Deck 13: Developing and Implementing Effective Accounting Information Systems
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Developing and Implementing Effective Accounting Information Systems
1
In developing and implementing IT, the study team and steering committee must consider organizational goals. These include:
a. General, technical, and top management goals
b. General, operating management, and technical goals
c. Top management, operating management, and economic goals
d. Top management, operating management, and general systems goals
a. General, technical, and top management goals
b. General, operating management, and technical goals
c. Top management, operating management, and economic goals
d. Top management, operating management, and general systems goals
In performing its work developing and implementing information technology, the study team and steering committee must consider organizational goals. This includes top management goals, operating management goals and general system goals. Then the study team is required to prepare a report which describes its findings in the company system.
Hence the best answer:
(d) Top management, operating management and general system goals.
Hence the best answer:
(d) Top management, operating management and general system goals.
2
Discuss the two major ways that a company's software can be acquired. Which of these ways for acquiring software do you recommend? Explain your reasoning.
Normally the organizations merge in numerous business activities. Due to the advancement of the tasks and technology, the company software may not be able to perform the activities. Therefore the companies acquire the required software in two major ways. That is through;
1. Developing and maintaining the former software by providing further modifications to it.
2. Acquiring latest sophisticated software that can be able to perform both small and larger transactions.
I prefer to recommend the software which is suitable for advanced tasks along with simple activities though they are expensive. The reasons are explained below:
• No need to modify the applications of the software.
• No need to invest again for further modifications
• Not required to feel tense with the advancement of the tasks.
• In the long run, they are capable of saving business money and be maintained for long future.
1. Developing and maintaining the former software by providing further modifications to it.
2. Acquiring latest sophisticated software that can be able to perform both small and larger transactions.
I prefer to recommend the software which is suitable for advanced tasks along with simple activities though they are expensive. The reasons are explained below:
• No need to modify the applications of the software.
• No need to invest again for further modifications
• Not required to feel tense with the advancement of the tasks.
• In the long run, they are capable of saving business money and be maintained for long future.
3
What is the purpose of a systems feasibility evaluation? Should this activity precede or follow the preparation of a systems specifications report for computer vendor evaluation? Explain.
The design team is assigned to perform a complete investigation of potential systems often receiving favorable response from the steering committee. This investigation includes five procedures in which feasibility evolution stands first.
Purpose of feasibility:
System feasibility evolution determines whether the alternative and the proposals of steering committee are practical to implement in the concepts of technical, operational, schedule, legal and economy. It helps to avert the loss of time, effort and wealth.
Generally feasibility evolution arrives before the preparation of system specification report for computer vendor evolution. Sometimes steering committee desires to acquire most system resources from vendor outside. This report helps the committee to create a request for proposal highlighting the required desired systems.
Purpose of feasibility:
System feasibility evolution determines whether the alternative and the proposals of steering committee are practical to implement in the concepts of technical, operational, schedule, legal and economy. It helps to avert the loss of time, effort and wealth.
Generally feasibility evolution arrives before the preparation of system specification report for computer vendor evolution. Sometimes steering committee desires to acquire most system resources from vendor outside. This report helps the committee to create a request for proposal highlighting the required desired systems.
