Deck 35: Stem Structure and Transport
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 35: Stem Structure and Transport
1
Which of the following is a function of stems?
A) Sexually reproduce
B) Absorb nutrient minerals
C) Produce new tissues
D) Transport dissolved gases
E) Anchor plants
A) Sexually reproduce
B) Absorb nutrient minerals
C) Produce new tissues
D) Transport dissolved gases
E) Anchor plants
C
2
Dissolved sugars are transported in:
A) cork cambium.
B) epidermis.
C) pith.
D) phloem.
E) xylem.
A) cork cambium.
B) epidermis.
C) pith.
D) phloem.
E) xylem.
D
3
Monocots such as palms and bamboo achieve considerable increase in girth by:
A) a modified form of secondary growth in which parenchyma cells divide and enlarge.
B) primary growth.
C) a modified form of primary growth in which parenchyma cells divide and enlarge.
D) enlargement of primary xylem.
E) enlargement of primary phloem.
A) a modified form of secondary growth in which parenchyma cells divide and enlarge.
B) primary growth.
C) a modified form of primary growth in which parenchyma cells divide and enlarge.
D) enlargement of primary xylem.
E) enlargement of primary phloem.
C
4
Monocot stems do not possess __________ that gives rise to secondary growth.
A) sclerenchyma tissue
B) lateral meristems
C) parenchyma tissue
D) apical meristems
E) vascular tissue
A) sclerenchyma tissue
B) lateral meristems
C) parenchyma tissue
D) apical meristems
E) vascular tissue

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements about monocots is true?
A) They lack sclerenchyma tissue.
B) They have a well-developed vascular cambium.
C) They do not produce bark.
D) Their lateral meristems give rise to wood.
E) Secondary growth occurs rather slowly.
A) They lack sclerenchyma tissue.
B) They have a well-developed vascular cambium.
C) They do not produce bark.
D) Their lateral meristems give rise to wood.
E) Secondary growth occurs rather slowly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Figure 35-1
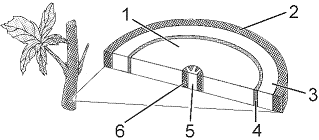
In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 2 is:
A) known as wood.
B) produced by cork cambium (not shown).
C) composed largely of secondary tissue.
D) composed largely of cells that are alive at maturity.
E) commonly called scales.

In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 2 is:
A) known as wood.
B) produced by cork cambium (not shown).
C) composed largely of secondary tissue.
D) composed largely of cells that are alive at maturity.
E) commonly called scales.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Periderm arises from ________.
A) xylem
B) cork cambium
C) pith
D) cortex
E) sclerenchyma
A) xylem
B) cork cambium
C) pith
D) cortex
E) sclerenchyma

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Cells produced on the inside of the vascular cambium differentiate to form which vascular tissue?
A) Cork cambium
B) Primary phloem
C) Primary xylem
D) Secondary phloem
E) Secondary xylem
A) Cork cambium
B) Primary phloem
C) Primary xylem
D) Secondary phloem
E) Secondary xylem

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements about the cortex is true?
A) It secretes a protective layer of cutin.
B) It is at the core of the herbaceous eudicot stem.
C) It is filled with cork cells.
D) It translocates sugar by means of a pressure gradient.
E) It may contain collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
A) It secretes a protective layer of cutin.
B) It is at the core of the herbaceous eudicot stem.
C) It is filled with cork cells.
D) It translocates sugar by means of a pressure gradient.
E) It may contain collenchyma and sclerenchyma.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Figure 35-1
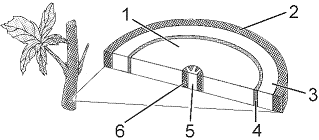
In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 3 is:
A) the secondary xylem.
B) formed by the division of the vascular cambium.
C) found adjacent to the pith.
D) usually referred to as wood.
E) the cork cambium.

