Deck 13: Chemical Kinetics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/148
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Chemical Kinetics
1
A sample of 0.200 moles of NO and 0.300 moles of Cl2 are placed in a 1.00 liter vessel at 400 K. The reaction 2 NO + Cl2→2 NOCl occurs and after 5 seconds measurements show that the [Cl2] has decreased to 0.290 M . Calculate D [NOCl]/ D t for this time interval, in units of mol/L × s.
A) 0.0040
B) - 0.0020
C) 0.0010
D) 0.0020
E) - 0.0040
A) 0.0040
B) - 0.0020
C) 0.0010
D) 0.0020
E) - 0.0040
0.0040
2
Exhibit 13-2 Use the data set below for the reaction of C4H9Cl with water to answer the following question(s). C4H9Cl + H2O→C4H9OH + HCl 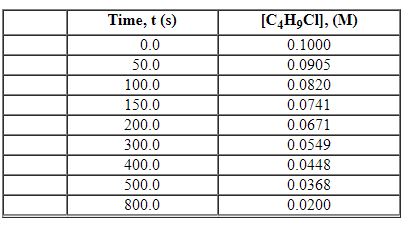
Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 0.0 seconds to 800.0 seconds?
A) 0.56×10 - 4 M/s
B) 1.00×10 - 4 M/s
C) 1.23×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.27×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.31×10 - 4 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 0.0 seconds to 800.0 seconds?
A) 0.56×10 - 4 M/s
B) 1.00×10 - 4 M/s
C) 1.23×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.27×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.31×10 - 4 M/s
1.00×10 - 4 M/s
3
Exhibit 13-3 Consider the following reaction and the corresponding time-concentration table to answer the following question(s). C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g) The concentration of ozone, O3, was monitored for this reaction as a function of time and is given in the table that follows 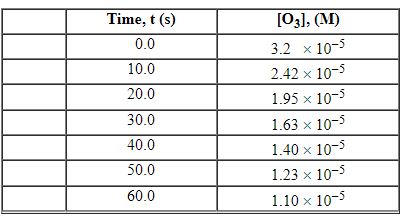
Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 20.0 seconds tO60.0 seconds?
A) 2.13×10 - 7 M/s
B) 3.5×10 - 7 M/s
C) 3.66×10 - 7 M/s
D) 1.83×10 - 6 M/s
E) 1.40×10 - 5 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 20.0 seconds tO60.0 seconds?
A) 2.13×10 - 7 M/s
B) 3.5×10 - 7 M/s
C) 3.66×10 - 7 M/s
D) 1.83×10 - 6 M/s
E) 1.40×10 - 5 M/s
2.13×10 - 7 M/s
4
Exhibit 13-3 Consider the following reaction and the corresponding time-concentration table to answer the following question(s). C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g) The concentration of ozone, O3, was monitored for this reaction as a function of time and is given in the table that follows. 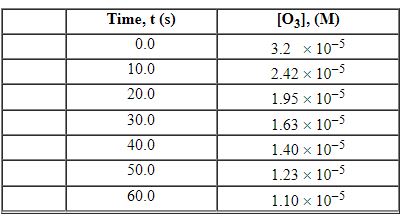
Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 10.0 seconds tO5 0.0 seconds?
A) 2.98×10 - 7 M/s
B) 9.13×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.63×10 - 5 M/s
D) 1.73×10 - 5 M/s
E) 1.83×10 - 5 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 10.0 seconds tO5 0.0 seconds?
A) 2.98×10 - 7 M/s
B) 9.13×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.63×10 - 5 M/s
D) 1.73×10 - 5 M/s
E) 1.83×10 - 5 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Exhibit 13-2 Use the data set below for the reaction of C4H9Cl with water to answer the following question(s). C4H9Cl + H2O→C4H9OH +HCl 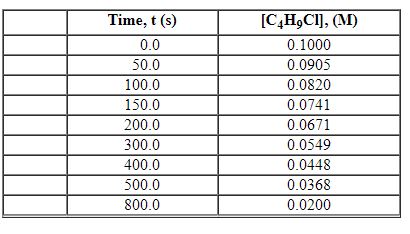
Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 150.0 seconds to 300.0 seconds?
A) 3.80×10 - 5 M/s
B) 1.01×10 - 4 M/s
C) 3.36×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.28×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.60×10 - 4 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 150.0 seconds to 300.0 seconds?
A) 3.80×10 - 5 M/s
B) 1.01×10 - 4 M/s
C) 3.36×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.28×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.60×10 - 4 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following would increase the rate of the following reaction?
C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g)
I. Add more O3 to this reaction.
II. Decrease the temperature.
III. Add a catalyst.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g)
I. Add more O3 to this reaction.
II. Decrease the temperature.
III. Add a catalyst.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Exhibit 13-3 Consider the following reaction and the corresponding time-concentration table to answer the following question(s). C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g) The concentration of ozone, O3, was monitored for this reaction as a function of time and is given in the table that follows 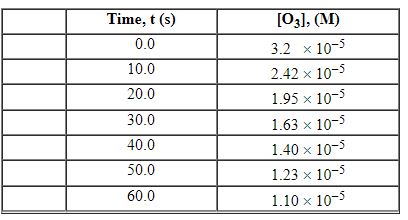
Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 20.0 seconds tO60.0 seconds?
A) 2.13×10 - 7 M/s
B) 3.5×10 - 7 M/s
C) 3.66×10 - 7 M/s
D) 1.83×10 - 6 M/s
E) 1.40×10 - 5 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 20.0 seconds tO60.0 seconds?
A) 2.13×10 - 7 M/s
B) 3.5×10 - 7 M/s
C) 3.66×10 - 7 M/s
D) 1.83×10 - 6 M/s
E) 1.40×10 - 5 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Exhibit 13-2 Use the data set below for the reaction of C4H9Cl with water to answer the following question(s). C4H9Cl + H2O→C4H9OH + HCl 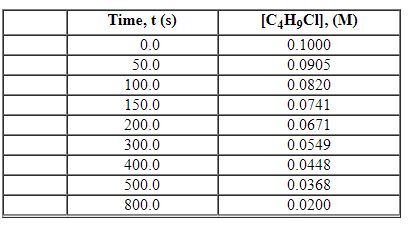
Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 50.0 seconds tO5 00.0 seconds?
A) 0.560×10 - 4 M/s
B) 0.800×10 - 4 M/s
C) 1.13×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.19×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.70×10 - 4 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 50.0 seconds tO5 00.0 seconds?
A) 0.560×10 - 4 M/s
B) 0.800×10 - 4 M/s
C) 1.13×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.19×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.70×10 - 4 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Consider the reaction in aqueous solution:
3 I - + S2O82 - →I3 - + 2 SO42 - . Under a given set of conditions, the concentration of I3 - changes from 0 to 7.6×10 - 4 M in 20 seconds. Calculate D [I - ]/ D t (in mol/L × s) for this time interval.
A) 3.8×10 - 5
B) - 2.5×10 - 5
C) - 3.8×10 - 5
D) - 1.1×10 - 4
E) 7.6×10 - 5
3 I - + S2O82 - →I3 - + 2 SO42 - . Under a given set of conditions, the concentration of I3 - changes from 0 to 7.6×10 - 4 M in 20 seconds. Calculate D [I - ]/ D t (in mol/L × s) for this time interval.
A) 3.8×10 - 5
B) - 2.5×10 - 5
C) - 3.8×10 - 5
D) - 1.1×10 - 4
E) 7.6×10 - 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Exhibit 13-2 Use the data set below for the reaction of C4H9Cl with water to answer the following question(s). C4H9Cl + H2O→C4H9OH + HCl 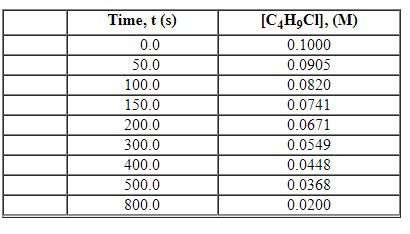
Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 100.0 seconds tO400.0 seconds?
A) 0.800×10 - 4 M/s
B) 1.01×10 - 4 M/s
C) 1.20×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.24×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.60×10 - 4 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-2. What is the average rate of reaction over the time interval from 100.0 seconds tO400.0 seconds?
A) 0.800×10 - 4 M/s
B) 1.01×10 - 4 M/s
C) 1.20×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.24×10 - 4 M/s
E) 1.60×10 - 4 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The diagram below is a time-concentration curve for the reaction CO₂ (g) C (s) + O₂(g). What is the average rate at which CO₂ (g) disappears over the first 25 minutes of the reaction?
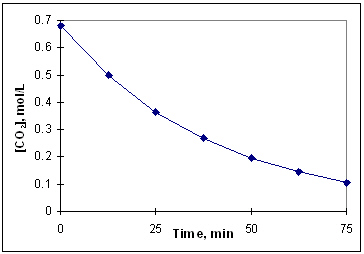
A) 0.34 mol/L × min
B) 0.17 mol/L × s
C) 0.04 mol/L × min
D) 0.68 mol/L × hr
E) 0.014 mol/L × min

