Deck 16: Monetary Policy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/213
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 16: Monetary Policy
1
The transactions demand for money is the demand for money by households for:
A)rainy day spending.
B)predictable spending purposes.
C)liquidity purposes.
D)investing purposes.
A)rainy day spending.
B)predictable spending purposes.
C)liquidity purposes.
D)investing purposes.
predictable spending purposes.
2
The demand for money that households keep for emergency purposes is known as the:
A)precautionary demand.
B)emergency demand.
C)speculative demand.
D)transactions demand.
E)temporary demand.
A)precautionary demand.
B)emergency demand.
C)speculative demand.
D)transactions demand.
E)temporary demand.
precautionary demand.
3
Keynes called the money people hold in order to pay unforeseen or unexpected expenses the:
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)store of value demand for holding money.
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)store of value demand for holding money.
precautionary demand for holding money.
4
The quantity of money held in response to interest rates is the:
A)transactions motive for holding money.
B)precautionary motive for holding money.
C)speculative motive for holding money.
D)unit-of-account motive for holding money.
A)transactions motive for holding money.
B)precautionary motive for holding money.
C)speculative motive for holding money.
D)unit-of-account motive for holding money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The precautionary demand for money:
A)varies inversely with the income level.
B)varies inversely with the price level.
C)is used as an insurance agent against unexpected needs.
D)states that nominal income must exceed real income.
E)is a classical concept in monetary theory.
A)varies inversely with the income level.
B)varies inversely with the price level.
C)is used as an insurance agent against unexpected needs.
D)states that nominal income must exceed real income.
E)is a classical concept in monetary theory.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
When people hold money to transact purchases they expect to make, this is known as the:
A)precautionary demand for money.
B)liquidity demand for money.
C)spending demand for money.
D)speculative demand for money.
E)transactions demand for money.
A)precautionary demand for money.
B)liquidity demand for money.
C)spending demand for money.
D)speculative demand for money.
E)transactions demand for money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The stock of money people hold to pay everyday predictable expenses is the:
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)store of value demand for holding money.
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)store of value demand for holding money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
People learn to hold a specific quantity of money for the groceries, theater tickets, gasoline, clothes, film, and other items they habitually purchase. This behavior is representative of the:
A)precautionary demand.
B)speculative demand.
C)transactions demand.
D)volatility demand.
E)liquidity demand.
A)precautionary demand.
B)speculative demand.
C)transactions demand.
D)volatility demand.
E)liquidity demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which type of demand for money causes the demand for money curve to slope downward?
A)Speculative demand.
B)Precautionary demand.
C)Transactions demand.
D)Foreign-exchange demand.
A)Speculative demand.
B)Precautionary demand.
C)Transactions demand.
D)Foreign-exchange demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
If you hold money in anticipation of household emergency expense, this represents the::
A)speculative demand for holding money.
B)transactions demand for holding money.
C)opportunity cost motive for holding money.
D)precautionary demand for holding money.
E)regressive cost of holding money.
A)speculative demand for holding money.
B)transactions demand for holding money.
C)opportunity cost motive for holding money.
D)precautionary demand for holding money.
E)regressive cost of holding money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Keynes called money people hold to make routine day-to-day purchases the:
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)store of value demand for holding money.
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)store of value demand for holding money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The speculative demand for money is the stock of money that people hold to:
A)pay their predictable, everyday expenses.
B)pay for any unexpected expenses that may occur.
C)buy stocks, bonds, and other financial assets.
D)buy the foreign currencies needed to purchase imports.
A)pay their predictable, everyday expenses.
B)pay for any unexpected expenses that may occur.
C)buy stocks, bonds, and other financial assets.
D)buy the foreign currencies needed to purchase imports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The transactions demand for holding money is when people hold money:
A)instead of near money.
B)to transact purchases they expect to make.
C)as insurance against unexpected expenses.
D)to speculate in the stock market.
E)to take advantage of changes in interest rates.
A)instead of near money.
B)to transact purchases they expect to make.
C)as insurance against unexpected expenses.
D)to speculate in the stock market.
E)to take advantage of changes in interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Keynes called the money people hold in order to buy bonds, stocks, or other nonmoney financial assets the:
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)unit of account demand for holding money.
