Deck 3: Introduction to Economic Growth
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/63
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 3: Introduction to Economic Growth
1
Saving is income that is not consumed.
True
2
The standard of living of people in a country is their per capita income.
True
3
World growth data reveals that from 1960 to 2011:
A)all countries grew at similar rates.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew moderately.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew rapidly.
D)the US and other OECD countries stagnated.
A)all countries grew at similar rates.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew moderately.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew rapidly.
D)the US and other OECD countries stagnated.
some countries particularly East Asian countries grew rapidly.
4
A in the production function Y = A • F(K,L) is:
A)the marginal product of labour.
B)the capital to labour ratio (K/L).
C)the marginal product of capital.
D)the level of technology.
A)the marginal product of labour.
B)the capital to labour ratio (K/L).
C)the marginal product of capital.
D)the level of technology.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If the production function Y = A • (K,L) is divided by L, then
A)(Y/L) = A•f(K/L).
B)output per capita equals technology times a function of the capital labour ratio.
C)y = A•f(k).
D)all of the above.
A)(Y/L) = A•f(K/L).
B)output per capita equals technology times a function of the capital labour ratio.
C)y = A•f(k).
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Real saving equals gross investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If A in the production function Y = A • F(K,L) rises, then:
A)output rises for any level of K and L.
B)the marginal product of labour rises.
C)the marginal product of capital rises.
D)all of the above.
A)output rises for any level of K and L.
B)the marginal product of labour rises.
C)the marginal product of capital rises.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In the production function Y = A • F(K,L), L is:
A)leisure.
B)labour.
C)the marginal product of labour.
D)the marginal product of leisure.
A)leisure.
B)labour.
C)the marginal product of labour.
D)the marginal product of leisure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Diminishing returns to labour implies that eventually the marginal product of labour will become negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
World growth data reveals that from 1960 to 2011:
A)the US and other OECD countries stagnated.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew at low or negative rates.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew at low or negative rates.
D)all of the above.
A)the US and other OECD countries stagnated.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew at low or negative rates.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew at low or negative rates.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The marginal product of labour is:
A)how much output rises for when labour increases one unit.
B)capital divided by labuor (K/L).
C)labour divided by capital (L/K)
D)the level of technology.
A)how much output rises for when labour increases one unit.
B)capital divided by labuor (K/L).
C)labour divided by capital (L/K)
D)the level of technology.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
World growth data shows that from 1960 to 2011:
A)the US and other OECD countries grew at moderate rates.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew at low rates or declined.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew rapidly.
D)all of the above.
A)the US and other OECD countries grew at moderate rates.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew at low rates or declined.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew rapidly.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
World growth data reveals that from 1960 to 2011:
A)the US and other OECD countries grew at moderate rates.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew rapidly.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew a low rates or declined.
D)all of the above.
A)the US and other OECD countries grew at moderate rates.
B)sub-Saharan African countries grew rapidly.
C)some countries particularly East Asian countries grew a low rates or declined.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
For the production function Y = A • F(K,L) constant returns to scale means:
A)if capital and labour double output doubles.
B)capital and labour increase at a constant rate.
C)the marginal products of capital and labour are constant.
D)technology is constant.
A)if capital and labour double output doubles.
B)capital and labour increase at a constant rate.
C)the marginal products of capital and labour are constant.
D)technology is constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The US and other OECD countries had high levels of GDP per person in 2011 despite growing at a moderate rate from 1960 to 2011 because:
A)of exploitation of foreign countries.
B)their economies had grown at a moderate rate for a century or more.
C)they stole the wealth of less developed countries.
D)all of the above.
A)of exploitation of foreign countries.
B)their economies had grown at a moderate rate for a century or more.
C)they stole the wealth of less developed countries.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Diminishing marginal product of capital (MPK) means:
A)output rises as capital rises.
B)the MPK eventually falls as capital rises.
C)output rises as the MPK rises.
D)the marginal product of capital eventually becomes negative as capital rises.
