Deck 5: Microbial Metabolism
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 5: Microbial Metabolism
1
The molecule that an enzyme acts upon is known as its
A) substrate.
B) coenzyme.
C) apoenzyme.
D) product.
E) catalyst.
A) substrate.
B) coenzyme.
C) apoenzyme.
D) product.
E) catalyst.
A
2
An organic compound gains an electron from another molecule. The organic compound
A) has been oxidized.
B) is an electron donor.
C) has been reduced.
D) has become more positively charged.
E) has lost a hydrogen atom.
A) has been oxidized.
B) is an electron donor.
C) has been reduced.
D) has become more positively charged.
E) has lost a hydrogen atom.
C
3
How many ATP molecules can theoretically be produced from the NADH generated by the catabolism of a molecule of glucose during aerobic respiration?
A) 34
B) 30
C) 38
D) 36
E) 4
A) 34
B) 30
C) 38
D) 36
E) 4
B
4
Which of the following is a by-product of the catabolism of proteins?
A) lactic acid
B) acetyl-CoA
C) proteases
D) ammonia
E) carbon dioxide
A) lactic acid
B) acetyl-CoA
C) proteases
D) ammonia
E) carbon dioxide

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following is/are common to chemiosmosis and the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
A) reduction of NADP⁺ only
B) electron transport only
C) a proton gradient only
D) both electron transport and a proton gradient
E) electron transport, a proton gradient, and reduction of NADP⁺
A) reduction of NADP⁺ only
B) electron transport only
C) a proton gradient only
D) both electron transport and a proton gradient
E) electron transport, a proton gradient, and reduction of NADP⁺

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Anabolic reactions may be characterized as
A) exergonic.
B) breaking large molecules into smaller molecules.
C) forming large molecules from smaller molecules.
D) producing ATP.
E) breaking large molecules into smaller molecules to produce ATP.
A) exergonic.
B) breaking large molecules into smaller molecules.
C) forming large molecules from smaller molecules.
D) producing ATP.
E) breaking large molecules into smaller molecules to produce ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements concerning enzymes is FALSE?
A) They are usually, but not always, proteins.
B) They always function best at 37°C.
C) They can be denatured if the pH of their environment is too high or too low.
D) They form a temporary intermediate compound with a substrate.
E) They can be used to catalyze a chemical reaction over and over again.
A) They are usually, but not always, proteins.
B) They always function best at 37°C.
C) They can be denatured if the pH of their environment is too high or too low.
D) They form a temporary intermediate compound with a substrate.
E) They can be used to catalyze a chemical reaction over and over again.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Sulfanilamide is an antimicrobial drug that mimics the shape of an important substrate for a particular bacterial enzyme, thereby inhibiting the enzyme. This type of inhibition is known as
A) allosteric inhibition.
B) competitive inhibition.
C) allosteric activation.
D) noncompetitive inhibition.
E) feedback inhibition.
A) allosteric inhibition.
B) competitive inhibition.
C) allosteric activation.
D) noncompetitive inhibition.
E) feedback inhibition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following produces NADPH?
A) the pentose phosphate pathway only
B) the Calvin-Benson cycle only
C) the Embden-Meyerhof pathway only
D) both the Embden-Meyerhof and Calvin-Benson cycle pathways
E) both the pentose phosphate and Entner-Doudoroff pathways
A) the pentose phosphate pathway only
B) the Calvin-Benson cycle only
C) the Embden-Meyerhof pathway only
D) both the Embden-Meyerhof and Calvin-Benson cycle pathways
E) both the pentose phosphate and Entner-Doudoroff pathways

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The electron transport chain provides the energy for
A) oxidative phosphorylation.
B) substrate-level phosphorylation.
C) beta-oxidation.
D) photophosphorylation.
E) anabolic reactions.
A) oxidative phosphorylation.
B) substrate-level phosphorylation.
C) beta-oxidation.
D) photophosphorylation.
E) anabolic reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Pyruvic acid is a product of
A) the Krebs cycle.
B) fermentation.
C) glycolysis.
D) the pentose phosphate pathway.
E) both fermentation and the Krebs cycle.
A) the Krebs cycle.
B) fermentation.
C) glycolysis.
D) the pentose phosphate pathway.
E) both fermentation and the Krebs cycle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a non-protein carrier found in some electron transport chains?
A) flavoproteins
B) metal-containing proteins
C) ribozymes
D) cytochromes
E) ubiquinones
A) flavoproteins
B) metal-containing proteins
C) ribozymes
D) cytochromes
E) ubiquinones

