Deck 15: Risk and Information
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 15: Risk and Information
1
Given the possible outcomes to a lottery being only the values 2, 6 with equal probabilities, calculate the expected value, variance and standard deviation?
A)EV = 4, variance = 16, standard deviation = 4
B)EV = 4, variance = 4, standard deviation = 2
C)EV = 4, variance = 4, standard deviation = 4
D)EV = 3.5, variance = 4, standard deviation = 2
A)EV = 4, variance = 16, standard deviation = 4
B)EV = 4, variance = 4, standard deviation = 2
C)EV = 4, variance = 4, standard deviation = 4
D)EV = 3.5, variance = 4, standard deviation = 2
B
2
Large firms that can take on a number of small investment projects whose returns are independent of each other would most likely be characterized as:
A)risk-averse, because large firms do not like to take any risk.
B)risk-neutral, because each investment project is small relative to the total and firms are incentivized to maximize profits.
C)risk-loving, because there are a lot of benefits to being the biggest and most powerful firm.
D)risk-gaining, because there are a lot of benefits to being the biggest and most powerful firm.
A)risk-averse, because large firms do not like to take any risk.
B)risk-neutral, because each investment project is small relative to the total and firms are incentivized to maximize profits.
C)risk-loving, because there are a lot of benefits to being the biggest and most powerful firm.
D)risk-gaining, because there are a lot of benefits to being the biggest and most powerful firm.
B
3
The variance of a lottery is:
A)the average payoff you would get from the lottery if the lottery were repeated many times.
B)the sum of the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes of the lottery.
C)a measure of risk preference.
D)the amount an agent would be willing to pay to enter a lottery.
A)the average payoff you would get from the lottery if the lottery were repeated many times.
B)the sum of the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes of the lottery.
C)a measure of risk preference.
D)the amount an agent would be willing to pay to enter a lottery.
B
4
Consider a lottery with four equally likely outcomes, A, B, C, and D. The associated payoffs are: $10, $30, $70, and $150, respectively. The expected value of this lottery is what?
A)$30
B)$65
C)$130
D)$260
A)$30
B)$65
C)$130
D)$260

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A person who gets increasing marginal utility as income increases is described as:
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Consider a lottery with four equally likely outcomes, A, B, C, and D. The associated payoffs are: $10, $30, $70, and $150, respectively. The variance of this lottery is what?
A)2,875
B)5,750
C)8,625
D)11,500
A)2,875
B)5,750
C)8,625
D)11,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Consider four lotteries, A, B, C, and D, all with an expected value of $100. The associated standard deviations of the lotteries are: A is 10, B is 15, C is 5, and D is 20. Which lottery is the riskiest?
A)Lottery A
B)Lottery B
C)Lottery C
D)Lottery D
A)Lottery A
B)Lottery B
C)Lottery C
D)Lottery D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In economics, a lottery is:
A)the likelihood that a particular outcome occurs.
B)a depiction of all possible outcomes of an event and their associated probabilities.
C)any event for which the outcome is uncertain.
D)a measure of risk associated with some event.
A)the likelihood that a particular outcome occurs.
B)a depiction of all possible outcomes of an event and their associated probabilities.
C)any event for which the outcome is uncertain.
D)a measure of risk associated with some event.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
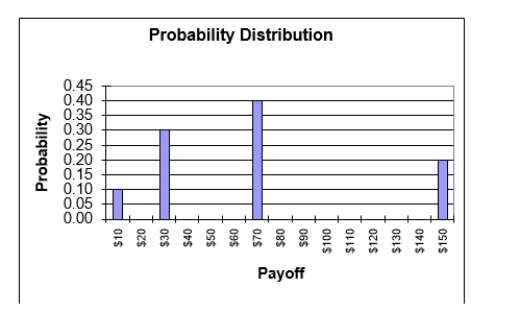
Given the probability distribution for the lottery above, what is the standard deviation of this lottery?
A)2,401
B)2,116
C)49
D)46

