Deck 4: Origins of Modern Astronomy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Origins of Modern Astronomy
1
Ptolemy based his model on theories first developed by Plato, who believed each celestial body traveled around a small circle that followed a larger circle around Earth.
False
2
In 1632, which book did the Inquisition order sales to be stopped?
A) De Revolutionibus
B) Stederreus Nunctus
C) Dialogo
D) De Stella Nova
E) Astronomia Nova
A) De Revolutionibus
B) Stederreus Nunctus
C) Dialogo
D) De Stella Nova
E) Astronomia Nova
C
3
The most important idea in De Revolutionibus was placing the Sun at the center of the Universe.
True
4
What was the most controversial issue surrounding the nature of the Universe during the Renaissance?
A) The movement of visible galaxies
B) The origins of the Universe
C) The number of planets in the Solar System
D) The position of Earth in the Universe
E) The existence of life on planets other than Earth
A) The movement of visible galaxies
B) The origins of the Universe
C) The number of planets in the Solar System
D) The position of Earth in the Universe
E) The existence of life on planets other than Earth

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Kepler's first law of planetary motion states "The orbits of the planets are _____ with the Sun at one focus."
A) spheres
B) ellipses
C) circular
D) rigid
E) random
A) spheres
B) ellipses
C) circular
D) rigid
E) random

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Galileo's discovery of Saturn's moons proved that Earth, too, could move and still keep its satellite.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Kepler discovered that planets do not move at uniform speeds along their elliptical orbits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Though their contributions to astronomy were different, Galileo and Copernicus were astronomers during the same time period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Kepler's third law of planetary motion states, "A planet's _____ squared is proportional to its average distance from the Sun cubed."
A) radius
B) diameter
C) rotational speed
D) orbital period
E) rotational period
A) radius
B) diameter
C) rotational speed
D) orbital period
E) rotational period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Greek philosophers used religion and astrology to understand the mysteries of the Universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Spheres are an essential part of Kepler's three fundamental rules of planetary motion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Most Greek philosophers believed in a geocentric Universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The Inquisition condemned Galileo for heresy in 1616.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Claudius Ptolemy was a contemporary of Aristotle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Why did Copernicus hesitate to consider alternatives to the Ptolemaic Universe?
A) A heliocentric Universe contradicted Christian theology at the time.
B) There was no way to prove uniform circular motion.
C) New star formation showed no parallax.
D) Most people already believed in a heliocentric Universe.
E) His mathematics could not disprove Ptolemy's epicycles, deferents and equants.
A) A heliocentric Universe contradicted Christian theology at the time.
B) There was no way to prove uniform circular motion.
C) New star formation showed no parallax.
D) Most people already believed in a heliocentric Universe.
E) His mathematics could not disprove Ptolemy's epicycles, deferents and equants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
In the Copernican system, Earth moves slower along its orbit than the planets that lie farther from the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Kepler's second law of planetary motion states "A line from a planet to the Sun sweeps over equal areas in equal intervals of ____."
A) time
B) space
C) arcs
D) ellipses
E) spheres
A) time
B) space
C) arcs
D) ellipses
E) spheres

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which book was authored by Copernicus that explained the Sun as the center of a planetary system?
A) Alfonsine Tables
B) De Revolutionibus
C) Stderreus Nunctus
D) The Prutenie Tables
E) The Forerunner of the Universe, Containing the Mystery of the Universe
A) Alfonsine Tables
B) De Revolutionibus
C) Stderreus Nunctus
D) The Prutenie Tables
E) The Forerunner of the Universe, Containing the Mystery of the Universe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Eudoxus of Cnidus (408-355 BCE) , a student of Plato's, applied the principle of heliocentric motion to produce a mathematical description of the motions of the Universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Pythagoras believed that the underlying rules to understanding the Universe were mathematical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which publication was Kepler's masterpiece, providing strong evidence to planetary motion and a heliocentric Universe?
A) Alfonsine Tables
B) De Revolutionibus
C) Rudolphine Tables
D) The Prutenic Tables
E) Sidereus Nuncius
A) Alfonsine Tables
B) De Revolutionibus
C) Rudolphine Tables
D) The Prutenic Tables
E) Sidereus Nuncius