A)transactions demand for holding money.
B)precautionary demand for holding money.
C)speculative demand for holding money.
D)unit of account demand for holding money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
One reason that people hold money is to pay for unexpected car repairs and other unpredictable expenses. This motive for holding money is called:
A)transactions demand.
B)precautionary demand.
C)speculative demand.
D)noncyclical demand.
A)transactions demand.
B)precautionary demand.
C)speculative demand.
D)noncyclical demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The precautionary demand for money is the demand for money:
A)for normal transactions purposes.
B)for normal investment purposes.
C)for special stock purchases.
D)to protect against inflation.
E)to cover unexpected events.
A)for normal transactions purposes.
B)for normal investment purposes.
C)for special stock purchases.
D)to protect against inflation.
E)to cover unexpected events.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
When a household takes extra (unbudgeted)money on a trip, economists would classify this money as held for a(n):
A)speculative demand.
B)transactions demand.
C)emergency motive.
D)precautionary demand.
E)inflationary motive.
A)speculative demand.
B)transactions demand.
C)emergency motive.
D)precautionary demand.
E)inflationary motive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The stock of money people hold to take advantage of expected future changes in the price of bonds, stocks, or other nonmoney financial assets is the:
A)unit-of-account motive for holding money.
B)precautionary motive for holding money.
C)speculative motive for holding money.
D)transactions motive for holding money.
A)unit-of-account motive for holding money.
B)precautionary motive for holding money.
C)speculative motive for holding money.
D)transactions motive for holding money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The quantity of money demanded to satisfy transactions needs:
A)is intended for unexpected expenditures.
B)increases with the level of real GDP.
C)decreases with the level of real GDP.
D)is unrelated to either national income or the interest rate.
E)varies inversely with the liquidity demand for money.
A)is intended for unexpected expenditures.
B)increases with the level of real GDP.
C)decreases with the level of real GDP.
D)is unrelated to either national income or the interest rate.
E)varies inversely with the liquidity demand for money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The precautionary demand for holding money is when people hold money:
A)instead of near money.
B)to transact purchases they expect to make.
C)as insurance against unexpected needs.
D)to speculate in the stock market.
E)to take advantage of changes in interest rates.
A)instead of near money.
B)to transact purchases they expect to make.
C)as insurance against unexpected needs.
D)to speculate in the stock market.
E)to take advantage of changes in interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The speculative demand for money:
A)varies inversely with income.
B)is only concerned with active money.
C)involves holding money for unexpected problems.
D)varies directly with the transactions demand for money.
E)varies inversely with the interest rate.
A)varies inversely with income.
B)is only concerned with active money.
C)involves holding money for unexpected problems.
D)varies directly with the transactions demand for money.
E)varies inversely with the interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A decrease in the interest rate, other things being equal, causes a(n):
A)upward movement along the demand curve for money.
B)downward movement along the demand curve for money.
C)rightward shift of the demand curve for money.
D)leftward shift of the demand curve for money.
A)upward movement along the demand curve for money.
B)downward movement along the demand curve for money.
C)rightward shift of the demand curve for money.
D)leftward shift of the demand curve for money.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Other things being equal, an increase in the rate of interest causes a(n):
A)upward movement along the demand for money curve.
B)downward movement along the demand for money curve.
C)rightward shift of the demand for money curve.
D)leftward shift of the demand for money curve.
A)upward movement along the demand for money curve.
B)downward movement along the demand for money curve.
C)rightward shift of the demand for money curve.
D)leftward shift of the demand for money curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The speculative demand curve for money is:
A)downward sloping.
B)upward sloping.
C)vertical.
D)horizontal.
E)spiral.
A)downward sloping.
B)upward sloping.
C)vertical.
D)horizontal.
E)spiral.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following explains why the demand for money curve has an inverse relationship between the interest rates and the quantity of money demanded?
A)As the interest rate rises, the opportunity cost of holding money rises, and people respond by converting cash or checking account balances into interest-bearing financial investments.
B) As the interest rate rises, people find it advantageous to borrow money, which increases the quantity of money demanded.
C)As the interest rate falls, the opportunity cost of holding money rises, and people respond by converting cash or checking account balances into interest-bearing financial investments.
