Deck 8: Tests for Significance: Z-Tests and One-Sample T-Tests
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Tests for Significance: Z-Tests and One-Sample T-Tests
1
Which of the following compares a single sample mean to a given population mean?
A) one-sample test
B) z-test
C) one-sample t test
D) all of these
A) one-sample test
B) z-test
C) one-sample t test
D) all of these
D
2
In order to conduct any one-sample test, you must always have a ______.
A) population mean
B) population standard deviation
C) sample standard deviation
D) none of these
A) population mean
B) population standard deviation
C) sample standard deviation
D) none of these
A
3
You should conduct a z-test instead of a one-sample t-test when ______.
A) and s are known
B) x̄ and s are known
C) and are known
D) all of these
A) and s are known
B) x̄ and s are known
C) and are known
D) all of these
and are known
4
You should conduct a one-sample t-test instead of a z-test when ______.
A) and s are known
B) x̄ and s are known
C) and are known
D) all of these
A) and s are known
B) x̄ and s are known
C) and are known
D) all of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The basic question we ask when conducting a one-sample test is ______.
A) How likely is this sample mean given the population mean described by the null hypothesis?
B) How likely is this population mean given the sample mean described by the alternative hypothesis?
C) What are the likely values for the sample mean given a particular population mean?
D) What are the likely values for the population mean given a particular sample mean?
A) How likely is this sample mean given the population mean described by the null hypothesis?
B) How likely is this population mean given the sample mean described by the alternative hypothesis?
C) What are the likely values for the sample mean given a particular population mean?
D) What are the likely values for the population mean given a particular sample mean?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A one-sample test can be characterized as a mean difference expressed in ______.
A) standard deviation units
B) standard error units
C) variance units
D) none of these
A) standard deviation units
B) standard error units
C) variance units
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If you want to test the hypothesis, "Do customers at our London branch purchase more than our company-wide averages?", assuming = .05, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) -1.960
B) +1.960
C) -1.645
D) +1.645
A) -1.960
B) +1.960
C) -1.645
D) +1.645

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
You collect a sample of n = 31 and want to know if this sample is significantly different from the population. If is known and = .05, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) ±1.645
B) ±1.960
C) ±2.042
D) none of these
A) ±1.645
B) ±1.960
C) ±2.042
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
You collect a sample of n = 16 and want to know if the sample is significantly smaller than the population. If is unknown and = .05, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) -1.645
B) -1.960
C) -1.753
D) -1.746
A) -1.645
B) -1.960
C) -1.753
D) -1.746

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
You collect a sample of n = 10 and want to know if the sample is significantly different than the population. If is unknown and = .05, what is the appropriate critical value?
A) -2.262
B) +2.262
C) both a and b
D) none of these
A) -2.262
B) +2.262
C) both a and b
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
You want to compare a sample of n = 16 to a population where = 2 and = 10. If x̄ = 6, what is the value of the test statistic?
A) -16
B) -4
C) -8
D) -11
A) -16
B) -4
C) -8
D) -11

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
You want to compare a sample of n = 25 to a population where = 5 and = 12. If x̄ = 15, what is the value of the test statistic?
A) 3
B) -3
C) 15
D) -15
A) 3
B) -3
C) 15
D) -15

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
You want to demonstrate that a sample of n = 36 has a greater mean than a population where = 4 and = 8. If x̄ = 10, what is the critical value?
A) 3.00
B) 1.96
C) 1.645
D) 2.02
A) 3.00
B) 1.96
C) 1.645
D) 2.02

