Deck 19: Chi-Square
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 19: Chi-Square
1
When our emphasis is on sorting outcomes into categories of data, we are concerned with
A) frequency data.
B) categorical data.
C) bean counting.
D) both a and b
A) frequency data.
B) categorical data.
C) bean counting.
D) both a and b
both a and b
2
The most common level of α when running a goodness-of-fit chi-square is
A) .05
B) .01
C) .05/ c
D) .95
A) .05
B) .01
C) .05/ c
D) .95
.05
3
An example of data that would be analyzed with a chi-square is
A) the mean scores received by men and women on a computer science lab report.
B) the average number of meals eaten by cats and dogs.
C) the numbers of Republican and Democrats who voted for and against stricter drunk-driving laws.
D) the deviations from the median shown in the visual acuity levels of children and adults.
A) the mean scores received by men and women on a computer science lab report.
B) the average number of meals eaten by cats and dogs.
C) the numbers of Republican and Democrats who voted for and against stricter drunk-driving laws.
D) the deviations from the median shown in the visual acuity levels of children and adults.
the numbers of Republican and Democrats who voted for and against stricter drunk-driving laws.
4
A goodness-of-fit test is
A) only used when we want to test the hypothesis that the categories are equally represented.
B) used when we want to test the hypothesis that some categories are more frequent that others.
C) used to test the null hypothesis that the data are distributed in a way that would be predicted by a theory.
D) probably the most common statistical test we have.
A) only used when we want to test the hypothesis that the categories are equally represented.
B) used when we want to test the hypothesis that some categories are more frequent that others.
C) used to test the null hypothesis that the data are distributed in a way that would be predicted by a theory.
D) probably the most common statistical test we have.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The chi-square distribution is
A) a sampling distribution.
B) the distribution against which we evaluate chi-square values.
C) a distribution whose shape varies with the number of degrees of freedom.
D) all of the above
A) a sampling distribution.
B) the distribution against which we evaluate chi-square values.
C) a distribution whose shape varies with the number of degrees of freedom.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A significant result with a goodness-of-fit test might suggest to us that
A) observations are not distributed in line with the null hypothesis.
B) the category means are different.
C) some assumption was likely to have been violated.
D) we have a very flat distribution.
A) observations are not distributed in line with the null hypothesis.
B) the category means are different.
C) some assumption was likely to have been violated.
D) we have a very flat distribution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the formula for a standard chi-square test?
A)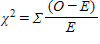
B)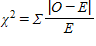
C)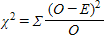
D) none of the above
A)
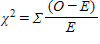
B)
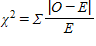
C)
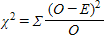
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The chi-square test is used when we have
A) measurement data.
B) ratio data.
C) interval data.
D) categorical data.
A) measurement data.
B) ratio data.
C) interval data.
D) categorical data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
You should be careful about using a chi-square test when
A) the expected frequencies are quite small.
B) the obtained frequencies are quite small.
C) the expected frequencies are different across the categories.
D) both a and c
A) the expected frequencies are quite small.
B) the obtained frequencies are quite small.
C) the expected frequencies are different across the categories.
D) both a and c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
When using the chi-square tables, we reject the null hypothesis when
A) chi-square is larger than the tabled value.
B) chi-square is smaller than the tabled value.
C) chi-square is far from the tabled value in either direction.
D) It depends.
A) chi-square is larger than the tabled value.
B) chi-square is smaller than the tabled value.
C) chi-square is far from the tabled value in either direction.
D) It depends.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The critical value of χ2
A) decreases as we increase the degrees of freedom.
B) increases as we increase the degrees of freedom.
C) increases as we increase the number of observations ( N ).
D) varies only as a function of α, not as a function of the degrees of freedom.
A) decreases as we increase the degrees of freedom.
