Deck 13: Queuing Analysis
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/27
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Queuing Analysis
1
The following payoff table shows the profit for a decision problem with two states of nature and two decision alternatives: 
a. Use graphical sensitivity analysis to determine the range of probabilities of state of nature s 1 for which each of the decision alternatives has the largest expected value.
b. Suppose P ( s 1 ) = 0.2 and P ( s 2 ) = 0.8. What is the best decision using the expected value approach?
c. Perform sensitivity analysis on the payoffs for decision alternative d 1. Assume the probabilities are as given in part (b) and find the range of payoffs under states of nature s 1 and s 2 that will keep the solution found in part (b) optimal. Is the solution more sensitive to the payoff under state of nature s 1 or s 2 ?

a. Use graphical sensitivity analysis to determine the range of probabilities of state of nature s 1 for which each of the decision alternatives has the largest expected value.
b. Suppose P ( s 1 ) = 0.2 and P ( s 2 ) = 0.8. What is the best decision using the expected value approach?
c. Perform sensitivity analysis on the payoffs for decision alternative d 1. Assume the probabilities are as given in part (b) and find the range of payoffs under states of nature s 1 and s 2 that will keep the solution found in part (b) optimal. Is the solution more sensitive to the payoff under state of nature s 1 or s 2 ?
Determine the range of probabilities of state of nature  for each of the decision alternatives.
for each of the decision alternatives.
Expected value of decision alternative:
The expected value of decision approach must be applied in order to identify the decision alternatives. The value is calculated by using the following formula: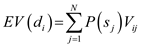 Let N be the number of states of nature and
Let N be the number of states of nature and  be the probability of state of nature.
be the probability of state of nature.
Expected value for :
:  …… (1)
…… (1)
Expected value for :
:  …… (2)
…… (2)
Graphical representation of expected value for the decision alternatives as a function of p: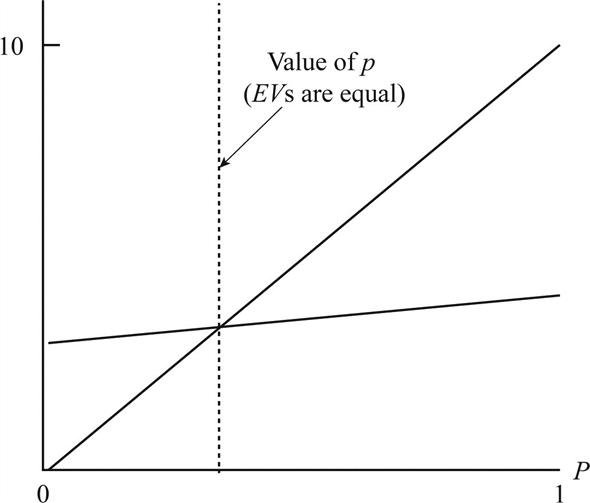 Solve Equations (1) and (2) to calculate the value of p as follows:
Solve Equations (1) and (2) to calculate the value of p as follows: 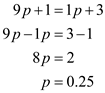 The value of p is 0.25. Hence, the optimal for
The value of p is 0.25. Hence, the optimal for  is
is 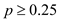 , and
, and  is
is 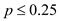 . Since the value of p is 0.20 which is less than 0.25, the best decision is
. Since the value of p is 0.20 which is less than 0.25, the best decision is  .
.
(b)Determine the best decision alternative:
It is given that the is 0.2 and
is 0.2 and 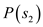 is 0.8.
is 0.8.
Now, calculate the expected value for as follows:
as follows:
Expected value for :
: 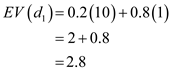 Expected value for
Expected value for  :
: 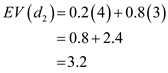 Hence, the best decision is
Hence, the best decision is  as a expected value of 3.2.
as a expected value of 3.2.
(c)
Sensitivity analysis on the payoffs for the decision alternative:
Let s be the payoff for under
under 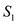 ;
;  will be optimal only when
will be optimal only when 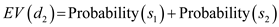
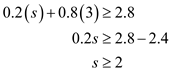 Hence, the payoff for
Hence, the payoff for  is less or equal to 2; then the
is less or equal to 2; then the  will remain optimal.
will remain optimal.
 for each of the decision alternatives.
for each of the decision alternatives. Expected value of decision alternative:
The expected value of decision approach must be applied in order to identify the decision alternatives. The value is calculated by using the following formula:
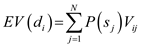 Let N be the number of states of nature and
Let N be the number of states of nature and  be the probability of state of nature.
be the probability of state of nature.Expected value for
 :
:  …… (1)
…… (1) Expected value for
 :
:  …… (2)
…… (2) Graphical representation of expected value for the decision alternatives as a function of p:
 Solve Equations (1) and (2) to calculate the value of p as follows:
Solve Equations (1) and (2) to calculate the value of p as follows: 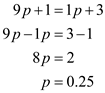 The value of p is 0.25. Hence, the optimal for
The value of p is 0.25. Hence, the optimal for  is
is 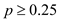 , and
, and  is
is 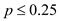 . Since the value of p is 0.20 which is less than 0.25, the best decision is
. Since the value of p is 0.20 which is less than 0.25, the best decision is  .
.(b)Determine the best decision alternative:
It is given that the
 is 0.2 and
is 0.2 and 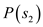 is 0.8.
is 0.8.Now, calculate the expected value for
 as follows:
as follows:Expected value for
 :
: 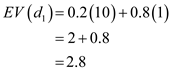 Expected value for
Expected value for  :
: 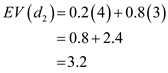 Hence, the best decision is
Hence, the best decision is  as a expected value of 3.2.
as a expected value of 3.2. (c)
Sensitivity analysis on the payoffs for the decision alternative:
Let s be the payoff for
 under
under 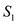 ;
;  will be optimal only when
will be optimal only when 
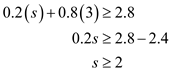 Hence, the payoff for
Hence, the payoff for  is less or equal to 2; then the
is less or equal to 2; then the  will remain optimal.
will remain optimal. 2
To save on expenses, Rona and Jerry agreed to form a carpool for traveling to and from work. Rona prefers to use the somewhat longer but more consistent Queen City Avenue. Although Jerry prefers the quicker expressway, he agreed with Rona that they should take Queen City Avenue if the expressway has a traffic jam. The following payoff table provides the one-way time estimate in minutes for traveling to or from work: Based on their experience with traffic problems, Rona and Jerry agreed on a 0.15 probability that the expressway would be jammed.
In addition, they agreed that weather seemed to affect the traffic conditions on the expressway.
Let
The following conditional probabilities apply: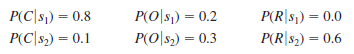
a. Use Bayes' theorem for probability revision to compute the probability of each weather condition and the conditional probability of the expressway being open, s 1, or jammed, s 2, given each weather condition.
b. Show the decision tree for this problem.
c. What is the optimal decision strategy, and what is the expected travel time?
In addition, they agreed that weather seemed to affect the traffic conditions on the expressway.
Let

The following conditional probabilities apply:
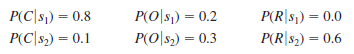
a. Use Bayes' theorem for probability revision to compute the probability of each weather condition and the conditional probability of the expressway being open, s 1, or jammed, s 2, given each weather condition.
b. Show the decision tree for this problem.
c. What is the optimal decision strategy, and what is the expected travel time?
not answer
3
Myrtle Air Express decided to offer direct service from Cleveland to Myrtle Beach. Management must decide between a full-price service using the company's new fleet of jet aircraft and a discount service using smaller-capacity commuter planes. It is clear that the best choice depends on the market reaction to the service Myrtle Air offers. Management developed estimates of the contribution to profit for each type of service based on two possible levels of demand for service to Myrtle Beach: strong and weak. The following table shows the estimated quarterly profits (in thousands of dollars): 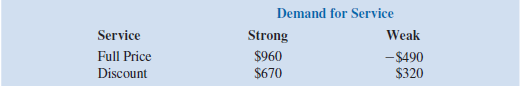
a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence for this problem? How many decision alternatives are there? How many outcomes are there for the chance event?
b. If nothing is known about the probabilities of the chance outcomes, what is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
c. Suppose that management of Myrtle Air Express believes that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3. Use the expected value approach to determine an optimal decision.
d. Suppose that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2. What is the optimal decision using the expected value approach?
e. Use sensitivity analysis to determine the range of demand probabilities for which each of the decision alternatives has the largest expected value.