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A)A risk-averse decision maker will choose the alternative with the lowest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.
B)A risk-neutral decision maker will always choose the alternative with the lowest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.
C)A risk-loving decision maker will choose the alternative with the highest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.
D)The expected utility of a lottery is the expected value of the utility levels that the decision maker receives from the payoffs in the lottery.
A)A risk-averse decision maker will choose the alternative with the lowest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.
B)A risk-neutral decision maker will always choose the alternative with the lowest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.
C)A risk-loving decision maker will choose the alternative with the highest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.
D)The expected utility of a lottery is the expected value of the utility levels that the decision maker receives from the payoffs in the lottery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13

The variance of a probability distribution can be described as:
A)a measure of the riskiness of a probability distribution and is calculated by finding the square root of the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes.
B)a measure of the riskiness of a probability distribution and is calculated by finding the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes times two.
C)a measure of the amplitude of a probability distribution and is calculated by finding the square root of the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes.
D)a measure of the riskiness of a probability distribution and is calculated by finding the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What would be the expected value, variance and standard deviation of an event that always took the value one as its outcome?
A)1, 1, 1
B)1, 0, 1
C)1, 0, 0
D)1, 1, 0
A)1, 1, 1
B)1, 0, 1
C)1, 0, 0
D)1, 1, 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Suppose a fair, two-sided coin is flipped. If it comes up heads you receive $5; if it comes up tails you lose $1. The variance of this lottery is what?
A)4.5
B)9.0
C)13.5
D)18.0
A)4.5
B)9.0
C)13.5
D)18.0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16

Suppose you purchase a collectible baseball card from an acquaintance for $50. You think it could be worth $1,000 with a 10% probability and $0 with a 90% probability. What is your expected value for the baseball card?
A)$150
B)$100
C)$1000
D)$50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Suppose a fair, two-sided coin is flipped. If it comes up heads you receive $5; if it comes up tails you lose $1. The expected value of this lottery is what?
A)$2
B)$3
C)$4
D)$5
A)$2
B)$3
C)$4
D)$5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is false?
A)Some probabilities result from laws of nature; some reflect subjective beliefs about risky events.
B)The probability of any particular outcome is between 0 and 1.
C)The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes can exceed one.
D)The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes must equal exactly one.
A)Some probabilities result from laws of nature; some reflect subjective beliefs about risky events.
B)The probability of any particular outcome is between 0 and 1.
C)The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes can exceed one.
D)The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes must equal exactly one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Use the following probability distribution for a lottery to answer this question. 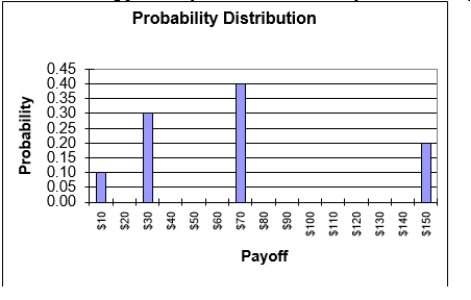
Given the probability distribution for the lottery above, what is the expected value of this lottery?
A)$83
B)$71
C)$68
D)$65

Given the probability distribution for the lottery above, what is the expected value of this lottery?
A)$83
B)$71
C)$68
D)$65

