Deck 2: A Users Guide to the Sky
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: A Users Guide to the Sky
1
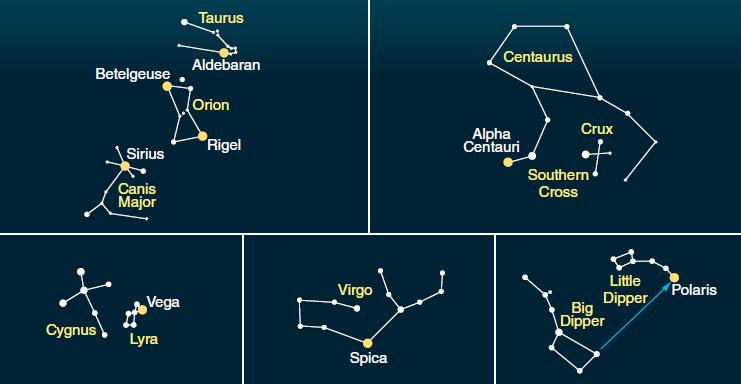 Figure 2-5
Figure 2-5Examine the accompanying figure. Which term would be the correct scientific designation for Polaris in Ursa Minoris?
A) North Star
B) α Ursa Major
C) -0.3 Ursa Minoris
D) α Ursae Minoris
E) β Ursae Minoris
α Ursae Minoris
2
From which language did the majority of star names originate?
A) Arabic
B) Latin
C) Greek
D) Spanish
E) Italian
A) Arabic
B) Latin
C) Greek
D) Spanish
E) Italian
Arabic
3
The constellations are an ancient heritage handed down for thousands of years as ways to tell stories of mythical heroes and monsters.
True
4
Earth spins completely upright like a giant top.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In ancient times, constellation boundaries were well defined.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What is an asterism?
A) A legend or folklore association to a grouping of stars
B) Less formally defined group of stars outside the official 88 constellations
C) The council of astronomers who defined the 88 constellations
D) The northern pivot point of the celestial sphere
E) Constellations close enough to a celestial pole that they do not appear to rise from the east and set in the west
A) A legend or folklore association to a grouping of stars
B) Less formally defined group of stars outside the official 88 constellations
C) The council of astronomers who defined the 88 constellations
D) The northern pivot point of the celestial sphere
E) Constellations close enough to a celestial pole that they do not appear to rise from the east and set in the west

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which ancient astronomer recorded the magnitude of stars in his star catalog and was used successfully by astronomers for generations?
A) Ptolemy
B) Copernicus
C) Galileo
D) Kepler
E) Aristotle
A) Ptolemy
B) Copernicus
C) Galileo
D) Kepler
E) Aristotle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The scale of apparent visual magnitudes extends into negative numbers to represent the faintest objects in the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The International Astronomical Union established 88 constellations that represent a defined area of the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which is an example of an asterism?
A) Andromeda
B) Canis Major
C) Ursa Major
D) Big Dipper
E) Pegasus
A) Andromeda
B) Canis Major
C) Ursa Major
D) Big Dipper
E) Pegasus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The sky appears to rotate eastward around Earth each day, but that is a consequence of the westward rotation of Earth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
What was the purpose of the IAU establishing 88 official constellations?
A) To allow ancient stories of each constellation to be preserved
B) To name all constellations the same across any culture
C) To identify which constellation was created by which culture
D) To define boundaries for constellations including every part of the sky
E) To include additional, fainter stars within a constellation
A) To allow ancient stories of each constellation to be preserved
B) To name all constellations the same across any culture
C) To identify which constellation was created by which culture
D) To define boundaries for constellations including every part of the sky
E) To include additional, fainter stars within a constellation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The nadir marks the point of the celestial sphere directly above your head.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The seasons are caused by Earth's orbit moving closer to or farther from the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Most individual star names come from Latin and have been altered through passing centuries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Because Earth's axis of rotation is inclined 23.4 degrees from vertical, the Sun moves into the northern sky in the spring and into the southern sky in the fall.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which is an asterism of Pegasus?
A) Great Square
B) Orion
C) Andromeda
D) Scorpio
E) Cassiopeia
A) Great Square
B) Orion
C) Andromeda
D) Scorpio
E) Cassiopeia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Astronomers describe the brightness of stars using the brilliance scale.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Flux is a measure of the light energy from a star that hits a collecting area of one square meter in one second.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What did the IAU establish in 1928?
A) The IAU classified Pluto as a dwarf planet.
B) The IAU published official names of all constellations.
C) The IAU recorded 88 constellations with defined boundaries.
D) The IAU recognized additional orbiting bodies in the Kuiper Belt.
E) The IAU recorded all the mythologies associated with 88 constellations.
A) The IAU classified Pluto as a dwarf planet.
B) The IAU published official names of all constellations.
C) The IAU recorded 88 constellations with defined boundaries.
D) The IAU recognized additional orbiting bodies in the Kuiper Belt.
E) The IAU recorded all the mythologies associated with 88 constellations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Within the Northern Hemisphere, the vernal equinox marks the start of ____.
A) winter
B) fall
C) summer
D) spring
E) a new year
A) winter
B) fall
C) summer
D) spring
E) a new year

