Deck 2: A Users Guide to the Sky
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: A Users Guide to the Sky
1
The apparent visual magnitude of a star is 7.3. This tells us that the star is
A) one of the brighter stars in the sky.
B) bright enough that it would be visible even during the day.
C) not visible with the unaided eye.
D) very far from Earth.
E) very close to Earth.
A) one of the brighter stars in the sky.
B) bright enough that it would be visible even during the day.
C) not visible with the unaided eye.
D) very far from Earth.
E) very close to Earth.
not visible with the unaided eye.
2
A(n) ____ is 1/60th of a minute of arc.
A) precession
B) second of arc
C) degree
D) nadir
E) angular diameter
A) precession
B) second of arc
C) degree
D) nadir
E) angular diameter
second of arc
3
An observer at Earth's geographic north pole would find _______
A) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the northern horizon.
B) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the southern horizon.
C) that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
D) the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) None of the above are true.
A) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the northern horizon.
B) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the southern horizon.
C) that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
D) the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) None of the above are true.
that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
4
In contrast to Ursa Major, the Big Dipper is not a(n) ___ but is instead a(n) ______
A) star; constellation.
B) asterism; constellation.
C) a constellation; asterism.
D) Wrong! Both are asterisms.
E) Wrong! Both are official constellations.
A) star; constellation.
B) asterism; constellation.
C) a constellation; asterism.
D) Wrong! Both are asterisms.
E) Wrong! Both are official constellations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
An observer's nadir is
A) the point directly opposite the observer's zenith.
B) the north point on the observer's horizon.
C) located at the center of Earth.
D) always located near a circumpolar constellation.
E) directly opposite the north celestial pole.
A) the point directly opposite the observer's zenith.
B) the north point on the observer's horizon.
C) located at the center of Earth.
D) always located near a circumpolar constellation.
E) directly opposite the north celestial pole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The ____ of an object can be measured in degrees.
A) apparent brightness
B) apparent magnitude
C) zenith
D) angular diameter
E) color
A) apparent brightness
B) apparent magnitude
C) zenith
D) angular diameter
E) color

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The apparent visual magnitude of a star is a measure of the star's
A) size.
B) intensity.
C) distance.
D) color.
E) temperature.
A) size.
B) intensity.
C) distance.
D) color.
E) temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The star Vega has an apparent visual magnitude of 0.03 and the star HR 4374 has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.87. It has been determined that both stars are at the same distance from Earth. What does this information tell us about the two stars?
A) Vega must be closer to Earth than HR 4374.
B) Vega must be farther from Earth than HR 4374.
C) Vega must produce less energy per second than HR 4374.
D) Vega must produce more energy per second than HR 4374.
E) Vega will appear fainter to us than HR 4374.
A) Vega must be closer to Earth than HR 4374.
B) Vega must be farther from Earth than HR 4374.
C) Vega must produce less energy per second than HR 4374.
D) Vega must produce more energy per second than HR 4374.
E) Vega will appear fainter to us than HR 4374.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A(n) ____ is 1/60th of a degree.
A) precession
B) second of arc
C) minute of arc
D) nadir
E) angular diameter
A) precession
B) second of arc
C) minute of arc
D) nadir
E) angular diameter

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
An observer in the Northern Hemisphere watches the sky for several hours. Due to the motion of Earth, this observer notices that the stars near the north celestial pole appear to move
A) counter-clockwise around the celestial pole.
B) clockwise around the celestial pole.
C) from left to right.
D) from right to left.
E) nearly vertically upward.
A) counter-clockwise around the celestial pole.
B) clockwise around the celestial pole.
C) from left to right.
D) from right to left.
E) nearly vertically upward.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Seen from the northern latitudes (mid-northern hemisphere), the star Polaris
A) is never above the horizon during the day.
B) always sets directly in the west.
C) is always above the northern horizon.
D) is never visible during the winter.
E) is the brightest star in the sky.
A) is never above the horizon during the day.
B) always sets directly in the west.
C) is always above the northern horizon.
D) is never visible during the winter.
E) is the brightest star in the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Precession of the rotation axis of Earth is caused by
A) the force of gravity from the sun and moon on Earth's equatorial bulge.
B) the force of gravity from the sun and Jupiter on the Earth-moon system.
C) the magnetic field of Earth.
D) the formation and subsequent melting of glaciers during the ice-ages.
E) the impact of asteroids.
A) the force of gravity from the sun and moon on Earth's equatorial bulge.
B) the force of gravity from the sun and Jupiter on the Earth-moon system.
C) the magnetic field of Earth.
D) the formation and subsequent melting of glaciers during the ice-ages.
E) the impact of asteroids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
An observer on Earth's geographic north pole would find
A) Polaris directly overhead.
B) Polaris 40° above the northern horizon.
C) that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
D) that the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) that the ecliptic coincides with the horizon.
A) Polaris directly overhead.
B) Polaris 40° above the northern horizon.
C) that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
D) that the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) that the ecliptic coincides with the horizon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Most star names, such as Aldebaran and Betelgeuse, are___ in origin.
A) Latin
B) Greek
C) Arabic
D) English
E) Italian
A) Latin
B) Greek
C) Arabic
D) English
E) Italian