A)output rises as capital rises.
B)the MPK eventually falls as capital rises.
C)output rises as the MPK rises.
D)the marginal product of capital eventually becomes negative as capital rises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
In the production function Y = A • F(K,L), Y is:
A)good Y.
B)production.
C)the marginal product of good Y.
D)constant returns to scale.
A)good Y.
B)production.
C)the marginal product of good Y.
D)constant returns to scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The marginal product of capital is:
A)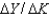 .
.
B)the change in output for a unit change in capital.
C)the slope of the production when technology and labour are held constant.
D)all of the above.
A)
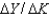 .
.B)the change in output for a unit change in capital.
C)the slope of the production when technology and labour are held constant.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Among the assumptions made about the production function Y = A • (K,L) is:
A)diminishing marginal product of labour.
B)constant returns to scale.
C)diminishing marginal product of capital.
D)all of the above.
A)diminishing marginal product of labour.
B)constant returns to scale.
C)diminishing marginal product of capital.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The marginal product of capital is how much output changes when capital increases by one unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Figure 3.1 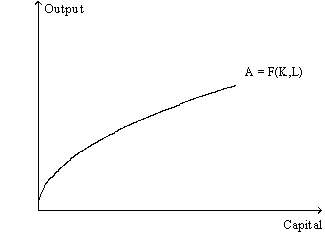
In Figure 3.1 the average product of capital is:
A)rising.
B)constant.
C)falling.
D)unknown.

In Figure 3.1 the average product of capital is:
A)rising.
B)constant.
C)falling.
D)unknown.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Depreciation of the capital stock occurs due to:
A)machines deteriorating.
B)vehicles needing parts.
C)buildings needing repair.
D)all of the above.
A)machines deteriorating.
B)vehicles needing parts.
C)buildings needing repair.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The average product of capital is:
A)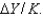
B)Y/K.
C)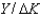 .
.
D)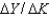 .
.
A)
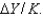
B)Y/K.
C)
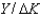 .
.D)
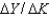 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Depreciation of the capital stock occurs due to:
A)inflation.
B)buildings needing repair.
C)bonds falling in value.
D)all of the above.
A)inflation.
B)buildings needing repair.
C)bonds falling in value.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
In a closed economy with no government sector, the change in the capital stock is equal to:
A)net investment less depreciation.
B)nominal saving.
C)gross investment.
D)real saving.
A)net investment less depreciation.
B)nominal saving.
C)gross investment.
D)real saving.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The growth accounting formula is:
A)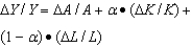
B)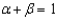
C)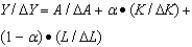
D)Y= A • F(K,L)
A)
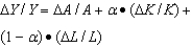
B)
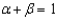
C)
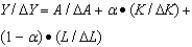
D)Y= A • F(K,L)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In a closed economy with no government sector, the change in the capital stock is:
A)net investment less depreciation.
B)gross investment less depreciation.
C)gross investment.
D)nominal saving.
A)net investment less depreciation.
B)gross investment less depreciation.
C)gross investment.
D)nominal saving.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If there are 120 machines in an economy and the depreciation rate is 5% per year, then:
A)depreciation is 5 machines a year.
B)depreciation is 6 machines a year.
C)depreciation is 115 machines per year.
D)depreciation is 114 machines per year.
A)depreciation is 5 machines a year.
B)depreciation is 6 machines a year.
C)depreciation is 115 machines per year.
D)depreciation is 114 machines per year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If a country has a population of 300 million and a labour force of 200 million, then its labour force participation rate is:
A)0.67
B)1.5
C)100 million.
D)200 million.
A)0.67
B)1.5
C)100 million.
D)200 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The labour force participation rate is:
A)the labour force divided into population.
B)the labour force divide by population.
C)the labour force times population.
D)the labour population minus the labour force.
A)the labour force divided into population.
B)the labour force divide by population.
C)the labour force times population.
D)the labour population minus the labour force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Depreciation of the capital stock occurs due to:
A)deflation.
B)vehicles requiring new parts.
