Deck 12: Useful Facts About Sugars Starches and Fiber
ملء الشاشة (f)
سؤال
Artificial sweeteners that are currently approved for use exactly mimic the taste and properties of sugar.
استخدم زر المسافة أو 
 لقلب البطاقة.
لقلب البطاقة.
سؤال
Lactose maldigestion should be managed by omitting milk and milk products from the diet.
سؤال
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the body?
A) fluid balance
B) energy source
C) nerve conduction
D) growth and repair of body tissues
E) insulation
A) fluid balance
B) energy source
C) nerve conduction
D) growth and repair of body tissues
E) insulation
سؤال
Fluoridated water reduces the incidences of tooth decay, but may increase rates of cancer and obesity.
سؤال
The fiber value of foods is dependent on whether the fiber foods are cooked, mashed, or chopped.
سؤال
High-fructose corn syrup contains the same amount of fructose and glucose as sucrose.
سؤال
Alcohol sugars that are labeled sugar-free will also be calorie-free.
سؤال
Insoluble fiber is found primarily in oat and wheat bran, the coating on seeds, and the skins of fruits and vegetables.
سؤال
Glycogen is stored in the _____.
A) brain only
B) liver only
C) muscles only
D) brain and muscles
E) liver and muscles
A) brain only
B) liver only
C) muscles only
D) brain and muscles
E) liver and muscles
سؤال
Alcohol sugars and alcohol are similar in chemical structure to carbohydrates.
سؤال
The simple sugars the body uses directly to form energy are starch and glycogen.
سؤال
Carbohydrates are the major source of energy for people throughout the world.
سؤال
Some types of simple and complex carbohydrates in foods elevate blood glucose levels more than do others.
سؤال
Teeth are capable of replacing small amounts of minerals lost from enamel.
سؤال
Storage of glycogen is limited.
سؤال
Lactose maldigestion is rare in very young children.
سؤال
Dietary fiber has no caloric value.
سؤال
What is the recommended amount of total dietary fiber for adults per day?
A) 10 grams for women and 15 grams for men
B) 17 grams for women and 23 grams for men
C) 28 grams for women and 35 grams for men
D) 33 grams for women and 42 grams for men
E) 45 grams for women and 55 grams for men
A) 10 grams for women and 15 grams for men
B) 17 grams for women and 23 grams for men
C) 28 grams for women and 35 grams for men
D) 33 grams for women and 42 grams for men
E) 45 grams for women and 55 grams for men
سؤال
Studies have found that aspartame promotes cancer, nerve disorders, and other health problems in humans.
سؤال
Xylitol, mannitol, and sorbitol promote tooth decay.
سؤال
Which food has the highest "stickiness" value?
A) pretzels
B) milk chocolate
C) fruit juice
D) cereal
E) honey
A) pretzels
B) milk chocolate
C) fruit juice
D) cereal
E) honey
سؤال
Sucralose is primarily known as _____ on product labels.
A) NutraSweet
B) Sweet and Low
C) Splenda
D) PureVia
E) Sunnette
A) NutraSweet
B) Sweet and Low
C) Splenda
D) PureVia
E) Sunnette
سؤال
Which food is recommended for people who experience lactose maldigestion?
A) low-fat or soy milk
B) fortified rice milk or fat-free milk
C) yogurt only
D) low-fat milk and fortified rice milk
E) fortified rice milk and yogurt
A) low-fat or soy milk
B) fortified rice milk or fat-free milk
C) yogurt only
D) low-fat milk and fortified rice milk
E) fortified rice milk and yogurt
سؤال
Dietary fiber can be constipating if _____.
A) added to the diet gradually
B) consumed with milk products
C) consumed with added sugars
D) consumed with too little fluid
E) consumed with too much fat
A) added to the diet gradually
B) consumed with milk products
C) consumed with added sugars
D) consumed with too little fluid
E) consumed with too much fat
سؤال
What is a good source of insoluble fiber?
A) barley
B) dried beans
C) fruit pulp
D) psyllium husks
E) oat bran
A) barley
B) dried beans
C) fruit pulp
D) psyllium husks
E) oat bran
سؤال
Identify a monosaccharide.
A) maltose
B) honey
C) starch
D) glycogen
E) galactose
A) maltose
B) honey
C) starch
D) glycogen
E) galactose
سؤال
Artificial sweeteners _____.
A) are a significant source of energy
B) are sweeter than sucrose
C) are considered added sugars
D) promote weight loss without calorie restriction
E) promote tooth decay
A) are a significant source of energy
B) are sweeter than sucrose
C) are considered added sugars
D) promote weight loss without calorie restriction
E) promote tooth decay
سؤال
Which food has the highest fiber content?
A) pinto beans (½ cup)
B) corn (½ cup)
C) carrots (½ cup)
D) almonds (¼ cup)
E) granola (½ cup)
A) pinto beans (½ cup)
B) corn (½ cup)
C) carrots (½ cup)
D) almonds (¼ cup)
E) granola (½ cup)
سؤال
On average, dietary fiber supplies _____ calories per gram.
A) two
B) four
C) seven
D) nine
E) five
A) two
B) four
C) seven
D) nine
E) five
سؤال
Which food has the lowest glycemic index?
A) cornflakes
B) watermelon
C) spaghetti
D) milk
E) boiled potato
A) cornflakes
B) watermelon
C) spaghetti
D) milk
E) boiled potato
سؤال
High intake of sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup is associated with _____.
A) an elevated risk of Alzheimer's disease
B) an elevated risk of hypertension
C) increased cholesterol levels
D) the development of cancer
E) greater weight loss
A) an elevated risk of Alzheimer's disease
B) an elevated risk of hypertension
C) increased cholesterol levels
D) the development of cancer
E) greater weight loss
سؤال
Foods sweetened with xylitol can use the health claim "_____" on their labels.
A) Calorie-free
B) Sugar-free
C) Promotes health
D) Does not cause diarrhea
E) Cures diabetes
A) Calorie-free
B) Sugar-free
C) Promotes health
D) Does not cause diarrhea
E) Cures diabetes
سؤال
Maltose = _____
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
سؤال
Which carbohydrates supply the body with four calories per gram?
A) simple sugars only
B) complex carbohydrates only
C) dietary fiber only
D) simple sugars and complex carbohydrates
E) complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber
A) simple sugars only
B) complex carbohydrates only
C) dietary fiber only
D) simple sugars and complex carbohydrates
E) complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber
سؤال
Sucrose = _____
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
سؤال
Lactose = _____
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
سؤال
A good source of soluble fiber is _____.
A) barley
B) wheat bran
C) the coating on seeds
D) the skins of fruits
E) the skins of vegetables
A) barley
B) wheat bran
C) the coating on seeds
D) the skins of fruits
E) the skins of vegetables
سؤال
Starch is an example of a(n) _____.
A) artificial sugar
B) monosaccharide
C) alcohol sugar
D) complex carbohydrate
E) disaccharide
A) artificial sugar
B) monosaccharide
C) alcohol sugar
D) complex carbohydrate
E) disaccharide
سؤال
Compared with high glycemic index carbohydrate foods, intake of low glycemic index carbohydrate foods is associated with _____.
A) increased food intake
B) increased satiety
C) decreased weight loss
D) increased blood glucose levels
E) increased blood levels of insulin
A) increased food intake
B) increased satiety
C) decreased weight loss
D) increased blood glucose levels
E) increased blood levels of insulin
سؤال
Soluble fibers have been shown to _____.
A) increase calcium absorption
B) increase blood glucose levels after a meal
C) reduce blood levels of cholesterol
D) decrease lactose maldigestion
E) decrease the risk of osteoporosis
A) increase calcium absorption
B) increase blood glucose levels after a meal
C) reduce blood levels of cholesterol
D) decrease lactose maldigestion
E) decrease the risk of osteoporosis
سؤال
Which food has the highest simple sugar content?
A) Apple Jacks (1 oz)
B) skim milk (1 cup)
C) Raisin Bran (1 oz)
D) corn (½ cup)
E) apple (1 medium)
A) Apple Jacks (1 oz)
B) skim milk (1 cup)
C) Raisin Bran (1 oz)
D) corn (½ cup)
E) apple (1 medium)
سؤال
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
الردود:
carbohydrates
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
carbohydrates
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
carbohydrates
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
carbohydrates
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
carbohydrates
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
carbohydrates
the body's storage form of glucose
carbohydrates
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
carbohydrates
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
carbohydrates
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
carbohydrates
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
carbohydrates
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
carbohydrates
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
carbohydrates
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
carbohydrates
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
carbohydrates
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
carbohydrates
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
insulin resistance
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
insulin resistance
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
insulin resistance
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
insulin resistance
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
insulin resistance
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
insulin resistance
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
insulin resistance
the body's storage form of glucose
insulin resistance
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
insulin resistance
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
insulin resistance
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
insulin resistance
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
insulin resistance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
insulin resistance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
insulin resistance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
insulin resistance
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
insulin resistance
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
insulin resistance
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
insulin resistance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
insulin resistance
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
insulin resistance
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
insulin resistance