D)As the interest rate rises, the demand for money curve shifts outward to the right.
A)As the interest rate rises, the opportunity cost of holding money rises, and people respond by converting cash or checking account balances into interest-bearing financial investments.
B) As the interest rate rises, people find it advantageous to borrow money, which increases the quantity of money demanded.
C)As the interest rate falls, the opportunity cost of holding money rises, and people respond by converting cash or checking account balances into interest-bearing financial investments.
D)As the interest rate rises, the demand for money curve shifts outward to the right.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In a two-asset economy with money and T-bills, the quantity of money that people will want to hold, other things being equal, can be expected to:
A)decrease as real GDP increases.
B)increase as the interest rate decreases.
C)increase as the interest rate increases.
D)all of these.
A)decrease as real GDP increases.
B)increase as the interest rate decreases.
C)increase as the interest rate increases.
D)all of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is true ?
A)The speculative demand for money at possible interest rates gives the demand for money curve its upward slope.
B)There is an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate.
C)According to the quantity theory of money, any change in the money supply will have no effect on the price level.
D)All of these are true.
A)The speculative demand for money at possible interest rates gives the demand for money curve its upward slope.
B)There is an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate.
C)According to the quantity theory of money, any change in the money supply will have no effect on the price level.
D)All of these are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A graph illustrating the relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate would have a slope that is:
A)positive.
B)negative.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
A)positive.
B)negative.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The speculative demand for money shows the relationship between money demand and:
A)income levels.
B)interest rates.
C)prices
D)investment.
E)consumption.
A)income levels.
B)interest rates.
C)prices
D)investment.
E)consumption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The demand curve for money:
A)shows the amount of money balances that individuals and businesses wish to hold at various levels of private investment.
B)reflects the open market operations policy of the Federal Reserve.
C)shows the amount of money that households and businesses wish to hold at various rates of interest.
D)indicates the amount that consumers wish to borrow at a given interest rate.
A)shows the amount of money balances that individuals and businesses wish to hold at various levels of private investment.
B)reflects the open market operations policy of the Federal Reserve.
C)shows the amount of money that households and businesses wish to hold at various rates of interest.
D)indicates the amount that consumers wish to borrow at a given interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Why do people hold money (currency and checking account balances), and thereby forgo earning interest or dividends from a financial investment?
A)Some money is demanded for everyday transactions like parking fees, lunch, and buying groceries.
B)Some money is demanded as a precaution against unexpected costs such as automobile repairs, speeding tickets, or temporary loss of a job.
C)Some money is demanded for speculative purchases of stocks, bonds, or collectibles in case they become available at a particularly low price.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)Some money is demanded for everyday transactions like parking fees, lunch, and buying groceries.
B)Some money is demanded as a precaution against unexpected costs such as automobile repairs, speeding tickets, or temporary loss of a job.
C)Some money is demanded for speculative purchases of stocks, bonds, or collectibles in case they become available at a particularly low price.
D)All of the above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In a two-asset economy with money and T-bills, the quantity of money that people will want to hold, other things being equal, can be expected to:
A)increase as the real GDP interest rate increases.
B)decrease as the real GDP interest rate increases.
C)decrease as real GDP increases.
D)none of these.
A)increase as the real GDP interest rate increases.
B)decrease as the real GDP interest rate increases.
C)decrease as real GDP increases.
D)none of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Keynes argued that the downward slope of the demand for money curve depends on the:
A)equation of exchange.
B)rate of interest.
C)federal funds rate.
D)discount rate.
A)equation of exchange.
B)rate of interest.
C)federal funds rate.
D)discount rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The downward slope of the demand for money curve is created by the:
A)transactions demand for money.
B)precautionary demand for money.
C)speculative demand for money.
D)all of these.
A)transactions demand for money.
B)precautionary demand for money.
C)speculative demand for money.
D)all of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The money that households might hold either as money or in interest-bearing assets, depending on the interest rate, is called the:
A)precautionary demand.
B)transactions demand.
C)speculative demand.
D)liquidity motive.
E)investment motive.
A)precautionary demand.
B)transactions demand.
C)speculative demand.
D)liquidity motive.