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
An observer on Earth's equator would find _______
A) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the northern horizon.
B) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the southern horizon.
C) that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
D) the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) None of the above are true.
A) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the northern horizon.
B) the celestial equator passing at 45 degrees above the southern horizon.
C) that the celestial equator coincides with the horizon.
D) the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) None of the above are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The magnitude scale
A) originated just after the telescope was invented.
B) can be used to indicate the apparent intensity of a celestial object.
C) was devised by Galileo.
D) is no longer used today.
E) was used to determine the rate of precession.
A) originated just after the telescope was invented.
B) can be used to indicate the apparent intensity of a celestial object.
C) was devised by Galileo.
D) is no longer used today.
E) was used to determine the rate of precession.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
An observer on Earth's equator would find
A) Polaris directly overhead.
B) Polaris 40° above the northern horizon.
C) Polaris on the northern horizon.
D) that the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) that the ecliptic coincides with the horizon.
A) Polaris directly overhead.
B) Polaris 40° above the northern horizon.
C) Polaris on the northern horizon.
D) that the celestial equator passing directly overhead.
E) that the ecliptic coincides with the horizon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
You live at a latitude of 73° N. What is the angle between the northern horizon and the north celestial pole?
A) 73°
B) 27°
C) 17°
D) 23°
E) 5°
A) 73°
B) 27°
C) 17°
D) 23°
E) 5°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Constellation names are from _____ translated into _______, the language of science in Europe to the 19th century.
A) Greek; Latin
B) Latin; Greek
C) Latin; Arabic
D) Greek; English
E) Greek; Italian
A) Greek; Latin
B) Latin; Greek
C) Latin; Arabic
D) Greek; English
E) Greek; Italian

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The ____ is the point on the celestial sphere directly above an observer who can be at any point on the Earth..
A) north celestial pole
B) south celestial pole
C) zenith
D) celestial equator
E) nadir
A) north celestial pole
B) south celestial pole
C) zenith
D) celestial equator
E) nadir

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
You live at a latitude of 39° S. What is the angle between the southern horizon and the south celestial pole?
A) 45°
B) 23.5°
C) 39°
D) 51°
E) The answer depends on the day of the year.
A) 45°
B) 23.5°
C) 39°
D) 51°
E) The answer depends on the day of the year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram below? 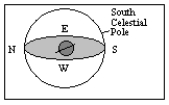
A) 20° N
B) 20° S
C) 70° N
D) 70° S
E) 0°

A) 20° N
B) 20° S
C) 70° N
D) 70° S
E) 0°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Table 2-1
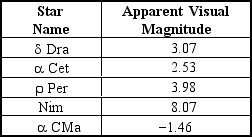
-Refer to Table 2-1. Which star in the table would not be visible to the unaided eye of an observer on Earth?
A) ( Cet)
B) ( Cma)
C) Nim
D) ( Per)
E) ( Dra)

