Deck 14: Market Structures I: Monopoly
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Market Structures I: Monopoly
1
The simplest way for a monopoly to arise is for a single firm to
A) decrease its price below its competitors' prices.
B) decrease production to increase demand for its product.
C) make pricing decisions jointly with other firms.
D) own a key resource.
A) decrease its price below its competitors' prices.
B) decrease production to increase demand for its product.
C) make pricing decisions jointly with other firms.
D) own a key resource.
own a key resource.
2
Most economists argue that the most efficient solution to the problem of monopoly is that the monopoly should be publicly owned.
False
3
Most markets are not monopolies in the real world because
A) firms usually face downward sloping demand curves.
B) supply curves slope upward.
C) price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms.
D) there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.
A) firms usually face downward sloping demand curves.
B) supply curves slope upward.
C) price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms.
D) there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.
there are reasonable substitutes for most goods.
4
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Both a competitive firm and a monopolist are price takers.
B) Both a competitive firm and a monopolist are price makers.
C) A competitive firm is a price taker, whereas a monopolist is a price maker.
D) A competitive firm is a price maker, whereas a monopolist is a price taker.
A) Both a competitive firm and a monopolist are price takers.
B) Both a competitive firm and a monopolist are price makers.
C) A competitive firm is a price taker, whereas a monopolist is a price maker.
D) A competitive firm is a price maker, whereas a monopolist is a price taker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If government officials break a natural monopoly up into several smaller firms, then
A) competition will force firms to attain economic profits rather than accounting profits.
B) competition will force firms to produce surplus output, which drives up price.
C) the average costs of production will increase.
D) the average costs of production will decrease.
A) competition will force firms to attain economic profits rather than accounting profits.
B) competition will force firms to produce surplus output, which drives up price.
C) the average costs of production will increase.
D) the average costs of production will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A monopolist produces an efficient quantity of output, but it is still inefficient because it charges a price that exceeds marginal cost, and the resulting profit is a social cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A monopoly
A) can set the price it charges for its output and earn unlimited profits.
B) takes the market price as given and earns small but positive profits.
C) can set the price it charges for its output, but faces a downward sloping demand curve so it cannot earn unlimited profits.
D) can set the price it charges for its output, but faces a horizontal demand curve so it can earn unlimited profits.
A) can set the price it charges for its output and earn unlimited profits.
B) takes the market price as given and earns small but positive profits.
C) can set the price it charges for its output, but faces a downward sloping demand curve so it cannot earn unlimited profits.
D) can set the price it charges for its output, but faces a horizontal demand curve so it can earn unlimited profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
For the monopolist, marginal revenue is always less than the price of the good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Monopolies use their market power to
A) charge prices that equal minimum average total cost.
B) attain normal profits in the long run.
C) restrict output and increase price.
D) dump excess supplies of their product on the market.
A) charge prices that equal minimum average total cost.
B) attain normal profits in the long run.
C) restrict output and increase price.
D) dump excess supplies of their product on the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Price discrimination is only possible if there is no arbitrage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A monopoly is the sole seller of a product with no close substitutes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Sizable economic profits can persist over time under monopoly if the monopolist
A) produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B) is protected by barriers to entry.
C) operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D) realises revenues that exceed variable costs.
A) produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B) is protected by barriers to entry.
C) operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D) realises revenues that exceed variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Price discrimination can raise economic welfare because output increases beyond that which would result under monopoly pricing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A benefit of a monopoly is
A) efficient production.
B) decreasing long-run marginal costs.
C) profit that can be invested in research and development.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) efficient production.
B) decreasing long-run marginal costs.
C) profit that can be invested in research and development.
D) All of the above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Universities are engaging in price discrimination when they charge different levels of tuition to poor and wealthy students.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Perfect price discrimination is efficient, but all of the surplus is received by the consumer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a characteristic of a monopoly?
A) Low fixed costs as a portion of total costs.
B) Free entry and exit.
C) Barriers to entry.
D) Declining marginal cost.
A) Low fixed costs as a portion of total costs.
B) Free entry and exit.
C) Barriers to entry.
D) Declining marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
One difference between a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly is that a perfectly competitive firm produces where
A) marginal cost equals price, while a monopolist produces where price exceeds marginal cost.
B) marginal cost equals price, while a monopolist produces where marginal cost exceeds price.
C) price exceeds marginal cost, while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.
D) marginal cost exceeds price, while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.
A) marginal cost equals price, while a monopolist produces where price exceeds marginal cost.