E)investment motive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Speculative demand for money is a(n):
A)positive function of prices.
B)inverse function of prices.
C)positive function of interest rates.
D)inverse function of interest rates.
E)function of unexpected needs.
A)positive function of prices.
B)inverse function of prices.
C)positive function of interest rates.
D)inverse function of interest rates.
E)function of unexpected needs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The speculative demand for holding money is when people hold money:
A)instead of near money.
B)to transact purchases they expect to make.
C)as insurance against unexpected needs.
D)to speculate in the stock market.
E)to take advantage of changes in interest rates.
A)instead of near money.
B)to transact purchases they expect to make.
C)as insurance against unexpected needs.
D)to speculate in the stock market.
E)to take advantage of changes in interest rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Other things being equal, the quantity of money that people wish to hold in currency and their checking accounts can be expected to:
A)increase as the interest rate increases.
B)decrease as the interest rate increases.
C)decrease as real GDP increases.
D)none of these.
A)increase as the interest rate increases.
B)decrease as the interest rate increases.
C)decrease as real GDP increases.
D)none of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
When interest rates rise, the quantity demanded of money held for the:
A)speculative motive rises.
B)precautionary motive rises.
C)transactions motive falls.
D)precautionary motive falls.
E)speculative motive falls.
A)speculative motive rises.
B)precautionary motive rises.
C)transactions motive falls.
D)precautionary motive falls.
E)speculative motive falls.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The opportunity cost of holding money balances increases when:
A)the inflation rate decreases.
B)the interest rate increases.
C)the interest rate decreases.
D)GDP is far from full employment.
A)the inflation rate decreases.
B)the interest rate increases.
C)the interest rate decreases.
D)GDP is far from full employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
As the interest rate decreases, the quantity of money people will hold:
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)stays the same.
D)rises and then falls.
E)falls and then rises.
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)stays the same.
D)rises and then falls.
E)falls and then rises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true ?
A)The speculative demand for money at possible interest rates gives the demand for money curve its upward slope.
B)There is an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate.
C)According to the quantity theory of money, any change in the money supply will have no effect on the price level.
D)All of these.
A)The speculative demand for money at possible interest rates gives the demand for money curve its upward slope.
B)There is an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate.
C)According to the quantity theory of money, any change in the money supply will have no effect on the price level.
D)All of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The demand for money curve shows that there is an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the:
A)quantity of money supplied.
B)gross domestic product (GDP).
C)price level.
D)interest rate.
A)quantity of money supplied.
B)gross domestic product (GDP).
C)price level.
D)interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
In Keynes's view, an excess quantity of money demanded causes people to:
A)sell bonds and the interest rate rises.
B)buy bonds and the interest rate falls.
C)buy bonds and the interest rate rises.
D)increase speculative balances.
A)sell bonds and the interest rate rises.
B)buy bonds and the interest rate falls.
C)buy bonds and the interest rate rises.
D)increase speculative balances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Suppose that the current money market equilibrium features an interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion. If the Fed raises the discount rate, which of the following is most likely to be the new money market equilibrium?
A)An interest rate of 6 percent and a quantity of $1.5 trillion.
B)An interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion.
C)An interest rate of 4 percent and a quantity of $2.5 trillion.
D)None of the above.
A)An interest rate of 6 percent and a quantity of $1.5 trillion.
B)An interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion.
C)An interest rate of 4 percent and a quantity of $2.5 trillion.
D)None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following policies could the Fed use to lower the interest rate?
A)A tax cut.
B)Selling government securities.
C)Raising the discount rate.
D)Reducing the required reserve ratio.
A)A tax cut.
B)Selling government securities.
C)Raising the discount rate.
D)Reducing the required reserve ratio.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Assume a fixed demand for money curve and the Fed decreases the money supply. In response, people will:
A)sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
A)sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following falls when bond prices rise?
A)Stock prices.
B)Interest rates.
C)Money demand.
D)Money supply.
A)Stock prices.
B)Interest rates.
C)Money demand.
D)Money supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Assume a fixed demand for money curve and the Fed increases the money supply. In response, people will:
A)sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
A)sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
If the Fed expands the money supply by $1 trillion, what will happen in the money market?
