Deck 24: Metabolic Pathways for Lipids and Amino Acids
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 24: Metabolic Pathways for Lipids and Amino Acids
1
The digestion of fats begins when the fat globules are
A)emulsified by bile salts.
B)hydrolyzed to glycerol and fatty acids.
C)hydrolyzed to glucose and amino acids.
D)attacked by protease enzymes to form smaller fat globules.
E)converted to lipoproteins for greater solubility.
A)emulsified by bile salts.
B)hydrolyzed to glycerol and fatty acids.
C)hydrolyzed to glucose and amino acids.
D)attacked by protease enzymes to form smaller fat globules.
E)converted to lipoproteins for greater solubility.
emulsified by bile salts.
2
Most of the glycerol produced by fatty acid breakdown is converted eventually to
A)amino acids.
B)fat.
C)glucose.
D)protein.
E)lactate.
A)amino acids.
B)fat.
C)glucose.
D)protein.
E)lactate.
glucose.
3
The 2-carbon segments removed from a fatty acid during metabolism are used to form
A)acetyl CoA.
B)lactate.
C)CoA.
D)glucose.
E)pyruvate.
A)acetyl CoA.
B)lactate.
C)CoA.
D)glucose.
E)pyruvate.
acetyl CoA.
4
Fat stores in the body are mobilized when
A)adipocyte concentrations are high.
B)blood glucose levels are high.
C)glucagon production is low.
D)glucose and glycogen stores are low.
E)insulin production is high.
A)adipocyte concentrations are high.
B)blood glucose levels are high.
C)glucagon production is low.
D)glucose and glycogen stores are low.
E)insulin production is high.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The source of energy for red blood cells is
A)fatty acids.
B)glycerol.
C)amino acids.
D)lactate.
E)glucose.
A)fatty acids.
B)glycerol.
C)amino acids.
D)lactate.
E)glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Fatty acids and glycerol are produced from the metabolism of
A)amino acids.
B)glucose.
C)proteins.
D)carbohydrates.
E)lipids.
A)amino acids.
B)glucose.
C)proteins.
D)carbohydrates.
E)lipids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which step is found in the breakdown of a fat?
A) direct substrate phosphorylation
B) an oxidation with CoQ
C) an activation that requires 2 ATP
D) an oxidation with a cytochrome
E) production of pyruvate
A) direct substrate phosphorylation
B) an oxidation with CoQ
C) an activation that requires 2 ATP
D) an oxidation with a cytochrome
E) production of pyruvate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The removal of 2-carbon segments of a fatty acid for further metabolism is called
A) dehydration.
B) decarboxylation.
C) deglyceration.
D)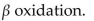
E) transamination
A) dehydration.
B) decarboxylation.
C) deglyceration.
D)
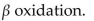
E) transamination

