B)decreases future income.
C)makes present consumption cheaper.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In the one period budget constraint the uses of funds include:
A)payment of transfers.
B)purchases of capital goods.
C)payment of wages.
D)all of the above.
A)payment of transfers.
B)purchases of capital goods.
C)payment of wages.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The measure used to reduce future consumption to today's values is called:
A)an implicit deflator.
B)a discount factor.
C)an escalator.
D)a future value.
A)an implicit deflator.
B)a discount factor.
C)an escalator.
D)a future value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Utility in economics is:
A)a product with a derived demand like electricity.
B)usefulness.
C)satisfaction or happiness.
D)all of the above.
A)a product with a derived demand like electricity.
B)usefulness.
C)satisfaction or happiness.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In the one period budget constraint the uses of funds include:
A)purchases of consumption goods.
B)purchases of capital goods.
C)purchases of bonds.
D)all of the above.
A)purchases of consumption goods.
B)purchases of capital goods.
C)purchases of bonds.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An increase in the interest rate:
A)makes consumption in period two relatively more expensive compared to consumption in period one.
B)does not change relative cost of consuming in either period.
C)makes consumption in period two relatively cheaper compared consumption in period one.
D)discourages savings in each period.
A)makes consumption in period two relatively more expensive compared to consumption in period one.
B)does not change relative cost of consuming in either period.
C)makes consumption in period two relatively cheaper compared consumption in period one.
D)discourages savings in each period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
An increase in the interest rate:
A)makes future consumption cheaper.
B)increases future income.
C)makes present consumption more expensive.
D)all of the above.
A)makes future consumption cheaper.
B)increases future income.
C)makes present consumption more expensive.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If a household consumes one less unit in period 1, they can consume:
A)on more unit in period two.
B)(1 + i) more units in period two.
C)one less unit in period two.
D)no more in period two.
A)on more unit in period two.
B)(1 + i) more units in period two.
C)one less unit in period two.
D)no more in period two.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The present value of sources of funds is:
A)the value of initial assets plus the present value of wage income plus the present value of assets at the end of year two.
B)the value of initial assets plus the present value of assets at the end of year two.
C)the present value of wage income plus the present value of assets at the end of year two.
D)the value of initial assets plus the present value of wage income.
A)the value of initial assets plus the present value of wage income plus the present value of assets at the end of year two.
B)the value of initial assets plus the present value of assets at the end of year two.
C)the present value of wage income plus the present value of assets at the end of year two.
D)the value of initial assets plus the present value of wage income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In the one period budget constraint sources of funds include:
A)capital gains.
B)inflation.
C)income from bonds.
D)all of the above.
A)capital gains.
B)inflation.
C)income from bonds.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If the interest rate is greater than zero, then the concept of present value is that a dollar today:
A)is worth more than a dollar a year from now.
B)is worth less than a dollar a year from now.
C)will be worthless a year from now.
D)is worth the same as a year from now.
A)is worth more than a dollar a year from now.
B)is worth less than a dollar a year from now.
C)will be worthless a year from now.
D)is worth the same as a year from now.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
In the one period budget constraint the uses of funds include:
A)purchases of consumption goods.
B)payment of wages.
C)payment profits.
D)all of the above.
A)purchases of consumption goods.
B)payment of wages.
C)payment profits.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
When a discount factor is multiplied times a future period variable it creates a:
A)future value.
B)a present value.
C)a real variable.
D)a nominal variable.
A)future value.
B)a present value.
C)a real variable.
D)a nominal variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
In the one period budget constraint the uses of funds include:
A)payment of transfers.
B)payment of wages.
C)purchases of bonds.
D)all of the above.
A)payment of transfers.
B)payment of wages.
C)purchases of bonds.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A yen today is worth more than a yen a year from now as long as:
A)the interest rate is negative.
B)the interest rate is positive.
C)the depreciation rate is negative.
D)the depreciation rate is positive.
A)the interest rate is negative.
B)the interest rate is positive.
C)the depreciation rate is negative.
D)the depreciation rate is positive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Utility in economics:
A)used to mean happiness.
B)used to mean satisfaction.
C)is what a person gets from a good.
D)all of the above.
A)used to mean happiness.
B)used to mean satisfaction.
C)is what a person gets from a good.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
An increase in the interest rate can cause an income effect by:
A)making future consumption cheaper.
B)changing real income in year two.
C)making present consumption cheaper.
D)all of the above.
A)making future consumption cheaper.
B)changing real income in year two.