A)The equilibrium interest rate will rise, and less money will be exchanged in equilibrium.
B)The equilibrium interest rate will fall, and more money will exchanged in equilibrium.
C)The equilibrium interest rate will not change.
D)None of the above.
A)The equilibrium interest rate will rise, and less money will be exchanged in equilibrium.
B)The equilibrium interest rate will fall, and more money will exchanged in equilibrium.
C)The equilibrium interest rate will not change.
D)None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
When the interest rate falls,
A)the opportunity cost of holding money rises.
B)people shift out of holding interest-yielding bonds into holding money.
C)the quantity of money people will hold decreases.
D)investment spending decreases.
E)real GDP will decrease.
A)the opportunity cost of holding money rises.
B)people shift out of holding interest-yielding bonds into holding money.
C)the quantity of money people will hold decreases.
D)investment spending decreases.
E)real GDP will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Suppose that the current money market equilibrium has an interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion. Suppose that at a 6 percent interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is $1.5 trillion, while at a 4 percent interest rate it is $2.5 trillion. If the Fed makes an open-market purchase of $50 billion, and the money multiplier is 10, what will be the new money market equilibrium?
A)An interest rate of 6 percent and a quantity of $1.5 trillion.
B)An interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion.
C)An interest rate of 4 percent and a quantity of $2.5 trillion.
D)None of the above.
A)An interest rate of 6 percent and a quantity of $1.5 trillion.
B)An interest rate of 5 percent and a quantity of $2 trillion.
C)An interest rate of 4 percent and a quantity of $2.5 trillion.
D)None of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Assume the Fed decreases the money supply and the demand for money curve is fixed. In response, people will:
A)sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
A)sell bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)buy bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buy bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)sell bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
If at the prevailing interest rate the quantity of money demanded is $2 trillion, and the supply of money is $1.5 trillion, then which of the following is true ?
A)There is a shortage of money, and consequently interest rates must fall in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
B)There is a surplus of money, and consequently interest rates must fall in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
C)There is shortage of money, and consequently interest rates must rise in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
D)There is a surplus of money, and consequently interest rates must rise in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
A)There is a shortage of money, and consequently interest rates must fall in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
B)There is a surplus of money, and consequently interest rates must fall in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
C)There is shortage of money, and consequently interest rates must rise in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.
D)There is a surplus of money, and consequently interest rates must rise in order to achieve an equilibrium in the money market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
If the Fed wants to raise interest rates, then it can use its open market operations to:
A)increase the money supply.
B)decrease the money supply.
C)increase money demand.
D)decrease money demand.
A)increase the money supply.
B)decrease the money supply.
C)increase money demand.
D)decrease money demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In Keynes's view, an excess quantity of money supplied causes people to:
A)sell bonds and the interest rate rises.
B)buy bonds and the interest rate falls.
C)buy bonds and the interest rate rises.
D)increase speculative balances.
A)sell bonds and the interest rate rises.
B)buy bonds and the interest rate falls.
C)buy bonds and the interest rate rises.
D)increase speculative balances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
People react to an excess supply of money by:
A)selling bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)selling bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buying bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)buying bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
A)selling bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)selling bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)buying bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)buying bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Assume a fixed demand for money curve and the Fed increases the money supply. The result is a temporary:
A)excess quantity of money demanded.
B)excess quantity of money supplied.
C)new equilibrium interest rate.
D)decrease in the demand for loans.
A)excess quantity of money demanded.
B)excess quantity of money supplied.
C)new equilibrium interest rate.
D)decrease in the demand for loans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If people attempt to sell bonds because of excess money demand, then the interest rate will:
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged
D)react unpredictably.
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)remain unchanged
D)react unpredictably.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Keynesians identify three principal motives for demanding money. They are the:
A)transactions demand, precautionary demand, and liquidity motive.
B)transactions demand, precautionary demand, and convertibility motive.
C)transactions demand, speculative demand, and volatility motive.
D)transactions demand, speculative demand, and liquidity motive.
E)transactions demand, speculative demand, and precautionary demand.
A)transactions demand, precautionary demand, and liquidity motive.
B)transactions demand, precautionary demand, and convertibility motive.
C)transactions demand, speculative demand, and volatility motive.
