Deck 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
What effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand or aggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and level of real output. Assume that all other things remain constant.
a. A widespread fear of depression on the part of consumers.
b. A $2 increase in the excise tax on a pack of cigarettes.
c. A reduction in interest rates at each price level.
d. A major increase in Federal spending for health care.
e. The expectation of rapid inflation.
f. The complete disintegration of OPEC, causing oil prices to fall by one-half.
g. A 10 percent reduction in personal income tax rates.
h. A sizable increase in labor productivity (with no change in nominal wages).
i. A 12 percent increase in nominal wages (with no change in productivity).
j. Depreciation in the international value of the dollar.
a. A widespread fear of depression on the part of consumers.
b. A $2 increase in the excise tax on a pack of cigarettes.
c. A reduction in interest rates at each price level.
d. A major increase in Federal spending for health care.
e. The expectation of rapid inflation.
f. The complete disintegration of OPEC, causing oil prices to fall by one-half.
g. A 10 percent reduction in personal income tax rates.
h. A sizable increase in labor productivity (with no change in nominal wages).
i. A 12 percent increase in nominal wages (with no change in productivity).
j. Depreciation in the international value of the dollar.
(a)
A wide spread fear of depression on the part of consumers leads to cut back in the consumption spending and investment spending, and hence a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve. This shift decreases price level and output level.
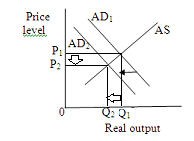 Thus the price level and equilibrium quantity falls.
Thus the price level and equilibrium quantity falls.
(b)
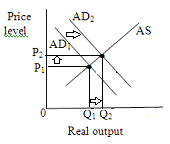
A $2 increase in the excise tax on a pack of cigarettes will increase per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve leftwards. This shift will increase price level and decrease output level.
 Thus the price level rises and equilibrium quantity falls.
Thus the price level rises and equilibrium quantity falls.
(c)
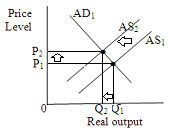
A reduction in interest rates at each price level will increase investment spending, and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
 Thus the equilibrium price and quantity both will incarses.
Thus the equilibrium price and quantity both will incarses.
(d)
A major increase in Federal spending for health care will increase government spending, and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level. Any real improvement in health care resulting from spending would eventually increase and shift the AS curve right.
But the immediate effect of increase in government spending is that the AD curve shift rightwards.
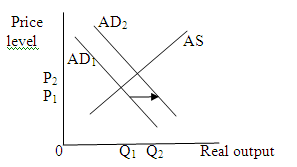 (e)
(e)
The expectation of rapid inflation will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
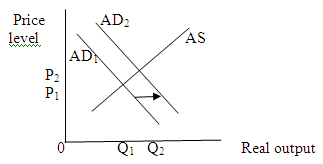 (f)
(f)
The complete disintegration of OPEC, causing oil prices to fall by one-half will decrease per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve rightwards. This shift will decrease price level and increase output level.
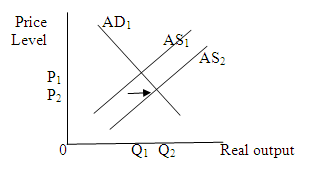 (g)
(g)
A 10 percent reduction in personal income tax rates will increase consumption spending, and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
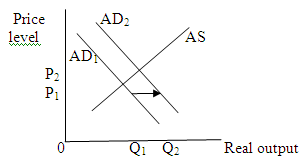 (h)
(h)
A sizable increase in labor productivity (with no change in nominal wages) will decrease per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve rightwards. This shift will decrease price level and increase output level.
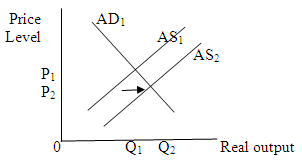 (i)
(i)
A 12 percent increase in nominal wages (with no change in productivity) will increase per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve leftwards. This shift will increase price level and decrease output level.
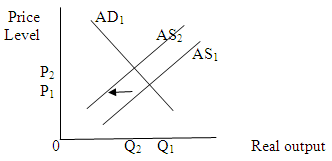 (j)
(j)
Depreciation in the international value of the dollar will increase net exports of U.S., and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
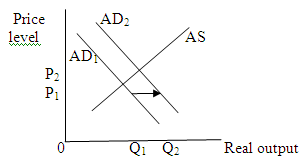
A wide spread fear of depression on the part of consumers leads to cut back in the consumption spending and investment spending, and hence a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve. This shift decreases price level and output level.
 Thus the price level and equilibrium quantity falls.
Thus the price level and equilibrium quantity falls. (b)
A $2 increase in the excise tax on a pack of cigarettes will increase per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve leftwards. This shift will increase price level and decrease output level.
 Thus the price level rises and equilibrium quantity falls.