B) increases as we increase the degrees of freedom.
C) increases as we increase the number of observations ( N ).
D) varies only as a function of α, not as a function of the degrees of freedom.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
When we sort subjects only into those who improved their performance over time, worsened their performance over time, and stayed the same, we have
A) a one-way classification.
B) a two-way classification.
C) a contingency table.
D) a set of ordered data.
A) a one-way classification.
B) a two-way classification.
C) a contingency table.
D) a set of ordered data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The null hypothesis for the previous example which used a chi-square is
A) men and women do not differ on computer science lab report scores.
B) cats and dogs eat the same number of meals.
C) political affiliation and voting behavior on drunk driving are independent variables.
D) children and adults do not show different deviations in visual acuity.
A) men and women do not differ on computer science lab report scores.
B) cats and dogs eat the same number of meals.
C) political affiliation and voting behavior on drunk driving are independent variables.
D) children and adults do not show different deviations in visual acuity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
With categorical data, the primary piece of data is
A) a measurement.
B) a cell frequency.
C) a mean.
D) both b and c
A) a measurement.
B) a cell frequency.
C) a mean.
D) both b and c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The denominator in chi-square is there to
A) keep the resulting answer in perspective relative to the total frequency.
B) keep the result in perspective relative to the size of the expected frequency.
C) keep people honest.
D) control the probability of a Type II error.
A) keep the resulting answer in perspective relative to the total frequency.
B) keep the result in perspective relative to the size of the expected frequency.
C) keep people honest.
D) control the probability of a Type II error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
For a goodness-of-fit chi-square test, the degrees of freedom are equal to
A) N - 1, where N is the number of observations.
B) C - 1, where C is the number of categories.
C) NC - 1.
D) ( N - 1)( C - 1).
A) N - 1, where N is the number of observations.
B) C - 1, where C is the number of categories.
C) NC - 1.
D) ( N - 1)( C - 1).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A goodness-of-fit test is used with
A) a contingency table.
B) normally distributed variables.
C) a one-way categorization.
D) a test of linearity.
A) a contingency table.
B) normally distributed variables.
C) a one-way categorization.
D) a test of linearity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A typical null hypothesis with a goodness-of-fit test as presented in the text might be
A) the hypothesis that the means increase evenly across categories.
B) the hypothesis that the representation in each category is equal.
C) the hypothesis that subjects are normally distributed.
D) the hypothesis that the expected values are uniformly large.
A) the hypothesis that the means increase evenly across categories.
B) the hypothesis that the representation in each category is equal.
C) the hypothesis that subjects are normally distributed.
D) the hypothesis that the expected values are uniformly large.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The multicategory goodness-of-fit case for chi-square is
A) a simple extension of the two-category case.
B) a way of comparing more that two categories.
C) a common situation.
D) all of the above
A) a simple extension of the two-category case.
B) a way of comparing more that two categories.
C) a common situation.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
If we run a chi-square test on a one-way classification, a significant result tells us that
A) science has triumphed over evil.
B) the categories are evenly represented in the data.
C) the frequencies differ by category.
D) we have made an error.
A) science has triumphed over evil.
B) the categories are evenly represented in the data.
C) the frequencies differ by category.
D) we have made an error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The chi-square test can run into trouble if
A) the observations are not independent.
B) the expected frequencies are too low.
C) the total number of subjects is very small.
D) all of the above
A) the observations are not independent.
B) the expected frequencies are too low.
C) the total number of subjects is very small.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
For the next several questions, assume that we had the following contingency table:
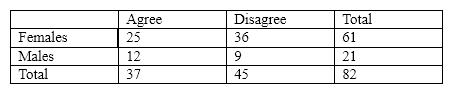
With a two-way contingency table the degrees of freedom are
A) RC - 1.
B) C - 1.
C) RC .
D) ( R - 1)( C - 1).