D)transactions demand, speculative demand, and liquidity motive.
E)transactions demand, speculative demand, and precautionary demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Exhibit 16-1 Money market demand and supply curves 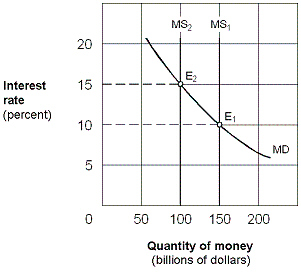 As shown in Exhibit 16-1, assume the money supply curve shifts leftward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
As shown in Exhibit 16-1, assume the money supply curve shifts leftward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
A)higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
B)lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
C)higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level.
D)higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.
 As shown in Exhibit 16-1, assume the money supply curve shifts leftward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
As shown in Exhibit 16-1, assume the money supply curve shifts leftward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:A)higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
B)lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
C)higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level.
D)higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
An increase in the supply of money will:
A)reduce the rate of interest and, thereby, trigger an increase in current spending by households and businesses.
B)reduce aggregate demand and real output.
C)increase only the general level of prices.
D)lead to a higher rate of unemployment.
A)reduce the rate of interest and, thereby, trigger an increase in current spending by households and businesses.
B)reduce aggregate demand and real output.
C)increase only the general level of prices.
D)lead to a higher rate of unemployment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Exhibit 16-3 Money market demand and supply curves  In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium with an interest rate of 15 percent and the money supply at $100 billion. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E2 with money supply of $150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. This change could be the result of a(n):
In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium with an interest rate of 15 percent and the money supply at $100 billion. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E2 with money supply of $150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. This change could be the result of a(n):
A)open market sale of securities by the Fed.
B)higher discount rate set by the Fed.
C)higher required-reserve ratio set by the Fed.
D)open market purchase of securities by the Fed.
 In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium with an interest rate of 15 percent and the money supply at $100 billion. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E2 with money supply of $150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. This change could be the result of a(n):
In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium with an interest rate of 15 percent and the money supply at $100 billion. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E2 with money supply of $150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. This change could be the result of a(n):A)open market sale of securities by the Fed.
B)higher discount rate set by the Fed.
C)higher required-reserve ratio set by the Fed.
D)open market purchase of securities by the Fed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Suppose that the Fed makes a $100 billion open-market sale of Treasury bonds, and the money multiplier is 6. Which of the following impacts are most likely to result?
A)The money supply shifts inward, and the equilibrium interest rate rises in the money market.
B)The money supply shifts outward, and the equilibrium interest rate falls in the money market.
C)Investment declines, causing the aggregate demand curve to shift leftward, reducing equilibrium real GDP and thus slowing the economy.
D)Both a. and c. are correct.
E)Both b. and c. above are correct.
A)The money supply shifts inward, and the equilibrium interest rate rises in the money market.
B)The money supply shifts outward, and the equilibrium interest rate falls in the money market.
C)Investment declines, causing the aggregate demand curve to shift leftward, reducing equilibrium real GDP and thus slowing the economy.
D)Both a. and c. are correct.
E)Both b. and c. above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
An increase in the money supply is represented by a(n):
A)rightward shift of the downward-sloping money supply curve.
B)upward shift of the money supply curve.
C)rightward shift of the money supply curve.
D)increase in the rate of interest.
A)rightward shift of the downward-sloping money supply curve.
B)upward shift of the money supply curve.
C)rightward shift of the money supply curve.
D)increase in the rate of interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
When the Fed increases the money supply, interest rates:
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)are unaffected.
D)rise and then fall.
E)fall and then rise.
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)are unaffected.
D)rise and then fall.
E)fall and then rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Exhibit 16-3 Money market demand and supply curves 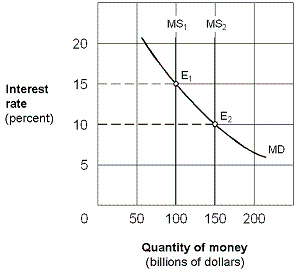 In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium at E2 with the money supply at $100 billion and the interest rate at 15 percent. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E1 with a money supply of 150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. As part of the adjustment to the new equilibrium, we would expect the:
In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium at E2 with the money supply at $100 billion and the interest rate at 15 percent. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E1 with a money supply of 150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. As part of the adjustment to the new equilibrium, we would expect the:
A)price of bonds to rise.