a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence for this problem? How many decision alternatives are there? How many outcomes are there for the chance event?
b. If nothing is known about the probabilities of the chance outcomes, what is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
c. Suppose that management of Myrtle Air Express believes that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3. Use the expected value approach to determine an optimal decision.
d. Suppose that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2. What is the optimal decision using the expected value approach?
e. Use sensitivity analysis to determine the range of demand probabilities for which each of the decision alternatives has the largest expected value.
Synopsis of M Air Express :
• M Air Express decides to provide direct service from C to M beach.
• Management should decide between full-price and discount services that depend on the market conditions.
• Based on the levels of demand for service, the management expanded estimates of the contribution to profit.
(a)Decision to be made:
The decision should be made to decide on the type of service to offer.
Chance event and consequences:
The chance event in this case is the level of demand for service to M beach. The amount of quarterly profit may vary based on the market conditions to the service.
Decision alternatives:
Full-price service and discount service are the two decision alternatives.
Number of outcomes for the change event:
There are two outcomes for the change event (level of demand for service) such as strong demand and weak demand.
(b)Maximum and minimum profit for each decision alternative: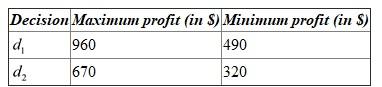 Optimistic approach:
Optimistic approach:
The following are the criteria for optimistic approach:
• For a maximization problem, select the largest payoff.
• For a minimization problem, select the smallest payoff.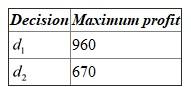 Justification:
Justification:
Under optimistic approach, should be selected, which is the maximum of the maximum payoff value. Decision alternative is evaluated in terms of the largest payoff that can arise.
should be selected, which is the maximum of the maximum payoff value. Decision alternative is evaluated in terms of the largest payoff that can arise.
Conservative approach:
Under conservative approach, first identify the minimum payoff for each alternative and select the alternative with the maximum of the minimum payoff.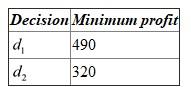 Hence,
Hence,  should be selected with the maximum of the minimum payoff value.
should be selected with the maximum of the minimum payoff value.
Minimax regret approach:
The maximum value of ,
,  ,
,  should be subtracted with the corresponding value in the table as follows:
should be subtracted with the corresponding value in the table as follows: 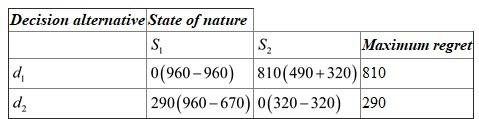 Hence,
Hence,  should be selected with a minimum loss of $290.
should be selected with a minimum loss of $290.
(c)
Determine an optimal decision using expected value approach:
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3.
Now, calculate the expected value for full service as follows:
as follows: 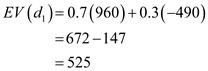 It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3.
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3.
Now, calculate the expected value for discount service as follows:
as follows: 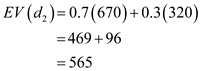 Hence, the optimal decision is discount service.
Hence, the optimal decision is discount service.
(d)Determine an optimal decision using expected value approach:
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2.
Now, calculate the expected value for full price service as follows:
as follows: 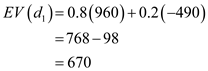 It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2.
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2.
Now, calculate the expected value for discount service as follows:
as follows: 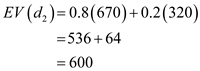 Hence, the optimal decision is full price service.
Hence, the optimal decision is full price service.
(e)Graphical sensitivity analysis to determine the range of demand probabilities
Let p be the probability of strong demand.
Expected value for :
: 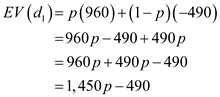 …… (1)
…… (1)
Expected value for :
: 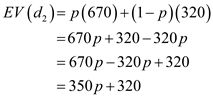 …… (2)
…… (2)
Solve Equations (1) and (2) to calculate the value of p as follows: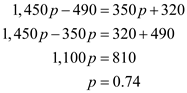 The value of p is 0.74. If the value of p is lesser than 0.74, discount service is considered as the best alternative. If the value of p is more than 0.74, full-price is considered as the best alternative.
The value of p is 0.74. If the value of p is lesser than 0.74, discount service is considered as the best alternative. If the value of p is more than 0.74, full-price is considered as the best alternative.
• M Air Express decides to provide direct service from C to M beach.
• Management should decide between full-price and discount services that depend on the market conditions.
• Based on the levels of demand for service, the management expanded estimates of the contribution to profit.
(a)Decision to be made:
The decision should be made to decide on the type of service to offer.
Chance event and consequences:
The chance event in this case is the level of demand for service to M beach. The amount of quarterly profit may vary based on the market conditions to the service.
Decision alternatives:
Full-price service and discount service are the two decision alternatives.
Number of outcomes for the change event:
There are two outcomes for the change event (level of demand for service) such as strong demand and weak demand.
(b)Maximum and minimum profit for each decision alternative:
 Optimistic approach:
Optimistic approach: The following are the criteria for optimistic approach:
• For a maximization problem, select the largest payoff.
• For a minimization problem, select the smallest payoff.
 Justification:
Justification: Under optimistic approach,
 should be selected, which is the maximum of the maximum payoff value. Decision alternative is evaluated in terms of the largest payoff that can arise.
should be selected, which is the maximum of the maximum payoff value. Decision alternative is evaluated in terms of the largest payoff that can arise.Conservative approach:
Under conservative approach, first identify the minimum payoff for each alternative and select the alternative with the maximum of the minimum payoff.
 Hence,
Hence,  should be selected with the maximum of the minimum payoff value.
should be selected with the maximum of the minimum payoff value.Minimax regret approach:
The maximum value of
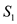 ,
,  ,
,  should be subtracted with the corresponding value in the table as follows:
should be subtracted with the corresponding value in the table as follows:  Hence,
Hence,  should be selected with a minimum loss of $290.
should be selected with a minimum loss of $290.(c)
Determine an optimal decision using expected value approach:
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3.
Now, calculate the expected value for full service
 as follows:
as follows: 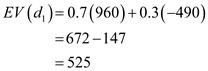 It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3.
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.7 and the probability of weak demand is 0.3.Now, calculate the expected value for discount service
 as follows:
as follows: 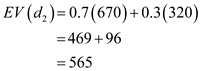 Hence, the optimal decision is discount service.
Hence, the optimal decision is discount service. (d)Determine an optimal decision using expected value approach:
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2.
Now, calculate the expected value for full price service
 as follows:
as follows: 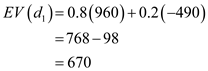 It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2.
It is given that the probability of strong demand is 0.8 and the probability of weak demand is 0.2.Now, calculate the expected value for discount service
 as follows:
as follows: 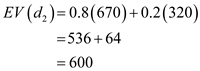 Hence, the optimal decision is full price service.
Hence, the optimal decision is full price service. (e)Graphical sensitivity analysis to determine the range of demand probabilities
Let p be the probability of strong demand.
Expected value for
 :
: 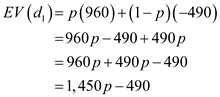 …… (1)
…… (1) Expected value for
 :
: 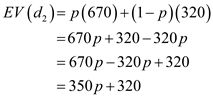 …… (2)
…… (2) Solve Equations (1) and (2) to calculate the value of p as follows:
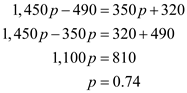 The value of p is 0.74. If the value of p is lesser than 0.74, discount service is considered as the best alternative. If the value of p is more than 0.74, full-price is considered as the best alternative.
The value of p is 0.74. If the value of p is lesser than 0.74, discount service is considered as the best alternative. If the value of p is more than 0.74, full-price is considered as the best alternative. 4
The Gorman Manufacturing Company must decide whether to manufacture a component part at its Milan, Michigan, plant or purchase the component part from a supplier. The resulting profit is dependent upon the demand for the product. The following payoff table shows the projected profit (in thousands of dollars): 
The state-of-nature probabilities are P ( s 1 ) = 0.35, P ( s 2 ) = 0.35, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.30.
a. Use a decision tree to recommend a decision.
b. Use EVPI to determine whether Gorman should attempt to obtain a better estimate of demand.
c. A test market study of the potential demand for the product is expected to report either a favorable ( F ) or unfavorable ( U ) condition. The relevant conditional probabilities are as follows:
What is the probability that the market research report will be favorable?
d. What is Gorman's optimal decision strategy?
e. What is the expected value of the market research information?
f. What is the efficiency of the information?