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
 Figure 4-2
Figure 4-2What field of science focuses most on the connections between ancient celestial observations and such structures as the one seen in the accompanying figure (Figure 4-2) ?
A) theology
B) astrology
C) archeology
D) archeoastronomy
E) archeophilosophy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What did the Greek philosopher Philolaus believe about the Universe?
A) No parallax seen of new stars means Earth is the center of the Universe.
B) Perfect heavens must be made of up spheres rotating at constant rates.
C) The most perfect geometrical form was the sphere.
D) The heavens are perfect and Earth is imperfect.
E) Earth moved around a central fire.
A) No parallax seen of new stars means Earth is the center of the Universe.
B) Perfect heavens must be made of up spheres rotating at constant rates.
C) The most perfect geometrical form was the sphere.
D) The heavens are perfect and Earth is imperfect.
E) Earth moved around a central fire.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Kepler's first law of planetary motion defied what long-held belief with ancient astronomers?
A) a heliocentric Universe
B) a geocentric Universe
C) uniform circular motion
D) parallax of newborn stars
E) perfection of the heavens
A) a heliocentric Universe
B) a geocentric Universe
C) uniform circular motion
D) parallax of newborn stars
E) perfection of the heavens

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which statement best describes a theory?
A) A group of ideas about how something should be done, made, or thought about
B) A specific statement about nature that needs further testing
C) An idea considered so obviously true that the idea does not need to be questioned
D) A fundamental principle in which scientists have great confidence
E) A general description of some aspect of nature that has been thoroughly tested and widely accepted
A) A group of ideas about how something should be done, made, or thought about
B) A specific statement about nature that needs further testing
C) An idea considered so obviously true that the idea does not need to be questioned
D) A fundamental principle in which scientists have great confidence
E) A general description of some aspect of nature that has been thoroughly tested and widely accepted

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Ptolemy tried to describe the motion of the planets by devising a small circle, called a(n) ____, which rotated around the edge of a larger circle.
A) epicycle
B) foci
C) deferent
D) equant
E) sphere
A) epicycle
B) foci
C) deferent
D) equant
E) sphere

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
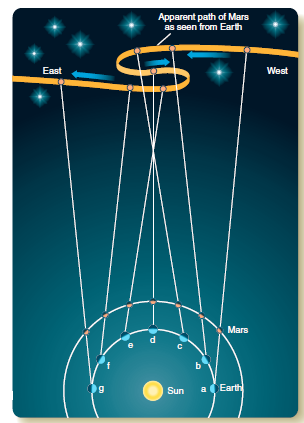 Figure 4-1
Figure 4-1The accompanying illustration (Figure 4-1) demonstrates Copernicus's theory of _______________.
A) uniform circular motion
B) retrograde motion
C) parallax
D) eccentricity
E) heliocentric Universe

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which planet did Galileo observe go through a complete set of phases, thus proving the Ptolemaic model wrong?
A) Saturn
B) Jupiter
C) Mars
D) Venus
E) Mercury
A) Saturn
B) Jupiter
C) Mars
D) Venus
E) Mercury