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The expected value of a lottery is:
A)the average payoff you would get from the lottery if the lottery were repeated many times.
B)the sum of the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes of the lottery.
C)a measure of risk preference.
D)the amount an individual would be willing to pay to enter a lottery.
A)the average payoff you would get from the lottery if the lottery were repeated many times.
B)the sum of the probability-weighted squared deviations of the possible outcomes of the lottery.
C)a measure of risk preference.
D)the amount an individual would be willing to pay to enter a lottery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A risk premium is:
A)a payment to an insurer by a policy-holder who faces a potential loss.
B)equal to the purchase price of an insurance policy.
C)the necessary difference between the expected value of a lottery and the payoff of a sure thing to make the decision maker indifferent between the lottery and the sure thing.
D)the difference between the expected value and the variance of a lottery.
A)a payment to an insurer by a policy-holder who faces a potential loss.
B)equal to the purchase price of an insurance policy.
C)the necessary difference between the expected value of a lottery and the payoff of a sure thing to make the decision maker indifferent between the lottery and the sure thing.
D)the difference between the expected value and the variance of a lottery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A decision maker can be described with utility that is only a function of income. If this function is linear, the decision maker is:
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A decision maker can be described with utility which is only a function of income and which exhibits diminishing marginal utility of income. This decision maker is:
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A decision-maker is faced with a choice between a lottery with a 30% chance of a payoff of $30 and a 70% chance of a payoff of $80, and a guaranteed payoff of $65. If the decision maker's utility function is , what is the risk premium associated with this choice?
A)$0
B)$1
C)$2
D)$3
A)$0
B)$1
C)$2
D)$3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A decision maker has a utility function U = 10I. This decision maker is:
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
An insurance company that sells fairly-priced insurance policies to a large number of individuals with similar realized accident risk probabilities should expect to:
A)break even.
B)lose money.
C)make a profit.
D)sell policies to individuals with all types of risk preference.
A)break even.
B)lose money.
C)make a profit.
D)sell policies to individuals with all types of risk preference.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is correct for a decision maker facing a choice between a sure thing and a lottery when the sure thing has the expected payoff of the lottery?
A)Risk-loving decision makers will require a positive risk premium to bear risk.
B)Risk-neutral decision makers will require a positive risk premium to bear risk.
C)Risk-averse decision makers will require a positive risk premium to bear risk.
D)The risk premium depends on the characteristics of the lottery, not on the characteristics of the utility function of the decision maker.
A)Risk-loving decision makers will require a positive risk premium to bear risk.
B)Risk-neutral decision makers will require a positive risk premium to bear risk.
C)Risk-averse decision makers will require a positive risk premium to bear risk.
D)The risk premium depends on the characteristics of the lottery, not on the characteristics of the utility function of the decision maker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Consider an insurance policy with $15,000 worth of coverage. If there is a 10% chance the owner of the policy will file a claim for the $15,000 (and a 90% chance they will not file a claim), a fair price for this policy is:
A)$1,000
B)$1,500
C)$13,000
D)$13,500
A)$1,000
B)$1,500
C)$13,000
D)$13,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A decision-maker is faced with a choice between a lottery with a 30% chance of a payoff of $30 and a 70% chance of a payoff of $80, and a guaranteed payoff of $65. If the decision maker's utility function is 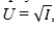 what is the risk premium associated with this choice?
what is the risk premium associated with this choice?
A)$1.59
B)$2.52
C)$0
D)$3.95
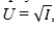 what is the risk premium associated with this choice?
what is the risk premium associated with this choice?A)$1.59
B)$2.52
C)$0
D)$3.95

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
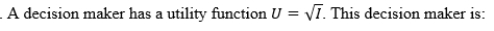
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A fairly-priced insurance policy is one in which:
A)the insurance premium is equal to the expected value of the promised insurance payment.
B)the insurance premium is equal to the expected value of the promised insurance payment plus a small profit for the insurance company.
C)the insurance premium is equal to the variance of the expected value of the promised insurance payment.
D)the insurance premium is equal to the variance of the expected value of the promised insurance payment plus a small profit for the insurance company.
A)the insurance premium is equal to the expected value of the promised insurance payment.
B)the insurance premium is equal to the expected value of the promised insurance payment plus a small profit for the insurance company.
C)the insurance premium is equal to the variance of the expected value of the promised insurance payment.
D)the insurance premium is equal to the variance of the expected value of the promised insurance payment plus a small profit for the insurance company.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Would you expect an insurance company in the "real world" to sell an insurance policy for exactly the "fairly-priced" level as defined in the text?
A)Yes, because the fairly-priced insurance policy includes some profit for the insurance company.
B)Yes, because insurance companies are required to sell their policy at the fairly-priced level by law.
C)Probably not, because the expected value of profits for the insurance company would be zero.
D)Probably not, because insurance companies are not in a competitive industry and are able to earn monopoly profits.
A)Yes, because the fairly-priced insurance policy includes some profit for the insurance company.
B)Yes, because insurance companies are required to sell their policy at the fairly-priced level by law.
C)Probably not, because the expected value of profits for the insurance company would be zero.
D)Probably not, because insurance companies are not in a competitive industry and are able to earn monopoly profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
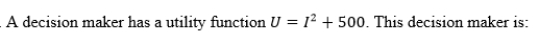
A)risk-averse.
B)risk-neutral.
C)risk-loving.
D)risk-gaining.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Suppose a decision maker has a utility function 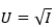 and is faced with a lottery where there is a 30% chance of earning $30 and a 70% chance of earning $80. What is the expected utility of this lottery?
and is faced with a lottery where there is a 30% chance of earning $30 and a 70% chance of earning $80. What is the expected utility of this lottery?
A)7.6
B)7.9
C)8.2
D)8.5
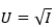 and is faced with a lottery where there is a 30% chance of earning $30 and a 70% chance of earning $80. What is the expected utility of this lottery?
and is faced with a lottery where there is a 30% chance of earning $30 and a 70% chance of earning $80. What is the expected utility of this lottery?A)7.6
B)7.9
C)8.2
D)8.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Lotteries A and B have the same expected value, but B has larger variance. Which of the following statements is true, all else equal?
A)If the decision maker is risk averse, lottery A will have the larger risk premium.
B)If the decision maker is risk neutral, lottery B will have the larger risk premium.
C)If the decision maker is risk loving, both lotteries will have a positive risk premium.
D)If the decision maker is risk averse, lottery B will have the larger risk premium.
A)If the decision maker is risk averse, lottery A will have the larger risk premium.
B)If the decision maker is risk neutral, lottery B will have the larger risk premium.
C)If the decision maker is risk loving, both lotteries will have a positive risk premium.
D)If the decision maker is risk averse, lottery B will have the larger risk premium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A risk premium, RP, can be computed with the following formula, where I1 and I2 are the two payoffs to a lottery, with probabilities p and (1-p), respectively: 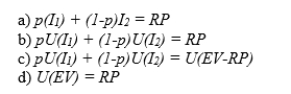
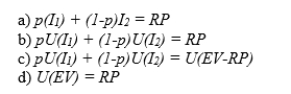