4
What is the difference between business process outsourcing (BPO) and knowledge process outsourcing (KPO)? Why do firms outsource their IT functions?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Prototyping, as an IT development approach, has both advantages and disadvantages. In general, prototyping is most appropriate when:
a. The design team is not pressed for time in creating a new system
b. Users have a thorough understanding of their information needs
c. There are high risks associated with developing and implementing an ineffective system
d. System requirements are easily defined
a. The design team is not pressed for time in creating a new system
b. Users have a thorough understanding of their information needs
c. There are high risks associated with developing and implementing an ineffective system
d. System requirements are easily defined

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The Chris Hall Company manufactures and distributes low-priced bottled wines to retailers. You are hired as a management consultant to help this company solve some of its systems problems. Describe the types of decision-making information that probably would be needed by the company's (a) supervisor of the production plant, (b) top management, and (c) mar- keting manager.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Discuss some of the annual cash benefits and annual cash costs that a company might have when it creates an online ordering system on the World Wide Web.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Lilly Li Apparel is a manufacturer of fashion apparel that has just opened its first large retail store for selling high-fashion clothes at high-fashion prices. The company's competitive strategy depends on a comprehensive point-of-sale (POS) system supporting online, up- to-the-minute sales totals, day-to-day tracking of stock information, and quick checkout of customer purchases. Because cashiers were already familiar with electronic cash registers, management decided that only minimal training was required. Cashiers enter four-digit stock tracking numbers (STNs) into one of the POS terminals that retrieves price and description data, computes the tax and total amount due, accepts the type of payment, and controls the cash drawer. A unique STN identifies each of the 9,500 pieces of merchandise. The central microcomputer server maintains stock information. In the first month of operation, new cashiers were awkward using the new system. They eventually became proficient users but were frustrated with the slow printing of sales tickets and the unpredictable action of their cash drawers. Each checkout stand has a telephone that cashiers use to call for approval of credit-card transactions. Customers became impatient when credit approvals delayed the checkout process or when the microcomputer was down, thus stopping all sales, including cash sales. Identify four problems with the system and describe how you would remedy each of them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In selecting a new accounting information system, the steering committee should consider:
a. All expected costs and benefits of the new systems, including maintenance and operating costs
b. Support that a vendor can provide, including training, maintenance, and backup
c. Compatibility of a new system with existing systems
d. All of the above are considerations in selecting a new system
e. Only a and b are important considerations in selecting the new system
a. All expected costs and benefits of the new systems, including maintenance and operating costs
b. Support that a vendor can provide, including training, maintenance, and backup
c. Compatibility of a new system with existing systems
d. All of the above are considerations in selecting a new system
e. Only a and b are important considerations in selecting the new system

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Jay Beck works for the AAZ Consulting Firm. His friend, Hank Henley, is the general manager and majority stockholder of the Pacific Worldwinds, a professional football team. Hank asked Jay to design an online, real-time computer system for ''the efficient operation of the football franchise.'' Jay was quite confused because he could not think of any possible uses for an online, real-time system within the operational activities of a football team (or any other type of athletic team). Assume that you are also employed at the AAZ Consulting Firm. Provide several suggestions to Jay concerning specific areas of athletic teams' (football teams, baseball teams, etc.) information systems, where an online, real-time computer configuration might be beneficial to managerial decision making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
What is prototyping? Under what circumstances should prototyping be used? Under what circumstances should it not be used?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Cook Consultants is currently in the process of completing the systems implementation activities for converting Samuel Company's old system to a new one. Because of unexpected delays in performing specific implementation activities, Jerry Hazen, the project manager, is concerned about finishing the project on time. The one remaining activity is testing the new computer system and subsequently eliminating the old one. Jerry's assistant, May Fong, suggests that they can still meet their completion deadline if they use direct conversion rather than parallel conversion. Assuming that you are the CIO of the company, how would you react to May Fong's suggestion? Discuss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A point-scoring analysis:
a. Is a useful tool in conducting a feasibility analysis
b. Helps the systems study team to decide whether or not to outsource their AIS
c. Provides a systems study team with an objective means for selecting a final AIS
d. Is a tool used for managing IT projects
a. Is a useful tool in conducting a feasibility analysis
b. Helps the systems study team to decide whether or not to outsource their AIS
c. Provides a systems study team with an objective means for selecting a final AIS
d. Is a tool used for managing IT projects

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
With the help of your instructor, identify a particular information system that is not working very well and perform a preliminary investigationofit.Inyourwork,besuretotalkto(1)at least one external customer who is affected by the system, (2) one employee who uses the system daily, and (3) one person who manages this type of employee. For example, at a university, you might study the student parking information system. The customers are those car owners who purchase parking permits (e.g., students, faculty, and university staff members), data input clerks are the employees who use the system daily, and the parking manager is the person who supervises these employees. Ask each such person what he or she feels are the problems of the system and what they think should be done to address these problems. Prepare a preliminary investigation report that describes your system and outlines the following items: (a) the problems that each person experiences with the system, (b) the actions that each person thinks might solve the problems, and (c) your opinion of which difficulties are the real problems and which are just symptoms of these problems. Also include some recommendations. Should the present system be replaced, or are just minor modifications required?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What is the purpose of a systems specifications report? In what ways, if any, do the data included in this report differ from the data accumulated by the design team during their feasibility evaluation work?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Do you understand PERT charts? Refer back to Figure 13-11 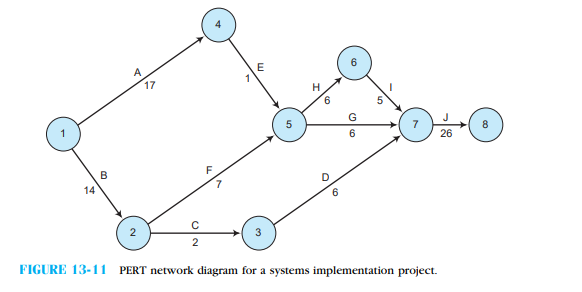 and answer the following questions:
and answer the following questions:
a. Which activity or activities must be completed before activity C can begin?