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
If two stars have a magnitude difference of 5, what is their flux ratio?
A) 10.0
B) 12.6
C) 100.0
D) 250.0
E) 625.3
A) 10.0
B) 12.6
C) 100.0
D) 250.0
E) 625.3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Even though modern astronomers know that stars are scattered through space at different distances, they still use what scientific model to describe celestial locations in the sky?
A) apparent visual magnitude
B) Copernican revolution
C) celestial sphere
D) scientific orb
E) planetarium dome
A) apparent visual magnitude
B) Copernican revolution
C) celestial sphere
D) scientific orb
E) planetarium dome

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which is a unit used to measure angular distance?
A) seconds
B) minutes
C) arc seconds
D) feet
E) kilometers
A) seconds
B) minutes
C) arc seconds
D) feet
E) kilometers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
When can Sirius, a favorite star of the Northern Hemisphere, be observed?
A) during summer
B) during spring
C) all year long
D) during winter
E) during fall
A) during summer
B) during spring
C) all year long
D) during winter
E) during fall

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
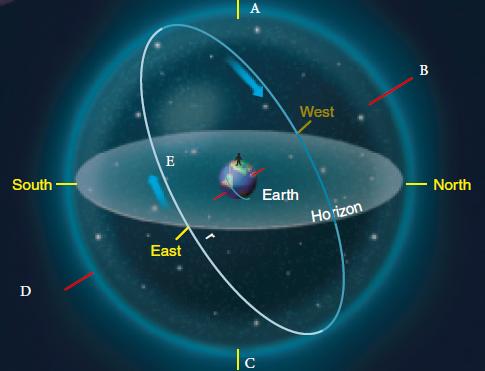 The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)
The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)Review the accompanying figure and identify point C.
A) celestial equator
B) north celestial pole
C) south celestial pole
D) zenith
E) nadir

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
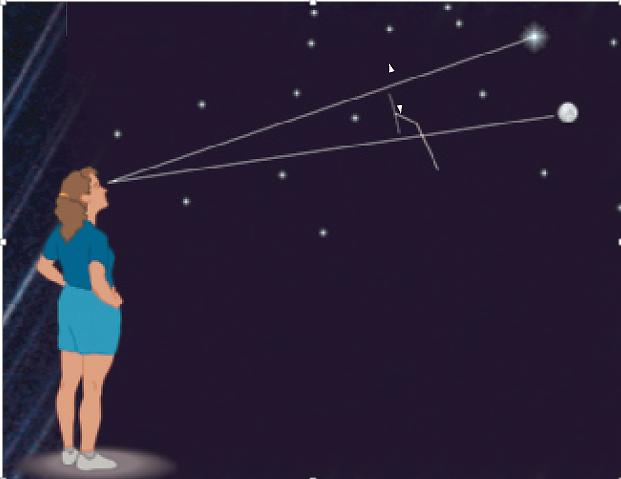 The Sky Around You - Page 19
The Sky Around You - Page 19In the above image, what is the observer measuring?
A) angle
B) arc
C) distance
D) angular distance
E) angular momentum