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
You want to demonstrate that a sample of n = 100 has a higher mean than a population where = 5 and = 11. If x̄ = 10, what is the correct decision?
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) Accept the alternative.
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) Accept the alternative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
You want to demonstrate that a sample of n = 25 has a different mean than a population where = 2 and = 7. If x̄ = 8, what is the correct decision?
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) none of these
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
You want to compare a sample of n = 9 to a population where = 6. If x̄ = 5 and s = 3, what is the value of the test statistic?
A) .33
B) -.33
C) 1
D) -1
A) .33
B) -.33
C) 1
D) -1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
You want to compare a sample of n = 100 to a population where = 6.5. If x̄ = 8 and s = 4, what is the value of the test statistic?
A) 37.5
B) 3.75
C) 7.5
D) 1.5
A) 37.5
B) 3.75
C) 7.5
D) 1.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
You want to demonstrate that a sample of n = 16 has a greater mean than a population where = 9. If x̄ = 6 and s = 7, what is the critical value?
A) 2.131
B) 1.746
C) 1.645
D) 1.753
A) 2.131
B) 1.746
C) 1.645
D) 1.753

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
You want to demonstrate that a sample of n = 36 has a lower mean than a population where = 22. If x̄ = 25 and s = 8, what is the correct decision?
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) Accept the alternative.
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) Accept the alternative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
You want to demonstrate that a sample of n = 16 has a different mean than a population where = 9. If x̄ = 7 and s = 3, what is the correct decision?
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) none of these
A) Fail to reject the null.
B) Reject the null.
C) Fail to reject the alternative.
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Why should you calculate an effect size?
A) because you found statistical significance
B) because effect size represents the practical significance of a finding
C) because significance may be difficult to interpret for large samples
D) all of these
A) because you found statistical significance
B) because effect size represents the practical significance of a finding
C) because significance may be difficult to interpret for large samples
D) all of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
When calculating an effect size, what is preferred?
A) unstandardized effect sizes
B) standardized effect sizes
C) unstandardized and/or standardized effect sizes, depending upon the situation
D) none of these
A) unstandardized effect sizes
B) standardized effect sizes
C) unstandardized and/or standardized effect sizes, depending upon the situation
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
You want to compare a sample of n = 80 to a population where = 6 and = 4. If x̄ = 8, what is the value of the standardized effect size?
A) 4
B) -4
C) .67
D) 5.96
A) 4
B) -4
C) .67
D) 5.96

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
You want to compare a sample of n = 64 to a population where = 10 and = 30. If x̄ = 27, what is the value of the unstandardized effect size?
A) -2.4
B) -3
C) -0.3
D) -1.645
A) -2.4
B) -3
C) -0.3
D) -1.645

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
You want to compare a sample of n = 49 to a population where = 18. If x̄ = 21 and s = 3.5, what is the value of the standardized effect size?
A) 3
B) .86
C) 6
D) -3
A) 3
B) .86
C) 6
D) -3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
You want to compare a sample of n = 81 to a population where = 27. If x̄ = 26 and s = 3, what is the value of the unstandardized effect size?
A) .33
B) -.33
C) -3.03
D) -1
A) .33
B) -.33
C) -3.03
D) -1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If you retain the null, what should you do next?
A) calculate an effect size alone
B) calculate an effect size and a confidence interval
C) calculate a confidence interval alone
D) nothing
A) calculate an effect size alone
B) calculate an effect size and a confidence interval
C) calculate a confidence interval alone
D) nothing

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If you conduct a z-test and find that z = 1.25 for a sample of n = 16, which of the following is the correct formal test of the hypothesis?
A) z(15) = 2.5, p > .05
B) z(15) = 2.5, p < .05
C) z = 2.5, p < .05
D) z = 2.5, p > .05
A) z(15) = 2.5, p > .05
B) z(15) = 2.5, p < .05
C) z = 2.5, p < .05
D) z = 2.5, p > .05

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If you conduct a right-tailed one-sample t-test and find that t = -1.83 for a sample of n = 12, which of the following is the correct formal test of the hypothesis?
A) t(11) = -1.83, p > .05
B) t(11) = -1.83, p < .05
C) t = -1.83, p > .05
D) t = -1.83, p < .05
A) t(11) = -1.83, p > .05
B) t(11) = -1.83, p < .05
C) t = -1.83, p > .05
D) t = -1.83, p < .05