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Red blood cells do not metabolize fatty acids because they have
A)a cell wall.
B)no mitochondria.
C)no DNA.
D)a cell membrane.
E)no nucleus.
A)a cell wall.
B)no mitochondria.
C)no DNA.
D)a cell membrane.
E)no nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The heart muscle's primary source of fuel is
A)lactate.
B)fatty acids.
C)glycogen.
D)glucose.
E)amino acids.
A)lactate.
B)fatty acids.
C)glycogen.
D)glucose.
E)amino acids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Most of the energy stored in the human body is in the form of
A)triacylglycerols.
B)the amino acid pool.
C)glucose.
D)glycogen.
E)muscle tissue.
A)triacylglycerols.
B)the amino acid pool.
C)glucose.
D)glycogen.
E)muscle tissue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
A chylomicron is a
A)transport lipoprotein.
B)triacylglycerol.
C)storage protein.
D)digestive enzyme.
E)lipase.
A)transport lipoprotein.
B)triacylglycerol.
C)storage protein.
D)digestive enzyme.
E)lipase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Most of the glycerol produced by fatty acid breakdown goes to the
A)brain.
B)liver.
C)small intestine.
D)pancreas.
E)gall bladder.
A)brain.
B)liver.
C)small intestine.
D)pancreas.
E)gall bladder.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The small droplets of fat that are the first step in the digestion of dietary fats are called
A)emulsions.
B)micelles.
C)lipoproteins.
D)bile drops.
E)detergents.
A)emulsions.
B)micelles.
C)lipoproteins.
D)bile drops.
E)detergents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The digestion of fats begins in the
A)mouth.
B)pancreas.
C)large intestine.
D)stomach.
E)small intestine.
A)mouth.
B)pancreas.
C)large intestine.
D)stomach.
E)small intestine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The enzymes that break down triacylglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol are called
A)hydrolases.
B)oxidoreductases.
C)lyases.
D)lipases.
E)aconitases.
A)hydrolases.
B)oxidoreductases.
C)lyases.
D)lipases.
E)aconitases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Fatty acids are not a source of energy for the brain because
A)they are metabolized before they get as far as the brain.
B)the citric acid cycle does not operate in the brain.
C)there is no lipase in the brain.
D)they cannot diffuse across the blood-brain barrier.
E)chylomicrons are too large for absorption by brain cells.
A)they are metabolized before they get as far as the brain.
B)the citric acid cycle does not operate in the brain.
C)there is no lipase in the brain.
D)they cannot diffuse across the blood-brain barrier.
E)chylomicrons are too large for absorption by brain cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The series of reactions that produces energy by hydrolyzing fats to units of acetyl CoA is called
A) hydration.
B)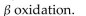
C) transamination.
D)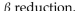
E)hydrolysis.
A) hydration.
B)
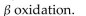
C) transamination.
D)
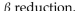
E)hydrolysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The action of pancreatic lipase on triacylglycerols produces
A)emulsions.
B)low-density lipoproteins.
C)monoacylglycerols and free fatty acids.
D)micelles.
E)high-density lipoproteins.
A)emulsions.
B)low-density lipoproteins.
C)monoacylglycerols and free fatty acids.
D)micelles.
E)high-density lipoproteins.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Fat cells are known as
A)monoacylglycerols.
B)islet cells.
C)glycerides.
D)adipocytes.
E)lysosomes.
A)monoacylglycerols.
B)islet cells.
C)glycerides.
D)adipocytes.
E)lysosomes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The energy released by the 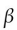 oxidation of a cis fatty acid is
oxidation of a cis fatty acid is
A) used immediately to form ATP.
B) slightly less than that obtained from a trans fatty acid.
C) less than that obtained from one glucose molecule.
D) slightly more than that obtained from a trans fatty acid.
E) the same as that obtained from a trans fatty acid.
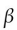 oxidation of a cis fatty acid is
oxidation of a cis fatty acid isA) used immediately to form ATP.
B) slightly less than that obtained from a trans fatty acid.
C) less than that obtained from one glucose molecule.
D) slightly more than that obtained from a trans fatty acid.
E) the same as that obtained from a trans fatty acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What is the total number of ATP molecules produced from the lauric acid  found in coconut oil?
found in coconut oil?
A) 95 ATP
B) 97 ATP
C) 90 ATP
D) 100 ATP
E) 78 ATP
 found in coconut oil?
found in coconut oil?A) 95 ATP
B) 97 ATP
C) 90 ATP
D) 100 ATP
E) 78 ATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In type 2 diabetes mellitus,
A)birth of a baby restores normal pancreatic function.
B)sufficient insulin is produced, but cannot be used.
C)glucose intake is too low.
D)the pancreas produces insufficient insulin.
E)blood glucose levels are too low.
A)birth of a baby restores normal pancreatic function.
B)sufficient insulin is produced, but cannot be used.
C)glucose intake is too low.
D)the pancreas produces insufficient insulin.
E)blood glucose levels are too low.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In type 1 diabetes mellitus,
A)glucose intake is too low.
B)sufficient insulin is produced, but cannot be used.
C)the pancreas produces insufficient insulin.
D)blood glucose levels are too low.
E)birth of a baby restores normal pancreatic function.
A)glucose intake is too low.
B)sufficient insulin is produced, but cannot be used.
C)the pancreas produces insufficient insulin.
D)blood glucose levels are too low.
E)birth of a baby restores normal pancreatic function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The complete oxidation of 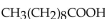 produces _____ molecules of ATP.
produces _____ molecules of ATP.
A) 82
B) 78
C) 80
D) 64
E) 76
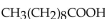 produces _____ molecules of ATP.
produces _____ molecules of ATP.A) 82
B) 78
C) 80
D) 64
E) 76