-Refer to Table 2-1. Which star in the table would not be visible to the unaided eye of an observer on Earth?
A) ( Cet)
B) ( Cma)
C) Nim
D) ( Per)
E) ( Dra)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
An observer in the Northern Hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky. If the illustration below depicts the photograph taken by the observer, which direction was the camera pointing? 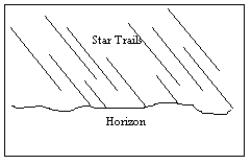
A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
You live at a latitude of 28° N. What is the angle between the northern horizon and the north celestial pole?
A) 62°
B) 28°
C) 40°
D) 23°
E) 5°
A) 62°
B) 28°
C) 40°
D) 23°
E) 5°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
You live at a latitude of 16° S. What is the angle between the southern horizon and the south celestial pole?
A) 74°
B) 164°
C) 16°
D) 23°
E) 5°
A) 74°
B) 164°
C) 16°
D) 23°
E) 5°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
You live at a latitude of 39° S. What is the angle between the southern horizon and the south celestial pole?
A) 45°
B) 23.5°
C) 39°
D) 51°
E) The answer depends on the day of the year.
A) 45°
B) 23.5°
C) 39°
D) 51°
E) The answer depends on the day of the year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship between stars and constellations?
A) Only stars close to the ecliptic (the Earth's orbital plane) are located in constellations.
B) Every star is located in a constellation.
C) Only the brighter stars are in constellations.
D) Only those stars that were visible to the ancient Greeks are located in constellations.
A) Only stars close to the ecliptic (the Earth's orbital plane) are located in constellations.
B) Every star is located in a constellation.
C) Only the brighter stars are in constellations.
D) Only those stars that were visible to the ancient Greeks are located in constellations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If the north celestial pole appears on your horizon, what is your latitude?
A) 90° N
B) 90° S
C) 0°
D) 45° N
E) The latitude of the observer cannot be determined from the information given.
A) 90° N
B) 90° S
C) 0°
D) 45° N
E) The latitude of the observer cannot be determined from the information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
An observer in the Southern Hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky. If the illustration below depicts the photograph taken by the observer, which direction was the camera pointing? 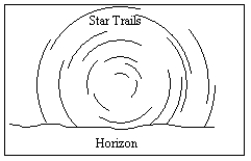
A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Table 2-1

Refer to Table 2-1. Based on the information in the table, what is the ratio of the intensity of Dra to that of Nim?
A) 2.512
B) 5
C) 8.07
D) 11.14
E) 100

Refer to Table 2-1. Based on the information in the table, what is the ratio of the intensity of Dra to that of Nim?
A) 2.512
B) 5
C) 8.07
D) 11.14
E) 100

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
An observer in the Northern Hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky. If the illustration below depicts the photograph taken by the observer, which direction was the camera pointing? 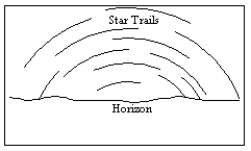
A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
An observer in the Southern Hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky. If the illustration below depicts the photograph taken by the observer, which direction was the camera pointing? 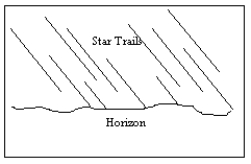
A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Table 2-1

-Refer to Table 2-1. Which star in the table would appear the brightest to an observer on Earth?
A) ( Cet)
B) ( CMa)
C) Nim
D) ( Per)
E) ( Dra)

-Refer to Table 2-1. Which star in the table would appear the brightest to an observer on Earth?
A) ( Cet)
B) ( CMa)
C) Nim
D) ( Per)
E) ( Dra)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Star A has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.4 and star B has an apparent visual magnitude of 15.4. Star A is ____ than star B.
A) 2 times fainter
B) 2 times brighter
C) 6.3 times fainter
D) 6.3 times brighter
E) 29.8 times fainter
A) 2 times fainter
B) 2 times brighter
C) 6.3 times fainter
D) 6.3 times brighter
E) 29.8 times fainter

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Polaris is a second magnitude star, and Phi Pegasi is about 16 times fainter than Polaris. What is the approximate magnitude of Phi Pegasi?
A) 18
B) (-14)
C) 3
D) (-3)
E) 5
A) 18
B) (-14)
C) 3
D) (-3)
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram below? 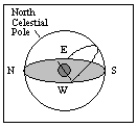
A) 90° N
B) 90° S
C) 50° N
D) 50° S
E) 0°