b. Which activity or activities must be completed before activity G can begin?
c. Which activity or activities must be completed before activity J can begin?
d. What are the five paths through the network? Which one is the critical path?
e. What is the earliest projected start time for activity F?
f. What is the earliest projected start time for activity G?
g. What is the latest time that activity J can begin without delaying the entire project?
h. What is the latest time that activity G can begin without delaying the entire project?
i. What is the slack time for activity G? (Hint: it's the difference between the early and late start times.)
 and answer the following questions:
and answer the following questions:a. Which activity or activities must be completed before activity C can begin?
b. Which activity or activities must be completed before activity G can begin?
c. Which activity or activities must be completed before activity J can begin?
d. What are the five paths through the network? Which one is the critical path?
e. What is the earliest projected start time for activity F?
f. What is the earliest projected start time for activity G?
g. What is the latest time that activity J can begin without delaying the entire project?
h. What is the latest time that activity G can begin without delaying the entire project?
i. What is the slack time for activity G? (Hint: it's the difference between the early and late start times.)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is not true with respect to managing IT projects:
a. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) allows management to determine the shortest time it will take to implement a new system, and any slack time that might exist between implementation activities
b. An advantage of PERT is that it allows managers to identify the critical path in implementation
c. Both PERT and Gantt charts are manual techniques used in managing IT implementations
d. Gantt charts are useful in scheduling and implementing IT because they allow you to indicate actual progress versus planned progress directly on the chart
a. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) allows management to determine the shortest time it will take to implement a new system, and any slack time that might exist between implementation activities
b. An advantage of PERT is that it allows managers to identify the critical path in implementation
c. Both PERT and Gantt charts are manual techniques used in managing IT implementations
d. Gantt charts are useful in scheduling and implementing IT because they allow you to indicate actual progress versus planned progress directly on the chart

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Do you understand Gantt charts? Use Figure 13-12  and test your understanding by answering the following questions. (Hint: you might also want to look at the PERT chart in Figure 13-11
and test your understanding by answering the following questions. (Hint: you might also want to look at the PERT chart in Figure 13-11 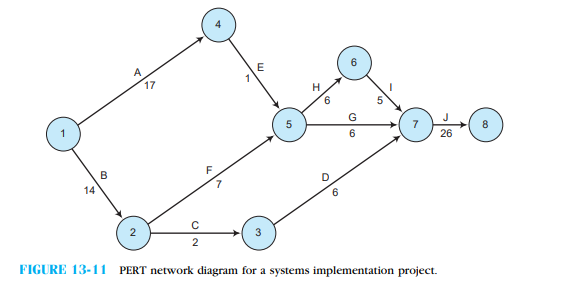 .)
.)
a. When is the activity convert data files scheduled to begin and end?
b. When is the activity test computer software scheduled to begin and end?
c. How much time did it actually take the company to complete the task prepare the physical site? Was this more or less time than planned?
d. How much time did it actually take the company to complete the task determine the functional changes? Was this more or less time than planned?
e. Given what has happened so far, when can the activity acquire and install computer equipment actually begin?
f. Given what has happened so far, when can the activity select and assign personnel actually begin?
 and test your understanding by answering the following questions. (Hint: you might also want to look at the PERT chart in Figure 13-11
and test your understanding by answering the following questions. (Hint: you might also want to look at the PERT chart in Figure 13-11  .)