C)bonds falling in value.
D)all of the above.
A)deflation.
B)vehicles requiring new parts.
C)bonds falling in value.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Growth accounting shows that economic growth depends on:
A)increases in technology.
B)the growth of the labour force.
C)growth in the capital stock.
D)all of the above.
A)increases in technology.
B)the growth of the labour force.
C)growth in the capital stock.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Growth accounting shows that GDP growth depends on:
A)growth of the capital stock.
B)holding environmental pollution in check.
C)government purchases.
D)having a reasonable distribution of income.
A)growth of the capital stock.
B)holding environmental pollution in check.
C)government purchases.
D)having a reasonable distribution of income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The change in the capital stock in an economy depends on:
A)the economy's saving.
B)the change in bond prices.
C)the economy's investment.
D)all of the above.
A)the economy's saving.
B)the change in bond prices.
C)the economy's investment.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Depreciation of the capital stock occurs due to:
A)machines deteriorating.
B)real estate rising in value.
C)bonds falling in value.
D)all of the above.
A)machines deteriorating.
B)real estate rising in value.
C)bonds falling in value.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
If a country has a population of 100 million and a labour force of 60 million, then its labour force participation rate is:
A)0.6.
B)1.67
C)40 million.
D)60 million.
A)0.6.
B)1.67
C)40 million.
D)60 million.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Growth accounting shows that economic growth depends on:
A)controlling environmental pollution.
B)international cooperation.
C)increases in technology.
D)all of the above.
A)controlling environmental pollution.
B)international cooperation.
C)increases in technology.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Among the categories the growth rate is broken down into by growth accounting is:
A)the growth rate of technology.
B)the marginal product of capital.
C)the capital labour ratio.
D)all of the above.
A)the growth rate of technology.
B)the marginal product of capital.
C)the capital labour ratio.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If there are 120 machines in an economy and the depreciation rate is 10% per year, then next year there are:
A)10 of the original machines left.
B)12 of the original machines left.
C)108 of the original machines left.
D)110 of the original machines left.
A)10 of the original machines left.
B)12 of the original machines left.
C)108 of the original machines left.
D)110 of the original machines left.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Growth accounting shows that economic growth depends on:
A)government tax receipts.
B)the growth of the labour force.
C)lowering environmental pollution.
D)all of the above.
A)government tax receipts.
B)the growth of the labour force.
C)lowering environmental pollution.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
During the transition to the steady state in the Solow growth model:
A)the output per worker rises.
B)the capital to labour ratio rises.
C)the rate of growth of capital falls.
D)all of the above.
A)the output per worker rises.
B)the capital to labour ratio rises.
C)the rate of growth of capital falls.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The Solow residual is that part of output growth attributed to:
A)the growth rate of the labour force.
B)the growth rate of output.
C)the growth rate of the capital stock.
D)the grow rate of technology.
A)the growth rate of the labour force.
B)the growth rate of output.
C)the growth rate of the capital stock.
D)the grow rate of technology.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Figure 3.1 
Figure 3.1 shows:
A)a production function with labour and technology constant.
B)a production function with capital and labour constant.
C)a production function with capital and technology constant.
D)a production function with capital, labour and technology constant.

Figure 3.1 shows:
A)a production function with labour and technology constant.
B)a production function with capital and labour constant.
C)a production function with capital and technology constant.
D)a production function with capital, labour and technology constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The Solow residual is:
A)that part of output growth not attributed to labour force growth.
B)that part of output growth not attributed to capital stock growth.
C)that part of output growth not attributed to capital stock growth and labour force growth.
D)the growth in output.
A)that part of output growth not attributed to labour force growth.
B)that part of output growth not attributed to capital stock growth.
C)that part of output growth not attributed to capital stock growth and labour force growth.
D)the growth in output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In the Solow growth model the optimal capital to labour ratio, K/L, is where:
A)s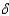 + n = s•(k/y).
+ n = s•(k/y).
B)s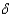 + n = s•(y/k).
+ n = s•(y/k).