With a two-way contingency table the degrees of freedom are
A) RC - 1.
B) C - 1.
C) RC .
D) ( R - 1)( C - 1).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
We can only use a chi-square test with frequency data if
A) the observations are independent.
B) the observations are sorted into categories.
C) the sample size is not very small.
D) all of these apply
A) the observations are independent.
B) the observations are sorted into categories.
C) the sample size is not very small.
D) all of these apply

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The text mentions a correction for continuity and suggests that
A) you always use it with a 2 × 2 table.
B) you always use it with any contingency table.
C) it is not needed.
D) you only use it with a goodness-of-fit test.
A) you always use it with a 2 × 2 table.
B) you always use it with any contingency table.
C) it is not needed.
D) you only use it with a goodness-of-fit test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
For the next several questions, assume that we had the following contingency table:
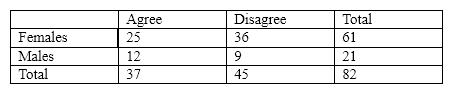
Which of the following are the cell totals?
A) 25, 36, 61, 21
B) 25, 12, 36, 9
C) 61, 21, 37, 45
D) 82

Which of the following are the cell totals?
A) 25, 36, 61, 21
B) 25, 12, 36, 9
C) 61, 21, 37, 45
D) 82

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If we want to use the chi-square test to test the difference between means we should
A) convert the means to standard scores.
B) convert the means to totals.
C) run a different test instead.
D) be sure the means are not too small.
A) convert the means to standard scores.
B) convert the means to totals.
C) run a different test instead.
D) be sure the means are not too small.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In a Chi-square, k refers to the number of categories.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If we want to test proportions, one wrong way to do so is to
A) put the proportions themselves directly into the chi-square formula.
B) convert proportions to frequencies.
C) take the difference in proportions and turn it into a z score.
D) You can't do any of these things.
A) put the proportions themselves directly into the chi-square formula.
B) convert proportions to frequencies.
C) take the difference in proportions and turn it into a z score.
D) You can't do any of these things.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The difference between the chi-square test for a 2 × 2 table and one for a larger table is
A) we must use a different formula.
B) a 2 × 2 is a goodness-of-fit chi-square.
C) you can't handle a contingency table larger than a 2 × 3.
D) There is no difference other than the number of cells we include.
A) we must use a different formula.
B) a 2 × 2 is a goodness-of-fit chi-square.
C) you can't handle a contingency table larger than a 2 × 3.
D) There is no difference other than the number of cells we include.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A contingency table involves
A) one category of classification.
B) more than one variable on which subjects are classified.
C) no more than two levels of classification.
D) a substantially different computational approach.
A) one category of classification.
B) more than one variable on which subjects are classified.
C) no more than two levels of classification.
D) a substantially different computational approach.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
For the next several questions, assume that we had the following contingency table:
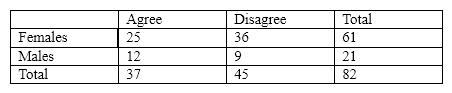
Which of the following are marginal totals?
A) 25 and 36
B) 12 and 36
C) 25, 9, and 82
D) 61 and 21

Which of the following are marginal totals?
A) 25 and 36
B) 12 and 36
C) 25, 9, and 82
D) 61 and 21

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If we want to use the chi-square test to test the difference between two proportions, we should
A) convert the proportions to means.
B) convert the proportions to frequencies.
C) run a z test.
D) either b or c
A) convert the proportions to means.
B) convert the proportions to frequencies.
C) run a z test.
D) either b or c

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The correction for continuity is known as
A) Fisher's correction.
B) Pearson's correction.
C) Howell's correction.
D) Yates' correction.
A) Fisher's correction.
B) Pearson's correction.
C) Howell's correction.
D) Yates' correction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Chi-square is used to analyze continuous data.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
For the next several questions, assume that we had the following contingency table:
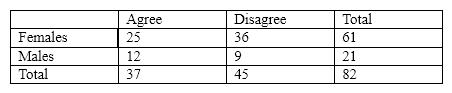
In the contingency table shown above, the degrees of freedom would equal
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.