.)a. When is the activity convert data files scheduled to begin and end?
b. When is the activity test computer software scheduled to begin and end?
c. How much time did it actually take the company to complete the task prepare the physical site? Was this more or less time than planned?
d. How much time did it actually take the company to complete the task determine the functional changes? Was this more or less time than planned?
e. Given what has happened so far, when can the activity acquire and install computer equipment actually begin?
f. Given what has happened so far, when can the activity select and assign personnel actually begin?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
When implementing a new computer system, two required activities are (1) establishing controls and (2) converting data files. What is the rationale for performing activity 1 before activity 2?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Prado Roberts Manufacturing (What Type of Computer System to Implement?) Prado Roberts Manufacturing is a medium-size company with regional offices in several western states and manufacturing facilities in both California and Nevada. The company performs most of its important data processing tasks, such as payroll, accounting, marketing, and inventory control, on a mainframe computer at corporate headquarters. However, almost all the managers at this company also have personal computers, which they use for such personal productivity tasks as word processing, analyzing budgets (using spreadsheets), and managing the data in small databases. The IT manager, Tonya Fisher, realizes that there are both advantages and disadvantages of using different types of systems to meet the processing needs of her company. While she acknowledges that many companies are racing ahead to install microcomputers and client/server systems, she also knows that the corporate mainframe system has provided her company with some advantages that smaller systems cannot match. Tonya knows that American companies annually purchase over $5 billion in used computers, primarily mainframes.
Requirements
1. Identify several advantages and disadvantages of operating a mainframe computer system that are likely to be present at Prado Roberts Manufacturing. Are these advantages and disadvantages likely to parallel those at other manufacturing companies?
2. Identify at least two factors or actions that companies experience or do to prolong the lives of their legacy systems. Are these factors or actions likely to apply to Prado Roberts Manufacturing?
3. Identify several advantages and disadvantages of microcomputer/client server systems. Would these advantages apply to Prado Roberts Manufacturing? (CMA Adapted)
Requirements
1. Identify several advantages and disadvantages of operating a mainframe computer system that are likely to be present at Prado Roberts Manufacturing. Are these advantages and disadvantages likely to parallel those at other manufacturing companies?
2. Identify at least two factors or actions that companies experience or do to prolong the lives of their legacy systems. Are these factors or actions likely to apply to Prado Roberts Manufacturing?
3. Identify several advantages and disadvantages of microcomputer/client server systems. Would these advantages apply to Prado Roberts Manufacturing? (CMA Adapted)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
When converting to a new system, which of the following conversion alternatives would
be the most risky for a financial services firm?
a. Direct conversion
b. Modular conversion
c. Parallel conversion
d. Turnkey conversion
be the most risky for a financial services firm?
a. Direct conversion
b. Modular conversion
c. Parallel conversion
d. Turnkey conversion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Wright Company (Analyzing System Reports) Wright Company employs a computer-based data processing system for maintaining all company records. The current system was developed in stages over the past 5 years and has been fully operational for the last 24 months. When the system was being designed, all department heads were asked to specify the types of information and reports they would need for planning and controlling operations. The systems department attempted to meet the specifications of each department head. Company management specified that certain other reports be prepared for department heads. During the 5 years of systems development and operation, there have been several changes in the department head positions because of attrition and promotions. The new department heads often made requests for additional reports according to their specifications. The systems department complied with all of these requests. Reports were discontinued only on request by a department head, and then only if it was not a standard report required by top management. As a result, few reports were discontinued and the information processing subsystem continued to generate a large quantity of reports each reporting period. Company man agement became concerned about the quantity of report information produced by the system, and therefore asked the internal audit department to evaluate their effectiveness. The audit staff determined early in the study that more information was being generated by the information processing subsystem than could be used effectively. They noted the following reactions to this information overload:
• Many department heads would not act on certain reports during periods of peak activity. The department heads would let these reports accumulate with the hope of catching up during subsequent lulls.