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
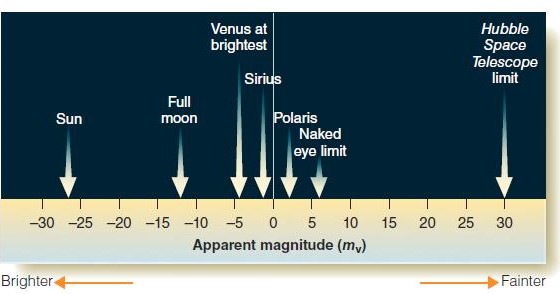 Figure 2-6
Figure 2-6 The star Vega has a magnitude of 0.03. Using the accompanying figure, which object is brighter than Vega?
A) Sun
B) Venus
C) Sirius
D) Polaris
E) full moon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Why is the term "arc" used to describe units of measure for angular distance?
A) To avoid confusion with the minutes and seconds of time
B) To describe the arc-shaped distance between the stars
C) To distinguish the base unit of 10 per degree
D) To distinguish the difference between northern and southern spheres
E) To describe the placement of the stars within each hemisphere
A) To avoid confusion with the minutes and seconds of time
B) To describe the arc-shaped distance between the stars
C) To distinguish the base unit of 10 per degree
D) To distinguish the difference between northern and southern spheres
E) To describe the placement of the stars within each hemisphere

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Earth's rapid rotation makes its axis sweep out the shape of a cone, like a heavy top slowing down. This motion is known as ____.
A) momentum
B) precession
C) revolution
D) precision
E) recession
A) momentum
B) precession
C) revolution
D) precision
E) recession

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Betelgeuse is the brightest star of which constellation?
A) Orion
B) Ursa Minor
C) Ursa Major
D) Southern Cross
E) Cassiopeia
A) Orion
B) Ursa Minor
C) Ursa Major
D) Southern Cross
E) Cassiopeia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If star A is 14.5 times brighter than star B, then what is their magnitude difference?
A) 1.2
B) 2.9
C) 63.1
D) 800
E) 6.2 x 105
A) 1.2
B) 2.9
C) 63.1
D) 800
E) 6.2 x 105

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
What is the flux ratio of two stars whose difference in magnitude is 2.6?
A) 6.3
B) 10.8
C) 21.3
D) 632
E) 1090
A) 6.3
B) 10.8
C) 21.3
D) 632
E) 1090

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Due to the cycle of precession, in 12,000 years, which star will replace Polaris as the guiding North Star?
A) Betelgeuse
B) Sirius
C) Vega
D) Rigel
E) Spica
A) Betelgeuse
B) Sirius
C) Vega
D) Rigel
E) Spica

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Earth's rotation is connected with a very slow celestial motion that can be detected only over _____
A) centuries
B) decades
C) a year
D) a few months
E) short brief periods
A) centuries
B) decades
C) a year
D) a few months
E) short brief periods

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What is the name of constellations that appear to never rise or set?
A) polar constellations
B) circumference constellations
C) circular constellations
D) celestial polar constellations
E) circumpolar constellations
A) polar constellations
B) circumference constellations
C) circular constellations
D) celestial polar constellations
E) circumpolar constellations

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
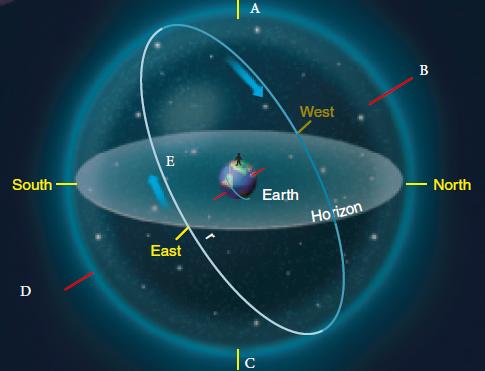 The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)
The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)Review the accompanying figure and identify point A.
A) south point
B) nadir
C) zenith
D) north celestial pole
E) south celestial pole

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
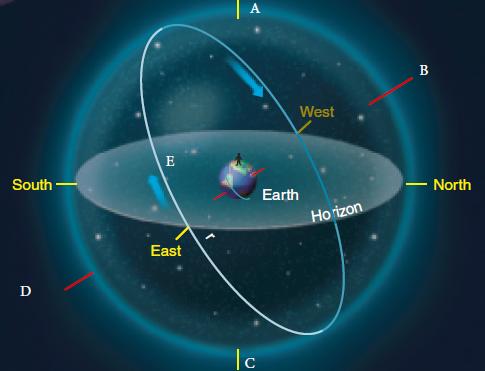 The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)
The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)Review the accompanying figure and identify point B.
A) zenith
B) north point
C) celestial equator
D) south celestial pole
E) north celestial pole

