Deck 5: Gravity
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
Match between columns
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: Gravity
1
Two objects in orbit around each other orbit their common center of mass.
True
2
Spring tides occur during the new and full lunar phases.
True
3
According to Galileo, the acceleration of a freely falling object due to gravity is ____.
A) larger if the object is dropped from a greater height
B) smaller if the object is dropped from a greater height
C) larger if the mass of the object is larger
D) smaller if the mass of the object is larger
E) the same regardless of the mass and the height from which it is dropped
A) larger if the object is dropped from a greater height
B) smaller if the object is dropped from a greater height
C) larger if the mass of the object is larger
D) smaller if the mass of the object is larger
E) the same regardless of the mass and the height from which it is dropped
E
4
If an object's velocity equals or exceeds the escape velocity, it will follow a closed parabolic or hyperbolic orbit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The escape velocity at a given distance from a planet is less than the circular velocity of an orbit around that planet at the same distance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Galileo determined that ____.
A) heavy objects accelerate at a slower speed than lighter objects
B) lighter objects accelerate at a slower speed than heavier objects
C) an object's acceleration is due to the height from which it is dropped
D) all objects fall at a constant speed
E) all objects fall at a constant acceleration
A) heavy objects accelerate at a slower speed than lighter objects
B) lighter objects accelerate at a slower speed than heavier objects
C) an object's acceleration is due to the height from which it is dropped
D) all objects fall at a constant speed
E) all objects fall at a constant acceleration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Newtonian gravity is often called universal mutual gravitation because every particle with mass in the Universe must attract every other particle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
According to Aristotle, an object with no forces acting on it will ____.
A) move faster and faster
B) eventually stop moving
C) move at a constant speed forever
D) first increase and then decrease in speed
E) first decrease and then increase in speed
A) move faster and faster
B) eventually stop moving
C) move at a constant speed forever
D) first increase and then decrease in speed
E) first decrease and then increase in speed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Galileo believed that motion stops in the absence of a force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Aristotle believed that objects falling to the ground fall at a constant rate of speed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In contradiction to the teachings of Aristotle, Galileo found that an object with no forces (and no friction) acting on it will ____.
A) move faster and faster
B) eventually stop moving
C) move at a constant speed forever
D) first increase and then decrease in speed
E) first decrease and then increase in speed
A) move faster and faster
B) eventually stop moving
C) move at a constant speed forever
D) first increase and then decrease in speed
E) first decrease and then increase in speed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Newton's third law states that forces occur in pairs acting in the same direction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Newton's first law of motion is essentially a restatement of Galileo's law of inertia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The M oon pulls more strongly on Earth's near and far side than on its center.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The second postulate of special relativity states that the speed of light, when measured in a vacuum, is constant for all observers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
According to Aristotle, which scenario illustrates violent motion?
A) An apple falling from a tree
B) A mass of warm air rising above hot pavement
C) An arrow moving through the air after leaving the bow
D) A person pushing a car along the street
E) A barrel rolling down a ramp
A) An apple falling from a tree
B) A mass of warm air rising above hot pavement
C) An arrow moving through the air after leaving the bow
D) A person pushing a car along the street
E) A barrel rolling down a ramp

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Special relativity states the relationship between energy and mass as 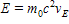 .
.
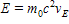 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Changing the direction of a moving body does not impact its velocity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The apparent positions of stars around the sun during an eclipse have been used to prove the general theory of relativity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The neap tides occur at the new moon and full moon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Spring tides occur ____.
A) only during spring months
B) when high tides are unusually low and low tides are unusually high
C) when high tides and low tides are unusually low
D) when high tides are unusually high and low tides are unusually low
E) simultaneously with neap tides
A) only during spring months
B) when high tides are unusually low and low tides are unusually high
C) when high tides and low tides are unusually low
D) when high tides are unusually high and low tides are unusually low
E) simultaneously with neap tides