The state-of-nature probabilities are P ( s 1 ) = 0.35, P ( s 2 ) = 0.35, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.30.
a. Use a decision tree to recommend a decision.
b. Use EVPI to determine whether Gorman should attempt to obtain a better estimate of demand.
c. A test market study of the potential demand for the product is expected to report either a favorable ( F ) or unfavorable ( U ) condition. The relevant conditional probabilities are as follows:

What is the probability that the market research report will be favorable?
d. What is Gorman's optimal decision strategy?
e. What is the expected value of the market research information?
f. What is the efficiency of the information?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Video Tech is considering marketing one of two new video games for the coming holiday season: Battle Pacific or Space Pirates. Battle Pacific is a unique game and appears to have no competition. Estimated profits (in thousands of dollars) under high, medium, and low demand are as follows: 
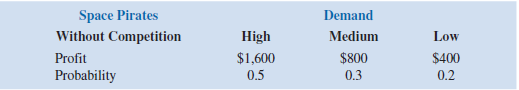
Video Tech is optimistic about its Space Pirates game. However, the concern is that profitability will be affected by a competitor's introduction of a video game viewed as similar to Space Pirates. Estimated profits (in thousands of dollars) with and without competition are as follows: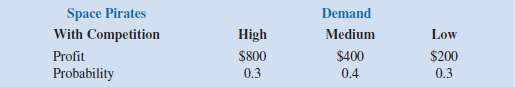
a. Develop a decision tree for the Video Tech problem.
b. For planning purposes, Video Tech believes there is a 0.6 probability that its competitor will produce a new game similar to Space Pirates. given this probability of competition, the director of planning recommends marketing the Battle Pacific video game. Using expected value, what is your recommended decision?
c. Show a risk profile for your recommended decision.
d. Use sensitivity analysis to determine what the probability of competition for Space Pirates would have to be for you to change your recommended decision alternative

Video Tech is optimistic about its Space Pirates game. However, the concern is that profitability will be affected by a competitor's introduction of a video game viewed as similar to Space Pirates. Estimated profits (in thousands of dollars) with and without competition are as follows:


a. Develop a decision tree for the Video Tech problem.
b. For planning purposes, Video Tech believes there is a 0.6 probability that its competitor will produce a new game similar to Space Pirates. given this probability of competition, the director of planning recommends marketing the Battle Pacific video game. Using expected value, what is your recommended decision?
c. Show a risk profile for your recommended decision.
d. Use sensitivity analysis to determine what the probability of competition for Space Pirates would have to be for you to change your recommended decision alternative

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
For the Pittsburgh Development Corporation problem in Section 13.3, the decision alternative to build the large condominium complex was found to be optimal using the expected value approach. In Section 13.4 we conducted a sensitivity analysis for the payoffs associated with this decision alternative. We found that the large complex remained optimal as long as the payoff for the strong demand was greater than or equal to $17.5 million and as long as the payoff for the weak demand was greater than or equal to -$19 million.
a. Consider the medium complex decision. How much could the payoff under strong demand increase and still keep decision alternative d 3 , the optimal solution?
b. Consider the small complex decision. How much could the payoff under strong demand increase and still keep decision alternative d 3 , the optimal solution?
a. Consider the medium complex decision. How much could the payoff under strong demand increase and still keep decision alternative d 3 , the optimal solution?
b. Consider the small complex decision. How much could the payoff under strong demand increase and still keep decision alternative d 3 , the optimal solution?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The distance from Potsdam to larger markets and limited air service have hindered the town in attracting new industry. Air Express. a major overnight delivery service, is considering establishing a regional distribution center in Potsdam. However, Air Express will not establish the center unless the length of the runway at the local airport is increased. Another candidate for new development is Diagnostic Research. Inc. (DRI), a leading producer of medical testing equipment. DRI is considering building a new manufacturing plant. Increasing the length of the runway is not a requirement for DRI, but the planning commission feels that doing so will help convince DRI to locate their new plant in Potsdam. Assuming that the town lengthens the runway, the Potsdam planning commission believes that the probabilities shown in the following table are applicable: 
For instance, the probability that Air Express will establish a distribution center and DRI will build a plant is 0.30.
The estimated annual revenue to the town, after deducting the cost of lengthening the runway, is as follows:
If the runway expansion project is not conducted, the planning commission assesses the probability DRI will locate their new plant in Potsdam at 0.6; in this case, the estimated annual revenue to the town will be $450,000. If the runway expansion project is not conducted and DRI does not locate in Potsdam, the annual revenue will be $0 because no cast will have been incurred and no revenues will be forthcoming.
a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence?
b. Compute the expected annual revenue associated with the decision alternative to lengthen the runway.
c. Compute the expected annual revenue associated with the decision alternative not to lengthen the runway.
d. Should the town elect to lengthen the runway? Explain.
e. Suppose that the probabilities associated with lengthening the runway were as following:
What effect, if any, would this change in the probabilities wave on the recommended decision?

For instance, the probability that Air Express will establish a distribution center and DRI will build a plant is 0.30.
The estimated annual revenue to the town, after deducting the cost of lengthening the runway, is as follows:

If the runway expansion project is not conducted, the planning commission assesses the probability DRI will locate their new plant in Potsdam at 0.6; in this case, the estimated annual revenue to the town will be $450,000. If the runway expansion project is not conducted and DRI does not locate in Potsdam, the annual revenue will be $0 because no cast will have been incurred and no revenues will be forthcoming.
a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence?
b. Compute the expected annual revenue associated with the decision alternative to lengthen the runway.
c. Compute the expected annual revenue associated with the decision alternative not to lengthen the runway.
d. Should the town elect to lengthen the runway? Explain.
e. Suppose that the probabilities associated with lengthening the runway were as following:

What effect, if any, would this change in the probabilities wave on the recommended decision?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Seneca Hill Winery recently purchased land for the purpose of establishing a new vineyard. Management is considering two varieties of white grapes for the new vineyard: Chardonnay and Riesling. The Chardonnay grapes would be used to produce a dry Chardonnay wine,
and the Riesling grapes would be used to produce a semidry Riesling wine. It takes approximately four years from the time of planting before new grapes can be harvested. This length of time creates a great deal of uncertainty concerning future demand and makes the decision about the type of grapes to plant difficult. Three possibilities are being considered:
Chardonnay grapes only; Riesling grapes only; and both Chardonnay and Riesling grapes. Seneca management decided that for planning purposes it would be adequate to consider only two demand possibilities for each type of wine: strong or weak. With two possibilities for each type of wine, it was necessary to assess four probabilities. With the help of some forecasts in industry publications, management made the following probability assessments: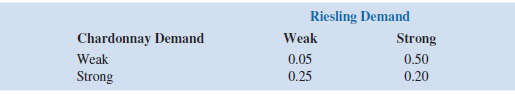
Revenue projections show an annual contribution to profit of $20,000 if Seneca Hill plants only Chardonnay grapes and demand is weak for Chardonnay wine, and $70,000 if Seneca plants only Chardonnay grapes and demand is strong for Chardonnay wine. If Seneca plants only Riesling grapes, the annual profit projection is $25,000 if demand is weak for Riesling grapes and $45,000 if demand is strong for Riesling grapes. If Seneca plants both types of grapes, the annual profit projections are shown in the following table: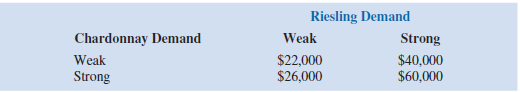
a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence? Identify the alternatives for the decisions and the possible outcomes for the chance events.
b. Develop a decision tree.
c. Use the expected value approach to recommend which alternative Seneca Hill Winery should follow in order to maximize expected annual profit.
d. Suppose management is concerned about the probability assessments when demand for Chardonnay wine is strong. Some believe it is likely for Riesling demand to also be strong in this case. Suppose the probability of strong demand for Chardonnay and weak demand for Riesling is 0.05 and that the probability of strong demand for
Chardonnay and strong demand for Riesling is 0.40. How does this change the recommended decision? Assume that the probabilities when Chardonnay demand is weak are still 0.05 and 0.50.
e. Other members of the management team expect the Chardonnay market to become saturated at some point in the future, causing a fall in prices. Suppose that the annual profit projections fall to $50,000 when demand for Chardonnay is strong and only Chardonnay grapes are planted. Using the original probability assessments, determine how this change would affect the optimal decision
and the Riesling grapes would be used to produce a semidry Riesling wine. It takes approximately four years from the time of planting before new grapes can be harvested. This length of time creates a great deal of uncertainty concerning future demand and makes the decision about the type of grapes to plant difficult. Three possibilities are being considered:
Chardonnay grapes only; Riesling grapes only; and both Chardonnay and Riesling grapes. Seneca management decided that for planning purposes it would be adequate to consider only two demand possibilities for each type of wine: strong or weak. With two possibilities for each type of wine, it was necessary to assess four probabilities. With the help of some forecasts in industry publications, management made the following probability assessments:

Revenue projections show an annual contribution to profit of $20,000 if Seneca Hill plants only Chardonnay grapes and demand is weak for Chardonnay wine, and $70,000 if Seneca plants only Chardonnay grapes and demand is strong for Chardonnay wine. If Seneca plants only Riesling grapes, the annual profit projection is $25,000 if demand is weak for Riesling grapes and $45,000 if demand is strong for Riesling grapes. If Seneca plants both types of grapes, the annual profit projections are shown in the following table:
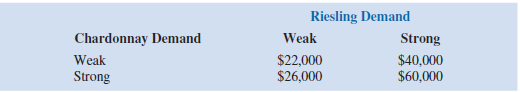
a. What is the decision to be made, what is the chance event, and what is the consequence? Identify the alternatives for the decisions and the possible outcomes for the chance events.
b. Develop a decision tree.
c. Use the expected value approach to recommend which alternative Seneca Hill Winery should follow in order to maximize expected annual profit.
d. Suppose management is concerned about the probability assessments when demand for Chardonnay wine is strong. Some believe it is likely for Riesling demand to also be strong in this case. Suppose the probability of strong demand for Chardonnay and weak demand for Riesling is 0.05 and that the probability of strong demand for
Chardonnay and strong demand for Riesling is 0.40. How does this change the recommended decision? Assume that the probabilities when Chardonnay demand is weak are still 0.05 and 0.50.
e. Other members of the management team expect the Chardonnay market to become saturated at some point in the future, causing a fall in prices. Suppose that the annual profit projections fall to $50,000 when demand for Chardonnay is strong and only Chardonnay grapes are planted. Using the original probability assessments, determine how this change would affect the optimal decision

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The following profit payoff table was presented in Problem 1: 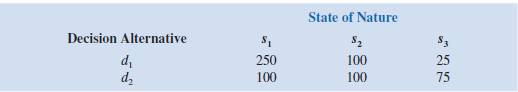
The probabilities for the states of nature are P ( s 1 ) = 0.65, P ( s 2 ) = 0.15, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.20.
a. What is the optimal decision strategy if perfect information were available?
b. What is the expected value for the decision strategy developed in part a?
c. Using the expected value approach, what is the recommended decision without perfect information? What is its expected value?
d. What is the expected value of perfect information?

The probabilities for the states of nature are P ( s 1 ) = 0.65, P ( s 2 ) = 0.15, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.20.
a. What is the optimal decision strategy if perfect information were available?
b. What is the expected value for the decision strategy developed in part a?
c. Using the expected value approach, what is the recommended decision without perfect information? What is its expected value?
d. What is the expected value of perfect information?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Property purchase Strategy
Glenn Foreman, president of Oceanview Development Corporation, is considering submitting a bid to purchase property that will be sold by sealed bid auction at a county tax foreclosure. glenn's initial judgment is to submit a bid of $5 million. Based on his experience, glenn estimates that a bid of $5 million will have a 0.2 probability of being the highest
bid and securing the property for Oceanview. The current date is June 1. Sealed bids for the property must be submitted by August 15. The winning bid will be announced on September 1.
If Oceanview submits the highest bid and obtains the property, the firm plans to build and sell a complex of luxury condominiums. However, a complicating factor is that the property is currently zoned for single-family residences only. glenn believes that a referendum could be placed on the voting ballot in time for the November election. Passage
of the referendum would change the zoning of the property and permit construction of the condominiums.
The sealed-bid procedure requires the bid to be submitted with a certified check for 10 percent of the amount bid. If the bid is rejected, the deposit is refunded. If the bid is accepted, the deposit is the down payment for the property. However, if the bid is accepted and the bidder does not follow through with the purchase and meet the remainder of the
financial obligation within six months, the deposit will be forfeited. In this case, the county will offer the property to the next highest bidder.
To determine whether Oceanview should submit the $5 million bid, glenn conducted some preliminary analysis. This preliminary work provided an assessment of 0.3 for the probability that the referendum for a zoning change will be approved and resulted in the following estimates of the costs and revenues that will be incurred if the condominiums
are built: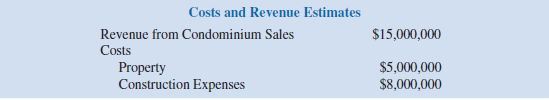
If Ocean view obtains the property and the zoning change is rejected in November, glenn believes that the best option would be for the firm not to complete the purchase of the property. In this case, Ocean view would forfeit the 10 percent deposit that accompanied the bid.
Because the likelihood that the zoning referendum will be approved is such an important factor in the decision process, glenn suggested that the firm hire a market research service to conduct a survey of voters. The survey would provide a better estimate of the likelihood that the referendum for a zoning change would be approved. The market research firm that Ocean view Development has worked with in the past has agreed to do the study for $15,000. The results of the study will be available August 1, so that Ocean view will have this information before the August 15 bid deadline. The results of the survey will be a prediction either that the zoning change will be approved or that the zoning change will be rejected. After considering the record of the market research service in previous studies conducted for Ocean view, glenn developed the following probability estimates concerning the accuracy of the market research information:
Managerial Report
Perform an analysis of the problem facing the Oceanview Development Corporation, and prepare a report that summarizes your findings and recommendations. Include the following items in your report:
1. A decision tree that shows the logical sequence of the decision problem
2. A recommendation regarding what Oceanview should do if the market research information is not available
3. A decision strategy that Oceanview should follow if the market research is conducted
4. A recommendation as to whether Oceanview should employ the market research firm, along with the value of the information provided by the market research firm
Include the details of your analysis as an appendix to your report.
Glenn Foreman, president of Oceanview Development Corporation, is considering submitting a bid to purchase property that will be sold by sealed bid auction at a county tax foreclosure. glenn's initial judgment is to submit a bid of $5 million. Based on his experience, glenn estimates that a bid of $5 million will have a 0.2 probability of being the highest
bid and securing the property for Oceanview. The current date is June 1. Sealed bids for the property must be submitted by August 15. The winning bid will be announced on September 1.
If Oceanview submits the highest bid and obtains the property, the firm plans to build and sell a complex of luxury condominiums. However, a complicating factor is that the property is currently zoned for single-family residences only. glenn believes that a referendum could be placed on the voting ballot in time for the November election. Passage
of the referendum would change the zoning of the property and permit construction of the condominiums.
The sealed-bid procedure requires the bid to be submitted with a certified check for 10 percent of the amount bid. If the bid is rejected, the deposit is refunded. If the bid is accepted, the deposit is the down payment for the property. However, if the bid is accepted and the bidder does not follow through with the purchase and meet the remainder of the
financial obligation within six months, the deposit will be forfeited. In this case, the county will offer the property to the next highest bidder.
To determine whether Oceanview should submit the $5 million bid, glenn conducted some preliminary analysis. This preliminary work provided an assessment of 0.3 for the probability that the referendum for a zoning change will be approved and resulted in the following estimates of the costs and revenues that will be incurred if the condominiums
are built:

If Ocean view obtains the property and the zoning change is rejected in November, glenn believes that the best option would be for the firm not to complete the purchase of the property. In this case, Ocean view would forfeit the 10 percent deposit that accompanied the bid.
Because the likelihood that the zoning referendum will be approved is such an important factor in the decision process, glenn suggested that the firm hire a market research service to conduct a survey of voters. The survey would provide a better estimate of the likelihood that the referendum for a zoning change would be approved. The market research firm that Ocean view Development has worked with in the past has agreed to do the study for $15,000. The results of the study will be available August 1, so that Ocean view will have this information before the August 15 bid deadline. The results of the survey will be a prediction either that the zoning change will be approved or that the zoning change will be rejected. After considering the record of the market research service in previous studies conducted for Ocean view, glenn developed the following probability estimates concerning the accuracy of the market research information:

Managerial Report
Perform an analysis of the problem facing the Oceanview Development Corporation, and prepare a report that summarizes your findings and recommendations. Include the following items in your report:
1. A decision tree that shows the logical sequence of the decision problem
2. A recommendation regarding what Oceanview should do if the market research information is not available
3. A decision strategy that Oceanview should follow if the market research is conducted
4. A recommendation as to whether Oceanview should employ the market research firm, along with the value of the information provided by the market research firm
Include the details of your analysis as an appendix to your report.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The Lake Placid Town Council decided to build a new community center to be used for conventions, concerts, and other public events, but considerable controversy surrounds the appropriate size. Many influential citizens want a large center that would be a showcase
for the area. But the mayor feels that if demand does not support such a center, the community will lose a large amount of money. To provide structure for the decision process, the council narrowed the building alternatives to three sizes: small, medium, andlarge. Everybody agreed that the critical factor in choosing the best size is the number of
people who will want to use the new facility. A regional planning consultant provided demand estimates under three scenarios: worst case, base case, and best case. The worst-case scenario corresponds to a situation in which tourism drops substantially; the base-case scenario corresponds to a situation in which Lake Placid continues to attract visitors at
current levels; and the best-case scenario corresponds to a substantial increase in tourism. The consultant has provided probability assessments of 0.10, 0.60, and 0.30 for the worstcase, base-case, and best-case scenarios, respectively.
The town council suggested using net cash flow over a 5-year planning horizon as the criterion for deciding on the best size. The following projections of net cash flow (in thousands of dollars) for a five-year planning horizon have been developed. All costs, including the consultant's fee, have been included.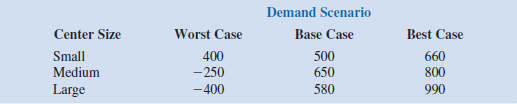
a. What decision should Lake Placid make using the expected value approach?
b. Construct risk profiles for the medium and large alternatives. given the mayor's concern over the possibility of losing money and the result of part a, which alternative would you recommend?
c. Compute the expected value of perfect information. Do you think it would be worth trying to obtain additional information concerning which scenario is likely to occur?
d. Suppose the probability of the worst-case scenario increases to 0.2, the probability of the base-case scenario decreases to 0.5, and the probability of the best-case scenario remains at 0.3. What effect, if any, would these changes have on the decision recommendation?
e. The consultant has suggested that an expenditure of $150,000 on a promotional campaign over the planning horizon will effectively reduce the probability of the worstcase scenario to zero. If the campaign can be expected to also increase the probability of the best-case scenario to 0.4, is it a good investment?
for the area. But the mayor feels that if demand does not support such a center, the community will lose a large amount of money. To provide structure for the decision process, the council narrowed the building alternatives to three sizes: small, medium, andlarge. Everybody agreed that the critical factor in choosing the best size is the number of
people who will want to use the new facility. A regional planning consultant provided demand estimates under three scenarios: worst case, base case, and best case. The worst-case scenario corresponds to a situation in which tourism drops substantially; the base-case scenario corresponds to a situation in which Lake Placid continues to attract visitors at
current levels; and the best-case scenario corresponds to a substantial increase in tourism. The consultant has provided probability assessments of 0.10, 0.60, and 0.30 for the worstcase, base-case, and best-case scenarios, respectively.
The town council suggested using net cash flow over a 5-year planning horizon as the criterion for deciding on the best size. The following projections of net cash flow (in thousands of dollars) for a five-year planning horizon have been developed. All costs, including the consultant's fee, have been included.

a. What decision should Lake Placid make using the expected value approach?
b. Construct risk profiles for the medium and large alternatives. given the mayor's concern over the possibility of losing money and the result of part a, which alternative would you recommend?
c. Compute the expected value of perfect information. Do you think it would be worth trying to obtain additional information concerning which scenario is likely to occur?
d. Suppose the probability of the worst-case scenario increases to 0.2, the probability of the base-case scenario decreases to 0.5, and the probability of the best-case scenario remains at 0.3. What effect, if any, would these changes have on the decision recommendation?
e. The consultant has suggested that an expenditure of $150,000 on a promotional campaign over the planning horizon will effectively reduce the probability of the worstcase scenario to zero. If the campaign can be expected to also increase the probability of the best-case scenario to 0.4, is it a good investment?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The following payoff table shows profit for a decision analysis problem with two decision alternatives and three states of nature: 
a. Construct a decision tree for this problem.
b. If the decision maker knows nothing about the probabilities of the three states of nature, what is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?

a. Construct a decision tree for this problem.
b. If the decision maker knows nothing about the probabilities of the three states of nature, what is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Consider a variation of the PDC decision tree shown in Figure 13.9. The company must first decide whether to undertake the market research study. If the market research study is conducted, the outcome will either be favorable ( F ) or unfavorable ( U ). Assume there are only two decision alternatives d 1 and d 2 and two states of nature s 1 and s 2. The payoff table showing profit it as follows: 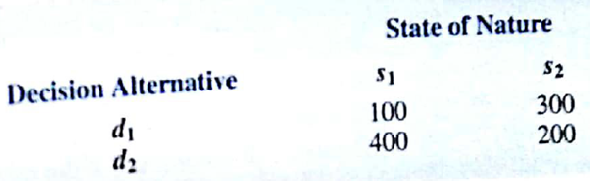
a. Show the decision tree.
b. Using the following probabilities, what is the optimal decision strategy?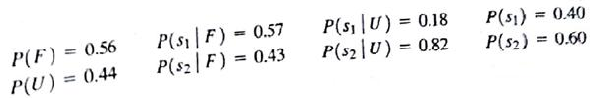
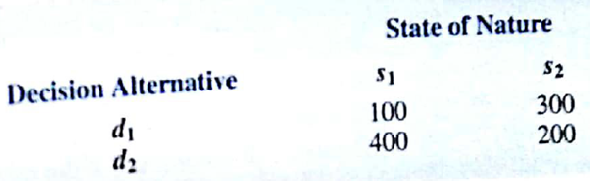
a. Show the decision tree.
b. Using the following probabilities, what is the optimal decision strategy?
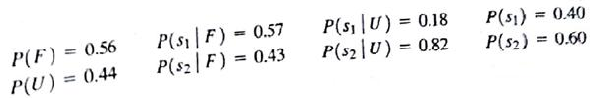