B)price of bonds to remain unchanged.
C)price of bonds to fall.
D)none of these.
 In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium at E2 with the money supply at $100 billion and the interest rate at 15 percent. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E1 with a money supply of 150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. As part of the adjustment to the new equilibrium, we would expect the:
In Exhibit 16-3, assume an equilibrium at E2 with the money supply at $100 billion and the interest rate at 15 percent. The Fed uses its policy tools to move the economy to a new equilibrium at E1 with a money supply of 150 billion and an interest rate of 10 percent. As part of the adjustment to the new equilibrium, we would expect the:A)price of bonds to rise.
B)price of bonds to remain unchanged.
C)price of bonds to fall.
D)none of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Assume the demand for money curve is stationary and the Fed increases the money supply. The result is that people:
A)increase the supply of bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)increase the supply of bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)increase the demand for bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)increase the demand for bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
A)increase the supply of bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
B)increase the supply of bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.
C)increase the demand for bonds, thus driving up the interest rate.
D)increase the demand for bonds, thus driving down the interest rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
If the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, ceteris paribus , the:
A)rate of interest decreases.
B)rate of interest increases.
C)rate of interest is unaffected.
D)Fed sells bonds.
A)rate of interest decreases.
B)rate of interest increases.
C)rate of interest is unaffected.
D)Fed sells bonds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Exhibit 16-2 Money market demand and supply curves 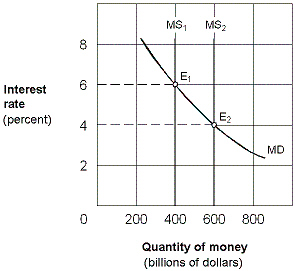 Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, an increase in the money supply from $400 billion to $600 billion causes people to:
Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, an increase in the money supply from $400 billion to $600 billion causes people to:
A)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
B)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds up.
C)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
D)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds up.
 Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, an increase in the money supply from $400 billion to $600 billion causes people to:
Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, an increase in the money supply from $400 billion to $600 billion causes people to:A)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
B)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds up.
C)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
D)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Starting from a position of macroeconomic equilibrium at below the full-employment level of real GDP, an increase in the money supply will:
A)raise interest rates, prices, and reduce real GDP.
B)raise interest rates, lower prices, and leave real GDP unchanged.
C)lower interest rates, raise prices, and increase real GDP.
A)raise interest rates, prices, and reduce real GDP.
B)raise interest rates, lower prices, and leave real GDP unchanged.
C)lower interest rates, raise prices, and increase real GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
When the Fed decreases the money supply, interest rates:
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)are unaffected.
D)rise and then fall.
E)fall and then rise.
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)are unaffected.
D)rise and then fall.
E)fall and then rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Exhibit 16-1 Money market demand and supply curves 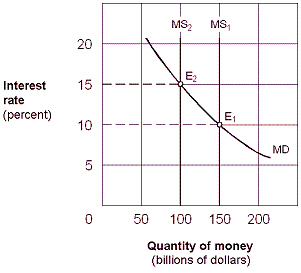 Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a leftward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:
Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a leftward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:
A)demand for money, leading people to sell bonds.
B)demand for money, leading people to buy bonds.
C)supply of money, leading people to sell bonds.
D)supply of money, leading people to buy bonds.
 Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a leftward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:
Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a leftward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:A)demand for money, leading people to sell bonds.
B)demand for money, leading people to buy bonds.
C)supply of money, leading people to sell bonds.
D)supply of money, leading people to buy bonds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Which of the following is the objective of expansionary monetary policy?
A)An increase in employment.
B)A decrease in employment.
C)An increase in the velocity of money.
D)An increase in prices proportional to the rise in the money supply.
A)An increase in employment.
B)A decrease in employment.
C)An increase in the velocity of money.
D)An increase in prices proportional to the rise in the money supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Exhibit 16-2 Money market demand and supply curves 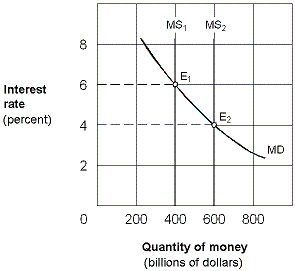 As shown in Exhibit 16-2, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
As shown in Exhibit 16-2, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
A)higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.