A) 0.34 mol/L × min
B) 0.17 mol/L × s
C) 0.04 mol/L × min
D) 0.68 mol/L × hr
E) 0.014 mol/L × min

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The following are factors that influence the rate of a reaction. Which are stated correctly?
I. The rate increases when the concentration of reactants decreases.
II. The rate increases when a catalyst is added.
III. The rate increases when the temperature increases.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. The rate increases when the concentration of reactants decreases.
II. The rate increases when a catalyst is added.
III. The rate increases when the temperature increases.
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The rate of a chemical reaction may be influenced by:
A) temperature.
B) concentrations of substances.
C) nature or composition of the substances.
D) stirring the reaction.
E) all of these.
A) temperature.
B) concentrations of substances.
C) nature or composition of the substances.
D) stirring the reaction.
E) all of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Exhibit 13-3 Consider the following reaction and the corresponding time-concentration table to answer the following question(s). C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g) The concentration of ozone, O3, was monitored for this reaction as a function of time and is given in the table that follows. 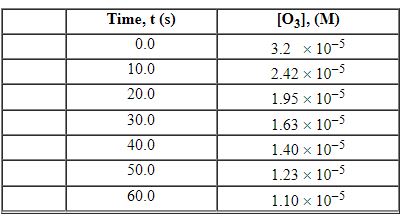
Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 40.0 seconds tO60 seconds?
A) 1.50×10 - 7 M/s
B) 6.25×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.10×10 - 5 M/s
D) 1.25×10 - 5 M/s
E) 1.40×10 - 5 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 40.0 seconds tO60 seconds?
A) 1.50×10 - 7 M/s
B) 6.25×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.10×10 - 5 M/s
D) 1.25×10 - 5 M/s
E) 1.40×10 - 5 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Exhibit 13-1 This graph shows the concentration vs. time data needed for the following question(s). 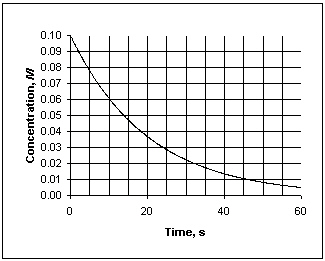
Refer to Exhibit 13-1. What is the average rate at which concentration decreases, measured between 10 and 30 seconds?
A) 530 mol/L × s
B) 1.9×10 - 3 mol/L × s
C) - 1.9×10 - 4 mol/L × s
D) - 530 mol/L × s
E) cannot answer from the data given

Refer to Exhibit 13-1. What is the average rate at which concentration decreases, measured between 10 and 30 seconds?
A) 530 mol/L × s
B) 1.9×10 - 3 mol/L × s
C) - 1.9×10 - 4 mol/L × s
D) - 530 mol/L × s
E) cannot answer from the data given

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Exhibit 13-3 Consider the following reaction and the corresponding time-concentration table to answer the following question(s). C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g) The concentration of ozone, O3, was monitored for this reaction as a function of time and is given in the table that follows. 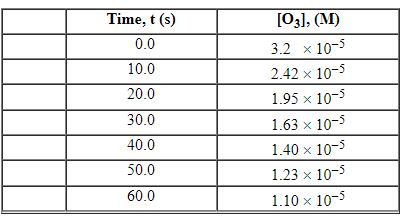
Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 0.00 seconds tO5 0.0 seconds?
A) 3.94×10 - 7 M/s
B) 8.86×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.17×10 - 5 M/s
D) 2.22×10 - 5 M/s
E) 3.18×10 - 5 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 0.00 seconds tO5 0.0 seconds?
A) 3.94×10 - 7 M/s
B) 8.86×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.17×10 - 5 M/s
D) 2.22×10 - 5 M/s
E) 3.18×10 - 5 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Exhibit 13-3 Consider the following reaction and the corresponding time-concentration table to answer the following question(s). C2H4 (g) + O3 (g)→C2H4O (g) + O2 (g) The concentration of ozone, O3, was monitored for this reaction as a function of time and is given in the table that follows 
Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 10.0 seconds tO5 0.0 seconds?
A) 2.98×10 - 7 M/s
B) 9.13×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.63×10 - 5 M/s
D) 1.73×10 - 5 M/s
E) 1.83×10 - 5 M/s

Refer to Exhibit 13-3. What is the average rate for the time interval from 10.0 seconds tO5 0.0 seconds?
A) 2.98×10 - 7 M/s
B) 9.13×10 - 7 M/s
C) 1.63×10 - 5 M/s
D) 1.73×10 - 5 M/s
E) 1.83×10 - 5 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Exhibit 13-1 This graph shows the concentration vs. time data needed for the following question(s). 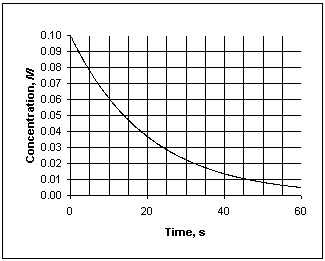
Refer to Exhibit 13-1. What is the instantaneous rate at which concentration decreases at 30 s?
A) - 1.1×10 - 4 mol/L × s
B) - 1.1×10 - 2 mol/L × s
C) 1.1×10 - 3 mol/L × s
D) 893 mol/L × s
E) cannot answer from the data given

Refer to Exhibit 13-1. What is the instantaneous rate at which concentration decreases at 30 s?
A) - 1.1×10 - 4 mol/L × s
B) - 1.1×10 - 2 mol/L × s
C) 1.1×10 - 3 mol/L × s
D) 893 mol/L × s
E) cannot answer from the data given

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The rate of reaction is influenced by:
A) concentration of the reactants.
B) temperature.
C) time.
D) none of these.
E) more than one of these.
A) concentration of the reactants.
B) temperature.
C) time.
D) none of these.
E) more than one of these.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Oxygen gas is formed by the following reaction:
2 NO (g)→O2 (g) + N2 (g). If during a given time period the rate of formation of O2 is 0.054 mol/L × s, what is D [NO]/ D t in mol/L × s?
A) 0.054
B) - 0.054
C) 0.11
D) - 0.11
E) - 0.027
2 NO (g)→O2 (g) + N2 (g). If during a given time period the rate of formation of O2 is 0.054 mol/L × s, what is D [NO]/ D t in mol/L × s?
A) 0.054
B) - 0.054
C) 0.11
D) - 0.11
E) - 0.027

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which units listed below is the best choice for a rate constant, k , of a second order rate law?
Rate = k [A]2
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1
Rate = k [A]2
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What units would be used for the rate constant , k , of a third order rate law ?
A) M/sec
B) M3/sec3
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1
A) M/sec
B) M3/sec3
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Consider the following reaction. 3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g) At a given instant, the rate of disappearance of [O2] is 2.35×10 - 5 M/sec. What is the rate of appearance of [O3] for this reaction at this moment?
A) 1.57×10 - 5 M/sec
B) 2.35×10 - 5 M/sec
C) 3.53×10 - 5 M/sec
D) 4.70×10 - 5 M/sec
E) 7.05×10 - 5 M/sec
A) 1.57×10 - 5 M/sec
B) 2.35×10 - 5 M/sec
C) 3.53×10 - 5 M/sec
D) 4.70×10 - 5 M/sec
E) 7.05×10 - 5 M/sec