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
LAWSUIT DEFENSE STRATEGY
John Campbell, an employee of Manhattan Construction Company, claims to have injured his back as a result of a fall while repairing the roof at one of the Eastview apartment buildings. He filed a lawsuit against Doug Reynolds, the owner of Eastview Apartments, asking for damages of $1,500,000. John claims that the roof had rotten section and that his fall could have been prevented if Mr. Reynolds had told Manhattan Construction about the problem. Mr. Reynolds notified his insurance company, Allied Insurance, of the lawsuit. Allied must defend Mr. Reynolds and decide what action to take regarding the lawsuit.
Some depositions and a series of discussions took place between both sides. As a result, John Campbell offered to accept a settlement of $750,000. Thus one option is for Allied to pay John $750,000 to settle the claim. Allied is also considering making John a counteroffer of $400,000 in the hope that he will accept a lesser amount to avoid the time and cost of going to trial. Allied's preliminary investigation show that John's case is strong; Allied is concerned that John may reject their counteroffer and request a jury trial. Allied's lawyers spent some time exploring John's likely reaction if they make a counteroffer of $400,000.
The lawyers concluded that it is adequate to consider three possible outcomes to represent John's possible reaction to a counteroffer of $400,000: (1) John will accept the counteroffer and the case will be closed; (2) John will reject the counteroffer and elect to have a jury decide the settlement amount; or (3) John will make a counteroffer to Allied of $600,000. If John does make a counteroffer, Allied has decided that they will not make additional counteroffer. They will either accept John's counteroffer of $600,000 or go to trial.
If the case goes to a jury trial, Allied considers three outcomes possible: (1) the jury may reject John's claim and Allied will not be required to pay any damages; (2) the jury will find in favour of John and award him $750,000 in damages; or (3) the jury will conclude that John has a strong case and award him the full amount of $1,500,000.
Key consideration as Allied develops its strategy for disposing of the case are the probabilities associated with John's response to an Allied counteroffer of $400,000 and the probabilities associate with the three possible trial outcomes. Allied's lawyers believe the probability that John will accept a counteroffer of $400,000 is 0.10, the probability that John will reject a counteroffer of $400,000 is 0.40, and the probability that John will, himself, make a counteroffer to Allied of $600,000 is 0.50. If the case goes to court, they believe that the probability the jury will award John damages of $750,000 is 0.50, and the probability that the jury will award john nothing is 0.20.
Managerial Report
Perform an analysis of the problem facing Allied Insurance and prepare a report that summarizes your findings and recommendations. Be sure to include the following item;
l. A decision tree
2. A recommendation regarding whether Allied should accept John's initial offer to settle the claim for $750,000
3. A decision strategy that Allied should follow if they decide to make John a counteroffer of $400,000
4. A risk profile for your recommended strategy
John Campbell, an employee of Manhattan Construction Company, claims to have injured his back as a result of a fall while repairing the roof at one of the Eastview apartment buildings. He filed a lawsuit against Doug Reynolds, the owner of Eastview Apartments, asking for damages of $1,500,000. John claims that the roof had rotten section and that his fall could have been prevented if Mr. Reynolds had told Manhattan Construction about the problem. Mr. Reynolds notified his insurance company, Allied Insurance, of the lawsuit. Allied must defend Mr. Reynolds and decide what action to take regarding the lawsuit.
Some depositions and a series of discussions took place between both sides. As a result, John Campbell offered to accept a settlement of $750,000. Thus one option is for Allied to pay John $750,000 to settle the claim. Allied is also considering making John a counteroffer of $400,000 in the hope that he will accept a lesser amount to avoid the time and cost of going to trial. Allied's preliminary investigation show that John's case is strong; Allied is concerned that John may reject their counteroffer and request a jury trial. Allied's lawyers spent some time exploring John's likely reaction if they make a counteroffer of $400,000.
The lawyers concluded that it is adequate to consider three possible outcomes to represent John's possible reaction to a counteroffer of $400,000: (1) John will accept the counteroffer and the case will be closed; (2) John will reject the counteroffer and elect to have a jury decide the settlement amount; or (3) John will make a counteroffer to Allied of $600,000. If John does make a counteroffer, Allied has decided that they will not make additional counteroffer. They will either accept John's counteroffer of $600,000 or go to trial.
If the case goes to a jury trial, Allied considers three outcomes possible: (1) the jury may reject John's claim and Allied will not be required to pay any damages; (2) the jury will find in favour of John and award him $750,000 in damages; or (3) the jury will conclude that John has a strong case and award him the full amount of $1,500,000.
Key consideration as Allied develops its strategy for disposing of the case are the probabilities associated with John's response to an Allied counteroffer of $400,000 and the probabilities associate with the three possible trial outcomes. Allied's lawyers believe the probability that John will accept a counteroffer of $400,000 is 0.10, the probability that John will reject a counteroffer of $400,000 is 0.40, and the probability that John will, himself, make a counteroffer to Allied of $600,000 is 0.50. If the case goes to court, they believe that the probability the jury will award John damages of $750,000 is 0.50, and the probability that the jury will award john nothing is 0.20.
Managerial Report
Perform an analysis of the problem facing Allied Insurance and prepare a report that summarizes your findings and recommendations. Be sure to include the following item;
l. A decision tree
2. A recommendation regarding whether Allied should accept John's initial offer to settle the claim for $750,000
3. A decision strategy that Allied should follow if they decide to make John a counteroffer of $400,000
4. A risk profile for your recommended strategy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Hemmingway, Inc. is considering a $5 million research and development (R D) project. Profit projections appear promising, but Hemmingway's president is concerned because the probability that the RR D project will be successful is only 0.50. Furthermore, the president knows that even if the project is successful, it will require that the company build a new production facility at a cost of $20 million in order to manufacture the product. If the facility is built, uncertainty remains about the demand and thus uncertainty about the profit that will be realized. Another option is that if the R D project is successful, the company could sell the rights to the product for an estimated $25 million. Under this option, the company would not build the $20 million production facility.
The decision tree follows. The profit projection for each outcome is shown at the end of the branches. For example, the revenue projection for the high demand outcome is $59 million. However, the cost of the R D project ($5 million) and the cost of the production facility ($20 million) show the profit of this outcome to be $59 ? $5 ? $20 = $34 million. Branch probabilities are also shown for the chance events.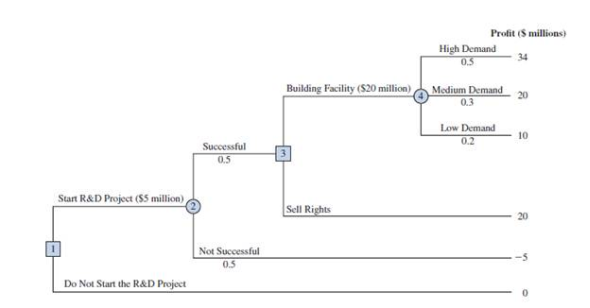
a. Analyze the decision tree to determine whether the company should undertake the R D project. If it does, and if the R D project is successful, what should the company do? What is the expected value of your strategy?
b. What must the selling price be for the company to consider selling the rights to the product?
c. Develop a risk profile for the optimal strategy.
The decision tree follows. The profit projection for each outcome is shown at the end of the branches. For example, the revenue projection for the high demand outcome is $59 million. However, the cost of the R D project ($5 million) and the cost of the production facility ($20 million) show the profit of this outcome to be $59 ? $5 ? $20 = $34 million. Branch probabilities are also shown for the chance events.

a. Analyze the decision tree to determine whether the company should undertake the R D project. If it does, and if the R D project is successful, what should the company do? What is the expected value of your strategy?
b. What must the selling price be for the company to consider selling the rights to the product?
c. Develop a risk profile for the optimal strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Suppose that a decision maker faced with four decision alternatives and four states of nature develops the following profit payoff table: 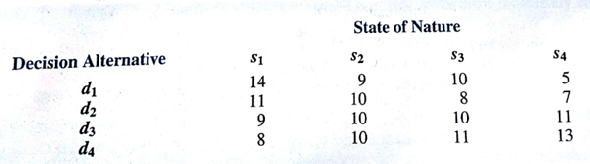
a. If the decision maker knows nothing about the probabilities of the four states of nature. What is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
b. Which approach do you prefer? Explain. Is establishing the most appropriate approach before analyzing the problem important for the decision maker? Explain.
c. Assume that the payoff table provides cost rather than profit payoff. What is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?

a. If the decision maker knows nothing about the probabilities of the four states of nature. What is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
b. Which approach do you prefer? Explain. Is establishing the most appropriate approach before analyzing the problem important for the decision maker? Explain.
c. Assume that the payoff table provides cost rather than profit payoff. What is the recommended decision using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Dante Development Corporation is considering bidding on a contract for a new office building complex. The following figure shows the decision tree prepared by one of Dante's analysts. At node 1, the company must decide whether to bid on the contract. The cost of preparing the bid is $200,000. The upper branch from node 2 shows that the company
has a 0.8 probability of winning the contract if it submits a bid. If the company wins the bid, it will have to pay $2 million to become a partner in the project. Node 3 shows that the company will then consider doing a market research study to forecast demand for the office units prior to beginning construction. The cost of this study is $150,000. Node 4 is
a chance node showing the possible outcomes of the market research study.
Nodes 5, 6, and 7 are similar in that they are the decision nodes for Dante to either build the office complex or sell the rights in the project to another developer. The decision to build the complex will result in an income of $5 million if demand is high and $3 million if demand is moderate. If Dante chooses to sell its rights in the project to another developer, income from the sale is estimated to be $3.5 million. The probabilities shown at nodes 4, 8, and 9 are based on the projected outcomes of the market research study.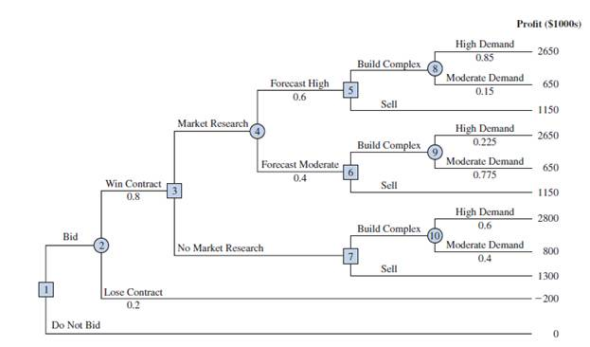
a. Verify Dante's profit projections shown at the ending branches of the decision tree by calculating the payoffs of $2,650,000 and $650,000 for first two outcomes.
b. What is the optimal decision strategy for Dante, and what is the expected profit for this project?
c. What would the cost of the market research study have to be before Dante would change its decision about the market research study?
d. Develop a risk profile for Dante.
has a 0.8 probability of winning the contract if it submits a bid. If the company wins the bid, it will have to pay $2 million to become a partner in the project. Node 3 shows that the company will then consider doing a market research study to forecast demand for the office units prior to beginning construction. The cost of this study is $150,000. Node 4 is
a chance node showing the possible outcomes of the market research study.
Nodes 5, 6, and 7 are similar in that they are the decision nodes for Dante to either build the office complex or sell the rights in the project to another developer. The decision to build the complex will result in an income of $5 million if demand is high and $3 million if demand is moderate. If Dante chooses to sell its rights in the project to another developer, income from the sale is estimated to be $3.5 million. The probabilities shown at nodes 4, 8, and 9 are based on the projected outcomes of the market research study.