B)lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
C)higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level.
D)higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
 As shown in Exhibit 16-2, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
As shown in Exhibit 16-2, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:A)higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.
B)lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
C)higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level.
D)higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
If the Fed reduces the discount rate, which of the following are most likely to result?
A)The money supply curve shifts rightward, and the equilibrium interest rate falls in the money market.
B)Investment declines, causing the aggregate demand curve to shift leftward, reducing equilibrium real GDP and thus slowing the economy.
C)Investment rises, causing the aggregate demand curve to shift rightward, increasing equilibrium real GDP and thus accelerating the economy.
D)Both a. and b. above are correct.
E)Both a. and c. above are correct.
A)The money supply curve shifts rightward, and the equilibrium interest rate falls in the money market.
B)Investment declines, causing the aggregate demand curve to shift leftward, reducing equilibrium real GDP and thus slowing the economy.
C)Investment rises, causing the aggregate demand curve to shift rightward, increasing equilibrium real GDP and thus accelerating the economy.
D)Both a. and b. above are correct.
E)Both a. and c. above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Exhibit 16-3 Money market demand and supply curves 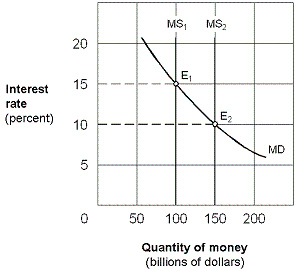 As shown in Exhibit 16-3, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
As shown in Exhibit 16-3, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
A)higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
B)lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
C)higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level.
D)higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.
 As shown in Exhibit 16-3, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:
As shown in Exhibit 16-3, assume the money supply curve shifts rightward from MS1 to MS2 and the economy is operating along the intermediate segment of the aggregate supply curve. The result will be a:A)higher investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
B)lower investment, lower real GDP, and lower price level.
C)higher investment, higher real GDP, and higher price level.
D)higher interest rate and no effect on real GDP or the price level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Exhibit 16-1 Money market demand and supply curves 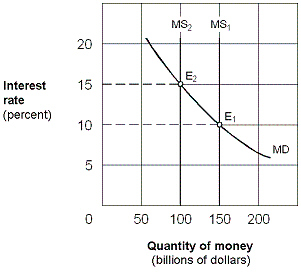 Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a decrease in the money supply from $150 billion to $100 billion causes people to:
Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a decrease in the money supply from $150 billion to $100 billion causes people to:
A)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
B)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds up.
C)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
D)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds up.
 Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a decrease in the money supply from $150 billion to $100 billion causes people to:
Beginning from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-1, a decrease in the money supply from $150 billion to $100 billion causes people to:A)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
B)sell bonds and drive the price of bonds up.
C)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds down.
D)buy bonds and drive the price of bonds up.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Exhibit 16-2 Money market demand and supply curves  Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, a rightward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:
Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, a rightward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:
A)demand for money, leading people to sell bonds.
B)supply of money, leading people to buy bonds.
C)supply of money, leading people to sell bonds.
D)demand for money, leading people to buy bonds.
 Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, a rightward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:
Starting from an equilibrium at E1 in Exhibit 16-2, a rightward shift of the money supply curve from MS1 to MS2 would cause an excess:A)demand for money, leading people to sell bonds.
B)supply of money, leading people to buy bonds.
C)supply of money, leading people to sell bonds.
D)demand for money, leading people to buy bonds.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The impact of an increase in the money supply is a(n):
A)increase in the interest rate, which in turn stimulates investment and GDP.
B)decrease in the interest rate, which in turn stimulates investment and GDP.
C)reduction in the general level of prices, which will increase the disposable income of households.
D)improvement in technology, which will stimulate both output and employment.
A)increase in the interest rate, which in turn stimulates investment and GDP.
B)decrease in the interest rate, which in turn stimulates investment and GDP.
C)reduction in the general level of prices, which will increase the disposable income of households.
D)improvement in technology, which will stimulate both output and employment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 213 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