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When excess acetyl CoA accumulates in the liver, a pathway called ________ is initiated.
A)gluconeogenesis
B)transamination
C)glycolysis
D)ketogenesis
E)emulsification
A)gluconeogenesis
B)transamination
C)glycolysis
D)ketogenesis
E)emulsification

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Ketosis can lower the blood pH below 7.4, producing the condition
A)ketoacidosis.
B)anemia.
C)hypokalemia.
D)ketoalkalosis.
E)hyponatremia.
A)ketoacidosis.
B)anemia.
C)hypokalemia.
D)ketoalkalosis.
E)hyponatremia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Myristic acid, a 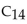 fatty acid, undergoes the
fatty acid, undergoes the 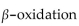 cycle times.
cycle times.
A) 6
B) 14
C) 2
D) 7
E) 4
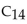 fatty acid, undergoes the
fatty acid, undergoes the 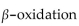 cycle times.
cycle times.A) 6
B) 14
C) 2
D) 7
E) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Fats are higher in caloric value than carbohydrates because
A) 1 gram of glucose weighs more than 1 gram of fat.
B) fats make use of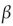 oxidation.
oxidation.
C) 1 gram of fat produces significantly more ATP than 1 gram of glucose.
D) 1 gram of glucose contains more moles than 1 gram of fat.
E) fats can make use of the citric acid cycle.
A) 1 gram of glucose weighs more than 1 gram of fat.
B) fats make use of
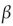 oxidation.
oxidation.C) 1 gram of fat produces significantly more ATP than 1 gram of glucose.
D) 1 gram of glucose contains more moles than 1 gram of fat.
E) fats can make use of the citric acid cycle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The function of fatty acyl CoA is to
A)activate a fatty acid for metabolism.
B)produce a 2-carbon segment for metabolism.
C)isomerize cis fatty acids.
D)produce a lipoprotein.
E)cross the blood-brain barrier.
A)activate a fatty acid for metabolism.
B)produce a 2-carbon segment for metabolism.
C)isomerize cis fatty acids.
D)produce a lipoprotein.
E)cross the blood-brain barrier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
During complete oxidation of the fatty acid 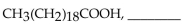 molecules of acetyl CoA are produced, and the fatty acid goes through the
molecules of acetyl CoA are produced, and the fatty acid goes through the 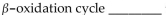
A) nine; eight
B) nine; nine
C) ten; nine
D) nine; ten
E) ten; ten
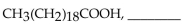 molecules of acetyl CoA are produced, and the fatty acid goes through the
molecules of acetyl CoA are produced, and the fatty acid goes through the 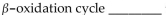
A) nine; eight
B) nine; nine
C) ten; nine
D) nine; ten
E) ten; ten

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Myristic acid, a C14 fatty acid, produces ________ acetyl CoA when completely metabolized.
A)14
B)12
C)5
D)7
E)2
A)14
B)12
C)5
D)7
E)2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Fatty acyl CoA cannot cross into the mitochondrial matrix until
A) the citric acid cycle has begun.
B) it binds with a charged carrier molecule called carnitine.
C) the mitochondrial membrane undergoes a modification.
D)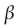 oxidation has taken place.
oxidation has taken place.
E) it is cut into 2-carbon segments
A) the citric acid cycle has begun.
B) it binds with a charged carrier molecule called carnitine.
C) the mitochondrial membrane undergoes a modification.
D)
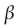 oxidation has taken place.
oxidation has taken place.E) it is cut into 2-carbon segments