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The radius of Earth is 6,378 km. The force of gravity on a 1 kg ball at Earth's surface is 9.8 kg m/s2. What is the force of gravity on this same ball when the ball is located 12,756 km from Earth's center? Hint: G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kg
A) 2.45 kg m/s2
B) 4.9 kg m/s2
C) 9.8 kg m/s2
D) 19.6 kg m/s2
E) 39.2 kg m/s2
A) 2.45 kg m/s2
B) 4.9 kg m/s2
C) 9.8 kg m/s2
D) 19.6 kg m/s2
E) 39.2 kg m/s2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A comet near the Sun whose orbit is ____ would never be near the Sun again.
A) apogee
B) circular
C) elliptical
D) hyperbolic
E) radial
A) apogee
B) circular
C) elliptical
D) hyperbolic
E) radial

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
When two objects of unequal mass orbit each other, the center of mass is ____.
A) at the center of the more massive object
B) at the center of the least massive object
C) half way between the centers of each object
D) always closer to the less massive of the two objects
E) always closer to the more massive of the two objects
A) at the center of the more massive object
B) at the center of the least massive object
C) half way between the centers of each object
D) always closer to the less massive of the two objects
E) always closer to the more massive of the two objects

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Spring tides occur at ____.
A) new moon and first quarter moon
B) new moon and full moon
C) first quarter moon and third quarter moon
D) first quarter moon and full moon
E) third quarter moon and full moon
A) new moon and first quarter moon
B) new moon and full moon
C) first quarter moon and third quarter moon
D) first quarter moon and full moon
E) third quarter moon and full moon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If the orbital velocity of the Moon is 1.0 km/s, what is the orbital velocity of a satellite that is 1/16th as far from Earth as the Moon? Hints: There is a long way and a short way to do this calculation. 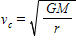 ; G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kg
; G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kg
A) 1/16 km/s
B) 1/8 km/s
C) 4 km/s
D) 8 km/s
E) 16 km/s
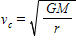 ; G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kg
; G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kgA) 1/16 km/s
B) 1/8 km/s
C) 4 km/s
D) 8 km/s
E) 16 km/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Mutual gravitation is ____.
A) a type of force that acts on an object moving at constant speed
B) the acceleration of an object in the absence of a force
C) a property of all matter in the universe
D) the limit of gravitational force from one object to another
E) a type of force that repels surrounding particles
A) a type of force that acts on an object moving at constant speed
B) the acceleration of an object in the absence of a force
C) a property of all matter in the universe
D) the limit of gravitational force from one object to another
E) a type of force that repels surrounding particles

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What is the circular velocity of an object orbiting Earth at a distance of 100,000 km from Earth's center? Hint: 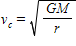 ; G = 6.67 10 -11m3 /s2 /kg
; G = 6.67 10 -11m3 /s2 /kg
A) 0.2 m/s
B) 2 m/s
C) 20 m/s
D) 200 m/s
E) 2,000 m/s
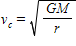 ; G = 6.67 10 -11m3 /s2 /kg
; G = 6.67 10 -11m3 /s2 /kgA) 0.2 m/s
B) 2 m/s
C) 20 m/s
D) 200 m/s
E) 2,000 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
One of the first tests of the general theory of relativity was the ____.
A) description of the orbit of the moon
B) determination of the speed of light as a constant
C) change in mass of a particle moving at a high speed
D) demonstration of a hammer and a feather falling at the same rate on the moon
E) determination of the rate of advance of the perihelion of Mercury's orbit
A) description of the orbit of the moon
B) determination of the speed of light as a constant
C) change in mass of a particle moving at a high speed
D) demonstration of a hammer and a feather falling at the same rate on the moon
E) determination of the rate of advance of the perihelion of Mercury's orbit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
What is the escape velocity from the Moon for a lunar landing module sitting on the Moon's surface? Hints: 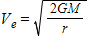 ;
;
The mass of the Moon is 7.2 × 1022 kg; its radius is 1738 km; G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kg
A) 2.3 m/s
B) 23 m/s
C) 2.3 km/s
D) 11 km/s
E) 23 km/s
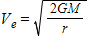 ;
;The mass of the Moon is 7.2 × 1022 kg; its radius is 1738 km; G = 6.67 10-11 m3/s2/kg
A) 2.3 m/s
B) 23 m/s
C) 2.3 km/s
D) 11 km/s
E) 23 km/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
According to the theory of general relativity, gravity is caused by the ____.
A) linear motion of stars
B) change in mass of a moving body
C) curvature of space-time
D) constant speed of light
E) inertia of a moving body
A) linear motion of stars
B) change in mass of a moving body
C) curvature of space-time
D) constant speed of light
E) inertia of a moving body