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Consider the following unbalanced reaction :
NO (g) + O2 (g)→N2O3 (g) After balancing this reaction, how fast is [O2] decreasing when [NO] is decreasing at a rate of 1.60×10 - 4 mol/L × sec?
A) 4.0×10 - 5 mol/L × sec
B) 8.0×10 - 5 mol/L × sec
C) 1.6×10 - 4 mol/L × sec
D) 3.2×10 - 4 mol/L × sec
E) 6.4×10 - 4 mol/L × sec
NO (g) + O2 (g)→N2O3 (g) After balancing this reaction, how fast is [O2] decreasing when [NO] is decreasing at a rate of 1.60×10 - 4 mol/L × sec?
A) 4.0×10 - 5 mol/L × sec
B) 8.0×10 - 5 mol/L × sec
C) 1.6×10 - 4 mol/L × sec
D) 3.2×10 - 4 mol/L × sec
E) 6.4×10 - 4 mol/L × sec

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Consider the combustion of methane as shown below:
CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g)→CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) What is the rate expression for each substance in this equation?
A) Rate = -D [CH4]/ D t = -D [O2]/ D t = D [CO2]/ D t = D [H2O]/ D t
B) Rate = -D [CH4]/ D t = -D [O2]/2 D t = D [CO2]/ D t = D [H2O]/2 D t
C) Rate = D [CH4]/ D t = D [O2]/ D t = -D [CO2]/ D t = -D [H2O]/ D t
D) Rate = -D [CH4]/ D t = - 2 D [O2]/ D t = D [CO2]/ D t = 2 D [H2O]/ D t
E) Rate = -D [CH4]/2 D t = - 2 D [O2]/ D t = D [CO2]/2 D t = 2 D [H2O]/ D t
CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g)→CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) What is the rate expression for each substance in this equation?
A) Rate = -D [CH4]/ D t = -D [O2]/ D t = D [CO2]/ D t = D [H2O]/ D t
B) Rate = -D [CH4]/ D t = -D [O2]/2 D t = D [CO2]/ D t = D [H2O]/2 D t
C) Rate = D [CH4]/ D t = D [O2]/ D t = -D [CO2]/ D t = -D [H2O]/ D t
D) Rate = -D [CH4]/ D t = - 2 D [O2]/ D t = D [CO2]/ D t = 2 D [H2O]/ D t
E) Rate = -D [CH4]/2 D t = - 2 D [O2]/ D t = D [CO2]/2 D t = 2 D [H2O]/ D t

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Consider the following reaction:
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)→2 NH3 (g) What is the rate expression for each substance in this equation?
A) Rate = D [N2]/ D t = D [H2]/ D t = D [NH3]/ D t
B) Rate = D [N2]/ D t = D [H2]/3 D t = D [NH3]/2 D t
C) Rate = -D [N2]/ D t = -D [H2]/3 D t = D [NH3]/2 D t
D) Rate = D [N2]/ D t = 3 D [H2]/ D t = - 2 D [NH3]/ D t
E) Rate = -D [N2]/ D t = - 3 D [H2]/ D t = 2 D [NH3]/ D t
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)→2 NH3 (g) What is the rate expression for each substance in this equation?
A) Rate = D [N2]/ D t = D [H2]/ D t = D [NH3]/ D t
B) Rate = D [N2]/ D t = D [H2]/3 D t = D [NH3]/2 D t
C) Rate = -D [N2]/ D t = -D [H2]/3 D t = D [NH3]/2 D t
D) Rate = D [N2]/ D t = 3 D [H2]/ D t = - 2 D [NH3]/ D t
E) Rate = -D [N2]/ D t = - 3 D [H2]/ D t = 2 D [NH3]/ D t

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations. ![<strong>Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations. Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [B]?</strong> A) 1 B) 2 C) 0 D) - 1 E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a4_765c_8da6_01779faac67a_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [B]?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 0
D) - 1
E) none of these
![<strong>Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations. Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [B]?</strong> A) 1 B) 2 C) 0 D) - 1 E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a4_765c_8da6_01779faac67a_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [B]?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 0
D) - 1
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If the unit for a particular rate constant is M - 1sec - 1, what is the order of the rate law?
A) zero order
B) 1st order
C) 2nd order
D) 3rd order
E) - 1 order
A) zero order
B) 1st order
C) 2nd order
D) 3rd order
E) - 1 order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations ![<strong>Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [A]?</strong> A) 1 B) 2 C) 0 D) - 1 E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a4_4f4b_8da6_29f37bfa8fc4_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [A]?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 0
D) - 1
E) none of these
![<strong>Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [A]?</strong> A) 1 B) 2 C) 0 D) - 1 E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a4_4f4b_8da6_29f37bfa8fc4_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What is the order of this reaction in [A]?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 0
D) - 1
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Consider the following unbalanced reaction :
NO (g) + O2 (g)→N2O3 (g) After balancing this reaction, how is the rate expressions for each substance in this equation related?
A) Rate = D [NO]/ D t = D [O2]/ D t = D [N2O3]/ D t
B) Rate = -D [NO]/ D t = -D [O2]/3 D t = D [N2O3]/2 D t
C) Rate = - 2 D [NO]/ D t = -D [O2]/3 D t = D [N2O3]/2 D t
D) Rate = 4 D [NO]/ D t = D [O2]/ D t = - 2 D [N2O3]/ D t
E) Rate = -D [NO]/4 D t = -D [O2]/ D t = D [N2O3]/2 D t
NO (g) + O2 (g)→N2O3 (g) After balancing this reaction, how is the rate expressions for each substance in this equation related?
A) Rate = D [NO]/ D t = D [O2]/ D t = D [N2O3]/ D t
B) Rate = -D [NO]/ D t = -D [O2]/3 D t = D [N2O3]/2 D t
C) Rate = - 2 D [NO]/ D t = -D [O2]/3 D t = D [N2O3]/2 D t
D) Rate = 4 D [NO]/ D t = D [O2]/ D t = - 2 D [N2O3]/ D t
E) Rate = -D [NO]/4 D t = -D [O2]/ D t = D [N2O3]/2 D t