B) marginal cost equals price, while a monopolist produces where marginal cost exceeds price.
C) price exceeds marginal cost, while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.
D) marginal cost exceeds price, while a monopolist produces where marginal cost equals price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Monopolists are price takers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The demand curve facing a monopolist is the market demand curve for its product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider the following demand and cost information
-Refer to the table above. The marginal revenue of the second unit is
A) R10
B) R20
C) R30
D) R40
-Refer to the table above. The marginal revenue of the second unit is
A) R10
B) R20
C) R30
D) R40

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
If a monopolist can sell 7 units when the price is R3 and 8 units when the price is R2, then marginal revenue of selling the eighth unit is equal to
A) R2.
B) R3.
C) R16.
D) -R5.
A) R2.
B) R3.
C) R16.
D) -R5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The inefficiency associated with monopoly is due to
A) the monopoly's profits.
B) underproduction of the good.
C) the monopoly's losses.
D) overproduction of the good.
A) the monopoly's profits.
B) underproduction of the good.
C) the monopoly's losses.
D) overproduction of the good.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The purpose of competition laws is to
A) Ensure prices are the same for all consumers.
B) regulate the prices charged by a monopoly.
C) increase merger activity to help generate synergies that reduce costs and raise efficiency.
D) create public ownership of natural monopolies.
E) increase competition in an industry by preventing mergers, and breaking up large firms.
A) Ensure prices are the same for all consumers.
B) regulate the prices charged by a monopoly.
C) increase merger activity to help generate synergies that reduce costs and raise efficiency.
D) create public ownership of natural monopolies.
E) increase competition in an industry by preventing mergers, and breaking up large firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Sizable economic profits can persist over time under monopoly if the monopolist
A) produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B) is protected by barriers to entry.
C) operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D) earns revenues that exceed variable costs.
A) produces that output where average total cost is at a maximum.
B) is protected by barriers to entry.
C) operates as a price taker rather than a price maker.
D) earns revenues that exceed variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Patents grant
A) permanent monopoly status to creators of inventions.
B) permanent right to creators of inventions to produce the product they have invented.
C) temporary monopoly status to creators of inventions.
D) temporary right to creators of inventions to produce the product they have invented.
A) permanent monopoly status to creators of inventions.
B) permanent right to creators of inventions to produce the product they have invented.
C) temporary monopoly status to creators of inventions.
D) temporary right to creators of inventions to produce the product they have invented.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
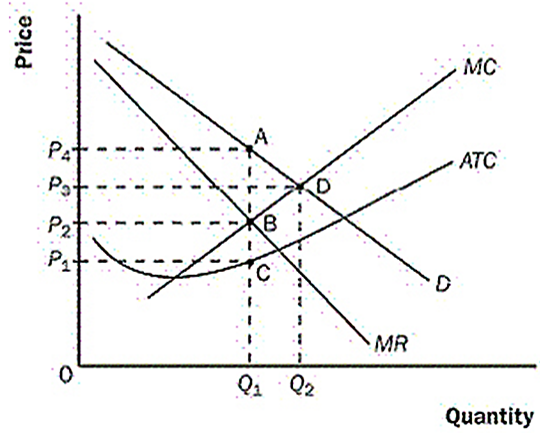
Refer to the above graph. The profit-maximising monopolist will choose the price and quantity represented by point
A) Point A.
B) Point B.
C) Point C.
D) Point D.
E) none of these four points

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Cengage is a monopolist in the production of your textbook because Cengage
A) is a very large company.
B) owns a key resource in the production of textbooks.
C) is a natural monopoly.
D) has a legally protected exclusive right to produce this textbook.
A) is a very large company.
B) owns a key resource in the production of textbooks.
C) is a natural monopoly.
D) has a legally protected exclusive right to produce this textbook.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
When a monopolist produces an additional unit, the marginal revenue generated by that unit must be
A) above the price because the output effect outweighs the price effect.
B) below the price because the price effect outweighs the output effect.
C) above the price because the price effect outweighs the output effect.
D) below the price because the output effect outweighs the price effect.
A) above the price because the output effect outweighs the price effect.
B) below the price because the price effect outweighs the output effect.
C) above the price because the price effect outweighs the output effect.
D) below the price because the output effect outweighs the price effect.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Using government regulations to force a natural monopoly to charge a price equal to its marginal cost will
A) improve efficiency.
B) cause the monopolist to exit the market.
C) raise the price of good.
D) attract additional firms to enter the market.
A) improve efficiency.
B) cause the monopolist to exit the market.
C) raise the price of good.