Thus the price level rises and equilibrium quantity falls. (c)
A reduction in interest rates at each price level will increase investment spending, and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
 Thus the equilibrium price and quantity both will incarses.
Thus the equilibrium price and quantity both will incarses.(d)
A major increase in Federal spending for health care will increase government spending, and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level. Any real improvement in health care resulting from spending would eventually increase and shift the AS curve right.
But the immediate effect of increase in government spending is that the AD curve shift rightwards.
 (e)
(e)The expectation of rapid inflation will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
 (f)
(f) The complete disintegration of OPEC, causing oil prices to fall by one-half will decrease per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve rightwards. This shift will decrease price level and increase output level.
 (g)
(g)A 10 percent reduction in personal income tax rates will increase consumption spending, and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.
 (h)
(h)A sizable increase in labor productivity (with no change in nominal wages) will decrease per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve rightwards. This shift will decrease price level and increase output level.
 (i)
(i)A 12 percent increase in nominal wages (with no change in productivity) will increase per-unit production cost which will shift aggregate supply curve leftwards. This shift will increase price level and decrease output level.
 (j)
(j)Depreciation in the international value of the dollar will increase net exports of U.S., and hence will increase aggregate demand at each price level. It will lead to a rightward shift in aggregate demand curve. This shift will increase price level and output level.

2
Assume that (a) the price level is flexible upward but not downward and (b) the economy is currently operating at its full-employment output. Other things equal, how will each of the following affect the equilibrium price level and equilibrium level of real output in the short run
a. An increase in aggregate demand.
b. A decrease in aggregate supply, with no change in aggregate demand.
c. Equal increases in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
d. A decrease in aggregate demand.
e. An increase in aggregate demand that exceeds an increase in aggregate supply.
a. An increase in aggregate demand.
b. A decrease in aggregate supply, with no change in aggregate demand.
c. Equal increases in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
d. A decrease in aggregate demand.
e. An increase in aggregate demand that exceeds an increase in aggregate supply.
a. An increase in aggregate demand shifts the demand curve rightward, which increases the equilibrium price and increases the real output.
b. A decrease in aggregate supply decreases real output and does not affect equilibrium price, because the price is inflexible downward.
c. Equal increases in demand and supply increases real output and does not affect the price level, because the effects on price from the change in demand and supply are of the same magnitude and set off each other.
d. A decrease in aggregate demand shifts the demand curve leftward and reduce real output, but does not change equilibrium price, because the price is inflexible downward.
e. An increase in aggregate demand that exceeds an increase in aggregate supply increases real output and increases equilibrium price, because the there is a net increase on demand which pushes up the price.
b. A decrease in aggregate supply decreases real output and does not affect equilibrium price, because the price is inflexible downward.
c. Equal increases in demand and supply increases real output and does not affect the price level, because the effects on price from the change in demand and supply are of the same magnitude and set off each other.
d. A decrease in aggregate demand shifts the demand curve leftward and reduce real output, but does not change equilibrium price, because the price is inflexible downward.
e. An increase in aggregate demand that exceeds an increase in aggregate supply increases real output and increases equilibrium price, because the there is a net increase on demand which pushes up the price.
3
KEY QUESTION What is meant when economists say that the Federal Reserve Banks are central banks, quasi-public banks, and bankers' banks What are the seven basic functions of the Federal Reserve System
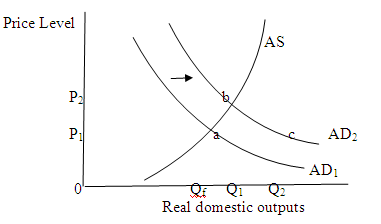
When aggregate supply curve is upward sloping then per-unit production cost increases with a rise in real output. In this case when government spending is increased then aggregate demand curve shifts rightwards and the aggregate demand increases. The increase in aggregate demand from AD 1 to AD 2 causes demand-pull inflation (P 1 to P 2 ). It also causes an inflationary GDP gap of Q 1 minus Q f. The rise in the price level reduces the effect of the multiplier effect. If price level is prevented from rising then the real output increases from Q f to Q 2 and the multiplier would have been at full strength.