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Your current disposable income is $10,000. There is a 10% chance you will get in a serious car accident, incurring damage of $1,900. (There is a 90% chance that nothing will happen.)Your utility function is 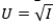 ,where I is income. If this policy is priced at $40, what is the change in your expected utility if you purchase the policy rather than no insurance?
,where I is income. If this policy is priced at $40, what is the change in your expected utility if you purchase the policy rather than no insurance?
A)1
B)0.8
C)0.2
D)0
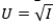 ,where I is income. If this policy is priced at $40, what is the change in your expected utility if you purchase the policy rather than no insurance?
,where I is income. If this policy is priced at $40, what is the change in your expected utility if you purchase the policy rather than no insurance?A)1
B)0.8
C)0.2
D)0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Your current disposable income is $10,000. There is a 10% chance you will get in a serious car accident, incurring damage of $1,900. (There is a 90% chance that nothing will happen.)Your utility function is 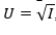 ,where I is income. What is the fair price of this policy?
,where I is income. What is the fair price of this policy?
A)$100
B)$190
C)$199
D)$270
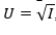 ,where I is income. What is the fair price of this policy?
,where I is income. What is the fair price of this policy?A)$100
B)$190
C)$199
D)$270

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Consider a fairly-priced insurance policy that fully indemnifies the purchaser against their loss. This insurance policy would most likely be purchased by:
A)a risk-loving decision maker.
B)a risk-neutral decision maker.
C)a risk-averse decision maker.
D)all decision makers.
A)a risk-loving decision maker.
B)a risk-neutral decision maker.
C)a risk-averse decision maker.
D)all decision makers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Your current disposable income is $10,000. There is a 10% chance you will get in a serious car accident, incurring damage of $1,900. (There is a 90% chance that nothing will happen.)Your utility function is 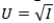 ,where I is income. What is the most you would be willing to pay for this policy (rather than no insurance)?
,where I is income. What is the most you would be willing to pay for this policy (rather than no insurance)?
A)$100
B)$190
C)$199
D)$270
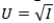 ,where I is income. What is the most you would be willing to pay for this policy (rather than no insurance)?
,where I is income. What is the most you would be willing to pay for this policy (rather than no insurance)?A)$100
B)$190
C)$199
D)$270

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Use the following decision tree to answer the next question.
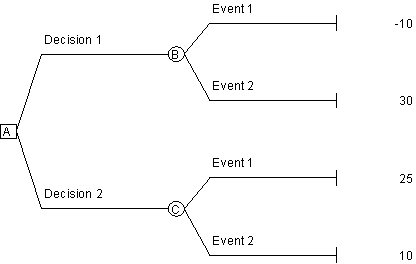
Consider the decision tree above. If the probability of Event 1 is 30% and the probability of Event 2 is 70%, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither; more information is needed to make an accurate assessment.