D) attract additional firms to enter the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry in a monopolised market?
A) A single firm is very large.
B) The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good.
C) The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
D) A key resource is owned by a single firm.
A) A single firm is very large.
B) The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good.
C) The costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers.
D) A key resource is owned by a single firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Patent and copyright laws encourage
A) creative activity.
B) lower prices due to decreasing average total costs.
C) competition among firms.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) creative activity.
B) lower prices due to decreasing average total costs.
C) competition among firms.
D) All of the above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The monopolist's supply curve
A) is the upward sloping portion of the average variable cost.
B) is the marginal cost curve above average variable cost.
C) is the marginal cost curve above average total cost.
D) is the upward sloping portion of the average total cost curve.
E) does not exist.
A) is the upward sloping portion of the average variable cost.
B) is the marginal cost curve above average variable cost.
C) is the marginal cost curve above average total cost.
D) is the upward sloping portion of the average total cost curve.
E) does not exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Consider the following demand and cost information
-Refer to the table above. To maximise profit, the monopolist sets the price at
A) R40
B) R20
C) R0
D) R10
-Refer to the table above. To maximise profit, the monopolist sets the price at
A) R40
B) R20
C) R0
D) R10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Consider the following demand and cost information
-Refer to the table above. The marginal cost of the fourth unit is
A) R60
B) R40
C) R20
D) R10
-Refer to the table above. The marginal cost of the fourth unit is
A) R60
B) R40
C) R20
D) R10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements about price and marginal cost in competitive and monopolised markets is true?
A) In competitive markets, price equals marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price exceeds marginal cost.
B) In competitive markets, price equals marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price equals marginal cost.
C) In competitive markets, price exceeds marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price exceeds marginal cost.
D) In competitive markets, price exceeds marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price equals marginal cost.
A) In competitive markets, price equals marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price exceeds marginal cost.
B) In competitive markets, price equals marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price equals marginal cost.
C) In competitive markets, price exceeds marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price exceeds marginal cost.
D) In competitive markets, price exceeds marginal cost; in monopolised markets, price equals marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A monopolist maximises profit by producing the quantity at which
A) marginal cost equals price.
B) marginal revenue equals price.
C) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) marginal cost equals demand.
E) marginal cost is minimised.
A) marginal cost equals price.
B) marginal revenue equals price.
C) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) marginal cost equals demand.
E) marginal cost is minimised.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38

Refer to the above graph. The efficient price and quantity are represented by point
A) Point A.
B) Point D.
C) Point B.
D) Point C.
E) none of these answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Compared to a perfectly competitive market, a monopoly market will usually generate
A) lower prices and lower output.
B) higher prices and higher output.
C) higher prices and lower output.
D) lower prices and higher output.
A) lower prices and lower output.
B) higher prices and higher output.
C) higher prices and lower output.
D) lower prices and higher output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A firm whose average total cost continually declines at least to the quantity that could supply the entire market is known as a
A) regulated monopoly.
B) perfect competitor.
C) government monopoly.
D) natural monopoly.
A) regulated monopoly.
B) perfect competitor.
C) government monopoly.
D) natural monopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, a monopolist should
A) raise the price.
B) decrease output.
C) keep output the same because profits are maximised when marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
D) increase output.
A) raise the price.
B) decrease output.
C) keep output the same because profits are maximised when marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
D) increase output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Graphically depict the deadweight loss caused by a monopoly. How is this similar to the deadweight loss from taxation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Why might economists prefer private ownership of monopolies over public ownership of monopolies?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of the following is an example of price discrimination?
A) Nestlé provides money off coupons for its products.
B) Gautrain offers a lower price for weekend travel compared to weekday rates on the same routes.
C) Hotel rates for members of the AA are lower than for non-members.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) Nestlé provides money off coupons for its products.
B) Gautrain offers a lower price for weekend travel compared to weekday rates on the same routes.
C) Hotel rates for members of the AA are lower than for non-members.
D) All of the above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What are the four ways that government policymakers can respond to the problem of monopoly?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A monopoly is able to continue to generate economic profits in the long run because
A) it can control both price and output in the market.
B) potential competitors sometimes don't notice the profits.
C) the monopolist is financially powerful.
D) competition laws eliminate competitors for a specified number of years.
E) there is some barrier to entry to that market.
A) it can control both price and output in the market.
B) potential competitors sometimes don't notice the profits.
C) the monopolist is financially powerful.
D) competition laws eliminate competitors for a specified number of years.