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The 2-carbon units obtained by degradation of a fatty acid are further metabolized in
A)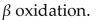
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) transamination.
E) gluconeogenesis.
A)
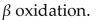
B) the citric acid cycle.
C) glycolysis.
D) transamination.
E) gluconeogenesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Each acetyl CoA produces ________ ATP in the citric acid cycle.
A)6
B)12
C)10
D)2
E)24
A)6
B)12
C)10
D)2
E)24

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Beta-oxidation takes place in the
A)cytoplasm.
B)Golgi body.
C)nucleus.
D)cytosol.
E)mitochondrial matrix.
A)cytoplasm.
B)Golgi body.
C)nucleus.
D)cytosol.
E)mitochondrial matrix.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Malonyl CoA contains a 3-carbon compound used in
A)the citric acid cycle.
B)acetyl CoA formation.
C)lipogenesis.
D)gluconeogenesis.
E)glycogenolysis.
A)the citric acid cycle.
B)acetyl CoA formation.
C)lipogenesis.
D)gluconeogenesis.
E)glycogenolysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Ketosis is a condition that can occur if
A)low fat intake occurs.
B)the brain is starved of glucose.
C)too many ketones are ingested.
D)too much protein is available in the diet.
E)ketone bodies instead of glucose are used for energy.
A)low fat intake occurs.
B)the brain is starved of glucose.
C)too many ketones are ingested.
D)too much protein is available in the diet.
E)ketone bodies instead of glucose are used for energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Stearic acid, a 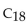 saturated fatty acid, produces acetyl CoA when completely metabolized.
saturated fatty acid, produces acetyl CoA when completely metabolized.
A) 9
B) 7
C) 8
D) 5
E) 2
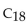 saturated fatty acid, produces acetyl CoA when completely metabolized.
saturated fatty acid, produces acetyl CoA when completely metabolized.A) 9
B) 7
C) 8
D) 5
E) 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In the activation of a fatty acid, energy from the hydrolysis of ATP is used to
A) cause a unit of acetyl CoA to separate from the fatty acid chain.
B) add a molecule of water across a double bond to give a hydroxyl group on the \beta carbon.
C) form a double bond in an oxidation reaction.
D) oxidize the hydroxyl group on the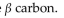
E) join the fatty acid to CoA.
A) cause a unit of acetyl CoA to separate from the fatty acid chain.
B) add a molecule of water across a double bond to give a hydroxyl group on the \beta carbon.
C) form a double bond in an oxidation reaction.
D) oxidize the hydroxyl group on the
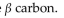
E) join the fatty acid to CoA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
All of the nonessential amino acids can be synthesized in the body by transamination, using an amino group from
A)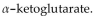
B) lactic acid.
C) glutamate.
D) pyruvate.
E) oxaloacetate.
A)
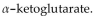
B) lactic acid.
C) glutamate.
D) pyruvate.
E) oxaloacetate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
To synthesize a 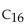 fatty acid, acetyl groups and cycles of fatty acid synthesis are needed.
fatty acid, acetyl groups and cycles of fatty acid synthesis are needed.
A) seven, seven
B) seven, eight
C) eight, seven
D) eight, eight
E) one, one
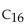 fatty acid, acetyl groups and cycles of fatty acid synthesis are needed.
fatty acid, acetyl groups and cycles of fatty acid synthesis are needed.A) seven, seven
B) seven, eight
C) eight, seven
D) eight, eight
E) one, one