In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 3 is:
A) the secondary xylem.
B) formed by the division of the vascular cambium.
C) found adjacent to the pith.
D) usually referred to as wood.
E) the cork cambium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Vascular cambium gives rise to which of the following tissues?
A) Primary phloem
B) Periderm
C) Epidermis
D) Secondary xylem
E) Cork cambium
A) Primary phloem
B) Periderm
C) Epidermis
D) Secondary xylem
E) Cork cambium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Periderm is produced by:
A) xylem.
B) cork cambium.
C) pith.
D) cortex.
E) phloem.
A) xylem.
B) cork cambium.
C) pith.
D) cortex.
E) phloem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The outermost cell layer of herbaceous stems is the:
A) bark.
B) cortex.
C) endodermis.
D) epidermis.
E) periderm.
A) bark.
B) cortex.
C) endodermis.
D) epidermis.
E) periderm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
One function of cortical parenchyma cells is:
A) photosynthesis.
B) to provide structural support and strength.
C) to produce cutin.
D) to conduct water and nutrient minerals.
E) to conduct sugars.
A) photosynthesis.
B) to provide structural support and strength.
C) to produce cutin.
D) to conduct water and nutrient minerals.
E) to conduct sugars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The thin layer of meristematic cells located between xylem and phloem is referred to as the:
A) apical meristem.
B) collenchyma.
C) cork cambium.
D) vascular cambium.
E) pith.
A) apical meristem.
B) collenchyma.
C) cork cambium.
D) vascular cambium.
E) pith.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Secondary growth occurs as a result of the activity of which two lateral meristems?
A) Vascular cambium and cork cambium
B) Apical meristem and cork cambium
C) Primary meristem and secondary meristem
D) Periderm and cork cambium
E) Apical meristem and vascular cambium
A) Vascular cambium and cork cambium
B) Apical meristem and cork cambium
C) Primary meristem and secondary meristem
D) Periderm and cork cambium
E) Apical meristem and vascular cambium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Vascular bundles of herbaceous _______ stems are arranged in a circle in cross section.
A) prodicot
B) monocot
C) eudicot
D) bryophyte
E) halophyte
A) prodicot
B) monocot
C) eudicot
D) bryophyte
E) halophyte

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Figure 35-1
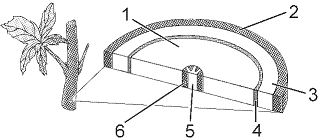
In the accompanying figure, the function of the structure labeled as 1 represents:
A) the formation of pith.
B) protection.
C) conduction of water and dissolved minerals from the roots.
D) conduction of sugars from the leaves.
E) photosynthesis.

In the accompanying figure, the function of the structure labeled as 1 represents:
A) the formation of pith.
B) protection.
C) conduction of water and dissolved minerals from the roots.
D) conduction of sugars from the leaves.
E) photosynthesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Cork cambium and the tissues it produces are collectively known as:
A) periderm.
B) epidermis.
C) xylem.
D) pith.
E) cortex.
A) periderm.
B) epidermis.
C) xylem.
D) pith.
E) cortex.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
At the center of an herbaceous eudicot stem is:
A) pith.
B) collenchyma.
C) sclerenchyma.
D) vascular cambium.
E) phloem.
A) pith.
B) collenchyma.
C) sclerenchyma.
D) vascular cambium.
E) phloem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Concentric rings found in the cross section of the wood of trees are known as:
A) summer rings.
B) spring rings.
C) annual rings.
D) dendrochrons.
E) pith rings.
A) summer rings.
B) spring rings.
C) annual rings.
D) dendrochrons.
E) pith rings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
____ is when water vapor evaporates from leaves.
A) Root pressure
B) Transpiration
C) Guttation
D) Hydration
E) Translocation
A) Root pressure
B) Transpiration
C) Guttation
D) Hydration
E) Translocation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Dendrochronology can be useful in determining:
A) the dates of past earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
B) future climate patterns.
C) the solution to global warming.
D) how tree growth affects air pollution.
E) the time of day.
A) the dates of past earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
B) future climate patterns.
C) the solution to global warming.
D) how tree growth affects air pollution.
E) the time of day.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The arrangement of the different cell types in secondary ______ produces the distinctive wood characteristics of each species.
A) parenchyma
B) xylem
C) phloem
D) cambium
E) ground tissue
A) parenchyma
B) xylem
C) phloem
D) cambium
E) ground tissue

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Softwood is the wood:
A) found at the center of a tree.
B) of cone-bearing gymnosperms.
C) of flowering plants.
D) formed when water is abundant.
E) formed when water is less abundant.
A) found at the center of a tree.
B) of cone-bearing gymnosperms.
C) of flowering plants.
D) formed when water is abundant.
E) formed when water is less abundant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In woody plants, the lateral transport of materials occurs through:
A) lenticels.
B) pith.
C) pith rays.
D) phloem fiber caps.
E) rays.
A) lenticels.
B) pith.
C) pith rays.
D) phloem fiber caps.
E) rays.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
____ is less dense than ____.
A) Heartwood; sapwood
B) Heartwood; softwood
C) Sapwood; hardwood
D) Sapwood; heartwood
E) Softwood; hardwood
A) Heartwood; sapwood
B) Heartwood; softwood
C) Sapwood; hardwood
D) Sapwood; heartwood
E) Softwood; hardwood