C)n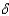 + s = s•(y/k).
+ s = s•(y/k).
D)s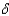 + s = n•(y/k).
+ s = n•(y/k).
A)s
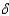 + n = s•(k/y).
+ n = s•(k/y).B)s
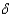 + n = s•(y/k).
+ n = s•(y/k).C)n
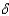 + s = s•(y/k).
+ s = s•(y/k).D)s
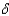 + s = n•(y/k).
+ s = n•(y/k).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
In the steady state of the Solow growth model:
A)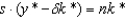
B)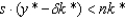
C)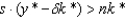
D)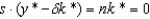
A)
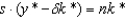
B)
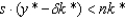
C)
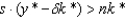
D)
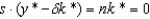

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The Solow residual:
A)is not directly observable.
B)attributed to labour force growth.
C)is attributed to capital stock growth.
D)is attributed to labour force growth and capital stock growth.
A)is not directly observable.
B)attributed to labour force growth.
C)is attributed to capital stock growth.
D)is attributed to labour force growth and capital stock growth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The Solow growth model shows that the growth rate of real GDP per worker depends on:
A)the saving rate, s
B)the growth rate of the labour force, n.
C)the depreciation rate,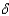 .
.
D)all of the above.
A)the saving rate, s
B)the growth rate of the labour force, n.
C)the depreciation rate,
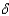 .
.D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What is a production function?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The Solow growth model shows that the growth rate of real GDP per worker depends on:
A)the rate of growth of the money supply.
B)the growth rate of the labour force, n.
C)rate of growth of government debt.
D)all of the above.
A)the rate of growth of the money supply.
B)the growth rate of the labour force, n.
C)rate of growth of government debt.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
During the transition to the steady state in the Solow growth model:
A)the output per worker rises.
B)labour force participation rises.
C)the rate of growth of capital rises.
D)all of the above.
A)the output per worker rises.
B)labour force participation rises.
C)the rate of growth of capital rises.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
During the transition to the steady state in the Solow growth model:
A)the output per worker falls.
B)labour force participation rises.
C)the rate of growth of capital falls.
D)all of the above.
A)the output per worker falls.
B)labour force participation rises.
C)the rate of growth of capital falls.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Figure 3.1 
In Figure 3.1 the marginal product of capital is:
A)rising.
B)declining.
C)constant.
D)unknown.

In Figure 3.1 the marginal product of capital is:
A)rising.
B)declining.
C)constant.
D)unknown.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
In the Solow growth model the economy reaches the optimal k*:
A)immediately.
B)over a period of time.
C)randomly.
D)cyclically.
A)immediately.
B)over a period of time.
C)randomly.
D)cyclically.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
In the Solow growth model the steady state is when the economy has:
A)full employment.
B)the optimal capital labour ratio, k*.
C)zero inflation.
D)all of the above.
A)full employment.
B)the optimal capital labour ratio, k*.
C)zero inflation.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The Solow growth model shows that the growth rate of real GDP per worker depends on:
A)the rate of growth of the money supply.
B)level of output in the economy.
C)the depreciation rate,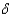 .
.
D)all of the above.
A)the rate of growth of the money supply.
B)level of output in the economy.
C)the depreciation rate,
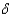 .
.D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The Solow growth model shows that the growth rate of real GDP per worker depends on:
A)the saving rate, s
B)government spending, G.
C)the rate of inflation.
D)all of the above.
A)the saving rate, s
B)government spending, G.
C)the rate of inflation.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What do constant returns to scale imply?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The Solow growth model assumes unemployment is:
A)zero.
B)falling.
C)rising.
D)constant.
A)zero.
B)falling.
C)rising.
D)constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The Solow growth model ignores:
A)the international sector.
B)the role of government.
C)changes in labour force participation.
D)all of the above.
A)the international sector.
B)the role of government.
C)changes in labour force participation.
D)all of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
What is the growth account formula and what does it tell us?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What is the key equation of the Solow growth model and what does it say to us?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Show why real saving equals net investment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 63 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