• Some department heads had so many reports that they did not act at all on the information, or they made incorrect decisions because of misuse of the information.
• Frequently, actions required by the nature of the report data were not taken until the department heads were reminded by others who needed the decisions. These department heads did not appear to have developed a priority system for acting on the information produced by the information processing subsystem.
• Department heads often would develop the information they needed from alternative, independent sources, rather than use the reports generated by the information processing subsystem. This was often easier than trying to search among the reports for the needed data.
Requirements
1. Indicate whether each of the foregoing four reactions contributes positively or negatively
to the Wright Company's operating effectiveness. Explain your answer for every one of the four reactions.
2. For each reaction that you indicated as negative, recommend alternative procedures the Wright Company could employ to eliminate this negative contribution to operating effectiveness. (CMA Adapted)
• Many department heads would not act on certain reports during periods of peak activity. The department heads would let these reports accumulate with the hope of catching up during subsequent lulls.
• Some department heads had so many reports that they did not act at all on the information, or they made incorrect decisions because of misuse of the information.
• Frequently, actions required by the nature of the report data were not taken until the department heads were reminded by others who needed the decisions. These department heads did not appear to have developed a priority system for acting on the information produced by the information processing subsystem.
• Department heads often would develop the information they needed from alternative, independent sources, rather than use the reports generated by the information processing subsystem. This was often easier than trying to search among the reports for the needed data.
Requirements
1. Indicate whether each of the foregoing four reactions contributes positively or negatively
to the Wright Company's operating effectiveness. Explain your answer for every one of the four reactions.
2. For each reaction that you indicated as negative, recommend alternative procedures the Wright Company could employ to eliminate this negative contribution to operating effectiveness. (CMA Adapted)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Discuss the major differences between the planning, analysis, and design phase of a systems study.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Three methods for implementing a new system in an organization are direct conversion, parallel conversion, and modular conversion. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using each of these three systems implementation methods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Kenbart Company (Redesigning Profit Plan Reports) The managers at Kenbart Company have decided that increased emphasis must be placed on profit planning and comparing results to plans. A new profit planning system was implemented to help with this objective. The company uses contribution margin reporting for internal reporting purposes and applies the concept of flexible budgeting for estimating variable costs. Kenbart's executive management uses the following terms when reviewing and analyzing actual results and the profit plan.
• Original plan. Profit plan approved and adopted by management for the year
• Revised plan. Original plan modified as a consequence of action taken during the year (usually quarterly) by executive management
• Flexed revised plan. The most current plan (i.e., either original plan or revised plan, if one has been prepared) adjusted for changes in volume and variable expense rates
• YTD actual results. The actual results of operations for the year
• Current outlook. The summation of the actual year-to-date results of operations plus the flexed revised plan for the remaining months of the year Executive management meets monthly to review the actual results compared with the profit plan. Any assumptions or major changes in the profit plan usually are incorporated on a quarterly basis once the first quarter is completed. Figure 13-14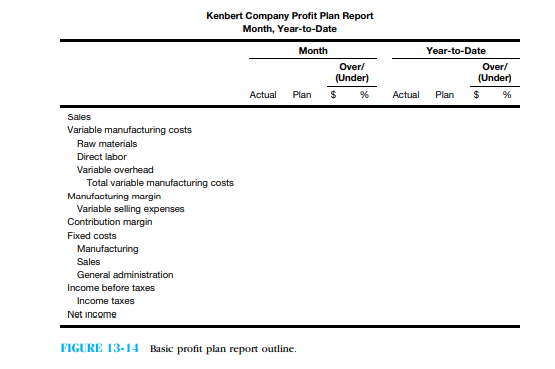 provides an outline of the basic Profit Plan Report designed by the information processing subsystem. The current system produces this report at the end of the month and whenever executive management initiates a change or modification in its plans. Consequently, many different versions of the firm's profit plan exist, which makes analysis difficult and confusing. Several members of the executive management have voiced disapproval of the Profit Plan Report because the ''Plan'' column is not well defined and varies in meaning from one report to another. Furthermore, the report does not include a current-outlook column. Therefore, the accounting subsystem has been asked to work with the information processing subsystem in modifying the report so that users can better understand the information being conveyed and the reference points for comparison of results.