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Gravity obeys the inverse square law, which implies that the gravitational force of one body on another will be ____ times stronger at two meters than at six meters apart.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 9
E) 10
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 9
E) 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The apogee of a(n) ____ orbit does not exist.
A) closed
B) elliptical
C) geosynchronous
D) hyperbolic
E) parabolic
A) closed
B) elliptical
C) geosynchronous
D) hyperbolic
E) parabolic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A(n) ____ orbit is one where the orbiting object is always above the same location on Earth's surface.
A) closed
B) elliptical
C) geosynchronous
D) hyperbolic
E) parabolic
A) closed
B) elliptical
C) geosynchronous
D) hyperbolic
E) parabolic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The ____ of an object is a measure of the amount of matter it contains. The ____ is a measure of the gravitational force on an object.
A) weight; mass
B) mass; weight
C) energy; force
D) force; energy
E) momentum; energy
A) weight; mass
B) mass; weight
C) energy; force
D) force; energy
E) momentum; energy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Perigee is the point in ____.
A) the Moon's orbit when the Moon is farthest from Earth
B) an object's orbit around Earth when the object is closest to Earth
C) an object's orbit around Earth when the object is closest to the Sun
D) a planet's orbit when the planet is closest to its sun
E) a planet's orbit when the planet is farthest from its sun
A) the Moon's orbit when the Moon is farthest from Earth
B) an object's orbit around Earth when the object is closest to Earth
C) an object's orbit around Earth when the object is closest to the Sun
D) a planet's orbit when the planet is closest to its sun
E) a planet's orbit when the planet is farthest from its sun

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The circular velocity of a satellite orbiting Earth is given by https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX9273/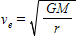 . In this equation, M represents the ____.
. In this equation, M represents the ____.
A) mass of the satellite, and r its radius
B) mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth to the satellite
C) mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth's surface to the satellite
D) mass of Earth, and r the radius of Earth
E) mass of Earth, and r is the distance from Earth to the satellite
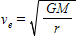 . In this equation, M represents the ____.
. In this equation, M represents the ____.A) mass of the satellite, and r its radius
B) mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth to the satellite
C) mass of the satellite, and r the distance from Earth's surface to the satellite
D) mass of Earth, and r the radius of Earth
E) mass of Earth, and r is the distance from Earth to the satellite

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The equivalence principle can be best illustrated by ____.
A) a person riding in an elevator
B) a rocket coasting through space at a constant velocity
C) the change in mass of a moving body
D) the formation of energy by nuclear fusion
E) a car ride on a highway with the windows open
A) a person riding in an elevator
B) a rocket coasting through space at a constant velocity
C) the change in mass of a moving body
D) the formation of energy by nuclear fusion
E) a car ride on a highway with the windows open

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Newtonian physics tells us that Kepler's second law is a result of the conservation of ____.
A) angular momentum
B) linear acceleration
C) energy
D) mass
E) velocity
A) angular momentum
B) linear acceleration
C) energy
D) mass
E) velocity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Newton concluded that some force must act on the Moon because ____.
A) a force is needed to pull the Moon away from straight-line motion
B) a force is needed to pull the Moon outward
C) a force is needed to keep the Moon in motion
D) the Moon has at a constant velocity
E) the Moon has a constant acceleration
A) a force is needed to pull the Moon away from straight-line motion
B) a force is needed to pull the Moon outward
C) a force is needed to keep the Moon in motion
D) the Moon has at a constant velocity
E) the Moon has a constant acceleration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which statement expresses Newton's first law of motion?
A) An object with no force on acting on it continues at rest or moves in uniform motion in a straight line with constant velocity.
B) An object with a force on it is accelerated in the direction of the force an amount inversely proportional to its mass and directly proportional to the size of the force.
C) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
D) The force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared.
E) The force between two objects is inversely proportional to the product of their masses and directly proportional to the distance between them squared.
A) An object with no force on acting on it continues at rest or moves in uniform motion in a straight line with constant velocity.
B) An object with a force on it is accelerated in the direction of the force an amount inversely proportional to its mass and directly proportional to the size of the force.
C) For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
D) The force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared.
E) The force between two objects is inversely proportional to the product of their masses and directly proportional to the distance between them squared.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
 Figure 5-15
Figure 5-15Consider the accompanying figure. Due to the curvature of space-time by the sun, light from stars that pass near the edge of the sun will ____.
A) be bent so that the stars appear further from the edge of the sun
B) be bent so that the stars appear closer to the edge of the sun
C) be bent so that the stars are no longer visible
D) be bent so that the stars will appear intermittently
E) not be affected by the curvature of space-time