In the contingency table shown above, the degrees of freedom would equal
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
With several categories in a goodness-of-fit test, a significant result means
A) the categories increase in frequency from left to right.
B) the categories decrease in frequency from left to right.
C) the categories are equally frequent.
D) The test doesn't pay any attention to which category is larger than which other categories.
A) the categories increase in frequency from left to right.
B) the categories decrease in frequency from left to right.
C) the categories are equally frequent.
D) The test doesn't pay any attention to which category is larger than which other categories.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
In a chi-square test the expected frequency is
A) the frequency you would expect if the null hypothesis were false.
B) the frequency you actually obtained.
C) the frequency you would expect if the null hypothesis were true.
D) Expected frequency has nothing to do with the null hypothesis.
A) the frequency you would expect if the null hypothesis were false.
B) the frequency you actually obtained.
C) the frequency you would expect if the null hypothesis were true.
D) Expected frequency has nothing to do with the null hypothesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Expected frequencies are the expected value for the number of observations in a cell if the alternative hypothesis is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A Goodness-of-fit test compares the observed number of frequencies with predicted frequencies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
For the next several questions, assume that we had the following contingency table:
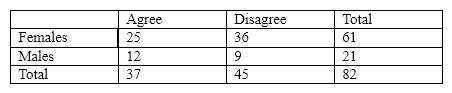
In the table above, the expected frequency in the Male/Disagree cell is closest to
A) 11.
B) 5.
C) 28.
D) 9.

In the table above, the expected frequency in the Male/Disagree cell is closest to
A) 11.
B) 5.
C) 28.
D) 9.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In a Chi-square including two variables, one with 4 categories, and the other with 3 categories, the df = 6.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Indicate whether or not the following Chi-square statistics are significant:
a. χ 2 = 2.75; k =2
b. χ 2 = 11.00; k =5
c. χ 2 = 12.40; df = 6
a. χ 2 = 2.75; k =2
b. χ 2 = 11.00; k =5
c. χ 2 = 12.40; df = 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A researcher wants to be sure that her random assignment to groups has been working. She wants to be sure that socio-economic status and treatment group are independent. Ideally, given her particular sample, there would be an equal number of people in each category. Calculate the marginal totals and the expected frequencies for each cell.



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Assuming the student body in the previous example is 30% male and 70% female,
a. What are the expected values
b. Calculate and interpret Chi-square
a. What are the expected values
b. Calculate and interpret Chi-square

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Calculate and interpret Chi-square for the previous example.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
In order for a Chi-square test to be valid, a general rule of thumb is that every cell have expected frequencies greater than or equal to 10.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A political science student did a survey to see if the political affiliation of voters was related to whether or not they would consider voting for a progressive candidate in the upcoming gubernatorial race. How would you calculate the marginals and expected frequencies for each cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A professor believes that a greater proportion of females than males have enrolled in her class. Assuming an equal number of males and females in the student body, calculate Chi-square, and evaluate her hypothesis based on the following data.



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
If a Chi-square is conducted based on data from 30 people who are categorized into one of 4 possible categories, the df = 26.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A social worker has been asked to testify before her state legislature about the impact of long-term foster care on child outcomes and government spending. She knows that 60% of children who remained in the foster care system without being adopted ended up in prison. The figure for foster care children who were eventually adopted was 25%. These data were based on 500 children who remained in foster care and 800 children who were eventually adopted. Create the appropriate contingency table.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
It is appropriate to use Chi-square when data from the same subject are in multiple cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Calculate and interpret Chi-square based on the contingency table you created.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
In a contingency table, the expected frequency of any given cell is represented by this formula:
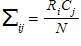
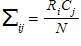

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Calculate and interpret the z score based on the proportion of youth who end up in prison using the data from the previous example.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Based on the previous example:
a. What are the df?
b. Calculate and interpret Chi-square.
a. What are the df?
b. Calculate and interpret Chi-square.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A marginal total is the sum of the level of one variable across all of the levels of the other variable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