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The letters ACP stand for
A)aconitate protein complex.
B)acyl carrier protein.
C)acetyl condensing protein.
D)acetyl CoA-palmitate.
E)acetyl Coenzyme P.
A)aconitate protein complex.
B)acyl carrier protein.
C)acetyl condensing protein.
D)acetyl CoA-palmitate.
E)acetyl Coenzyme P.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The digestion of protein begins in the
A)large intestine.
B)small intestine.
C)mouth.
D)stomach.
E)pancreas.
A)large intestine.
B)small intestine.
C)mouth.
D)stomach.
E)pancreas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following does NOT require 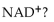
A) glycolysis
B) transamination
C) oxidative deamination
D) citric acid cycle
E)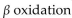
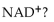
A) glycolysis
B) transamination
C) oxidative deamination
D) citric acid cycle
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
In mammals, the ammonium ion produced in oxidative deamination is
A)converted to uric acid, which is excreted by the liver.
B)excreted in the feces.
C)converted to uric acid, which is excreted in the urine.
D)converted to urea, which is excreted in the urine.
E)stored in the liver.
A)converted to uric acid, which is excreted by the liver.
B)excreted in the feces.
C)converted to uric acid, which is excreted in the urine.
D)converted to urea, which is excreted in the urine.
E)stored in the liver.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The initial digestion of protein is catalyzed by an enzyme called
A)chymotrypsin.
B)amylase.
C)trypsin.
D)peptidase.
E)pepsin.
A)chymotrypsin.
B)amylase.
C)trypsin.
D)peptidase.
E)pepsin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In the urea cycle, argininosuccinate lyase catalyzes the reaction of argininosuccinate to
A)arginine.
B)orthinine.
C)carbamoyl phosphate.
D)arginase.
E)citrulline.
A)arginine.
B)orthinine.
C)carbamoyl phosphate.
D)arginase.
E)citrulline.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The coenzyme(s)used in fatty acid synthesis is (are)
A)FADH2 and NADH.
B)FADH2.
C)NADH.
D)NADH and NADPH.
E)NADPH.
A)FADH2 and NADH.
B)FADH2.
C)NADH.
D)NADH and NADPH.
E)NADPH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which metabolic substrate can be produced from the carbon atoms in the amino acid valine?
A)pyruvate
B)succinyl CoA
C)acetoacetyl CoA
D)fumarate
A)pyruvate
B)succinyl CoA
C)acetoacetyl CoA
D)fumarate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Fatty acid synthesis takes place primarily in
A)liver cells.
B)muscle cells.
C)brain cells.
D)the cytosol.
E)intestinal cells.
A)liver cells.
B)muscle cells.
C)brain cells.
D)the cytosol.
E)intestinal cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The nitrogen for nucleotide synthesis comes from
A)DNA.
B)carbohydrates.
C)proteins.
D)RNA.
E)fats.
A)DNA.
B)carbohydrates.
C)proteins.
D)RNA.
E)fats.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
In a(n) ______ reaction, 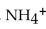 is produced when glutamate is converted to
is produced when glutamate is converted to 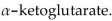
A)dehydrogenation
B)hydration
C)transamination
D)reduction
E)oxidative deamination
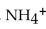 is produced when glutamate is converted to
is produced when glutamate is converted to 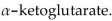
A)dehydrogenation
B)hydration
C)transamination
D)reduction
E)oxidative deamination

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which metabolic substrate can be produced from the carbon atoms in the amino acid phenylalanine?
A)pyruvate
B)succinyl CoA
C)acetoacetyl CoA
D)fumarate
A)pyruvate
B)succinyl CoA
C)acetoacetyl CoA
D)fumarate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which metabolic substrate can be produced from the carbon atoms in the amino acid lysine?
A)pyruvate
B)succinyl CoA
C)acetoacetyl CoA
D)fumarate
A)pyruvate
B)succinyl CoA
C)acetoacetyl CoA
D)fumarate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The production of new fatty acids is called
A) gluconeogenesis.
B) transesterification.
C) lipogenesis.
D) oxidation.
E)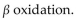
A) gluconeogenesis.
B) transesterification.
C) lipogenesis.
D) oxidation.
E)
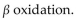

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