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
If the reaction A + B→C has the rate law:
Rate = k [A]2[B], the units of the rate constant are:
A) s - 1
B) mol/L × s
C) L/mol × s
D) L2/mol2 × s
E) L3/mol3 × s
Rate = k [A]2[B], the units of the rate constant are:
A) s - 1
B) mol/L × s
C) L/mol × s
D) L2/mol2 × s
E) L3/mol3 × s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Consider the following unbalanced reaction :
NO (g) + O2 (g)→N2O3 (g) How fast is N2O3 being formed when the [NO] is disappearing at a rate of 3.2×10 - 4 M/s?
A) 4.0×10 - 5 M/s
B) 1.6×10 - 4 M/s
C) 3.2×10 - 4 M/s
D) 6.4×10 - 4 M/s
E) 2.6×10 - 3 M/s
NO (g) + O2 (g)→N2O3 (g) How fast is N2O3 being formed when the [NO] is disappearing at a rate of 3.2×10 - 4 M/s?
A) 4.0×10 - 5 M/s
B) 1.6×10 - 4 M/s
C) 3.2×10 - 4 M/s
D) 6.4×10 - 4 M/s
E) 2.6×10 - 3 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The reaction A + B→C gave the following initial rate data:
Rate [A] [B] (mol/L × s) 0.03 0.03 3.0×10 - 4 0.06 0.06 1.2×10 - 3 0.06 0.09 2.7×10 - 3 The rate law for this reaction is:
Rate =
A) k [B]2
B) k [A][B]2
C) k [A][B] - 3
D) k [A]2
E) k [A]2[B]
Rate [A] [B] (mol/L × s) 0.03 0.03 3.0×10 - 4 0.06 0.06 1.2×10 - 3 0.06 0.09 2.7×10 - 3 The rate law for this reaction is:
Rate =
A) k [B]2
B) k [A][B]2
C) k [A][B] - 3
D) k [A]2
E) k [A]2[B]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
For the aqueous reaction 2 Cr3+ + 3 IO4 - + 10 OH - →2 CrO42 - + 3 IO3 - + 5 H2O, under a given set of conditions, the rate of appearance of CrO42 - is 3.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s. What is the rate of disappearance of IO4 - ?
A) 2.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s
B) 3.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s
C) 4.5×10 - 4 mol/L × s
D) 6.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s
E) none of these
A) 2.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s
B) 3.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s
C) 4.5×10 - 4 mol/L × s
D) 6.0×10 - 4 mol/L × s
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The decomposition of N2O5 proceeds according to the following equation:
2 N2O5 (g)→4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g) If the rate of decomposition of N2O5 at a particular instant in a reaction vessel is 5.3×10 - 5 M/s, what is the rate of appearance of NO2?
A) 5.3×10 - 5 M/s
B) 2.7×10 - 5 M/s
C) 1.1×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.3×10 - 5 M/s
E) 2.1×10 - 4 M/s
2 N2O5 (g)→4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g) If the rate of decomposition of N2O5 at a particular instant in a reaction vessel is 5.3×10 - 5 M/s, what is the rate of appearance of NO2?
A) 5.3×10 - 5 M/s
B) 2.7×10 - 5 M/s
C) 1.1×10 - 4 M/s
D) 1.3×10 - 5 M/s
E) 2.1×10 - 4 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Consider the conversion of oxygen, O2, to ozone, O3, as shown below:
3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g) How is the rate expression for oxygen related to the rate expression for ozone?
A) Rate = -D [O2]/ D t = D [O3]/ D t
B) Rate = -D [O2]/2 D t = D [O3]/3 D t
C) Rate = -D [O2]/3 D t = D [O3]/2 D t
D) Rate = - 3 D [O2]/ D t = 2 D [O3]/ D t
E) Rate = 3 D [O2]/ D t = - 2 D [O3]/2 D t
3 O2 (g)→2 O3 (g) How is the rate expression for oxygen related to the rate expression for ozone?
A) Rate = -D [O2]/ D t = D [O3]/ D t
B) Rate = -D [O2]/2 D t = D [O3]/3 D t
C) Rate = -D [O2]/3 D t = D [O3]/2 D t
D) Rate = - 3 D [O2]/ D t = 2 D [O3]/ D t
E) Rate = 3 D [O2]/ D t = - 2 D [O3]/2 D t

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Exhibit 13-5 Use the data below for NO + Cl2→NOCl2 to answer the following question(s):
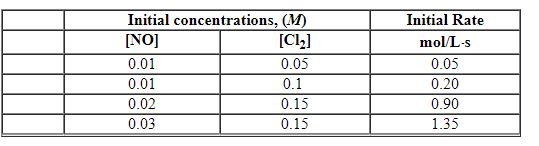
Refer to Exhibit 13-5. The order in Cl2 is:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) zero
E) none of these

Refer to Exhibit 13-5. The order in Cl2 is:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) zero
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Exhibit 13-5 Use the data below for NO + Cl2→NOCl2 to answer the following question(s):
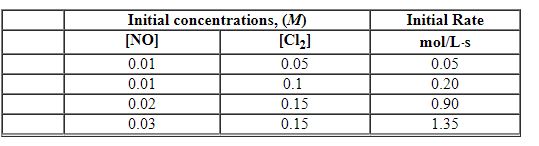
Refer to Exhibit 13-5. The order in NO is:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) zero
E) none of these

Refer to Exhibit 13-5. The order in NO is:
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) zero
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
For the reaction 2 O3 (g)→3 O2 (g), under a given set of conditions the rate of appearance of O2 is 6.1×10 - 5 mol/L × s. What is the rate of the disappearance of O3 under the same conditions?
A) 2.0×10 - 5 mol/L × s
B) 4.1×10 - 5 mol/L × s
C) 1.2×10 - 4 mol/L × s
D) 6.1×10 - 5 mol/L × s
E) none of these
A) 2.0×10 - 5 mol/L × s
B) 4.1×10 - 5 mol/L × s
C) 1.2×10 - 4 mol/L × s
D) 6.1×10 - 5 mol/L × s
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Exhibit 13-4 Use the information below for the reaction 2 A + B→C to answer the following question(s). Initial rates were measured at different molar concentrations. 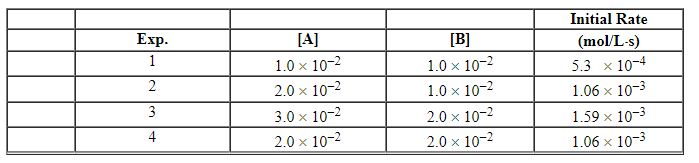
Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What units are appropriate for the specific rate constant in the rate law?
A) L/mol × s
B) s - 1
C) mol/L × s
D) The rate constant is dimensionless.
E) none of these

Refer to Exhibit 13-4. What units are appropriate for the specific rate constant in the rate law?
A) L/mol × s
B) s - 1
C) mol/L × s
D) The rate constant is dimensionless.
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 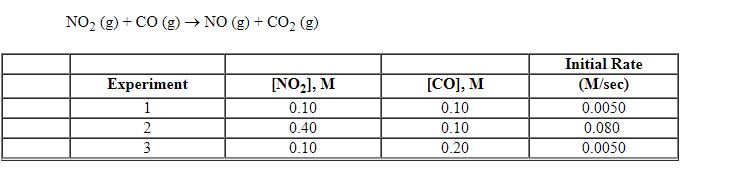
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. Which units listed below is the best choice for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

Refer to Exhibit 13-8. Which units listed below is the best choice for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Exhibit 13-6 The following question(s)
Refer to the table of experimental initial rate data below.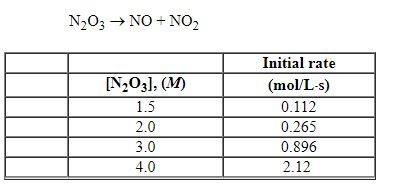
Refer to Exhibit 13-6. The overall order of the reaction is:
A) 1st
B) 2nd
C) 3rd
D) 4th
E) zero
Refer to the table of experimental initial rate data below.

Refer to Exhibit 13-6. The overall order of the reaction is:
A) 1st
B) 2nd
C) 3rd
D) 4th
E) zero