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The importance of the general theory of relativity lies in its description of ____.
A) acceleration
B) gravity
C) mass
D) space-time
E) velocity
A) acceleration
B) gravity
C) mass
D) space-time
E) velocity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Kinetic energy refers to the energy of a(n)____.
A) stationary body
B) moving body
C) moon
D) gravitational field
E) object due to its position
A) stationary body
B) moving body
C) moon
D) gravitational field
E) object due to its position

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Einstein revolutionized modern physics by ____.
A) documenting the existence of gravity through experiments on objects in motion
B) proving that Galileo and Newton were fundamentally incorrect about gravity
C) explaining how specific gravity impacts the geometry of curved space-time
D) providing an explanation of gravity based on the geometry of curved space-time
E) defining the difference between violent motion and natural motion
A) documenting the existence of gravity through experiments on objects in motion
B) proving that Galileo and Newton were fundamentally incorrect about gravity
C) explaining how specific gravity impacts the geometry of curved space-time
D) providing an explanation of gravity based on the geometry of curved space-time
E) defining the difference between violent motion and natural motion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is an example of the conservation of angular momentum?
A) A volleyball player serves a ball and it follows a parabolic path.
B) A baseball player strikes the ball with the bat
C) A cross-country skier accelerates as she moves in a straight line
D) A skateboarder maintains the same velocity in the same direction
E) A diver brings his arms and legs closer to his body
A) A volleyball player serves a ball and it follows a parabolic path.
B) A baseball player strikes the ball with the bat
C) A cross-country skier accelerates as she moves in a straight line
D) A skateboarder maintains the same velocity in the same direction
E) A diver brings his arms and legs closer to his body

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The first postulate of special relativity states that ____.
A) observers can always detect their uniform motion relative to other objects
B) observers can never detect their uniform motion except relative to other objects
C) the speed of light is constant regardless of location
D) the speed of light in a vacuum is constant
E) energy equals mass multiplied by the speed of light, squared
A) observers can always detect their uniform motion relative to other objects
B) observers can never detect their uniform motion except relative to other objects
C) the speed of light is constant regardless of location
D) the speed of light in a vacuum is constant
E) energy equals mass multiplied by the speed of light, squared

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
As described by Kepler's second law, an object in an elliptical orbit reaches its highest velocity when it is as at ____.
A) lowest; perigree
B) highest; apogee
C) highest; perigree
D) lowest; apogee
E) escape velocity; perigree
A) lowest; perigree
B) highest; apogee
C) highest; perigree
D) lowest; apogee
E) escape velocity; perigree

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Newton's second law of motion is represented by ____.
A)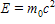
B)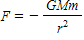
C)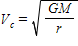
D)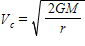
E)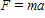
A)
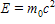
B)
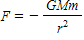
C)
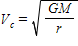
D)
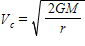
E)
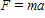