a. Verify Dante's profit projections shown at the ending branches of the decision tree by calculating the payoffs of $2,650,000 and $650,000 for first two outcomes.
b. What is the optimal decision strategy for Dante, and what is the expected profit for this project?
c. What would the cost of the market research study have to be before Dante would change its decision about the market research study?
d. Develop a risk profile for Dante.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Southland Corporation's decision to produce a new line of recreational products resulted in the need to construct either a small plant or a large planet. The best selection of plant size depends on how the marketplace reacts to the new product line. To conduct an analysis, marketing management has decided to view the possible long-run demand as low, medium, or high. The following payoff table shows the projected profit in millions of dollars: 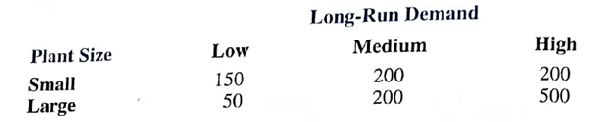
a. What is the decision to be made, and what is the chance event for Southland's problem?
b. Construct an influence diagram.
c. Construct a decision tree.
d. Recommend a decision based on the use of the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches.
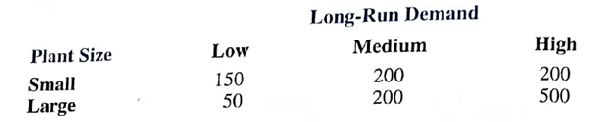
a. What is the decision to be made, and what is the chance event for Southland's problem?
b. Construct an influence diagram.
c. Construct a decision tree.
d. Recommend a decision based on the use of the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Hale's TV Productions is considering producing a pilot for a comedy series in the hope of selling it to a major television network. The network may decide to reject the series, but it may also decide to purchase the rights to the series for either one or two years. At this point in time, Hale may either produce the pilot and wait for the network's decision or transfer the rights for the pilot and series to a competitor for $100,000. Hale's decision alternatives and profits (in thousands of dollars) are as follows: 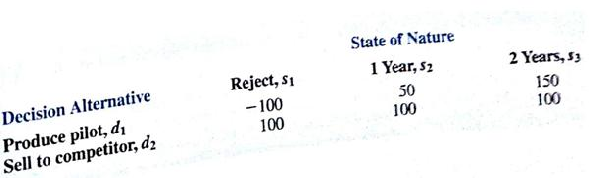
The probabilities for the states of nature are P ( s 1 ) = 0.20, P (s 2 ) = 0.30, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.50.
For a consulting fee of $5000, an agency will review the plans for the comedy Series indicate the overall chances of a favorable network reaction to the series. Assume that agency review will result in a favorable (F) or an unfavorable ( U ) review and that the following probabilities are relevant: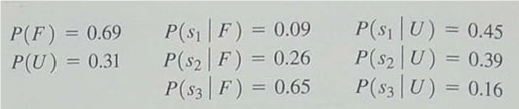
a. Construct a decision tree for this problem.
b. What is the recommended decision if the agency opinion is not used? What is the expected value?
c. What is the expected value of perfect information?
d. What is Hale's optimal decision strategy assuming the agency's information is used?
e. What is the expected value of the agency's information?
f. Is the agency's information worth the $5000 fee? What is the maximum that Hale should be willing to pay for the information?
g. What is the recommended decision?
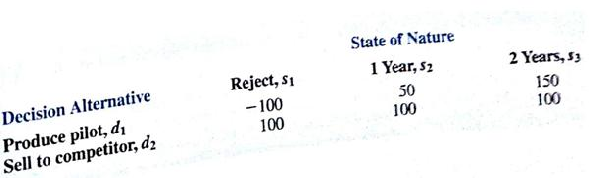
The probabilities for the states of nature are P ( s 1 ) = 0.20, P (s 2 ) = 0.30, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.50.
For a consulting fee of $5000, an agency will review the plans for the comedy Series indicate the overall chances of a favorable network reaction to the series. Assume that agency review will result in a favorable (F) or an unfavorable ( U ) review and that the following probabilities are relevant:
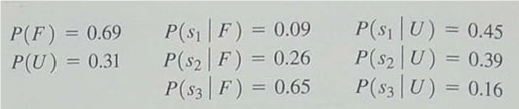
a. Construct a decision tree for this problem.
b. What is the recommended decision if the agency opinion is not used? What is the expected value?
c. What is the expected value of perfect information?
d. What is Hale's optimal decision strategy assuming the agency's information is used?
e. What is the expected value of the agency's information?
f. Is the agency's information worth the $5000 fee? What is the maximum that Hale should be willing to pay for the information?
g. What is the recommended decision?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The following profit payoff table was presented in Problem 1. Suppose that the decision marker obtained the probability assessments P ( s 1 ) = 0.65, P ( s 2 ) = 0.15 and P ( s 3 ) = 0.20. Use the expected value approach to determine the optimal decision. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Embassy Publishing Company received a six-chapter manuscript for a new college textbook. The editor of the college division is familiar with the manuscript and estimated a 0.65 probability that the textbook will be successful. If successful, a profit of $750,000 will be realized. If the company decides to publish the textbook and it is unsuccessful, a loss of $250,000 will occur.
Before making the decision to accept or reject the manuscript, the editor is considering sending the manuscript out for review. A review process provides either a favorable ( F ) or unfavorable ( u ) evaluation of the manuscript. Past experience with the review process suggests that probabilities P ( F ) 5 0.7 and P ( u ) 5 0.3 apply. Let s 1 5 the textbook is successful, and s 2 5 the textbook is unsuccessful. The editor's initial probabilities of s 1 and s 2 will be revised based on whether the review is favorable or unfavorable. The revised probabilities are as follows: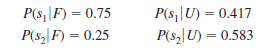
a. Construct a decision tree assuming that the company will first make the decision as to whether to send the manuscript out for review and then make the decision to accept or reject the manuscript.
b. Analyze the decision tree to determine the optimal decision strategy for the publishing company.
c. If the manuscript review costs $5,000, what is your recommendation?
d. What is the expected value of perfect information? What does this EVPI suggest for the company?
Before making the decision to accept or reject the manuscript, the editor is considering sending the manuscript out for review. A review process provides either a favorable ( F ) or unfavorable ( u ) evaluation of the manuscript. Past experience with the review process suggests that probabilities P ( F ) 5 0.7 and P ( u ) 5 0.3 apply. Let s 1 5 the textbook is successful, and s 2 5 the textbook is unsuccessful. The editor's initial probabilities of s 1 and s 2 will be revised based on whether the review is favorable or unfavorable. The revised probabilities are as follows:
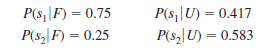
a. Construct a decision tree assuming that the company will first make the decision as to whether to send the manuscript out for review and then make the decision to accept or reject the manuscript.
b. Analyze the decision tree to determine the optimal decision strategy for the publishing company.
c. If the manuscript review costs $5,000, what is your recommendation?
d. What is the expected value of perfect information? What does this EVPI suggest for the company?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
An investor wants to select one of seven mutual funds for the coming Year. Data showing the percentage annual return for each fund five typical one- year periods are shown here. The assumption is that one of these five-year periods will occur again during the coming year. Thus, years A, B, C, D, and E are the states of nature for the mutual fund decision. 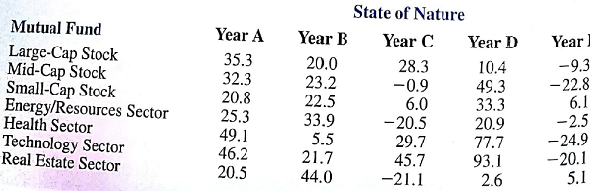
a. Assume that the investor is conservative. What is the recommended mutual fund? Using this mutual fund, what are the minimum and maximum annual returns?
b. Suppose that an experienced financial analyst reviews the five states of nature and provides the following probabilities: 0.1, 0.3, 0.1, and 0.4. Using the expected value, this mutual fund, what is the expected annual return? Using this mutual fund, what are minimum and maximum annual returns?
c. What is the expected annual return for the mutual fund recommended in part (a)? How much of an increase in the expected annual return can be obtained by following the recommendation in part (b)?
d. Which of the two mutual funds appears to have more risk? Why? Is the expected annual return greater for the mutual fund with more risk?
e. What mutual fund would you recommend to the investor? Explain.