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). ![<strong>Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>][CO] B) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>][CO]<sup>2</sup> C) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] D) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_2421_8da6_0b645396511e_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [NO2][CO]
B) Rate = k [NO2][CO]2
C) Rate = k [NO2]2[CO]
D) Rate = k [NO2]2[CO]2
E) Rate = k [NO2]2
![<strong>Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>][CO] B) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>][CO]<sup>2</sup> C) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] D) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_2421_8da6_0b645396511e_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [NO2][CO]
B) Rate = k [NO2][CO]2
C) Rate = k [NO2]2[CO]
D) Rate = k [NO2]2[CO]2
E) Rate = k [NO2]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A reaction follows the rate law:
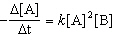 The overall order of the reaction is:
The overall order of the reaction is:
A) 1st
B) 2nd
C) 3rd
D) impossible rate law
E) none of these
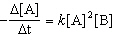 The overall order of the reaction is:
The overall order of the reaction is:A) 1st
B) 2nd
C) 3rd
D) impossible rate law
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 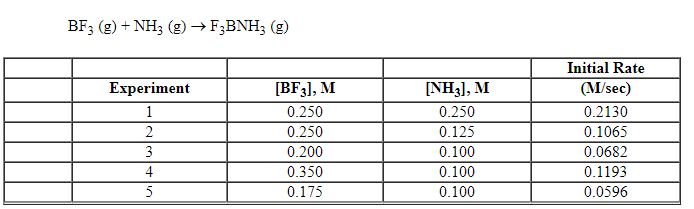
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the overall order of the rate law above?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the overall order of the rate law above?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 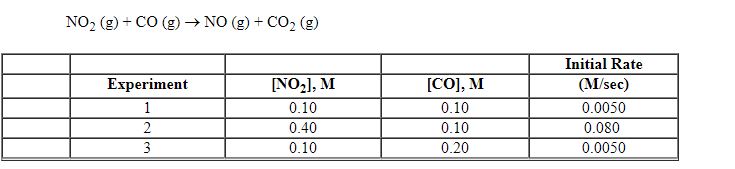
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the overall order of the rate law above?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the overall order of the rate law above?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
For NO + NO2 + O2→NO3 + NO2, the initial rate data in the table were collected. Initial Rate Expt. No. [NO], ( M ) [NO2], ( M ) [O2], ( M ) (mol/L × s) 1 1.0 0.5 0.1 0.250 2 2.0 0.5 0.1 0.500 3 2.0 1.0 0.1 2.00 4 2.0 0.5 0.2 0.500 5 2.0 2.0 0.2 8.00 The order of the reaction with respect to each reactant is:
NO NO2 O2
A) 1st 2nd 0
B) 1st 1st 1st
C) 2nd 1st 2nd
D) 0 0 1st
E) 1st 2nd 2nd
NO NO2 O2
A) 1st 2nd 0
B) 1st 1st 1st
C) 2nd 1st 2nd
D) 0 0 1st
E) 1st 2nd 2nd

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 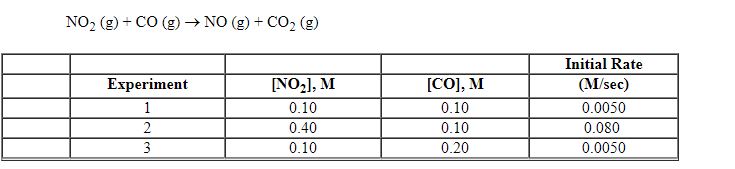
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the numerical value for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) 5.0×10 - 5
B) 0.50
C) 2.0
D) 5.0
E) 50

Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the numerical value for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) 5.0×10 - 5
B) 0.50
C) 2.0
D) 5.0
E) 50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). ![<strong>Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [BF<sub>3</sub>] = 0.500 M and [NH<sub>3</sub>] = 0.500 M?</strong> A) 0.213 M/sec B) 0.25 M/sec C) 0.426 M/sec D) 0.852 M/sec E) 3.41 M/sec](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_2420_8da6_99ad5ae87320_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [BF3] = 0.500 M and [NH3] = 0.500 M?
A) 0.213 M/sec
B) 0.25 M/sec
C) 0.426 M/sec
D) 0.852 M/sec
E) 3.41 M/sec
![<strong>Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [BF<sub>3</sub>] = 0.500 M and [NH<sub>3</sub>] = 0.500 M?</strong> A) 0.213 M/sec B) 0.25 M/sec C) 0.426 M/sec D) 0.852 M/sec E) 3.41 M/sec](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_2420_8da6_99ad5ae87320_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [BF3] = 0.500 M and [NH3] = 0.500 M?
A) 0.213 M/sec
B) 0.25 M/sec
C) 0.426 M/sec
D) 0.852 M/sec
E) 3.41 M/sec

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The reaction CO + Cl2→COCl2 was studied by the initial rate method and the following data were obtained:
![<strong>The reaction CO + Cl<sub>2</sub>→COCl<sub>2</sub> was studied by the initial rate method and the following data were obtained: The rate law is:</strong> A) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) Rate = k [CO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [Cl<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a4_eb92_8da6_9564512072ff_TBX8714_00.jpg) The rate law is:
The rate law is:
A) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]
B) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]1/2
C) Rate = k [CO]2[Cl2]
D) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]2
E) Rate = k [Cl2]
![<strong>The reaction CO + Cl<sub>2</sub>→COCl<sub>2</sub> was studied by the initial rate method and the following data were obtained: The rate law is:</strong> A) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) Rate = k [CO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [Cl<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a4_eb92_8da6_9564512072ff_TBX8714_00.jpg) The rate law is:
The rate law is:A) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]
B) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]1/2
C) Rate = k [CO]2[Cl2]
D) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]2
E) Rate = k [Cl2]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The following table of data was obtained for the gas phase reaction:
 What is the rate law?
What is the rate law?
A) Rate =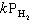
B) Rate =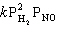
C) Rate =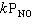
D) Rate =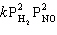
E) Rate =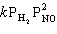
 What is the rate law?
What is the rate law?A) Rate =
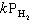
B) Rate =
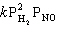
C) Rate =
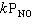
D) Rate =
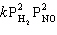
E) Rate =
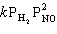

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 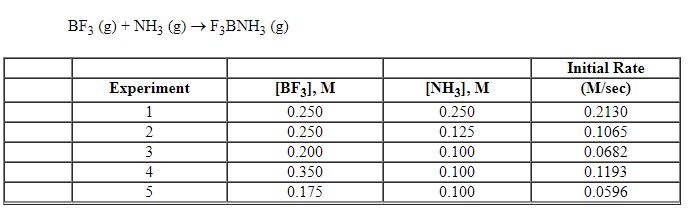
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the numerical value for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) 0.852
B) 3.41
C) 13.6
D) 54.5
E) 109

Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the numerical value for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) 0.852
B) 3.41
C) 13.6
D) 54.5
E) 109

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Exhibit 13-6 The following question(s)
Refer to the table of experimental initial rate data below.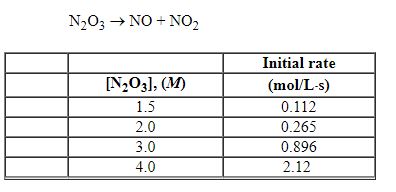
Refer to Exhibit 13-6. The value of the rate constant is:
A) 0.033
B) 0.11
C) 0.26
D) 0.33
E) 3.3
Refer to the table of experimental initial rate data below.

Refer to Exhibit 13-6. The value of the rate constant is:
A) 0.033
B) 0.11
C) 0.26
D) 0.33
E) 3.3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
For H2O2 + 3 I - + 2 H+→2 H2O + I3 - , the effect on the rate of reaction brought about by doubling the concentration of I - without changing the other concentrations would be:
A) increase by a factor of 3.
B) increase by a factor of 8.
C) decrease by a factor of 1/3.
D) increase by a factor of 9.
E) cannot be determined from information given.
A) increase by a factor of 3.
B) increase by a factor of 8.
C) decrease by a factor of 1/3.
D) increase by a factor of 9.
E) cannot be determined from information given.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The following table of initial rate data was obtained for: ![<strong>The following table of initial rate data was obtained for: The rate law is:</strong> A) Rate = k [MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup> B) Rate = k [H<sub>3</sub>IO<sub>6</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] C) Rate = k [MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>3</sub>IO<sub>6</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] D) Rate = k [MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>][H<sub>3</sub>IO<sub>6</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a5_12a4_8da6_d9f416605d37_TBX8714_00.jpg) The rate law is:
The rate law is:
A) Rate = k [MnO42 - ]2
B) Rate = k [H3IO62 - ]
C) Rate = k [MnO42 - ]2[H3IO62 - ]
D) Rate = k [MnO42 - ][H3IO62 - ]
E) none of these
![<strong>The following table of initial rate data was obtained for: The rate law is:</strong> A) Rate = k [MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup> B) Rate = k [H<sub>3</sub>IO<sub>6</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] C) Rate = k [MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>3</sub>IO<sub>6</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] D) Rate = k [MnO<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>][H<sub>3</sub>IO<sub>6</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a5_12a4_8da6_d9f416605d37_TBX8714_00.jpg) The rate law is:
The rate law is:A) Rate = k [MnO42 - ]2
B) Rate = k [H3IO62 - ]
C) Rate = k [MnO42 - ]2[H3IO62 - ]
D) Rate = k [MnO42 - ][H3IO62 - ]
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is the overall reaction order for the reaction that obeys the rate law below?
Rate = k [O3]2[O2] - 1
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 0
E) - 1
Rate = k [O3]2[O2] - 1
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 0
E) - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). ![<strong>Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>][NH<sub>3</sub>] B) Rate = k [F<sub>3</sub>BNH<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[NH<sub>3</sub>] D) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a5_aeec_8da6_1f46e94dcb11_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [BF3][NH3]
B) Rate = k [F3BNH3]
C) Rate = k [BF3]2[NH3]
D) Rate = k [BF3]2[NH3]2
E) Rate = k [BF3]2
![<strong>Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>][NH<sub>3</sub>] B) Rate = k [F<sub>3</sub>BNH<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[NH<sub>3</sub>] D) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [BF<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a5_aeec_8da6_1f46e94dcb11_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [BF3][NH3]
B) Rate = k [F3BNH3]
C) Rate = k [BF3]2[NH3]
D) Rate = k [BF3]2[NH3]2
E) Rate = k [BF3]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Exhibit 13-7 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 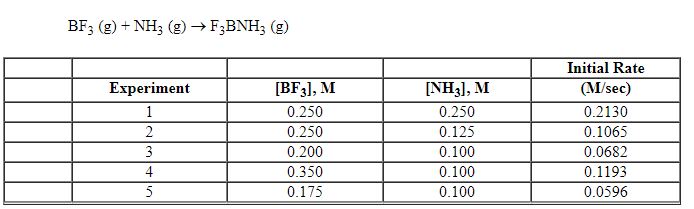
Refer to Exhibit 13-7. Which units listed below is the best choice for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