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Match between columns

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
How does gravity explain the presence of the tides we experience on Earth?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Explain why the term acceleration is important to the first postulate of special relativity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Newton's law of gravitational force states that ____.
A) an object with no force on acting on it continues at rest or moves in uniform motion in a straight line with constant velocity
B) an object with no force on it moves in a straight line with constant acceleration
C) for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
D) the force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared
E) an object with a force on it is accelerated in the direction of the force an amount inversely proportional to its mass and directly proportional to the size of the force
A) an object with no force on acting on it continues at rest or moves in uniform motion in a straight line with constant velocity
B) an object with no force on it moves in a straight line with constant acceleration
C) for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
D) the force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared
E) an object with a force on it is accelerated in the direction of the force an amount inversely proportional to its mass and directly proportional to the size of the force

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Describe two experiments that provide evidence of space-time curvature by the presence of a mass.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Explain why the spring and neap tides occur periodically.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Special relativity predicts that the observed mass of a moving particle depends on its ____.
A) inertia
B) curvature
C) velocity
D) force
E) true position
A) inertia
B) curvature
C) velocity
D) force
E) true position

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
An object's momentum is equal to its ____.
A) acceleration multiplied by its mass
B) acceleration divided by its weight
C) velocity multiplied by the gravitational constant
D) velocity multiplied by its mass
E) velocity divided by its weight
A) acceleration multiplied by its mass
B) acceleration divided by its weight
C) velocity multiplied by the gravitational constant
D) velocity multiplied by its mass
E) velocity divided by its weight

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The force due to the gravity between two objects depends on the ____,
A) combined mass and velocity of both objects
B) mass of each object and the distance between them
C) distance of each object from Earth and distance between them
D) speed of light and the distance of each object from Earth
E) mass of each object and the speed of light
A) combined mass and velocity of both objects
B) mass of each object and the distance between them
C) distance of each object from Earth and distance between them
D) speed of light and the distance of each object from Earth
E) mass of each object and the speed of light

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The second postulate of special relativity states that ____.
A) observers cannot detect their uniform motion except relative to other objects
B) observers cannot distinguish locally between inertial forces and uniform gravitational forces due to acceleration and the presence of a massive body
C) the laws of physics are the same for all observers regardless of their motion as long as their speed is constant
D) the speed of light is constant and will be the same for all observers independent of their motion relative to the light source
E) the acceleration of an object is proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to its mass
A) observers cannot detect their uniform motion except relative to other objects
B) observers cannot distinguish locally between inertial forces and uniform gravitational forces due to acceleration and the presence of a massive body
C) the laws of physics are the same for all observers regardless of their motion as long as their speed is constant
D) the speed of light is constant and will be the same for all observers independent of their motion relative to the light source
E) the acceleration of an object is proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to its mass

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
According to the inverse square law, the force due to gravity between two masses will ____.
A) increase as the distance between the two masses increases
B) decrease as the square of the distance between the two masses increases
C) cause the two masses to move away from each other
D) cause the two masses to move in a straight line
E) cause the two masses to orbit each other
A) increase as the distance between the two masses increases
B) decrease as the square of the distance between the two masses increases
C) cause the two masses to move away from each other
D) cause the two masses to move in a straight line
E) cause the two masses to orbit each other

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The _______________ states that an observer cannot distinguish locally the difference between inertial forces due to acceleration and uniform gravitational forces due to the presence of a massive object.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
How did Newton's Principia impact science?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The term _______________ refers to a change in velocity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
An object in a closed orbit under the influence of an attractive force that follows the inverse square law must behave a(n) _______________ path.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
How did Aristotle describe gravity and in what context?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The ______________ of the Moon's orbit is the location at which it is farthest from Earth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The velocity required to escape an astronomical body is known as the _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Newton's first law of motion was very similar to descriptions of motion proposed by _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Define and distinguish among the terms speed, velocity, and acceleration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
According to __________, _______________ motion occurs when natural motion has to be sustained by a force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The resistance of matter to changes in motion is known as _______________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Why does the circular velocity of an Earth satellite depend on the distance from Earth's center?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
How did Newton clarify prior laws of planetary motion?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
How can tidal forces affect the rotation of celestial bodies and their orbital motion?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
A ball is dropped from the top of a science building. After falling for three seconds, the speed of the ball would be _______________ m/sec.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
_______________ occur when tides caused by the Sun and Moon partially cancel out.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 76 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