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
According to Kepler's third law, calculate the orbital period of a planet approximately 6.0 AU away from the Sun.
A) ∼ 6 years
B) ∼ 15 years
C) ∼ 30 years
D) ∼ 36 years
E) ∼ 214 years
A) ∼ 6 years
B) ∼ 15 years
C) ∼ 30 years
D) ∼ 36 years
E) ∼ 214 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Galileo's book Dialogo strongly defended the work of which astronomer?
A) Ptolemy
B) Tycho
C) Copernicus
D) Kepler
E) Aristotle
A) Ptolemy
B) Tycho
C) Copernicus
D) Kepler
E) Aristotle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Kepler originally proposed that the planets were spaced apart by ____.
A) five spheres
B) five regular solids
C) six tetrahedrons
D) five epicycles
E) six regular solids
A) five spheres
B) five regular solids
C) six tetrahedrons
D) five epicycles
E) six regular solids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Kepler's laws of planetary motion were _____ because he could not provide an explanation for his conclusions.
A) unnatural
B) empirical
C) hypothetical
D) principles
E) assumptions
A) unnatural
B) empirical
C) hypothetical
D) principles
E) assumptions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which model did Galileo disprove by discovering the transit of Venus?
A) Ptolemaic
B) Copernican
C) Aristotelian
D) Plutonic
E) Kepler
A) Ptolemaic
B) Copernican
C) Aristotelian
D) Plutonic
E) Kepler

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What was Tycho Brahe's contribution to astronomy?
A) He proved that Earth rotates on its own axis and revolves around the Sun.
B) He designed the three laws of planetary motion.
C) He discovered satellites around Jupiter, which proved Earth could move and keep its satellite.
D) He described why each of the planets moved in uniform circular motion.
E) He compiled detailed observations of the positions of the Sun, Moon, and planets over a period of 20 years.
A) He proved that Earth rotates on its own axis and revolves around the Sun.
B) He designed the three laws of planetary motion.
C) He discovered satellites around Jupiter, which proved Earth could move and keep its satellite.
D) He described why each of the planets moved in uniform circular motion.
E) He compiled detailed observations of the positions of the Sun, Moon, and planets over a period of 20 years.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Whose geocentric model of the Universe dominated astronomy for 2,000 years?
A) Kepler
B) Copernicus
C) Aristotle
D) Galileo
E) Ptolemy
A) Kepler
B) Copernicus
C) Aristotle
D) Galileo
E) Ptolemy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What principle was Copernicus unable to provide evidence against?
A) uniform circular motion
B) heliocentric universe
C) geocentric universe
D) retrograde motion
E) Ptolemy's epicycles
A) uniform circular motion
B) heliocentric universe
C) geocentric universe
D) retrograde motion
E) Ptolemy's epicycles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What was Eratosthenes's mathematical contribution to the history of astronomy, even though it was incorrect?
A) He calculated the diameter of Earth by what he learned from travelers' itineraries.
B) He estimated Earth's revolution rate by measuring the length of shadows casted on the surface.
C) He determined that all the planets orbited Earth every 24 hrs.
D) He attempted to calculate Earth's radius by utilizing the position of sunlight.
E) He believed all of nature was underlain by musical principles.
A) He calculated the diameter of Earth by what he learned from travelers' itineraries.
B) He estimated Earth's revolution rate by measuring the length of shadows casted on the surface.
C) He determined that all the planets orbited Earth every 24 hrs.
D) He attempted to calculate Earth's radius by utilizing the position of sunlight.
E) He believed all of nature was underlain by musical principles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What tool did Galileo use to prove that the Moon was not perfect?
A) microscope
B) telescope
C) quadranoscope
D) thermometer
E) anemometer
A) microscope
B) telescope
C) quadranoscope
D) thermometer
E) anemometer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The 99 years that revolutionized Astronomy ended with whose death?
A) Aristotle
B) Kepler
C) Tycho
D) Copernicus
E) Galileo
A) Aristotle
B) Kepler
C) Tycho
D) Copernicus
E) Galileo

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Early astronomers believed that Earth did not move because they saw no ____, the apparent motion of an object because of the motion of the observer.
A) uniform circular motion
B) archeoastronomy
C) heliocentrism
D) eccentricity
E) parallax
A) uniform circular motion
B) archeoastronomy
C) heliocentrism
D) eccentricity
E) parallax