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Figure 35-2
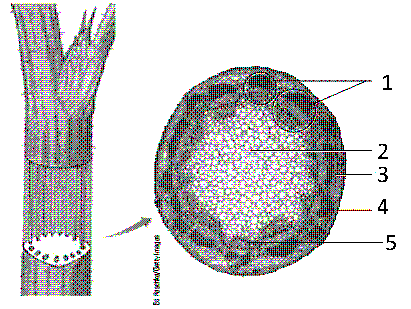
In the accompanying figure, the structure responsible for photosynthesis, storage, and support is labeled as:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

In the accompanying figure, the structure responsible for photosynthesis, storage, and support is labeled as:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Figure 35-3
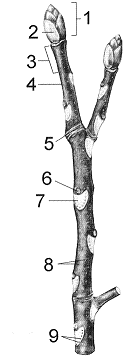
In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as ____ will form branches.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9

In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as ____ will form branches.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Water and dissolved mineral are transported laterally through chains of ____.
A) parenchyma cells
B) tracheids
C) sieve tube elements
D) companion cells
E) fibers
A) parenchyma cells
B) tracheids
C) sieve tube elements
D) companion cells
E) fibers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Embryonic shoots located at the tips of stems are covered by ____.
A) nodes
B) internodes
C) axillary buds
D) bud scale scars
E) bud scales
A) nodes
B) internodes
C) axillary buds
D) bud scale scars
E) bud scales

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Hardwood is the wood of _____ and softwood is the wood of ____.
A) flowering plants; conifers
B) conifers; flowering plants
C) conifers; bryophytes
D) flowering plants; bryophytes
E) conifers; ferns
A) flowering plants; conifers
B) conifers; flowering plants
C) conifers; bryophytes
D) flowering plants; bryophytes
E) conifers; ferns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Figure 35-3
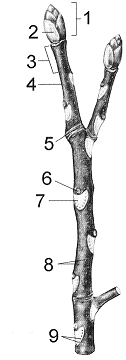
What is the age of the twig in the accompanying figure?
A) 0 years
B) 1 year
C) 2 years
D) 3 years
E) 5 years

What is the age of the twig in the accompanying figure?
A) 0 years
B) 1 year
C) 2 years
D) 3 years
E) 5 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Figure 35-2
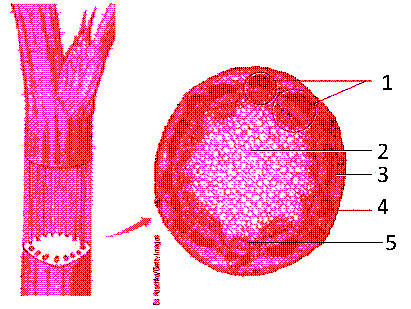
In the accompanying figure, the cell layer that contains xylem is labeled as:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