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
insulin resistance
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
lactose intolerance
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
lactose intolerance
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
lactose intolerance
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
lactose intolerance
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
lactose intolerance
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose intolerance
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
lactose intolerance
the body's storage form of glucose
lactose intolerance
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
lactose intolerance
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
lactose intolerance
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose intolerance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose intolerance
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
lactose intolerance
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose intolerance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
lactose intolerance
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
lactose intolerance
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
lactose intolerance
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
lactose intolerance
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
PKU
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
PKU
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
PKU
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
PKU
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
PKU
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
PKU
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
PKU
the body's storage form of glucose
PKU
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
PKU
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
PKU
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
PKU
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
PKU
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
PKU
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
PKU
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
PKU
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
PKU
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
PKU
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
PKU
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
PKU
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
PKU
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
PKU
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
PKU
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
lactose maldigestion
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
lactose maldigestion
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
lactose maldigestion
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
lactose maldigestion
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
lactose maldigestion
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose maldigestion
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
lactose maldigestion
the body's storage form of glucose
lactose maldigestion
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
lactose maldigestion
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
lactose maldigestion
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose maldigestion
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose maldigestion
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
lactose maldigestion
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose maldigestion
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
lactose maldigestion
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
lactose maldigestion
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
lactose maldigestion
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
lactose maldigestion
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
glycogen
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
glycogen
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
glycogen
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
glycogen
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
glycogen
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycogen
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
glycogen
the body's storage form of glucose
glycogen
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
glycogen
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
glycogen
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
glycogen
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
glycogen
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycogen
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
glycogen
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycogen
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
glycogen
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
glycogen
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycogen
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
glycogen
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
glycogen
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
glycogen
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
glycogen
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
complex carbohydrates
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
complex carbohydrates
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
complex carbohydrates
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
complex carbohydrates
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
complex carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
complex carbohydrates
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
complex carbohydrates
the body's storage form of glucose
complex carbohydrates
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
complex carbohydrates
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
complex carbohydrates
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
complex carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
complex carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
complex carbohydrates
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
complex carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
complex carbohydrates
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
complex carbohydrates
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
complex carbohydrates
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
complex carbohydrates
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
type 2 diabetes
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
type 2 diabetes
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
type 2 diabetes
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
type 2 diabetes
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
type 2 diabetes
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
type 2 diabetes
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
type 2 diabetes
the body's storage form of glucose
type 2 diabetes
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
type 2 diabetes
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
type 2 diabetes
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
type 2 diabetes
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
type 2 diabetes
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
type 2 diabetes
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
type 2 diabetes
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
type 2 diabetes
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
type 2 diabetes
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
type 2 diabetes
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
type 2 diabetes
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
disaccharides
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
disaccharides
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
disaccharides
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
disaccharides
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
disaccharides
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
disaccharides
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
disaccharides
the body's storage form of glucose
disaccharides
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
disaccharides
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
disaccharides
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
disaccharides
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
disaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
disaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
disaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
disaccharides
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
disaccharides
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
disaccharides
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
disaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
disaccharides
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
disaccharides
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
disaccharides
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
disaccharides
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
plaque
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
plaque
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
plaque
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
plaque
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
plaque
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
plaque
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
plaque
the body's storage form of glucose
plaque
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
plaque
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
plaque
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
plaque
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
plaque
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
plaque
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
plaque
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
plaque
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
plaque
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
plaque
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
plaque
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
plaque
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