Refer to Exhibit 13-7. Which units listed below is the best choice for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The reaction 2 O3→3 O2 has the rate law:
Rate = k [O3]2[O2] - 1 Calculate k , given that the rate of the reaction is 2.8×10 - 4 mol/L × s for the initial concentrations [O3]o = 0.050 M and [O2]o = 0.010 M .
A) 1.1×10 - 3 s - 1
B) 5.6×10 - 5 s - 1
C) 5.6×10 - 7 s - 1
D) 1.4×10 - 3 s - 1
E) 7.0×10 - 9 s - 1
Rate = k [O3]2[O2] - 1 Calculate k , given that the rate of the reaction is 2.8×10 - 4 mol/L × s for the initial concentrations [O3]o = 0.050 M and [O2]o = 0.010 M .
A) 1.1×10 - 3 s - 1
B) 5.6×10 - 5 s - 1
C) 5.6×10 - 7 s - 1
D) 1.4×10 - 3 s - 1
E) 7.0×10 - 9 s - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The following initial rate data were collected for the reaction:
![<strong>The following initial rate data were collected for the reaction: The rate law is:</strong> A) Rate = k [No]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> B) Rate = k [NO][H<sub>2</sub>] C) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [NO][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a5_12a3_8da6_a30893ccb56a_TBX8714_00.jpg) The rate law is:
The rate law is:
A) Rate = k [No]2[H2]2
B) Rate = k [NO][H2]
C) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]
D) Rate = k [NO][H2]2
E) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]2
![<strong>The following initial rate data were collected for the reaction: The rate law is:</strong> A) Rate = k [No]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> B) Rate = k [NO][H<sub>2</sub>] C) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [NO][H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a5_12a3_8da6_a30893ccb56a_TBX8714_00.jpg) The rate law is:
The rate law is:A) Rate = k [No]2[H2]2
B) Rate = k [NO][H2]
C) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]
D) Rate = k [NO][H2]2
E) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Exhibit 13-10 Consider the gas phase reaction and initial rate data below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + O2 (g)→2 NO2 (g) 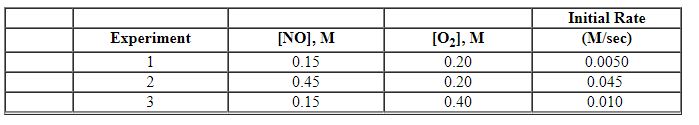
Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the overall order of the rate law above?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the overall order of the rate law above?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
If the overall chemical reaction A + B→C + D is studied and found to have the rate law:
Rate = k [A]2, which statement is correct?
A) A plot of log[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
B) A plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
C) A plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line.
D) The above is an impossible rate law.
E) A plot of 2.30 log![<strong>If the overall chemical reaction A + B→C + D is studied and found to have the rate law: Rate = k [A]<sup>2</sup>, which statement is correct?</strong> A) A plot of log[A] vs. time gives a straight line. B) A plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line. C) A plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line. D) The above is an impossible rate law. E) A plot of 2.30 log vs. time gives a straight line.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_83c4_8da6_a96ad059d7f4_TBX8714_11.jpg) vs. time gives a straight line.
vs. time gives a straight line.
Rate = k [A]2, which statement is correct?
A) A plot of log[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
B) A plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
C) A plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line.
D) The above is an impossible rate law.
E) A plot of 2.30 log
![<strong>If the overall chemical reaction A + B→C + D is studied and found to have the rate law: Rate = k [A]<sup>2</sup>, which statement is correct?</strong> A) A plot of log[A] vs. time gives a straight line. B) A plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line. C) A plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line. D) The above is an impossible rate law. E) A plot of 2.30 log vs. time gives a straight line.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_83c4_8da6_a96ad059d7f4_TBX8714_11.jpg) vs. time gives a straight line.
vs. time gives a straight line.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
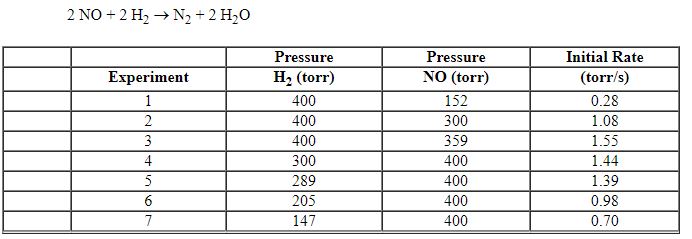
Exhibit 13-11 Consider the data that were collected for the rate of disappearance of NO in the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + 2 H2 (g)→N2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) ![<strong>Exhibit 13-11 Consider the data that were collected for the rate of disappearance of NO in the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + 2 H<sub>2</sub> (g)→N<sub>2</sub> (g) + 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (g) Refer to Exhibit 13-11. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> B) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1</sup> C) Rate = k [NO]<sup>1</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k [NO]<sup>1</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1</sup> E) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_c06c_8da6_dfa1375d8fcd_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-11. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]2
B) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]1
C) Rate = k [NO]1[H2]2
D) Rate = k [NO]1[H2]1
E) Rate = k [NO]2
![<strong>Exhibit 13-11 Consider the data that were collected for the rate of disappearance of NO in the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + 2 H<sub>2</sub> (g)→N<sub>2</sub> (g) + 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (g) Refer to Exhibit 13-11. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> B) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1</sup> C) Rate = k [NO]<sup>1</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k [NO]<sup>1</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1</sup> E) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_c06c_8da6_dfa1375d8fcd_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-11. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]2
B) Rate = k [NO]2[H2]1
C) Rate = k [NO]1[H2]2
D) Rate = k [NO]1[H2]1
E) Rate = k [NO]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl2 (aq) + C2O42 - (aq)→2 Cl - (aq) + 2 CO2 (g) + HgCl2 (s) 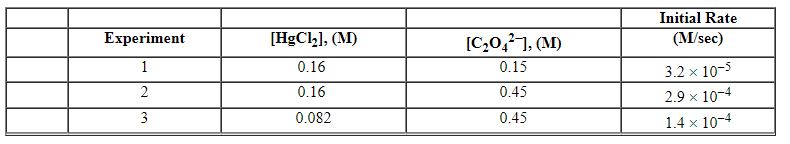
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What units would be used for the rate constant for the reaction above?
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What units would be used for the rate constant for the reaction above?
A) M/sec
B) M2/sec2
C) M - 1sec - 1
D) 1/sec
E) M - 2sec - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Exhibit 13-9 Use the reaction below to answer the following question(s). Phosgene is a toxic gas prepared by the reaction of carbon monoxide with chlorine:
CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→COCl2 (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation.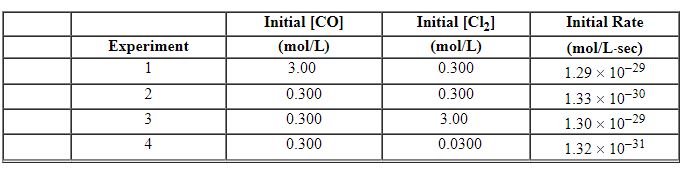
Refer to Exhibit 13-9. What is the overall order of the rate law for this reaction?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order
CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→COCl2 (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation.