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What part of the Copernican model was incorrect?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In Kepler's model of the Universe, what was the purpose of the five regular solids?
A) To differentiate the six planets
B) To define the shape of each of the orbits
C) To describe the internal shape of each planet
D) To be spacers for the orbits of the six planets
E) To support the calculations of each orbital period
A) To differentiate the six planets
B) To define the shape of each of the orbits
C) To describe the internal shape of each planet
D) To be spacers for the orbits of the six planets
E) To support the calculations of each orbital period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Ancient astronomers often saw certain planets viewed, while viewed from Earth, slowly stop and then move westward, of which they called this movement _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Kepler's analysis of planetary motion showed that the planets move _______________ when close to the Sun and _______________ when farther away.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which is not a feature of Ptolemy's mathematical model of the Aristotelian universe?
A) deferent
B) epicycle
C) equant
D) ellipse
E) rotation
A) deferent
B) epicycle
C) equant
D) ellipse
E) rotation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Pythagoras proposed that all nature was underlain by musical principles, by which he meant _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The most important idea in Copernicus' De Revolutionibus was placing the _______________ at the center of the Universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
When Tycho saw no parallax in the position of a new star, he published his evidence against which model of the Universe?
A) Aristotelian
B) Galilean
C) Ptolemaic
D) Copernican
E) Reinhold
A) Aristotelian
B) Galilean
C) Ptolemaic
D) Copernican
E) Reinhold

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Ancient astronomers often had difficulty explaining _____, the occasional westward motion of the planets.
A) parallax
B) eccentrics
C) retrograde motion
D) deferents
E) epicycles
A) parallax
B) eccentrics
C) retrograde motion
D) deferents
E) epicycles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What were the three discoveries Galileo made with his telescope observations and quickly published into Sidereus Nuncius ?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A(n) _______________is something that is held to be obviously true and needs no further examination.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What are Kepler's three laws of planetary motion?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What are the two primary components of the Ptolemaic Universe model?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The Greek philosopher who proposed that Earth rotates on its axis and revolves around the Sun was _________.
A) Alexandria
B) Plato
C) Aristotle
D) Eratosthenes
E) Aristarchus
A) Alexandria
B) Plato
C) Aristotle
D) Eratosthenes
E) Aristarchus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What did most Greek philosophers accept as a first principle?
A) Earth was the unmoving center of the Universe.
B) The heavens are imperfect.
C) The tetrahedron is the perfect geometric form.
D) There are only six planets in the Universe.
E) Earth travels on an elliptical orbit.
A) Earth was the unmoving center of the Universe.
B) The heavens are imperfect.
C) The tetrahedron is the perfect geometric form.
D) There are only six planets in the Universe.
E) Earth travels on an elliptical orbit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Who is often considered the founder of trigonometry?
A) Aristotle
B) Hipparchus
C) Aristarchus
D) Eratosthenes
E) Plato
A) Aristotle
B) Hipparchus
C) Aristarchus
D) Eratosthenes
E) Plato

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Eratosthenes used simple geometry to determine the distance between Alexandria to Syene so that he could calculate Earth's_______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A circle is an ellipse with an eccentricity of ____.
A) zero
B) one
C) two
D) four
E) eight
A) zero
B) one
C) two
D) four
E) eight

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
According to Kepler's _______ law, when a planet is farthest from the Sun, it moves slower than when it is nearest the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Explain the differences between a hypothesis, theory, and a natural law.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
In the Copernican system, Earth moves _______________ along its orbit than the planets that lie farther from the Sun.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Explain the geometry of an ellipse, which Kepler used to describe a planet's orbits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
A well-known structure located in Britain and investigated by archeoastronomist is called _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Explain why Copernicus' hypothesis, where the Sun was the center of the planetary system, became known as the Copernican Revolution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Explain why it is a common misconception that Galileo faced the Inquisition for his belief in a heliocentric Universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Most Greek philosophers believed in a(n) _______________ Universe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
_______________'s laws have been used for almost four centuries as a true description of orbital motion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
What was the evidence that ancient astronomers used to conclude that Earth did not move?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