plaque
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
plaque
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
plaque
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
stevia
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
stevia
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
stevia
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
stevia
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
stevia
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
stevia
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
stevia
the body's storage form of glucose
stevia
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
stevia
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
stevia
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
stevia
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
stevia
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
stevia
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
stevia
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
stevia
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
stevia
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
stevia
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
stevia
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
stevia
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
stevia
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
stevia
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
stevia
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
oligosaccharides
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
oligosaccharides
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
oligosaccharides
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
oligosaccharides
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
oligosaccharides
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
oligosaccharides
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
oligosaccharides
the body's storage form of glucose
oligosaccharides
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
oligosaccharides
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
oligosaccharides
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
oligosaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
oligosaccharides
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
oligosaccharides
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
oligosaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
oligosaccharides
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
oligosaccharides
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
oligosaccharides
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
oligosaccharides
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
xylitol
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
xylitol
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
xylitol
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
xylitol
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
xylitol
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
xylitol
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
xylitol
the body's storage form of glucose
xylitol
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
xylitol
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
xylitol
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
xylitol
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
xylitol
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
xylitol
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
xylitol
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
xylitol
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
xylitol
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
xylitol
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
xylitol
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
xylitol
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
xylitol
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
xylitol
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
xylitol
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
glycemic index
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
glycemic index
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
glycemic index
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
glycemic index
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
glycemic index
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycemic index
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
glycemic index
the body's storage form of glucose
glycemic index
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
glycemic index
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
glycemic index
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
glycemic index
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
glycemic index
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycemic index
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
glycemic index
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycemic index
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
glycemic index
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
glycemic index
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycemic index
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
glycemic index
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
glycemic index
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
glycemic index
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
glycemic index
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
simple sugars
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
simple sugars
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
simple sugars
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
simple sugars
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
simple sugars
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
simple sugars
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
simple sugars
the body's storage form of glucose
simple sugars
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
simple sugars
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
simple sugars
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
simple sugars
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
simple sugars
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
simple sugars
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
simple sugars
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
simple sugars
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
simple sugars
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
simple sugars
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
simple sugars
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
simple sugars
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
simple sugars
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
simple sugars
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
simple sugars
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
dietary fiber
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
dietary fiber
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
dietary fiber
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
dietary fiber
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
dietary fiber
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
dietary fiber
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
dietary fiber
the body's storage form of glucose
dietary fiber
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
dietary fiber
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
dietary fiber
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
dietary fiber
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
dietary fiber
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
dietary fiber
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
dietary fiber
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
dietary fiber
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
dietary fiber
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
dietary fiber
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
dietary fiber
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
dietary fiber
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
dietary fiber
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
dietary fiber
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
dietary fiber
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
cavities
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
cavities
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
cavities
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
cavities
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
cavities
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
cavities
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
cavities
the body's storage form of glucose
cavities
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
cavities
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
cavities
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
cavities
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
cavities
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
cavities
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
cavities
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
cavities
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
cavities
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
cavities
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
cavities
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
cavities
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
cavities
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
cavities
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
cavities
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
سؤال
Which artificial sweetener provides calories?
A) saccharin
B) aspartame
C) sucralose
D) acesulfame potassium
E) stevia
A) saccharin
B) aspartame
C) sucralose
D) acesulfame potassium
E) stevia
سؤال
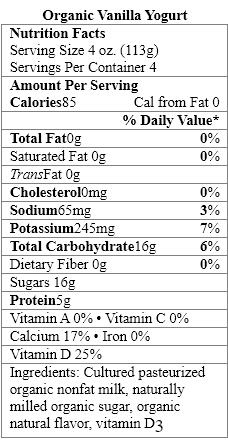
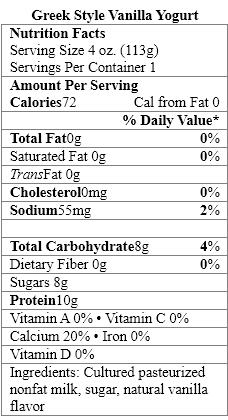
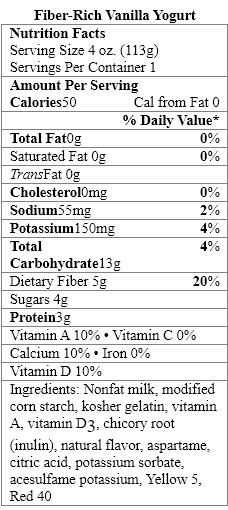
Which food items contain a nonnutritive sweetener?
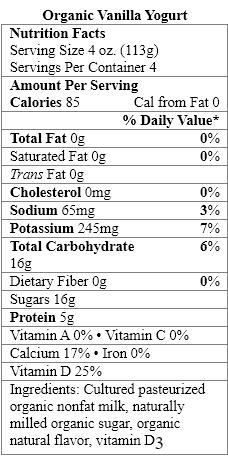
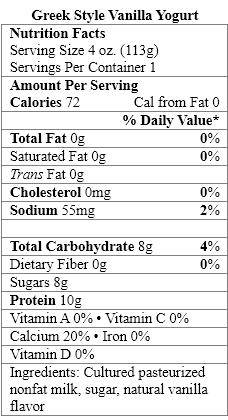
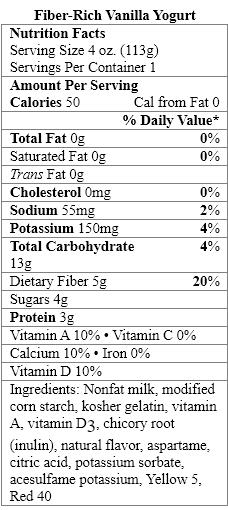
A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt



A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt
سؤال
Discuss how lactose maldigestion should be managed.
سؤال
Which food can promote tooth decay if allowed to remain in contact with gums and teeth?
A) honey
B) peanut butter
C) cheese
D) milk
E) fresh fruit
A) honey
B) peanut butter
C) cheese
D) milk
E) fresh fruit
سؤال
The aspartame in Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt provides _____ calories per gram.

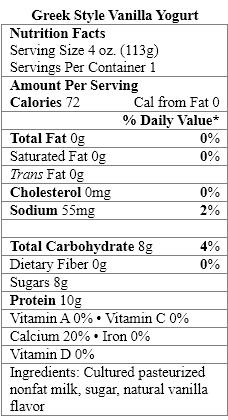
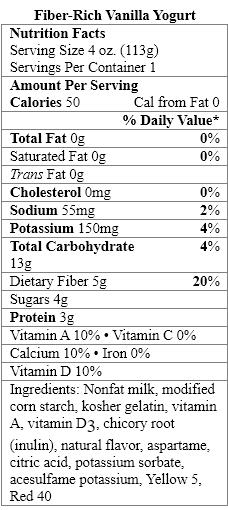
A) zero
B) two
C) four
D) seven
E) nine



A) zero
B) two
C) four
D) seven
E) nine
سؤال
Which is the sweetest alcohol sugar?
A) sorbitol
B) mannitol
C) saccharin
D) xylitol
E) neotame
A) sorbitol
B) mannitol
C) saccharin
D) xylitol
E) neotame
سؤال
Which ingredient is considered a nonnutritive sweetener?
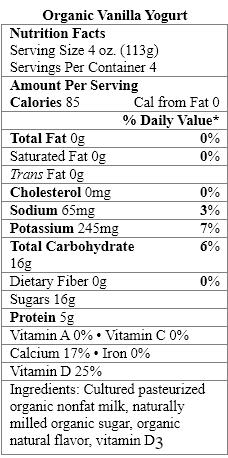
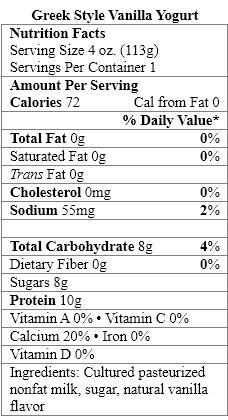
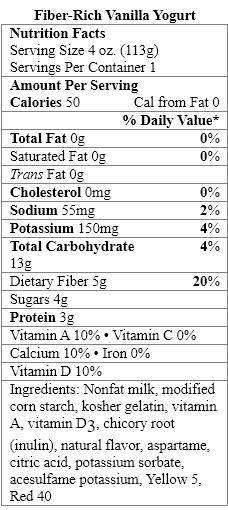
A) naturally milled organic sugar
B) acesulfame potassium
C) natural vanilla flavor
D) modified corn starch
E) chicory root



A) naturally milled organic sugar
B) acesulfame potassium
C) natural vanilla flavor
D) modified corn starch
E) chicory root
سؤال
Which yogurt products contain complex carbohydrates?
A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt



A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt
سؤال
Lactose maldigestion is most common among _____.
A) Asians
B) Native Americans
C) Mexicans
D) U.S. adults
E) Northern Europeans
A) Asians
B) Native Americans
C) Mexicans
D) U.S. adults
E) Northern Europeans
سؤال
A constant supply of glucose is needed by the _____.
A) liver
B) brain
C) pancreas
D) lungs
E) heart
A) liver
B) brain
C) pancreas
D) lungs
E) heart
سؤال
Which simple sugar is directly absorbed into the bloodstream during digestion?
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) maltose
D) lactose
E) glycogen
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) maltose
D) lactose
E) glycogen
سؤال
Which sweetener in the yogurt products should be avoided by people with the genetic disorder phenylketonuria?
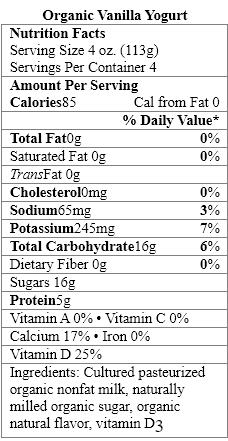
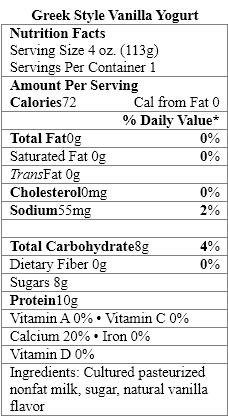
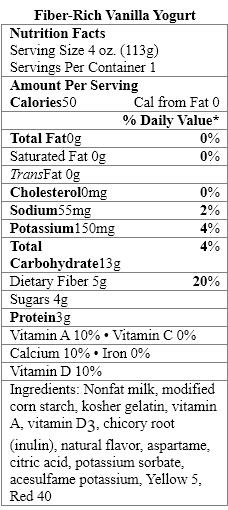
A) organic natural flavor
B) cultured pasteurized nonfat milk
C) modified corn starch
D) natural vanilla flavor
E) aspartame



A) organic natural flavor
B) cultured pasteurized nonfat milk
C) modified corn starch
D) natural vanilla flavor
E) aspartame

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: Useful Facts About Sugars Starches and Fiber
1
Artificial sweeteners that are currently approved for use exactly mimic the taste and properties of sugar.
False
2
Lactose maldigestion should be managed by omitting milk and milk products from the diet.
False
3
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the body?
A) fluid balance
B) energy source
C) nerve conduction
D) growth and repair of body tissues
E) insulation
A) fluid balance
B) energy source
C) nerve conduction
D) growth and repair of body tissues
E) insulation
B
4
Fluoridated water reduces the incidences of tooth decay, but may increase rates of cancer and obesity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The fiber value of foods is dependent on whether the fiber foods are cooked, mashed, or chopped.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
High-fructose corn syrup contains the same amount of fructose and glucose as sucrose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Alcohol sugars that are labeled sugar-free will also be calorie-free.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Insoluble fiber is found primarily in oat and wheat bran, the coating on seeds, and the skins of fruits and vegetables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Glycogen is stored in the _____.
A) brain only
B) liver only
C) muscles only
D) brain and muscles
E) liver and muscles
A) brain only
B) liver only
C) muscles only
D) brain and muscles
E) liver and muscles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Alcohol sugars and alcohol are similar in chemical structure to carbohydrates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The simple sugars the body uses directly to form energy are starch and glycogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Carbohydrates are the major source of energy for people throughout the world.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Some types of simple and complex carbohydrates in foods elevate blood glucose levels more than do others.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Teeth are capable of replacing small amounts of minerals lost from enamel.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Storage of glycogen is limited.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Lactose maldigestion is rare in very young children.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Dietary fiber has no caloric value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
What is the recommended amount of total dietary fiber for adults per day?
A) 10 grams for women and 15 grams for men
B) 17 grams for women and 23 grams for men
C) 28 grams for women and 35 grams for men
D) 33 grams for women and 42 grams for men
E) 45 grams for women and 55 grams for men
A) 10 grams for women and 15 grams for men
B) 17 grams for women and 23 grams for men
C) 28 grams for women and 35 grams for men
D) 33 grams for women and 42 grams for men
E) 45 grams for women and 55 grams for men

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Studies have found that aspartame promotes cancer, nerve disorders, and other health problems in humans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Xylitol, mannitol, and sorbitol promote tooth decay.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which food has the highest "stickiness" value?
A) pretzels
B) milk chocolate
C) fruit juice
D) cereal
E) honey
A) pretzels
B) milk chocolate
C) fruit juice
D) cereal
E) honey

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Sucralose is primarily known as _____ on product labels.
A) NutraSweet
B) Sweet and Low
C) Splenda
D) PureVia
E) Sunnette
A) NutraSweet
B) Sweet and Low
C) Splenda
D) PureVia
E) Sunnette

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which food is recommended for people who experience lactose maldigestion?
A) low-fat or soy milk
B) fortified rice milk or fat-free milk
C) yogurt only
D) low-fat milk and fortified rice milk
E) fortified rice milk and yogurt
A) low-fat or soy milk
B) fortified rice milk or fat-free milk
C) yogurt only
D) low-fat milk and fortified rice milk
E) fortified rice milk and yogurt