A) 90° N
B) 90° S
C) 50° N
D) 50° S
E) 0°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
An observer in the Northern Hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky. If the illustration below depicts the photograph taken by the observer, which direction was the camera pointing? 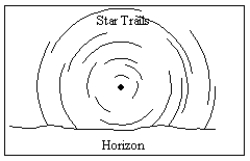
A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Do the constellations visible in the sky at a particular time of night (say 9 P.M.) follow a seasonal pattern?
A) No, the same constellations are visible at 9 P.M. on any clear night of the year.
B) No. As the year progresses, the constellations visible at 9 P.M. are the same but their shapes change.
C) Yes, at 9 P.M. during a clear winter night ALL of the constellations you can see are different from the ones that appear at the same time during a summer night.
D) Yes, at 9 P.M. during a summer night most of the constellations you can see are different from those you can see on a winter night. However, there are some constellations that are visible all year long.
A) No, the same constellations are visible at 9 P.M. on any clear night of the year.
B) No. As the year progresses, the constellations visible at 9 P.M. are the same but their shapes change.
C) Yes, at 9 P.M. during a clear winter night ALL of the constellations you can see are different from the ones that appear at the same time during a summer night.
D) Yes, at 9 P.M. during a summer night most of the constellations you can see are different from those you can see on a winter night. However, there are some constellations that are visible all year long.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
An observer in the Southern Hemisphere takes a time exposure photograph of the night sky. If the illustration below depicts the photograph taken by the observer, which direction was the camera pointing? 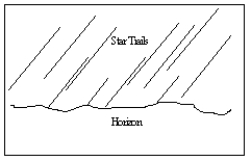
A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

A) straight north
B) straight east
C) straight south
D) straight west
E) straight up, directly overhead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In one way of naming stars, a(n) ____ letter indicates its brightness relative to the other stars in the constellation.
A) English
B) Arabic
C) Greek
D) Cyrillic
A) English
B) Arabic
C) Greek
D) Cyrillic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The ____________________ is the point on the celestial sphere directly above an observer, regardless of where the observer is located on Earth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
During the month of June the north celestial pole points towards Polaris, but during the month of December it points
A) just north of Polaris.
B) just south of Polaris.
C) towards the star Vega.
D) towards the star Thuban.
E) still towards Polaris.
A) just north of Polaris.
B) just south of Polaris.
C) towards the star Vega.
D) towards the star Thuban.
E) still towards Polaris.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
If you point toward the zenith right now and then point there again 6 hours later, you will have pointed twice in the same direction relative to
A) your horizon.
B) the sun.
C) the moon.
D) the fixed stars.
A) your horizon.
B) the sun.
C) the moon.
D) the fixed stars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Precession of the rotation axis of Earth takes ____ to complete a cycle.
A) 24 hours
B) one year
C) 260 years
D) 26,000 years
E) 260,000 years
A) 24 hours
B) one year
C) 260 years
D) 26,000 years
E) 260,000 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
If you were standing on the Earth's equator, which of the following in the sky would pass through your zenith during the entire day (24 hours)?
A) the north celestial pole
B) the south celestial pole
C) the celestial equator
D) the nadir
A) the north celestial pole
B) the south celestial pole
C) the celestial equator
D) the nadir

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
____________________ is a measure of the light energy that hits one square meter in one second.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
____ is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris.
A) ( Ursa Majoris)
B) ( Ursa Majoris)
C) ( Ursa Majoris)
D) Wrong! Ursa Majoris is the name of the brightest star.
A) ( Ursa Majoris)
B) ( Ursa Majoris)
C) ( Ursa Majoris)
D) Wrong! Ursa Majoris is the name of the brightest star.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Star A has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.3 and star B has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.3. Star A is ____________________ times ____________________ than star B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Stars in the same constellation
A) probably formed at the same time.
B) must be part of the same cluster of stars in space.
C) must have been discovered at about the same time at the same location in space.
D) may actually be very different distances away from the observer and from each other.
A) probably formed at the same time.
B) must be part of the same cluster of stars in space.
C) must have been discovered at about the same time at the same location in space.
D) may actually be very different distances away from the observer and from each other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A sketch of the Earth with its north and south poles and equator is shown. The zenith is located in the sky over your head if you are at 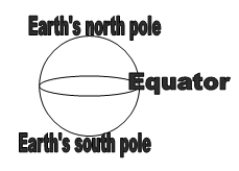
A) Earth's equator.
B) Earth's north pole.
C) Earth's south pole.
D) any of these.