Consider the decision tree above. If the probability of Event 1 is 30% and the probability of Event 2 is 70%, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither; more information is needed to make an accurate assessment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
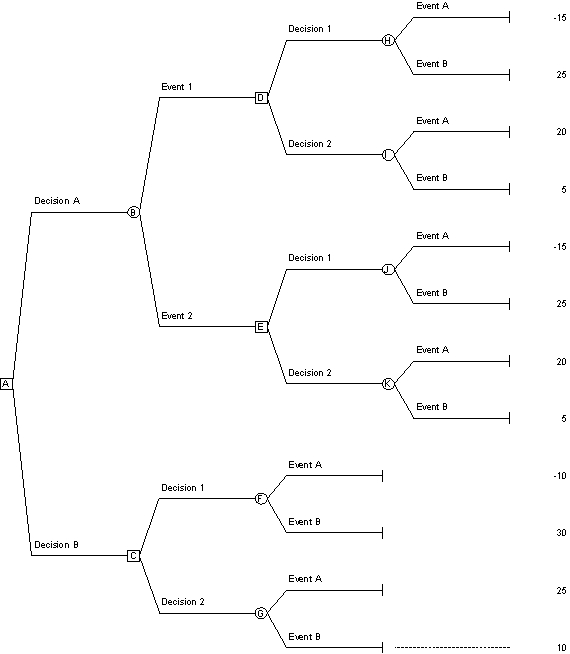
*At node A, which decision has the higher expected value?
A)Decision A
B)Decision B
C)Either decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither decision; more information is needed.
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*At node A, which decision has the higher expected value?
A)Decision A
B)Decision B
C)Either decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither decision; more information is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A good way to deal with moral hazard faced by an insurance company would be to:
A)fully indemnify its policy holders.
B)require applicants to take a physical examination.
C)require policy holders to pay a deductible.
D)conduct detailed investigations of every accident.
A)fully indemnify its policy holders.
B)require applicants to take a physical examination.
C)require policy holders to pay a deductible.
D)conduct detailed investigations of every accident.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
An English auction is an auction wherein:
A)the price called out continues to descend until someone is willing to pay that price.
B)participants cry out their bids and the bids keep rising until no participant is willing to pay a higher price for the object being sold.
C)bids are sealed and the individual with the highest bid wins.
D)bids are sealed and everyone with a price higher than the reservation price wins.
A)the price called out continues to descend until someone is willing to pay that price.
B)participants cry out their bids and the bids keep rising until no participant is willing to pay a higher price for the object being sold.
C)bids are sealed and the individual with the highest bid wins.
D)bids are sealed and everyone with a price higher than the reservation price wins.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the decision maker chooses Decision A and Event 1 occurs, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose at node D?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either Decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither Decision; more information is needed.
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the decision maker chooses Decision A and Event 1 occurs, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose at node D?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either Decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither Decision; more information is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A good way to deal with adverse selection faced by an insurance company would not be to:
A)fully indemnify its policy holders.
B)require applicants to take a physical examination.
C)require policy holders to pay a deductible.
D)insure groups of individuals (such as all employees of a particular firm).
A)fully indemnify its policy holders.
B)require applicants to take a physical examination.
C)require policy holders to pay a deductible.
D)insure groups of individuals (such as all employees of a particular firm).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
An auction in which participants cry out their bids, and each participant can increase his bid until the auction ends with the highest bidder winning the object is known as:
A)an English auction.
B)first-price sealed-bid auction.
C)second-price sealed-bid auction.
D)Dutch ascending auction.
A)an English auction.
B)first-price sealed-bid auction.
C)second-price sealed-bid auction.
D)Dutch ascending auction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the cost of obtaining information to determine Event 1 and Event 2 is $5, what is the value of perfect information?
A)-1.96
B)0
C)3.04
D)5
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the cost of obtaining information to determine Event 1 and Event 2 is $5, what is the value of perfect information?
A)-1.96
B)0
C)3.04
D)5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Use the following decision tree to answer the next question.
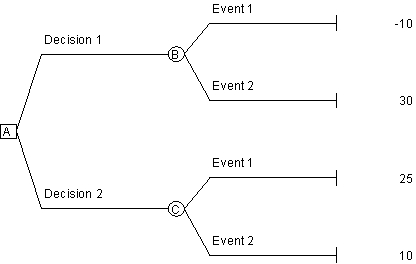
If the probability of Event 1 is 30% and the probability of Event 2 is 70% in the decision tree above, the expected value of Decision 1 is
A)-10
B)30
C)14.5
D)18