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Dietary fiber can be constipating if _____.
A) added to the diet gradually
B) consumed with milk products
C) consumed with added sugars
D) consumed with too little fluid
E) consumed with too much fat
A) added to the diet gradually
B) consumed with milk products
C) consumed with added sugars
D) consumed with too little fluid
E) consumed with too much fat

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
What is a good source of insoluble fiber?
A) barley
B) dried beans
C) fruit pulp
D) psyllium husks
E) oat bran
A) barley
B) dried beans
C) fruit pulp
D) psyllium husks
E) oat bran

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Identify a monosaccharide.
A) maltose
B) honey
C) starch
D) glycogen
E) galactose
A) maltose
B) honey
C) starch
D) glycogen
E) galactose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Artificial sweeteners _____.
A) are a significant source of energy
B) are sweeter than sucrose
C) are considered added sugars
D) promote weight loss without calorie restriction
E) promote tooth decay
A) are a significant source of energy
B) are sweeter than sucrose
C) are considered added sugars
D) promote weight loss without calorie restriction
E) promote tooth decay

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which food has the highest fiber content?
A) pinto beans (½ cup)
B) corn (½ cup)
C) carrots (½ cup)
D) almonds (¼ cup)
E) granola (½ cup)
A) pinto beans (½ cup)
B) corn (½ cup)
C) carrots (½ cup)
D) almonds (¼ cup)
E) granola (½ cup)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
On average, dietary fiber supplies _____ calories per gram.
A) two
B) four
C) seven
D) nine
E) five
A) two
B) four
C) seven
D) nine
E) five

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which food has the lowest glycemic index?
A) cornflakes
B) watermelon
C) spaghetti
D) milk
E) boiled potato
A) cornflakes
B) watermelon
C) spaghetti
D) milk
E) boiled potato

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
High intake of sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup is associated with _____.
A) an elevated risk of Alzheimer's disease
B) an elevated risk of hypertension
C) increased cholesterol levels
D) the development of cancer
E) greater weight loss
A) an elevated risk of Alzheimer's disease
B) an elevated risk of hypertension
C) increased cholesterol levels
D) the development of cancer
E) greater weight loss

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Foods sweetened with xylitol can use the health claim "_____" on their labels.
A) Calorie-free
B) Sugar-free
C) Promotes health
D) Does not cause diarrhea
E) Cures diabetes
A) Calorie-free
B) Sugar-free
C) Promotes health
D) Does not cause diarrhea
E) Cures diabetes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Maltose = _____
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which carbohydrates supply the body with four calories per gram?
A) simple sugars only
B) complex carbohydrates only
C) dietary fiber only
D) simple sugars and complex carbohydrates
E) complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber
A) simple sugars only
B) complex carbohydrates only
C) dietary fiber only
D) simple sugars and complex carbohydrates
E) complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Sucrose = _____
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Lactose = _____
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose
A) fructose + glucose
B) glucose + glucose
C) glucose + galactose
D) fructose + galactose
E) galactose + galactose

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A good source of soluble fiber is _____.
A) barley
B) wheat bran
C) the coating on seeds
D) the skins of fruits
E) the skins of vegetables
A) barley
B) wheat bran
C) the coating on seeds
D) the skins of fruits
E) the skins of vegetables

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Starch is an example of a(n) _____.
A) artificial sugar
B) monosaccharide
C) alcohol sugar
D) complex carbohydrate
E) disaccharide
A) artificial sugar
B) monosaccharide
C) alcohol sugar
D) complex carbohydrate
E) disaccharide

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Compared with high glycemic index carbohydrate foods, intake of low glycemic index carbohydrate foods is associated with _____.
A) increased food intake
B) increased satiety
C) decreased weight loss
D) increased blood glucose levels
E) increased blood levels of insulin
A) increased food intake
B) increased satiety
C) decreased weight loss
D) increased blood glucose levels
E) increased blood levels of insulin