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
You test the hypothesis that employees at Branch A have significantly higher sales than the branch average for the overall company. You find that z = 3.36, p < .05. Which of the following is a valid statement about these findings?
A) Employees at Branch A have significantly higher sales than other branches within the company.
B) Employees at Branch A have significantly lower sales than other branches within the company.
C) Employees at Branch A have significantly different sales than other branches within the company.
D) Employees at Branch A do not have significantly different sales than other branches within the company.
A) Employees at Branch A have significantly higher sales than other branches within the company.
B) Employees at Branch A have significantly lower sales than other branches within the company.
C) Employees at Branch A have significantly different sales than other branches within the company.
D) Employees at Branch A do not have significantly different sales than other branches within the company.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A z-test is a type of one-sample test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
You do not need to know the population mean to conduct a z-test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
You do not need to know the population standard deviation to conduct a one-sample t-test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
If you want to know the range of likely values for a sample mean given a particular population mean, you should conduct a z-test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
When we compute a z-statistic, we are determining how many standard errors the sample mean is away from the population mean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
For a two-tailed z-test when n = 10 and = .05, the correct critical value is 1.645.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
For a one-tailed t-test when n = 6 and = .05, the correct critical value is 2.015.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
When conducting a two-tailed test at = .05, you'd expect 2.5% of the sampling distribution to be in each tail.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
To compare a sample of n = 16 to a population where = 10 and 2 = 16, you will conduct a one-sample t-test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
You draw a sample of n = 30 from a population where = 10 and = 2. If x̄ = 8, z = -5.48.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
You draw a sample of n = 64 from a population where = 36 and = 4. If s = 5 and x̄ = 36, z = .06.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
You draw a sample of n = 17 from a population where = 4. If x̄ = 3 and s = 4, t = -.82.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
You draw a sample of n = 21 from a population where = 3 and x̄ = 6 and s = 5, t = 2.75.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
If you run a non-directional z-test and find that z = 1.68, you should reject the null.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If you run a two-tailed one-sample t-test where n = 12 and find that t = 2.57, you should reject the null.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
If you run a right-tailed z-test when n = 176 and find that z = 1.78, then p < .05.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
If you conduct a left-tailed t-test with a sample size of 101 and find that t = 2.58, then p < .05.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If you find a significant different in a one-sample test, you should determine both a confidence interval and an effect size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Effect size calculations provide an estimate of the real-world value of a particular finding.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A difference score is an example of a standardized effect size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
How do you know if a z-test or one-sample t-test is appropriate given a particular dataset?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Once you've calculate an obtained test statistic, how do you determine if it is statistically significant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Define "effect size" and explain when one should be calculated and why.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Describe the different types of effect sizes and explain how to interpret them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
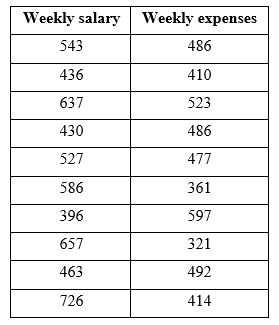 For the following questions:
For the following questions:-In the population, we'd expect Weekly Salary to have a mean of 621, but you want to know if your sample comes from a different population.
1)State the research question.
2)State the hypotheses.
3)State the critical value.
4)Provide the formal test of the hypothesis.
5)State the confidence interval.
6)Is an effect size calculation appropriate? How do you know? If yes, calculate both a standardized and unstandardized effect size.
7)State all appropriate conclusions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
 For the following questions:
For the following questions:-In the population, we'd expect Weekly Expenses to have a mean of 525, but you want to know if your sample comes from a different population with a lower mean.
1)State the research question.
2)State the hypotheses.
3)State the critical value.
4)Provide the formal test of the hypothesis.
5)State the confidence interval.
6)Is an effect size calculation appropriate? How do you know? If yes, calculate both a standardized and unstandardized effect size.
7)State all appropriate conclusions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