If the probability of Event 1 is 30% and the probability of Event 2 is 70% in the decision tree above, the expected value of Decision 1 is
A)-10
B)30
C)14.5
D)18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In a first-price sealed-bid auction when bidders have private values, the best bidding strategy is to bid:
A)your value for the object since this gives you the highest probability of winning the auction.
B)the value of the second highest bidder since this gives you the highest probability of winning while maximizing your surplus.
C)something less than your maximum willingness to pay, although how much less depends on a variety of factors.
D)continuing bidding until you win if you like the object.
A)your value for the object since this gives you the highest probability of winning the auction.
B)the value of the second highest bidder since this gives you the highest probability of winning while maximizing your surplus.
C)something less than your maximum willingness to pay, although how much less depends on a variety of factors.
D)continuing bidding until you win if you like the object.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

A decision tree is:
A)a diagram that describes the options available to a decision marker as well as the certain events that can occur at each point in time.
B)a diagram that helps the observer calculate the expected value, variance and standard deviation of a probability distribution.
C)not applicable to making decisions under conditions of uncertainty.
D)a diagram that describes the options available to a decision marker as well as the risky events that can occur at each point in time.
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

A decision tree is:
A)a diagram that describes the options available to a decision marker as well as the certain events that can occur at each point in time.
B)a diagram that helps the observer calculate the expected value, variance and standard deviation of a probability distribution.
C)not applicable to making decisions under conditions of uncertainty.
D)a diagram that describes the options available to a decision marker as well as the risky events that can occur at each point in time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In general, with a first-price sealed-bid auction with private values, the Nash equilibrium bids will:
A)increase as the number of bidders goes up.
B)decrease as the number of bidders goes up.
C)not be affected by the number of bidders in the auction.
D)decrease at a rate of 1/N where N is the number of bidders in the auction.
A)increase as the number of bidders goes up.
B)decrease as the number of bidders goes up.
C)not be affected by the number of bidders in the auction.
D)decrease at a rate of 1/N where N is the number of bidders in the auction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
With common values in an auction:
A)each bidder has his own personalized valuation of an object.
B)no bidder knows how much the object is worth to the other bidders.
C)the object has the same value to all bidders.
D)individuals are likely to have idiosyncratic assessments of the value of the object.
A)each bidder has his own personalized valuation of an object.
B)no bidder knows how much the object is worth to the other bidders.
C)the object has the same value to all bidders.
D)individuals are likely to have idiosyncratic assessments of the value of the object.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Moral hazard in auto insurance might refer to:
A)an auto owner failing to maintain the car, increasing the likelihood of an accident.
B)an applicant withholding information from the insurance company about the likelihood of having an accident.
C)an applicant lying on their application form about their health history.
D)an applicant having more cars than they announce when they complete their application.
A)an auto owner failing to maintain the car, increasing the likelihood of an accident.
B)an applicant withholding information from the insurance company about the likelihood of having an accident.
C)an applicant lying on their application form about their health history.
D)an applicant having more cars than they announce when they complete their application.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Asymmetric information refers to:
A)bad information.
B)incomplete information.
C)misleading information.
D)differences in the amount of information the parties have.
A)bad information.
B)incomplete information.
C)misleading information.
D)differences in the amount of information the parties have.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Use the following decision tree to answer the next question.
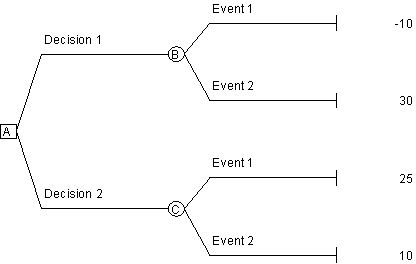
In the decision tree above, for what probability of Event 1 will Decision 1 and Decision 2 have the same expected value?
A)0.24
B)0.36
C)0.44
D)0.56