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Soluble fibers have been shown to _____.
A) increase calcium absorption
B) increase blood glucose levels after a meal
C) reduce blood levels of cholesterol
D) decrease lactose maldigestion
E) decrease the risk of osteoporosis
A) increase calcium absorption
B) increase blood glucose levels after a meal
C) reduce blood levels of cholesterol
D) decrease lactose maldigestion
E) decrease the risk of osteoporosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which food has the highest simple sugar content?
A) Apple Jacks (1 oz)
B) skim milk (1 cup)
C) Raisin Bran (1 oz)
D) corn (½ cup)
E) apple (1 medium)
A) Apple Jacks (1 oz)
B) skim milk (1 cup)
C) Raisin Bran (1 oz)
D) corn (½ cup)
E) apple (1 medium)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
الردود:
carbohydrates
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
carbohydrates
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
carbohydrates
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
carbohydrates
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
carbohydrates
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
carbohydrates
the body's storage form of glucose
carbohydrates
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
carbohydrates
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
carbohydrates
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
carbohydrates
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
carbohydrates
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
carbohydrates
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
carbohydrates
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
carbohydrates
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
carbohydrates
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
carbohydrates
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
insulin resistance
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
insulin resistance
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
insulin resistance
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
insulin resistance
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
insulin resistance
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
insulin resistance
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
insulin resistance
the body's storage form of glucose
insulin resistance
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
insulin resistance
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
insulin resistance
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
insulin resistance
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
insulin resistance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
insulin resistance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
insulin resistance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
insulin resistance
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
insulin resistance
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
insulin resistance
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
insulin resistance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
insulin resistance
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
insulin resistance
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
insulin resistance
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
insulin resistance
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
lactose intolerance
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
lactose intolerance
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
lactose intolerance
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
lactose intolerance
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
lactose intolerance
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose intolerance
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
lactose intolerance
the body's storage form of glucose
lactose intolerance
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
lactose intolerance
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
lactose intolerance
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose intolerance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose intolerance
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
lactose intolerance
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
lactose intolerance
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose intolerance
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
lactose intolerance
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
lactose intolerance
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
lactose intolerance
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
lactose intolerance
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
PKU
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
PKU
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
PKU
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
PKU
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
PKU
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
PKU
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
PKU
the body's storage form of glucose
PKU
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
PKU
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
PKU
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
PKU
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
PKU
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
PKU
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
PKU
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
PKU
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
PKU
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
PKU
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
PKU
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
PKU
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
PKU
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
PKU
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
PKU
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
lactose maldigestion
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
lactose maldigestion
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
lactose maldigestion
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
lactose maldigestion
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
lactose maldigestion
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose maldigestion
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
lactose maldigestion
the body's storage form of glucose
lactose maldigestion
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
lactose maldigestion
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
lactose maldigestion
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose maldigestion
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
lactose maldigestion
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
lactose maldigestion
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
lactose maldigestion
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
lactose maldigestion
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
lactose maldigestion
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
lactose maldigestion
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
lactose maldigestion
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
lactose maldigestion
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
glycogen
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
glycogen
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
glycogen
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
glycogen
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
glycogen
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycogen
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
glycogen
the body's storage form of glucose
glycogen
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
glycogen
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
glycogen
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
glycogen
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
glycogen
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycogen
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
glycogen
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycogen
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
glycogen
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
glycogen
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycogen
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
glycogen
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
glycogen
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
glycogen
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
glycogen
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
complex carbohydrates
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
complex carbohydrates
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
complex carbohydrates
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
complex carbohydrates
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
complex carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
complex carbohydrates
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
complex carbohydrates
the body's storage form of glucose
complex carbohydrates
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
complex carbohydrates
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
complex carbohydrates
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
complex carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
complex carbohydrates
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
complex carbohydrates
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
complex carbohydrates
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
complex carbohydrates
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
complex carbohydrates
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
complex carbohydrates
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
complex carbohydrates
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
complex carbohydrates
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
type 2 diabetes
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
type 2 diabetes
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
type 2 diabetes
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
type 2 diabetes
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
type 2 diabetes
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
type 2 diabetes
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
type 2 diabetes
the body's storage form of glucose
type 2 diabetes
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
type 2 diabetes
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
type 2 diabetes
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
type 2 diabetes
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
type 2 diabetes
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
type 2 diabetes
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
type 2 diabetes
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
type 2 diabetes
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
type 2 diabetes
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
type 2 diabetes
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
type 2 diabetes
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
type 2 diabetes
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
disaccharides
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
disaccharides
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
disaccharides
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
disaccharides
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
disaccharides
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
disaccharides
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
disaccharides
the body's storage form of glucose
disaccharides
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
disaccharides
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
disaccharides
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
disaccharides
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
disaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
disaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
disaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
disaccharides
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
disaccharides
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
disaccharides
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
disaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
disaccharides
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
disaccharides
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
disaccharides
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
disaccharides
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
plaque
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
plaque
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
plaque
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
plaque
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
plaque
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
plaque
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
plaque
the body's storage form of glucose
plaque
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
plaque
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
plaque
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
plaque
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
plaque
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
plaque
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
plaque
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
plaque
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
plaque
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
plaque
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
plaque
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
plaque
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
plaque
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
plaque
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
plaque
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
stevia
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
stevia
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
stevia
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
stevia
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
stevia
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
stevia
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
stevia
the body's storage form of glucose
stevia
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
stevia
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
stevia
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
stevia
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
stevia
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
stevia
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
stevia
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
stevia
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
stevia
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
stevia
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
stevia
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
stevia
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
stevia
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
stevia
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
stevia
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
oligosaccharides
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
oligosaccharides
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
oligosaccharides
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
oligosaccharides
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
oligosaccharides
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
oligosaccharides
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
oligosaccharides
the body's storage form of glucose
oligosaccharides
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
oligosaccharides
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
oligosaccharides
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
oligosaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
oligosaccharides
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
oligosaccharides
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
oligosaccharides
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
oligosaccharides
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
oligosaccharides
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
oligosaccharides
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
oligosaccharides
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
oligosaccharides
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
xylitol
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
xylitol
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
xylitol
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
xylitol
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
xylitol
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
xylitol
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
xylitol
the body's storage form of glucose
xylitol
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
xylitol
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
xylitol
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
xylitol
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
xylitol
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
xylitol
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
xylitol
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
xylitol
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
xylitol
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
xylitol
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
xylitol
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
xylitol
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
xylitol
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
xylitol
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
xylitol
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
glycemic index
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
glycemic index
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
glycemic index
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
glycemic index
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
glycemic index
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycemic index
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
glycemic index
the body's storage form of glucose
glycemic index
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
glycemic index
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
glycemic index
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
glycemic index
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
glycemic index
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycemic index
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
glycemic index
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
glycemic index
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
glycemic index
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
glycemic index
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
glycemic index
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
glycemic index
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
glycemic index
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
glycemic index
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
glycemic index
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
simple sugars
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
simple sugars
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
simple sugars
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
simple sugars
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
simple sugars
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
simple sugars
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
simple sugars
the body's storage form of glucose
simple sugars
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
simple sugars
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
simple sugars
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
simple sugars
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
simple sugars
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
simple sugars
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
simple sugars
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
simple sugars
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
simple sugars
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
simple sugars
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
simple sugars
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
simple sugars
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
simple sugars
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
simple sugars
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
simple sugars
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
dietary fiber
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
dietary fiber
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
dietary fiber
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
dietary fiber
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
dietary fiber
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
dietary fiber
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
dietary fiber
the body's storage form of glucose
dietary fiber
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
dietary fiber
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
dietary fiber
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
dietary fiber
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
dietary fiber
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
dietary fiber
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
dietary fiber
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
dietary fiber
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
dietary fiber
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
dietary fiber
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
dietary fiber
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
dietary fiber
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
dietary fiber
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
dietary fiber
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
dietary fiber
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar
cavities
a simple sugar containing an alcohol group in its molecular structure
cavities
chemical substances in foods that consist of a simple sugar molecule or multiples of them in various forms
cavities
the form of carbohydrate found in starchy vegetables, grains, and dried beans and in many types of dietary fiber
cavities
components of plants that cannot be digested by human digestive enzymes and confer health benefits
cavities
simple sugars consisting of two molecules of monosaccharides linked together
cavities
a measure of the extent to which blood glucose is raised by a 50 gram portion of a carbohydrate-containing food compared to 50 grams of glucose
cavities
the body's storage form of glucose
cavities
a condition in which cell membranes have reduced sensitivity to insulin so that more insulin than normal is required to transport a given amount of glucose into cells
cavities
an artificial sweetener that is approved for use by the FDA
cavities
a rare genetic disorder related to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
cavities
carbohydrates consisting of 3 to 10 monosaccharides
cavities
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
cavities
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally or to produce enough insulin
cavities
carbohydrates that consist of a glucose, fructose, or galactose molecule, or a combination of glucose and either fructose or galactose
cavities
simple sugars consisting of one sugar molecule
cavities
simple sugars containing an alcohol group in their molecular structure
cavities
carbohydrates containing many molecules of monosaccharides linked together
cavities
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to use insulin normally, or to produce enough insulin
cavities
the term for gastrointestinal symptoms resulting from the consumption of more lactose than can be digested with available lactase
cavities
a disorder characterized by reduced digestion of lactose due to low availability of the enzyme lactase
cavities
a soft, sticky, white material on teeth that is formed by bacteria
cavities
the disintegration of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that feed on sugar