Refer to Exhibit 13-9. What is the overall order of the rate law for this reaction?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Graphical analysis can be used to determine the rate law for a general reaction of reactant "A" going to product "B". Which function of the molar concentration of reactant "A" when plotted versus time is associated with a second order rate law?
A) [A]
B) 1/[A]
C) ln[A]
D) [A]2
E) ln[A]2
A) [A]
B) 1/[A]
C) ln[A]
D) [A]2
E) ln[A]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Consider the Integral Time-Concentration plots for each of the following:
Zero, first and second order rate laws. Which of these plots have a negative slope ?
I. Zero order rate law
II. First order rate law
III. Second order rate law
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III
Zero, first and second order rate laws. Which of these plots have a negative slope ?
I. Zero order rate law
II. First order rate law
III. Second order rate law
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Exhibit 13-9 Use the reaction below to answer the following question(s). Phosgene is a toxic gas prepared by the reaction of carbon monoxide with chlorine:
CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→COCl2 (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation.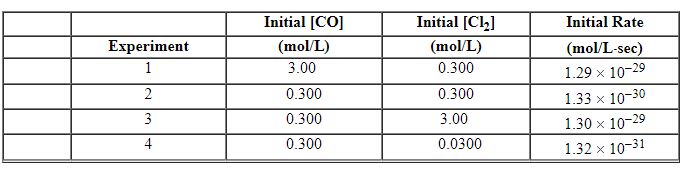
Refer to Exhibit 13-9. Using Experiment 3 data, what is the numerical value for the rate constant , k , for this reaction?
A) k = 4.81×10 - 30
B) k = 1.44×10 - 29
C) k = 1.60×10 - 29
D) k = 4.81×10 - 29
E) k = 6.92×1028
CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→COCl2 (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation.

Refer to Exhibit 13-9. Using Experiment 3 data, what is the numerical value for the rate constant , k , for this reaction?
A) k = 4.81×10 - 30
B) k = 1.44×10 - 29
C) k = 1.60×10 - 29
D) k = 4.81×10 - 29
E) k = 6.92×1028

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Exhibit 13-9 Use the reaction below to answer the following question(s). Phosgene is a toxic gas prepared by the reaction of carbon monoxide with chlorine:
CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→COCl2 (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation.![<strong>Exhibit 13-9 Use the reaction below to answer the following question(s). Phosgene is a toxic gas prepared by the reaction of carbon monoxide with chlorine: CO (g) + Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)→COCl<sub>2</sub> (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation. Refer to Exhibit 13-9. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>][COCl<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] C) Rate = k [CO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [CO] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [CO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_7246_8da6_ff71778c32f2_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-9. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [CO][Cl2][COCl2]
B) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]
C) Rate = k [CO]2[Cl2]
D) Rate = k [CO] [Cl2]2
E) Rate = k [CO]2[Cl2]2
CO (g) + Cl2 (g)→COCl2 (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation.
![<strong>Exhibit 13-9 Use the reaction below to answer the following question(s). Phosgene is a toxic gas prepared by the reaction of carbon monoxide with chlorine: CO (g) + Cl<sub>2</sub> (g)→COCl<sub>2</sub> (g) The following data were obtained in a kinetic study of its formation. Refer to Exhibit 13-9. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>][COCl<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k [CO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] C) Rate = k [CO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [CO] [Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [CO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_7246_8da6_ff71778c32f2_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-9. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [CO][Cl2][COCl2]
B) Rate = k [CO][Cl2]
C) Rate = k [CO]2[Cl2]
D) Rate = k [CO] [Cl2]2
E) Rate = k [CO]2[Cl2]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl2 (aq) + C2O42 - (aq)→2 Cl - (aq) + 2 CO2 (g) + HgCl2 (s) ![<strong>Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl<sub>2</sub> (aq) + C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup> (aq)→2 Cl<sup> - </sup> (aq) + 2 CO<sub>2</sub> (g) + HgCl<sub>2</sub> (s) Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] [C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] B) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] C) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] [C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] [C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>1/2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_0e8e_8da6_4f0059a62172_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [HgCl2] [C2O42 - ]
B) Rate = k [HgCl2]2[C2O42 - ]
C) Rate = k [HgCl2] [C2O42 - ]2
D) Rate = k [HgCl2]2[C2O42 - ]2
E) Rate = k [HgCl2] [C2O42 - ]1/2
![<strong>Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl<sub>2</sub> (aq) + C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup> (aq)→2 Cl<sup> - </sup> (aq) + 2 CO<sub>2</sub> (g) + HgCl<sub>2</sub> (s) Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] [C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] B) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>] C) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] [C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] [C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup>]<sup>1/2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_0e8e_8da6_4f0059a62172_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [HgCl2] [C2O42 - ]
B) Rate = k [HgCl2]2[C2O42 - ]
C) Rate = k [HgCl2] [C2O42 - ]2
D) Rate = k [HgCl2]2[C2O42 - ]2
E) Rate = k [HgCl2] [C2O42 - ]1/2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). ![<strong>Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [NO<sub>2</sub>] = 0.500 M and [CO] = 0.25 M?</strong> A) 0.063 M/sec B) 0.13 M/sec C) 0.50 M/sec D) 0.63 M/sec E) 2.0 M/sec](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_4b35_8da6_9d5360cd81cc_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [NO2] = 0.500 M and [CO] = 0.25 M?
A) 0.063 M/sec
B) 0.13 M/sec
C) 0.50 M/sec
D) 0.63 M/sec
E) 2.0 M/sec
![<strong>Exhibit 13-8 Consider the gas phase reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [NO<sub>2</sub>] = 0.500 M and [CO] = 0.25 M?</strong> A) 0.063 M/sec B) 0.13 M/sec C) 0.50 M/sec D) 0.63 M/sec E) 2.0 M/sec](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_4b35_8da6_9d5360cd81cc_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-8. What is the initial rate of this reaction when the concentration of the two reactants are [NO2] = 0.500 M and [CO] = 0.25 M?
A) 0.063 M/sec
B) 0.13 M/sec
C) 0.50 M/sec
D) 0.63 M/sec
E) 2.0 M/sec

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Exhibit 13-10 Consider the gas phase reaction and initial rate data below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + O2 (g)→2 NO2 (g) 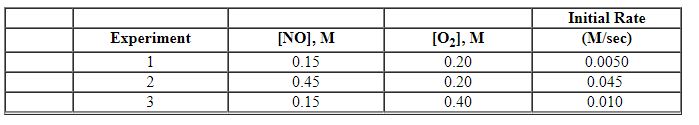
Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the numerical value for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) 2.3×10 - 5
B) 0.17
C) 0.83
D) 0.90
E) 1.1

Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the numerical value for the rate constant, k , of the reaction above?
A) 2.3×10 - 5
B) 0.17
C) 0.83
D) 0.90
E) 1.1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl2 (aq) + C2O42 - (aq)→2 Cl - (aq) + 2 CO2 (g) + HgCl2 (s) ![<strong>Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl<sub>2</sub> (aq) + C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup> (aq)→2 Cl<sup> - </sup> (aq) + 2 CO<sub>2</sub> (g) + HgCl<sub>2</sub> (s) Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the initial rate for this reaction when the concentration of [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] equals 0.18 M and that of C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup> equals 0.12 M?</strong> A) 2.2×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec B) 2.5×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec C) 2.8×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec D) 3.1×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec E) 3.10×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_5cb2_8da6_e974a1db369f_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the initial rate for this reaction when the concentration of [HgCl2] equals 0.18 M and that of C2O42 - equals 0.12 M?
A) 2.2×10 - 5 M/sec
B) 2.5×10 - 5 M/sec
C) 2.8×10 - 5 M/sec
D) 3.1×10 - 5 M/sec
E) 3.10×10 - 5 M/sec
![<strong>Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl<sub>2</sub> (aq) + C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup> (aq)→2 Cl<sup> - </sup> (aq) + 2 CO<sub>2</sub> (g) + HgCl<sub>2</sub> (s) Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the initial rate for this reaction when the concentration of [HgCl<sub>2</sub>] equals 0.18 M and that of C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2 - </sup> equals 0.12 M?</strong> A) 2.2×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec B) 2.5×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec C) 2.8×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec D) 3.1×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec E) 3.10×10<sup> - 5</sup> M/sec](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_5cb2_8da6_e974a1db369f_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the initial rate for this reaction when the concentration of [HgCl2] equals 0.18 M and that of C2O42 - equals 0.12 M?
A) 2.2×10 - 5 M/sec
B) 2.5×10 - 5 M/sec
C) 2.8×10 - 5 M/sec
D) 3.1×10 - 5 M/sec
E) 3.10×10 - 5 M/sec

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Exhibit 13-11 Consider the data that were collected for the rate of disappearance of NO in the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + 2 H2 (g)→N2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) 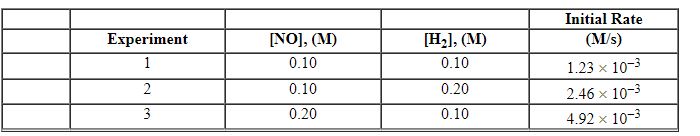
Refer to Exhibit 13-11. What is the value and units of the rate constant, k , for this reaction?
A) 0.062 M - 1s - 1
B) 0.62 M - 2s - 1
C) 6.2 M - 3s - 1
D) 1.2 M - 2sec - 1
E) 12 M - 3s - 1

Refer to Exhibit 13-11. What is the value and units of the rate constant, k , for this reaction?
A) 0.062 M - 1s - 1
B) 0.62 M - 2s - 1
C) 6.2 M - 3s - 1
D) 1.2 M - 2sec - 1
E) 12 M - 3s - 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Exhibit 13-10 Consider the gas phase reaction and initial rate data below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + O2 (g)→2 NO2 (g) ![<strong>Exhibit 13-10 Consider the gas phase reaction and initial rate data below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g)→2 NO<sub>2</sub> (g) Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [NO][O<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k [NO][O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> C) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_9959_8da6_77da2d5c38a3_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [NO][O2]
B) Rate = k [NO][O2]2
C) Rate = k [NO]2[O2]
D) Rate = k [NO]2[O2]2
E) Rate = k [NO]2
![<strong>Exhibit 13-10 Consider the gas phase reaction and initial rate data below to answer the following question(s). 2 NO (g) + O<sub>2</sub> (g)→2 NO<sub>2</sub> (g) Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) Rate = k [NO][O<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k [NO][O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> C) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>] D) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>[O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> E) Rate = k [NO]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a6_9959_8da6_77da2d5c38a3_TBX8714_00.jpg)
Refer to Exhibit 13-10. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = k [NO][O2]
B) Rate = k [NO][O2]2
C) Rate = k [NO]2[O2]
D) Rate = k [NO]2[O2]2
E) Rate = k [NO]2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl2 (aq) + C2O42 - (aq)→2 Cl - (aq) + 2 CO2 (g) + HgCl2 (s) 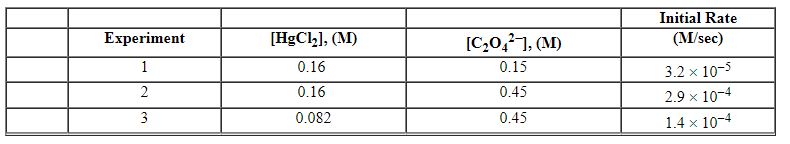
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the numerical value of the rate constant , k , for the reaction above?
A) 5.0×10 - 4
B) 1.3×10 - 3
C) 7.9×10 - 3
D) 8.7×10 - 3
E) 5.3×10 - 2

Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the numerical value of the rate constant , k , for the reaction above?
A) 5.0×10 - 4
B) 1.3×10 - 3
C) 7.9×10 - 3
D) 8.7×10 - 3
E) 5.3×10 - 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
For a reaction with the rate law below:
Rate = k [A]
A) a plot of ln[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
B) a plot of 1/[A] vs. 1/time gives a straight line.
C) a plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line.
D) a plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
E) a plot of log![<strong>For a reaction with the rate law below: Rate = k [A]</strong> A) a plot of ln[A] vs. time gives a straight line. B) a plot of 1/[A] vs. 1/time gives a straight line. C) a plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line. D) a plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line. E) a plot of log vs. 1/time gives a straight line.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_83c3_8da6_97755b74dad4_TBX8714_00.jpg) vs. 1/time gives a straight line.
vs. 1/time gives a straight line.
Rate = k [A]
A) a plot of ln[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
B) a plot of 1/[A] vs. 1/time gives a straight line.
C) a plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line.
D) a plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line.
E) a plot of log
![<strong>For a reaction with the rate law below: Rate = k [A]</strong> A) a plot of ln[A] vs. time gives a straight line. B) a plot of 1/[A] vs. 1/time gives a straight line. C) a plot of [A] vs. time gives a straight line. D) a plot of 1/[A] vs. time gives a straight line. E) a plot of log vs. 1/time gives a straight line.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8a7_83c3_8da6_97755b74dad4_TBX8714_00.jpg) vs. 1/time gives a straight line.
vs. 1/time gives a straight line.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Exhibit 13-12 Consider the aqueous reaction and data below to answer the following question(s). 2 HgCl2 (aq) + C2O42 - (aq)→2 Cl - (aq) + 2 CO2 (g) + HgCl2 (s) 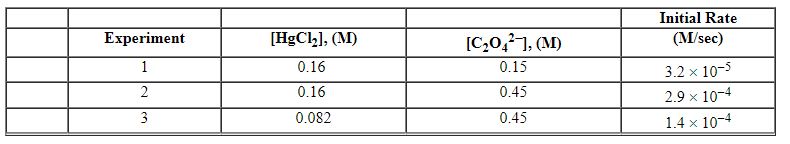
Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the overall order of the rate law?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

Refer to Exhibit 13-12. What is the overall order of the rate law?
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Consider the Time-Concentration plots for each of the following:
Zero, first and second order rate laws. Which of these plots have a positive slope ?
I. Zero order rate law
II. First order rate law
III. Second order rate law
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III
Zero, first and second order rate laws. Which of these plots have a positive slope ?
I. Zero order rate law
II. First order rate law
III. Second order rate law
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) II and III

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Exhibit 13-13 Graphical analysis can be used to determine the rate law for a general reaction of reactant "A" going to products "B" and "C".
A→B + C
Refer to Exhibit 13-13. Which of the Time-Concentration plots shown below would be expected if a particular reaction follows a second order rate law ?
A)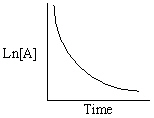
B)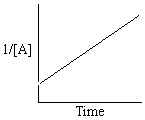
C)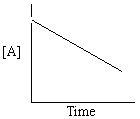
D)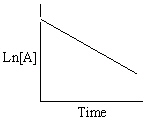
E)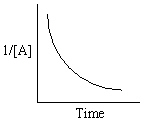
A→B + C
Refer to Exhibit 13-13. Which of the Time-Concentration plots shown below would be expected if a particular reaction follows a second order rate law ?
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