A) Earth's equator.
B) Earth's north pole.
C) Earth's south pole.
D) any of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
At the Earth's north pole, the north celestial pole is directly overhead and stars near the horizon travel in straight lines
A) straight up from the horizon.
B) straight up from the horizon slanting toward the right.
C) straight up from the horizon slanting toward the left.
D) parallel to the horizon.
A) straight up from the horizon.
B) straight up from the horizon slanting toward the right.
C) straight up from the horizon slanting toward the left.
D) parallel to the horizon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
How much of the night sky is north of the celestial equator?
A) less than one-half, because of the tilt of the equator to the ecliptic plane
B) more than one-half, because of the precession of the poles
C) exactly one-half
D) all of the night sky
A) less than one-half, because of the tilt of the equator to the ecliptic plane
B) more than one-half, because of the precession of the poles
C) exactly one-half
D) all of the night sky

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
During one day and night in the mid-northern hemisphere, the stars near the north celestial pole
A) rise in the east.
B) set in the west.
C) circle the north celestial pole counter-clockwise.
D) circle the north celestial pole clockwise.
A) rise in the east.
B) set in the west.
C) circle the north celestial pole counter-clockwise.
D) circle the north celestial pole clockwise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
How much of the night sky is north of the celestial equator?
A) less than one-half, because of the tilt of the equator to the ecliptic plane
B) more than one-half, because of the precession of the poles
C) exactly one-half
D) all of the night sky
A) less than one-half, because of the tilt of the equator to the ecliptic plane
B) more than one-half, because of the precession of the poles
C) exactly one-half
D) all of the night sky

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
If an observer walks north toward increasing latitude, the number of circumpolar stars would
A) remain constant.
B) decrease.
C) increase.
D) Unknown unless you also state the longitude of the observer.
A) remain constant.
B) decrease.
C) increase.
D) Unknown unless you also state the longitude of the observer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
If you are standing at the Earth's north pole, which of the following would be located at the zenith?
A) the nadir
B) the star Vega
C) the celestial equator
D) the north celestial pole
A) the nadir
B) the star Vega
C) the celestial equator
D) the north celestial pole

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Seen from the northern latitudes, the star Polaris
A) is never above the horizon during the day.
B) always sets directly in the west.
C) is always above the northern horizon.
D) is never visible during the winter.
E) is the brightest star in the sky.
A) is never above the horizon during the day.
B) always sets directly in the west.
C) is always above the northern horizon.
D) is never visible during the winter.
E) is the brightest star in the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Precession of the rotation axis of Earth is caused by
A) the force of gravity from the sun and moon on Earth's equatorial bulge.
B) the force of gravity from Neptune and Jupiter on the Earth-moon system.
C) the magnetic field of Earth.
D) the formation and subsequent melting of glaciers during the ice-ages.
E) the impact of asteroids.
A) the force of gravity from the sun and moon on Earth's equatorial bulge.
B) the force of gravity from Neptune and Jupiter on the Earth-moon system.
C) the magnetic field of Earth.
D) the formation and subsequent melting of glaciers during the ice-ages.
E) the impact of asteroids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
As seen from the Earth's southern hemisphere, the celestial equator passes
A) north of overhead.
B) south of overhead.
C) through the north celestial pole.
D) through the south celestial pole.
A) north of overhead.
B) south of overhead.
C) through the north celestial pole.
D) through the south celestial pole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
What causes precession and why does it "move" the celestial equator among the stars?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Hipparchus devised the magnitude system in the late 1700's.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Navigators can find their latitude in the northern hemisphere by measuring the angle from the northern horizon to the north celestial pole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
All the constellations in the sky were created by the Greeks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The constellation of Orion is currently visible in the evenings in January. Precession will not affect this and Orion will still be visible in January 13,000 years from now.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
What information does a star's Greek-letter designation convey?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
A second magnitude star in Ursa Major is brighter than a fourth magnitude star in Orion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
How is a constellation different from an asterism?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The celestial equator always crosses the horizon at the east point and west point.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Describe the location of Polaris in the sky relative to the horizon as seen by observers in Alaska (lat. = 60° N), Texas (lat. = 33° N), Ecuador (lat. = 0°), and Australia (lat. = 30° S).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Earth's rotation axis ____________________ slowly so that in a few thousand years Polaris will no longer be the North Star.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The celestial equator always passes directly overhead.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Polaris has always been the star nearest the north celestial pole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
What advantage is there in referring to a star by its Greek-letter designation and constellation name rather using its traditional name?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
How are the celestial poles and equator defined by Earth's rotation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A scientific model is a mental conception that provides a framework that helps us think about some aspect of nature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Describe the path that a star on the celestial equator follows from the time it rises until it sets for a person at a latitude of 60° N and a person at the equator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The Greek letter designation conveys information about a star's location and brightness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
A 3rd magnitude star is 3 times brighter than a 1st magnitude star.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
As Earth rotates, circumpolar stars appear to move counterclockwise around the north celestial pole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 80 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