provides an outline of the basic Profit Plan Report designed by the information processing subsystem. The current system produces this report at the end of the month and whenever executive management initiates a change or modification in its plans. Consequently, many different versions of the firm's profit plan exist, which makes analysis difficult and confusing. Several members of the executive management have voiced disapproval of the Profit Plan Report because the ''Plan'' column is not well defined and varies in meaning from one report to another. Furthermore, the report does not include a current-outlook column. Therefore, the accounting subsystem has been asked to work with the information processing subsystem in modifying the report so that users can better understand the information being conveyed and the reference points for comparison of results.
Requirements
1. Redesign the layout of the Profit Plan Report so that it will be more useful to Kenbart's executive management in its task of reviewing results and planning operations.
2. Explain the reason for each modification you make in the report.
• Original plan. Profit plan approved and adopted by management for the year
• Revised plan. Original plan modified as a consequence of action taken during the year (usually quarterly) by executive management
• Flexed revised plan. The most current plan (i.e., either original plan or revised plan, if one has been prepared) adjusted for changes in volume and variable expense rates
• YTD actual results. The actual results of operations for the year
• Current outlook. The summation of the actual year-to-date results of operations plus the flexed revised plan for the remaining months of the year Executive management meets monthly to review the actual results compared with the profit plan. Any assumptions or major changes in the profit plan usually are incorporated on a quarterly basis once the first quarter is completed. Figure 13-14
 provides an outline of the basic Profit Plan Report designed by the information processing subsystem. The current system produces this report at the end of the month and whenever executive management initiates a change or modification in its plans. Consequently, many different versions of the firm's profit plan exist, which makes analysis difficult and confusing. Several members of the executive management have voiced disapproval of the Profit Plan Report because the ''Plan'' column is not well defined and varies in meaning from one report to another. Furthermore, the report does not include a current-outlook column. Therefore, the accounting subsystem has been asked to work with the information processing subsystem in modifying the report so that users can better understand the information being conveyed and the reference points for comparison of results.
provides an outline of the basic Profit Plan Report designed by the information processing subsystem. The current system produces this report at the end of the month and whenever executive management initiates a change or modification in its plans. Consequently, many different versions of the firm's profit plan exist, which makes analysis difficult and confusing. Several members of the executive management have voiced disapproval of the Profit Plan Report because the ''Plan'' column is not well defined and varies in meaning from one report to another. Furthermore, the report does not include a current-outlook column. Therefore, the accounting subsystem has been asked to work with the information processing subsystem in modifying the report so that users can better understand the information being conveyed and the reference points for comparison of results.Requirements
1. Redesign the layout of the Profit Plan Report so that it will be more useful to Kenbart's executive management in its task of reviewing results and planning operations.
2. Explain the reason for each modification you make in the report.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is not true:
a. A preliminary investigation of a current system is conducted by the steering committee
b. Implementation, follow-up, and maintenance of IT includes acquiring resources for the new system
c. In designing an AIS, the design team will begin with outputs
d. The more work done during planning and analysis, the less likely the new system will fail
a. A preliminary investigation of a current system is conducted by the steering committee
b. Implementation, follow-up, and maintenance of IT includes acquiring resources for the new system
c. In designing an AIS, the design team will begin with outputs
d. The more work done during planning and analysis, the less likely the new system will fail

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which one of the four stages in the systems development life cycle is likely to be the most costly for a new system?