a. Assume that the investor is conservative. What is the recommended mutual fund? Using this mutual fund, what are the minimum and maximum annual returns?
b. Suppose that an experienced financial analyst reviews the five states of nature and provides the following probabilities: 0.1, 0.3, 0.1, and 0.4. Using the expected value, this mutual fund, what is the expected annual return? Using this mutual fund, what are minimum and maximum annual returns?
c. What is the expected annual return for the mutual fund recommended in part (a)? How much of an increase in the expected annual return can be obtained by following the recommendation in part (b)?
d. Which of the two mutual funds appears to have more risk? Why? Is the expected annual return greater for the mutual fund with more risk?
e. What mutual fund would you recommend to the investor? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A real estate investor has the opportunity to purchase land currently zoned residential. If the county board approves a request to rezone the property as commercial within the next year, the investor will be able to lease the land to a large discount firm that wants to open a new store on the property. However, if the zoning change is not approved, the investor will have to sell the property at a loss. Profits (in thousands of dollars) are shown in the following payoff table: 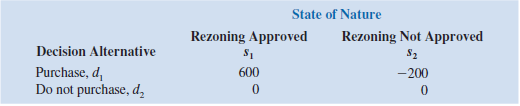
a. If the probability that the rezoning will be approved is 0.5, what decision is recommended? What is the expected profit?
b. The investor can purchase an option to buy the land. Under the option, the investor maintains the rights to purchase the land anytime during the next three months while learning more about possible resistance to the rezoning proposal from area residents. Probabilities are as follows: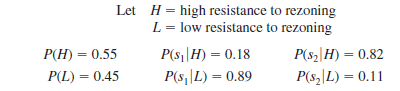
What is the optimal decision strategy if the investor uses the option period to learn more about the resistance from area residents before making the purchase decision?
c. If the option will cost the investor an additional $10,000, should the investor purchase the option? Why or why not? What is the maximum that the investor should be willing to pay for the option?

a. If the probability that the rezoning will be approved is 0.5, what decision is recommended? What is the expected profit?
b. The investor can purchase an option to buy the land. Under the option, the investor maintains the rights to purchase the land anytime during the next three months while learning more about possible resistance to the rezoning proposal from area residents. Probabilities are as follows:
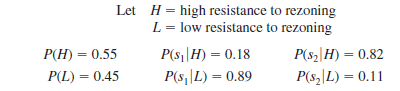
What is the optimal decision strategy if the investor uses the option period to learn more about the resistance from area residents before making the purchase decision?
c. If the option will cost the investor an additional $10,000, should the investor purchase the option? Why or why not? What is the maximum that the investor should be willing to pay for the option?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Amy Lloyd is interested in leasing a new saab and has contacted three automobile dealers for pricing information. Each dealer offered Amy a closed-end 36-monthly lease with no down payment due at the time of signing. Each lease includes a monthly charge and a mileage allowance. Additional miles receive a surcharge on a per-mile basis. The monthly lease cost, the mileage allowance, and the cost for additional miles follow: 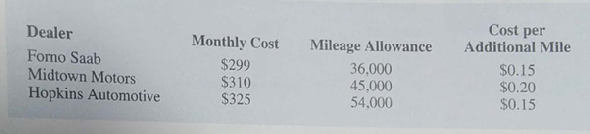
Amy decided to choose the lease option that will minimize her total 36-month cost. The difficulty is that Amy is not sure how many miles she will drive over the next three years. For purposes of this decision she believes it is reasonable to assume that she will drive 12,000 miles per year, 15,000 miles per year, or 18,000 miles per year. With this assumption Amy estimated her total costs for the three lease options. For example she figures that the For no Saab lease will cost her $10,764 if she drives 12,000 miles per year, $12,114 if she drives 15,000 miles per year, or $13,464 if she drives 18.000 miles per year.
a. What is the decision, and what is the chance event?
b. Construct a payoff table for Amy's problem.
c. If Amy has no idea which of the three mileage assumptions is most appropriate what is the recommended decision (leasing option) using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
d. Suppose that the probabilities that Amy drives 12,000, 15,000, and 18,000 miles per year are 0.5, 0.4, and 0.1, respectively. What option should Amy choose using the expected value approach?
e. Develop a risk profile for the decision selected in part (d). What is the most likely cost, and what is its probability?
f. suppose that after further consideration Amy concludes that the probabilities that she will drive 12,000,15,000, and 18,000 miles per year are 0.3,0.4, and 0.3 respectively What decision should Amy make using the expected value approach?

Amy decided to choose the lease option that will minimize her total 36-month cost. The difficulty is that Amy is not sure how many miles she will drive over the next three years. For purposes of this decision she believes it is reasonable to assume that she will drive 12,000 miles per year, 15,000 miles per year, or 18,000 miles per year. With this assumption Amy estimated her total costs for the three lease options. For example she figures that the For no Saab lease will cost her $10,764 if she drives 12,000 miles per year, $12,114 if she drives 15,000 miles per year, or $13,464 if she drives 18.000 miles per year.
a. What is the decision, and what is the chance event?
b. Construct a payoff table for Amy's problem.
c. If Amy has no idea which of the three mileage assumptions is most appropriate what is the recommended decision (leasing option) using the optimistic, conservative, and minimax regret approaches?
d. Suppose that the probabilities that Amy drives 12,000, 15,000, and 18,000 miles per year are 0.5, 0.4, and 0.1, respectively. What option should Amy choose using the expected value approach?
e. Develop a risk profile for the decision selected in part (d). What is the most likely cost, and what is its probability?
f. suppose that after further consideration Amy concludes that the probabilities that she will drive 12,000,15,000, and 18,000 miles per year are 0.3,0.4, and 0.3 respectively What decision should Amy make using the expected value approach?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Lawson's Department Store faces a buying decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium, or low. The purchaser for Lawson's can order 1, 2, or 3 lots of the product before the season begins but cannot recorder later. Profit projections (in thousands of dollars) are shown. 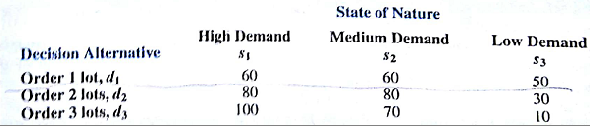
a. If the prior probabilities for the three states of nature are 0.3, 0.3, and 0.4, respectively, what is the recommended order quantity?
b. At each preseason sales meeting, the vice president of sales provides a personal opinion regarding potential demand for this product. Because of the vice president's enthusiasm and optimistic nature, the predictions of market conditions have always been either 'excellent' (E) or 'very good" (V). Probabilities are as follows: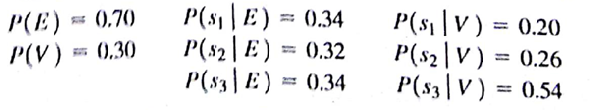
What is the optimal decision strategy?
c. Use the efficiency of sample information and discuss whether the firm should consider a consulting expert who could provide independent forecasts of market conditions for the product.

a. If the prior probabilities for the three states of nature are 0.3, 0.3, and 0.4, respectively, what is the recommended order quantity?
b. At each preseason sales meeting, the vice president of sales provides a personal opinion regarding potential demand for this product. Because of the vice president's enthusiasm and optimistic nature, the predictions of market conditions have always been either 'excellent' (E) or 'very good" (V). Probabilities are as follows:
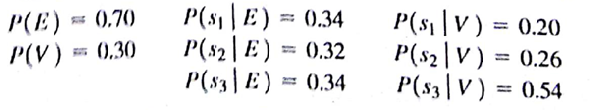
What is the optimal decision strategy?
c. Use the efficiency of sample information and discuss whether the firm should consider a consulting expert who could provide independent forecasts of market conditions for the product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Hudson Corporation is considering three options for managing its data processing operation: continuing with its own staff, hiring an outside vendor lo do the managing (referred to as outsourcing ), or using a combination of its own staff and an outside vendor. The cost of the operation depends on future demand. The annual cost of each option (in thousands of dollars) depends on demand as follows: 
a. If the demand probabilities are 0.2, 0.5, and 0.3, which decision alternative will minimize the expected cost of the what cost associated with that recommendation.
b. Construct a risk profile for the optimal decision in part (a). What is the probability of the cost exceeding $700,000?

a. If the demand probabilities are 0.2, 0.5, and 0.3, which decision alternative will minimize the expected cost of the what cost associated with that recommendation.
b. Construct a risk profile for the optimal decision in part (a). What is the probability of the cost exceeding $700,000?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Suppose that you are given a decision situation with three possible states of nature: s 1 , s 2 , and s 3. The prior probabilities are P ( s 1 ) = 0.2, P ( s 2 ) = 0.5, and P ( s 3 ) = 0.3. With sample information I , P ( I | s 1 ) = 0.1, P ( I | s 2 ) = 0.05, and P ( I = s 3 ) = 0.2. Compute the revised (or posterior) probabilities: P ( s 1 | I ), P ( s 2 | I ), and P ( s 3 | I ).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 27 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