E) there is some barrier to entry to that market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Assume that a monopolist decides to maximise revenue rather than profit. How does this operating objective change the size of the deadweight loss? If you are a "benevolent" manager of a monopoly firm and are interested in reducing the deadweight loss of monopoly, should you maximise profits or maximise revenue? Explain your answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In many countries, the government chooses to "internalise" the monopoly by owning monopoly providers of goods and services. In some cases, these firms are "nationalised," and the government actually buys or confiscates firms that operate in monopoly markets. What would be the advantages and disadvantages of such an approach to ensure that the "best interest of society" is promoted in these markets? Explain your answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The task of economic regulation is to
A) protect monopoly profits.
B) approximate the results of the competitive market.
C) replace competition with government ownership.
D) increase competition within the market.
A) protect monopoly profits.
B) approximate the results of the competitive market.
C) replace competition with government ownership.
D) increase competition within the market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
One example of price discrimination occurs in the publishing industry when a publisher initially releases an expensive hardcover edition of a popular novel and later releases a cheaper paperback edition. Use this example to demonstrate the benefits and potential pitfalls of a price discrimination pricing strategy. The answer should address the three basic lessons of price discrimination.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Public ownership of natural monopolies
A) creates synergies between the newly acquired firm and other government owned companies.
B) usually lowers the cost of production dramatically.
C) tends to be inefficient.
D) does none of the things described in these answers.
A) creates synergies between the newly acquired firm and other government owned companies.
B) usually lowers the cost of production dramatically.
C) tends to be inefficient.
D) does none of the things described in these answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
If regulators break up a natural monopoly into many smaller firms, the cost of production
A) will remain the same.
B) will fall.
C) will rise.
D) could either rise or fall depending on the elasticity of the monopolist's supply curve.
A) will remain the same.
B) will fall.
C) will rise.
D) could either rise or fall depending on the elasticity of the monopolist's supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A monopolist's profits with price discrimination will be
A) lower than if the firm charged a single, profit-maximising price.
B) the same as if the firm charged a single, profit-maximising price.
C) higher than if the firm charged just one price, because the firm will capture more consumer surplus.
D) higher than if the firm charged a single price, because the costs of selling the good will be lower.
A) lower than if the firm charged a single, profit-maximising price.
B) the same as if the firm charged a single, profit-maximising price.
C) higher than if the firm charged just one price, because the firm will capture more consumer surplus.
D) higher than if the firm charged a single price, because the costs of selling the good will be lower.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Describe how government is involved in creating a monopoly. Why might the government create one? Give an example.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Explain how a profit-maximising monopolist chooses its level of output and the price of its goods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Give some examples of the benefits and costs of competition laws.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A monopolist that practises perfect price discrimination
A) creates no deadweight loss.
B) charges one group of buyers a higher price than another group, such as offering a student discount.
C) produces the same monopoly level of output as when a single price is charged.
D) charges some customers a price below marginal cost because costs are covered by the high-priced buyers.
A) creates no deadweight loss.
B) charges one group of buyers a higher price than another group, such as offering a student discount.
C) produces the same monopoly level of output as when a single price is charged.
D) charges some customers a price below marginal cost because costs are covered by the high-priced buyers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which of the following strategies is not an effective strategy to reduce monopoly inefficiency?
A) Competition laws.
B) Price discrimination.
C) Doing nothing.
D) Breaking up a natural monopoly into more than one firm.
A) Competition laws.
B) Price discrimination.
C) Doing nothing.
D) Breaking up a natural monopoly into more than one firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What is the deadweight loss due to profit-maximising monopoly pricing under the following conditions: The price charged for goods produced is R10. The intersection of the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves occurs where output is 100 units and marginal revenue is R5. The socially efficient level of production is 110 units. The demand curve is linear and downward sloping, and the marginal cost curve is constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Which of the follow statements about price discrimination is not true?
A) Price discrimination increases a monopolist's profits.
B) Price discrimination can raise economic welfare.
C) Price discrimination requires that the seller be able to separate buyers according to their willingness to pay.
D) Perfect price discrimination generates a deadweight loss.
E) For a monopolist to engage in price discrimination, buyers must be unable to engage in arbitrage.
A) Price discrimination increases a monopolist's profits.
B) Price discrimination can raise economic welfare.
C) Price discrimination requires that the seller be able to separate buyers according to their willingness to pay.
D) Perfect price discrimination generates a deadweight loss.
E) For a monopolist to engage in price discrimination, buyers must be unable to engage in arbitrage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