In the accompanying figure, the cell layer that contains xylem is labeled as:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Secondary xylem contains all of the following cell types except :
A) tracheids.
B) vessel elements.
C) sieve tube elements
D) fibers.
E) parenchyma.
A) tracheids.
B) vessel elements.
C) sieve tube elements
D) fibers.
E) parenchyma.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Lenticels function to:
A) protect undeveloped embryonic shoots.
B) permit gas exchange through the periderm.
C) support leaves and flowers.
D) absorb water and dissolved nutrient minerals.
E) anchor a plant in the ground.
A) protect undeveloped embryonic shoots.
B) permit gas exchange through the periderm.
C) support leaves and flowers.
D) absorb water and dissolved nutrient minerals.
E) anchor a plant in the ground.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Sapwood develops from:
A) secondary xylem.
B) secondary phloem.
C) primary phloem.
D) primary xylem.
E) cork parenchyma.
A) secondary xylem.
B) secondary phloem.
C) primary phloem.
D) primary xylem.
E) cork parenchyma.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The driving force for the movement of water in plants is difference in water _______.
A) pressure
B) osmolarity
C) potential
D) temperature
E) pH
A) pressure
B) osmolarity
C) potential
D) temperature
E) pH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Functional secondary xylem that conducts water and dissolved minerals is known as:
A) softwood.
B) springwood.
C) hardwood.
D) sapwood.
E) heartwood.
A) softwood.
B) springwood.
C) hardwood.
D) sapwood.
E) heartwood.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements about heartwood is false ?
A) It functions in conduction.
B) It is a storage site for waste products.
C) It is resistant to decay.
D) It provides structural support.
E) It is located in the center of a tree.
A) It functions in conduction.
B) It is a storage site for waste products.
C) It is resistant to decay.
D) It provides structural support.
E) It is located in the center of a tree.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Periderm is the functional replacement of the bark.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Water is capable of rising to the tops of the tallest trees due to the:
A) chemical bonds of water molecules.
B) push of gravity.
C) adhesion of water molecules to each other.
D) push of ground water.
E) pull of transpiration.
A) chemical bonds of water molecules.
B) push of gravity.
C) adhesion of water molecules to each other.
D) push of ground water.
E) pull of transpiration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The transport of sucrose from companion cells into sieve tube elements depends upon ______.
A) diffusion
B) pump
C) cotransport
D) antitransport
E) osmosis
A) diffusion
B) pump
C) cotransport
D) antitransport
E) osmosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Compare transpiration and translocation, and be sure to cover the five points below.
1. Principal substance(s) transported
2. Direction of transport
3. Tissue through which transport occurs
4. Name of model that explains the process
5. Does the plant expend energy to carry out the process?
1. Principal substance(s) transported
2. Direction of transport
3. Tissue through which transport occurs
4. Name of model that explains the process
5. Does the plant expend energy to carry out the process?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Using severed aphid mouthparts, scientists have verified that, in most species, the phloem can translocate ____, _____, and _______.
A) glucose; xylitol; amino acids
B) sucrose; cholesterol, glycerol
C) glucose; ribose, starch
D) sucrose; raffinose, sorbitol
E) sucrose; glucose; fructose
A) glucose; xylitol; amino acids
B) sucrose; cholesterol, glycerol
C) glucose; ribose, starch
D) sucrose; raffinose, sorbitol
E) sucrose; glucose; fructose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Before being loaded into the phloem for translocation, the carbohydrates produced during photosynthesis must be converted into which molecule?
A) Glucose
B) Fructose
C) Maltose
D) Sucrose
E) Galactose
A) Glucose
B) Fructose
C) Maltose
D) Sucrose
E) Galactose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The loading of dissolved sugars into the sieve tube elements of phloem is:
A) passive transport.
B) active transport.
C) osmosis.
D) simple diffusion.
E) facilitated diffusion.
A) passive transport.
B) active transport.
C) osmosis.
D) simple diffusion.
E) facilitated diffusion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Compare and contrast the structure of an herbaceous eudicot stem and that of a monocot.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The predominant photosynthetic product carried in phloem is _______.
A) glucose
B) water
C) sucrose
D) oxygen
E) carbon dioxide
A) glucose
B) water
C) sucrose
D) oxygen
E) carbon dioxide

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Sugar is translocated in phloem from a ______, an area of high sugar concentration, to a ______, an area of low sugar concentration.
A) root; leaf
B) source; sink
C) sink; root
D) leaf; source
E) sink; source
A) root; leaf
B) source; sink
C) sink; root
D) leaf; source
E) sink; source

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Xylem transports water and dissolved nutrient minerals in which direction?
A) Upward
B) Downward
C) Inward laterally
D) Outward laterally
E) Both upward and downward
A) Upward
B) Downward
C) Inward laterally
D) Outward laterally
E) Both upward and downward

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Bundle scars would be found within a leaf scar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Guttation results from:
A) water pressure.
B) transpiration pull.
C) osmotic pressure.
D) root pressure.
E) sink-to-source transport.
A) water pressure.
B) transpiration pull.
C) osmotic pressure.
D) root pressure.
E) sink-to-source transport.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
When cells of the vascular cambium divide, they produce xylem toward the outside.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Sapwood is functional secondary xylem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In the very center of a monocot stem is pith.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
In a monocot stem, vascular bundles are arranged in a circle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Define water potential and explain how it affects water flow.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Immediately inside the epidermis of a eudicot stem is the pith.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Diagram and label a cross section of (1) a woody stem before the vascular cambium becomes active and (2) a woody stem from the same plant after the vascular cambium has been active for a considerable length of time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
A growth ring is composed of xylem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
How is it possible for water to defy gravity and travel from the roots to the tops of plants? Use the tension-cohesion model to explain your answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
One reason that water is able to form unbroken columns is because water molecules are cohesive.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Water is transported vertically through the plant via the process of translocation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Explain how dissolved sugar is transported in the phloem by means of a pressure gradient.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Springwood has narrower conducting cells and many fibers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Sugars are loaded into sieve tubes via simple diffusion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Hardwood is the wood of gymnosperms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Describe how water potential is related to water movement in a plant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
In a plant, most water is transported vertically by being pushed to the top.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Sucrose is translocated from source to sink.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The transport of xylem sap is the most rapid movement of any material in plants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 91 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