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which artificial sweetener provides calories?
A) saccharin
B) aspartame
C) sucralose
D) acesulfame potassium
E) stevia
A) saccharin
B) aspartame
C) sucralose
D) acesulfame potassium
E) stevia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which food items contain a nonnutritive sweetener?



A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt



A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Discuss how lactose maldigestion should be managed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which food can promote tooth decay if allowed to remain in contact with gums and teeth?
A) honey
B) peanut butter
C) cheese
D) milk
E) fresh fruit
A) honey
B) peanut butter
C) cheese
D) milk
E) fresh fruit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The aspartame in Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt provides _____ calories per gram.



A) zero
B) two
C) four
D) seven
E) nine



A) zero
B) two
C) four
D) seven
E) nine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which is the sweetest alcohol sugar?
A) sorbitol
B) mannitol
C) saccharin
D) xylitol
E) neotame
A) sorbitol
B) mannitol
C) saccharin
D) xylitol
E) neotame

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Which ingredient is considered a nonnutritive sweetener?



A) naturally milled organic sugar
B) acesulfame potassium
C) natural vanilla flavor
D) modified corn starch
E) chicory root



A) naturally milled organic sugar
B) acesulfame potassium
C) natural vanilla flavor
D) modified corn starch
E) chicory root

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which yogurt products contain complex carbohydrates?



A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt



A) Organic Vanilla Yogurt only
B) Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt only
C) Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt only
D) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Greek Style Vanilla Yogurt
E) Organic Vanilla Yogurt and Fiber-Rich Vanilla Yogurt

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Lactose maldigestion is most common among _____.
A) Asians
B) Native Americans
C) Mexicans
D) U.S. adults
E) Northern Europeans
A) Asians
B) Native Americans
C) Mexicans
D) U.S. adults
E) Northern Europeans

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A constant supply of glucose is needed by the _____.
A) liver
B) brain
C) pancreas
D) lungs
E) heart
A) liver
B) brain
C) pancreas
D) lungs
E) heart

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which simple sugar is directly absorbed into the bloodstream during digestion?
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) maltose
D) lactose
E) glycogen
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) maltose
D) lactose
E) glycogen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which sweetener in the yogurt products should be avoided by people with the genetic disorder phenylketonuria?



A) organic natural flavor
B) cultured pasteurized nonfat milk
C) modified corn starch
D) natural vanilla flavor
E) aspartame



A) organic natural flavor
B) cultured pasteurized nonfat milk
C) modified corn starch
D) natural vanilla flavor
E) aspartame

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 54 في هذه المجموعة.