C)making present consumption cheaper.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An increase in the interest rate:
A)makes future consumption more expensive.
B)decreases future income.
C)makes present consumption more expensive.
D)all of the above.
A)makes future consumption more expensive.
B)decreases future income.
C)makes present consumption more expensive.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
If the present value of assets at the end of year two is constant, an increase in the present value of sources of funds must cause:
A)consumption in periods one and two to rise.
B)consumption in periods one and two to fall.
C)consumption to rise in period one and fall in period two.
D)consumption to fall in period one and rise in period two.
A)consumption in periods one and two to rise.
B)consumption in periods one and two to fall.
C)consumption to rise in period one and fall in period two.
D)consumption to fall in period one and rise in period two.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Show the relationship between the household budget constraint and net national product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
If the household budget constraint is aggregated over all household, it shows that:
A)consumption plus net investment equal net national product.
B)consumption plus net investment equals real GDP less depreciation.
C)C +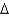 K = Y -
K = Y -  K
K
D)all of the above.
A)consumption plus net investment equal net national product.
B)consumption plus net investment equals real GDP less depreciation.
C)C +
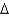 K = Y -
K = Y -  K
KD)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In the multi-year budget constraint the present value of consumption equals the value of initial assets plus the:
A)present value of savings.
B)present value of final assets.
C)present value of wage incomes.
D)the present value of time.
A)present value of savings.
B)present value of final assets.
C)present value of wage incomes.
D)the present value of time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The marginal propensity to consume out of a temporary change in income is approximately:
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The marginal propensity to save out of a permanent change in income is approximately:
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
An intertemporal substitution effect is caused by a change in:
A)a price from one period to another.
B)wealth.
C)income.
D)all of the above.
A)a price from one period to another.
B)wealth.
C)income.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The marginal propensity to save out of a temporary change in income is approximately:
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What are the effects of an increase in the interest rate on the choice of consumption over time?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
If the household budget constraint is aggregated over all household, it shows that:
A)consumption less net investment equal net national product.
B)consumption plus net investment equals real GDP less depreciation.
C)C -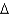 K = Y +
K = Y +  K
K
D)all of the above.
A)consumption less net investment equal net national product.
B)consumption plus net investment equals real GDP less depreciation.
C)C -
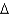 K = Y +
K = Y +  K
KD)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
An increase in the interest rate:
A)makes future consumption more expensive.
B)increases future income.
C)makes present consumption cheaper.
D)all of the above.
A)makes future consumption more expensive.
B)increases future income.
C)makes present consumption cheaper.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Derive the household's two period real budget constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
If a worker gets a promotion that doubles their salary, with the increase in salary we would expect them to:
A)save most of it.
B)reject it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half of it and save half of it.
A)save most of it.
B)reject it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half of it and save half of it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The marginal propensity to consume out of a permanent change in income is approximately:
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.
A)1
B)0.5
C)0
D)none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
If the household budget constraint is aggregated over all household, it shows that:
A)consumption plus net investment equal net national product.
B)consumption less net investment equals real GDP less depreciation.
C)C -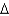 K = Y +
K = Y + 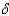 K.
K.
D)all of the above.
A)consumption plus net investment equal net national product.
B)consumption less net investment equals real GDP less depreciation.
C)C -
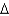 K = Y +
K = Y + 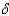 K.
K.D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
If a worker receives a onetime bonus we would expect them to:
A)save most of it.
B)refuse it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half and save half of it.
A)save most of it.
B)refuse it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half and save half of it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is an intertemporal substitution effect and what can cause one?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
If a worker receives a bonus every Christmas, we would expect them to:
A)save most of it.
B)reject it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half of it and save half of it.
A)save most of it.
B)reject it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half of it and save half of it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
If a person wins €500 in a scratch-off lottery game, we would expect them to:
A)save most of it.
B)refuse it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half and save half of it.
A)save most of it.
B)refuse it.
C)consume most of it.
D)consume half and save half of it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If the household budget constraint is aggregated over all household, it shows that:
A)profit is zero.
B)PC+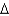 B+P•
B+P• 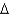 K =
K = 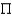 + wL + i(B + PK),
+ wL + i(B + PK),
C)C +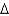 K = Y -
K = Y - 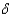 K
K
D)all of the above.
A)profit is zero.
B)PC+
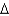 B+P•
B+P• 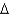 K =
K = 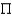 + wL + i(B + PK),
+ wL + i(B + PK),C)C +
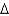 K = Y -
K = Y - 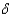 K
KD)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
What is an income effect and what can cause one?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