4
Following are two hypothetical ways in which the Federal Reserve Board might be appointed. Would you favor either of these two methods over the present method Why or why not
a. Upon taking office, the U.S. president appoints seven people to the Federal Reserve Board, including a chair. Each appointee must be confirmed by a majority vote of the Senate, and each serves the same 4-year term as the president.
b. Congress selects seven members from its ranks (four from the House of Representatives and three from the Senate) to serve at its pleasure as the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
a. Upon taking office, the U.S. president appoints seven people to the Federal Reserve Board, including a chair. Each appointee must be confirmed by a majority vote of the Senate, and each serves the same 4-year term as the president.
b. Congress selects seven members from its ranks (four from the House of Representatives and three from the Senate) to serve at its pleasure as the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
What are the major categories of firms that make up the U.S. financial services industry Did the bank and thrift share of the financial services market rise, fall, or stay the same between 1980 and 2005 Are there more or fewer bank firms today than a decade ago Why are the lines between the categories of financial firms becoming more blurred than in the past

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
How does a debit card differ from a credit card How does a stored-value card differ from both Suppose that a person has a credit card, debit card, and stored-value card. Create a fictional scenario in which the person uses all three cards in the same day. Explain the person's logic for using one card rather than one of the others for each transaction. How do Fedwire and ACH transactions differ from credit card, debit card, and stored-value card transactions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
LAST WORD Over the years, the Federal Reserve Banks have printed many billions of dollars more in currency than U.S. households, businesses, and financial institutions now hold. Where is this "missing" money Why is it there

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What are the three basic functions of money Describe how rapid inflation can undermine money's ability to perform each of the three functions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
WHO ARE THE MEMBERS OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE BOARD The Federal Reserve Board Web site, www.federalreserve.gov/BIOS/ , provides a detailed biography of the seven members of the Board of Governors. What is the composition of the Board with regard to age, gender, education, previous employment, and ethnic background Which Board members are near the ends of their terms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which two of the following financial institutions offer checkable deposits included within the M 1 money supply: mutual fund companies; insurance companies; commercial banks; securities firms; thrift institutions Which of the following is not included in either M 1 or M 2: currency held by the public; checkable deposits; money market mutual fund balances; small (less than $100,000) time deposits; currency held by banks; savings deposits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
CURRENCY TRIVIA Visit the Web site of the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, www.frbatlanta.org/publica/brochure/fundfac/money.htm , to answer the following questions: What are the denominations of Federal Reserve Notes now being printed What was the largest-denomination Federal Reserve Note ever printed and circulated, and when was it last printed What are some tips for spotting counterfeit currency When was the last silver dollar minted What have been the largest and smallest U.S. coin denominations since the Coinage Act of 1792 .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Explain and evaluate the following statements:
a. The invention of money is one of the great achievements of humankind, for without it the enrichment that comes from broadening trade would have been impossible.
b. Money is whatever society says it is.
c. In most economies of the world, the debts of government and commercial banks are used as money.
d. People often say they would like to have more money, but what they usually mean is that they would like to have more goods and services.
e. When the price of everything goes up, it is not because everything is worth more but because the currency is worth less.
f. Any central bank can create money; the trick is to create enough, but not too much, of it.
a. The invention of money is one of the great achievements of humankind, for without it the enrichment that comes from broadening trade would have been impossible.
b. Money is whatever society says it is.
c. In most economies of the world, the debts of government and commercial banks are used as money.
d. People often say they would like to have more money, but what they usually mean is that they would like to have more goods and services.
e. When the price of everything goes up, it is not because everything is worth more but because the currency is worth less.
f. Any central bank can create money; the trick is to create enough, but not too much, of it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Suppose that aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown:
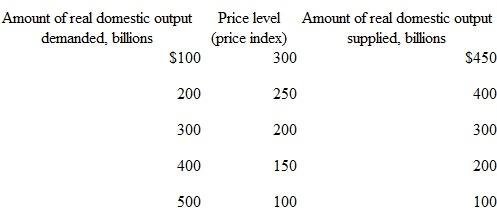
a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What is the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full capacity real output Explain.
b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy Why not 250
c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real domestic output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD 1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output
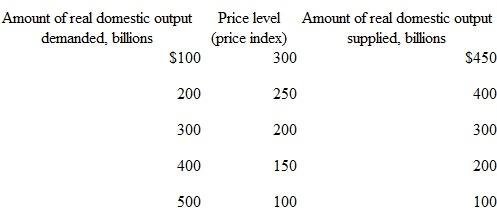
a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What is the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full capacity real output Explain.
b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy Why not 250
c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real domestic output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD 1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Suppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real output and the input quantities necessary for producing that level of output:
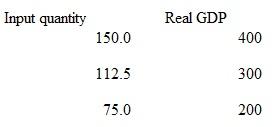
a. What is productivity in this economy
b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2
c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production In what direction did the $1 increase in input price push the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift in aggregate supply have upon the price level and the level of real output
d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but instead that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production What effect would this change in per unit production cost have on the aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift in aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
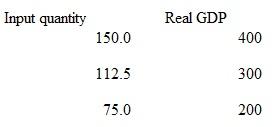
a. What is productivity in this economy
b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2
c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production In what direction did the $1 increase in input price push the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift in aggregate supply have upon the price level and the level of real output
d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but instead that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production What effect would this change in per unit production cost have on the aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift in aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 14 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