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
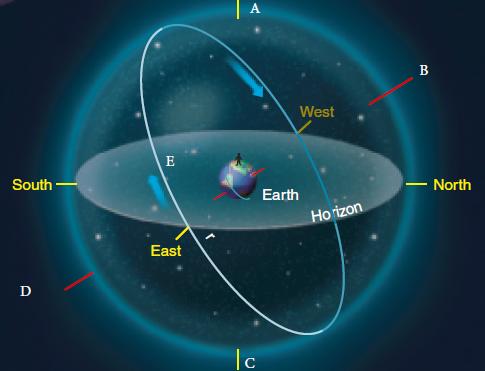 The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)
The Sky Around You - Page 18 (For the following questions)Review the accompanying figure. Where does the celestial equator always meet the horizon?
A) at the north and south celestial poles
B) at the north and south poles
C) at the east and west points
D) at the zenith and nadir
E) at the equinox

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What is the cause for the slow movement of reference marks, such as the celestial poles and equator, to move across the sky?
A) precession
B) evolution
C) climate change
D) continental drift
E) angular revolution
A) precession
B) evolution
C) climate change
D) continental drift
E) angular revolution

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
If Earth rotated about its axis completely upright, what would we fail to experience?
A) holidays
B) seasons
C) weather
D) day and night
E) a 365 day year
A) holidays
B) seasons
C) weather
D) day and night
E) a 365 day year

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
What is the apparent path of the Sun against the background of stars?
A) ecliptic
B) zenith
C) nadir
D) elliptic
E) shadow
A) ecliptic
B) zenith
C) nadir
D) elliptic
E) shadow

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Earth _______________ once a year around the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Explain why we have seasons and compare/contrast the cycle of seasons for both hemispheres.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is the Milankovitch hypothesis and what evidence is there to support this hypothesis?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Why can someone in the United States almost always be able to observe the constellations such as Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, and Perseus?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which planet is often called our most brilliant "morning star"?
A) Venus
B) Jupiter
C) Mars
D) Mercury
E) Saturn
A) Venus
B) Jupiter
C) Mars
D) Mercury
E) Saturn

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What date is the autumnal equinox for the Southern hemisphere?
A) December 21
B) September 22
C) June 22
D) March 20
E) December 25
A) December 21
B) September 22
C) June 22
D) March 20
E) December 25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In 1928, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) established _______________ official constellations with carefully defined boundaries that together include every part of the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Day and night cycles are caused by the ____ of Earth.
A) revolution
B) location
C) axis tilt
D) rotation
E) boundaries
A) revolution
B) location
C) axis tilt
D) rotation
E) boundaries

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The eastward rotation of Earth causes the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars to move _______________ in the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Astronomers use the _______________ alphabet to identify the bright stars in a constellation in approximate order of brightness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
During which event does the Sun reach its most southern point in the celestial sphere within the Northern hemisphere?
A) nadir
B) summer solstice
C) vernal equinox
D) autumnal equinox
E) winter solstice
A) nadir
B) summer solstice
C) vernal equinox
D) autumnal equinox
E) winter solstice

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The Milankovitch hypothesis suggests that the shape of Earth's orbit, its precession, and tilted axis can influence climatic changes and thus cause _____.
A) hurricanes
B) ice ages
C) season shift
D) longer days
E) warmer weather
A) hurricanes
B) ice ages
C) season shift
D) longer days
E) warmer weather

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Earth's axis is tilted at an angle of _______________ degrees.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Why do many people think stars are not in the sky during the daytime?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Why is Earth's orbit often referred to be a "nearly perfect circle" and not a true ellipse?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The ecliptic is often called the _______________ of Earth's orbit on the sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Arc seconds are _______________th of an arc minute.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Astrology is an example of _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Scientists constructed a history of ocean temperatures using deep ocean cores that convincingly matched the predictions of the _______________, describing the cause of multiple ice ages on Earth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Explain why it is difficult to see Mercury in the night sky.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Describe the process of precession.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
On the day of the _______________ in late June, Earth's Northern Hemisphere is inclined toward the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
On the day of summer solstice, explain the position of Earth and the light received by each of the hemispheres.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Describe the magnitude scale and compare the ancient method to the current methodology used today.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Many of the ancient astronomers applied astrology alongside astronomy, but that no longer holds true for modern astronomers. Explain why astrology is no longer considered useful to the modern scientist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 68 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