In the decision tree above, for what probability of Event 1 will Decision 1 and Decision 2 have the same expected value?
A)0.24
B)0.36
C)0.44
D)0.56

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Adverse selection in auto insurance might refer to:
A)an auto owner failing to maintain the car, increasing the likelihood of an accident.
B)an insured party driving faster than an uninsured party.
C)an applicant lying on their application form about their health history.
D)an insured driver using the car to conduct driving lessons for new learners.
A)an auto owner failing to maintain the car, increasing the likelihood of an accident.
B)an insured party driving faster than an uninsured party.
C)an applicant lying on their application form about their health history.
D)an insured driver using the car to conduct driving lessons for new learners.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*What is the expected value at node B?
A)18.60
B)16.04
C)13.76
D)12.50
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*What is the expected value at node B?
A)18.60
B)16.04
C)13.76
D)12.50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the decision maker chooses Decision A and Event 2 occurs, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose at node E?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either Decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither Decision; more information is needed.
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the decision maker chooses Decision A and Event 2 occurs, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose at node E?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either Decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither Decision; more information is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Heading: Analyzing Risky Decisions
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the decision maker chooses Decision B, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose at node C?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither decision; more information is needed.
**Reference: Use the decision tree along with the given probabilities to answer the next six questions
Probability Event A = 30% Probability Event B = 70%
Probability Event 1 = 58% Probability Event 2 = 42%
Probability of Event A given that Event 1 occurs = 16%
Probability of Event B given that Event 1 occurs = 84%
Probability of Event A given that Event 2 occurs = 50%
Probability of Event B given that Event 2 occurs = 50%

*If the decision maker chooses Decision B, which decision alternative should the decision maker choose at node C?
A)Decision 1
B)Decision 2
C)Either decision; they both have the same expected value.
D)Neither decision; more information is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In a second-price sealed-bid auction the best bidding strategy is to bid:
A)your maximum willingness to pay for the object.
B)the value of the second highest bidder since this gives you the highest probability of winning while maximizing your surplus.
C)something less than your maximum willingness to pay, although how much less depends on a variety of factors.
D)continuing bidding until you win if you like the object.
A)your maximum willingness to pay for the object.
B)the value of the second highest bidder since this gives you the highest probability of winning while maximizing your surplus.
C)something less than your maximum willingness to pay, although how much less depends on a variety of factors.
D)continuing bidding until you win if you like the object.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The winner's curse refers to:
A)bidding an amount higher than your maximum willingness to pay in an effort to 'win' in a private values auction.
B)winning a private values auction and later determining that you bid more than you had really intended to.
C)winning a common values auction and bidding more than the object is worth.
D)winning an item in a common values auction that you don't really want.
A)bidding an amount higher than your maximum willingness to pay in an effort to 'win' in a private values auction.
B)winning a private values auction and later determining that you bid more than you had really intended to.
C)winning a common values auction and bidding more than the object is worth.
D)winning an item in a common values auction that you don't really want.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The expected utility of a lottery is the expected value of the utility levels that the decision maker receives from the payoffs in the lottery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The probability of any particular outcome is between 0 and 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
A risk-averse decision maker will choose the alternative with the lowest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A risk-loving decision maker will choose the alternative with the highest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Some probabilities result from laws of nature; some reflect subjective beliefs about risky events.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
In a second-price sealed-bid auction with private values, the winner of the auction is:
A)the second-highest bidder and pays the bid of the highest bidder.
B)the second-highest bidder and pays the bid of the third-highest bidder.
C)the highest-bidder and pays the bid of the second-highest bidder.
D)the highest-bidder and pays the amount they bid.
A)the second-highest bidder and pays the bid of the highest bidder.
B)the second-highest bidder and pays the bid of the third-highest bidder.
C)the highest-bidder and pays the bid of the second-highest bidder.
D)the highest-bidder and pays the amount they bid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A risk-neutral decision maker will always choose the alternative with the lowest variance among alternatives with identical expected utilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes must equal exactly one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes can exceed one.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