a. Planning and investigation
b. Analysis
c. Design
d. Implementation, follow-up, and maintenance
a. Planning and investigation
b. Analysis
c. Design
d. Implementation, follow-up, and maintenance

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Stephen Kerr Cosmetics (Point-Scoring Analysis) Stephen Kerr Cosmetics distributes cosmetic products to large retailers across the country. The firm was started in 1975 by its first president, Stephen Kerr, who still serves as chairman of the board. Over the years, the company has grown in size and complexity. As the company has prospered, Richard Mason, the controller, has acquired and installed new accounting software to accommodate the increasing demands on the firm's accounting systems. This year, Richard has convinced Stephen that it is time to upgrade their payroll system, which is now 7 years old. The company hires an outside consultant, who examines their situation and concludes that either one of two systems can meet their requirements. Richard therefore asks two of his most competent employees, Fritz Grupe and Meg Chrisman, to help him perform a point-scoring analysis and make a final choice. The three individuals meet as a study team and agree upon five qualities for rating the two vendors: (1) need for further modifications, (2) ease of use, (3) strength of internal controls, (4) flexibility for updating and Internet options, and (5) vendor support. To help them rate the two vendors on these five criteria, the committee invites representatives from each vendor to visit the company and make a presentation. Fritz makes arrangements for the presentation team from Vendor A to present on a Friday morning and a similar team from Vendor B to visit that same afternoon. Unfortunately, an emergency makes it impossible for Richard to attend either presentation. Meg and Fritz attend both sessions but come away with very different impressions of the competing software. The table below provides some relevant data.
Requirements
1. To start their analysis, Meg and Fritz decide to use their own ratings to perform separate point-scoring analyses. For this part, use equal weightings of 0.2 for each category. Perform similar analyses using a spreadsheet. Which vendor does each person prefer?
2. Both Meg and Fritz decide that using equal weight for each category doesn't make sense. After some discussion, they agree to the ''compromise weights'' shown on the following page. They again perform their analyses. Which vendor does each person prefer now?
3. Fritz and Meg show their results to Richard, who suggests that they use their ''com promise weights'' but use combined averages for their ''grades'' for each vendor. They perform yet a third analysis. Which vendor receives the highest total now?
4. What do these exercises suggest about point-scoring analyses? Does this method still seem ''objective'' to you? Why or why not?
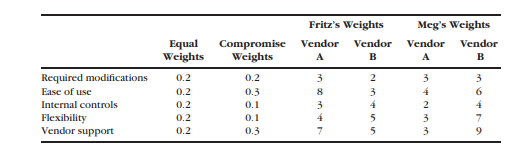
Requirements
1. To start their analysis, Meg and Fritz decide to use their own ratings to perform separate point-scoring analyses. For this part, use equal weightings of 0.2 for each category. Perform similar analyses using a spreadsheet. Which vendor does each person prefer?
2. Both Meg and Fritz decide that using equal weight for each category doesn't make sense. After some discussion, they agree to the ''compromise weights'' shown on the following page. They again perform their analyses. Which vendor does each person prefer now?
3. Fritz and Meg show their results to Richard, who suggests that they use their ''com promise weights'' but use combined averages for their ''grades'' for each vendor. They perform yet a third analysis. Which vendor receives the highest total now?
4. What do these exercises suggest about point-scoring analyses? Does this method still seem ''objective'' to you? Why or why not?


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
What is a steering committee? Discuss its role in a systems study performed by a consulting firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
What is a PERT chart? What is a Gantt chart? Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using PERT network diagrams versus Gantt charts for planning and controlling the activities involved in implementing an information system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The feasibility evaluation:
a. Is completed prior to detailed systems design
b. Includes economic, schedule, technical, legal, and operational feasibility
c. Both a and b are true
d. Neither a nor b is true
a. Is completed prior to detailed systems design
b. Includes economic, schedule, technical, legal, and operational feasibility
c. Both a and b are true
d. Neither a nor b is true

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following would be most helpful to managers of a project where the precedence of activities is important?
a. Outsourcing
b. PERT
c. AGranitechart
d. A turnkey system
a. Outsourcing
b. PERT
c. AGranitechart
d. A turnkey system

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A systems study team should understand three levels of corporate goals: general systems goals, top management systems goals, and operating management systems goals. If you had to select one of these categories of systems goals as the most important to the effective operation of an organization's information system, which one would you choose? Explain the reasons for your choice.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What is the purpose of follow-up in a systems study? Describe some of the specific activities that the management implementation team would perform in their follow-up work.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