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements concerning cellular metabolism is FALSE?
A) Energy obtained from nutrients or light is stored in the bonds of ATP.
B) Enzymes are used in both catabolic and anabolic reactions.
C) Macromolecules are converted into cell structures via catabolism.
D) The goal of metabolism is reproduction of the organism.
E) ATP is used in the formation of macromolecules.
A) Energy obtained from nutrients or light is stored in the bonds of ATP.
B) Enzymes are used in both catabolic and anabolic reactions.
C) Macromolecules are converted into cell structures via catabolism.
D) The goal of metabolism is reproduction of the organism.
E) ATP is used in the formation of macromolecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements concerning glycolysis is TRUE?
A) The first step of glycolysis involves oxidative phosphorylation.
B) The glycolytic pathway is cyclical.
C) Glucose is activated by substrate-level phosphorylation.
D) Ribulose 5-phosphate is an intermediate of glycolysis.
E) Two NADH molecules are reduced during glycolysis.
A) The first step of glycolysis involves oxidative phosphorylation.
B) The glycolytic pathway is cyclical.
C) Glucose is activated by substrate-level phosphorylation.
D) Ribulose 5-phosphate is an intermediate of glycolysis.
E) Two NADH molecules are reduced during glycolysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Many vitamins are important ________ of enzymes.
A) protein cofactors
B) coenzymes
C) allosteric inhibitors
D) competitive inhibitors
E) activators
A) protein cofactors
B) coenzymes
C) allosteric inhibitors
D) competitive inhibitors
E) activators

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Anaerobic bacteria may use ________ as the final electron acceptor during anaerobic respiration.
A) nitrate only
B) carbon dioxide only
C) sulfate only
D) both nitrate and sulfate
E) carbon dioxide, nitrate and sulfate
A) nitrate only
B) carbon dioxide only
C) sulfate only
D) both nitrate and sulfate
E) carbon dioxide, nitrate and sulfate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
All of the following are forms of oxidation EXCEPT
A) loss of an electron.
B) loss of hydrogen atom.
C) a dehydrogenation event.
D) substrate-level phosphorylation.
E) gain of an oxygen atom and its electrons.
A) loss of an electron.
B) loss of hydrogen atom.
C) a dehydrogenation event.
D) substrate-level phosphorylation.
E) gain of an oxygen atom and its electrons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a fermentation product useful in the manufacture of cheese?
A) acetic acid
B) ammonia
C) ethanol
D) lactic acid
E) pyruvic acid
A) acetic acid
B) ammonia
C) ethanol
D) lactic acid
E) pyruvic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following is an active enzyme?
A) apoenzyme
B) cofactor
C) coenzyme
D) holoenzyme
E) subtrate
A) apoenzyme
B) cofactor
C) coenzyme
D) holoenzyme
E) subtrate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The various types of chlorophyll differ in the
A) amount of light they can absorb.
B) amount of ATP they produce.
C) number of electrons they release.
D) amount of oxygen they utilize.
E) wavelengths of light they absorb.
A) amount of light they can absorb.
B) amount of ATP they produce.
C) number of electrons they release.
D) amount of oxygen they utilize.
E) wavelengths of light they absorb.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Although glycolysis requires an input of ATP, this pathway results in a net gain of two ATP; therefore it is a(n) ________ pathway.
A) exergonic
B) endergonic
C) oxidative
D) reductive
E) neither exergonic nor endergonic
A) exergonic
B) endergonic
C) oxidative
D) reductive
E) neither exergonic nor endergonic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The metabolic processes called fermentation
A) produce substrates for the Krebs cycle.
B) are alternatives for the pentose phosphate pathway.
C) use an organic molecule as a final electron acceptor.
D) occur only when oxygen is readily available.
E) produce substrates for glycolysis.
A) produce substrates for the Krebs cycle.
B) are alternatives for the pentose phosphate pathway.
C) use an organic molecule as a final electron acceptor.
D) occur only when oxygen is readily available.
E) produce substrates for glycolysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The energy captured by photophosphorylation is used to produce glucose
A) through the Calvin-Benson cycle.
B) through the Krebs cycle.
C) by cyclic phosphorylation.
D) through the pentose-phosphate pathway.
E) by beta-oxidation.
A) through the Calvin-Benson cycle.
B) through the Krebs cycle.
C) by cyclic phosphorylation.
D) through the pentose-phosphate pathway.
E) by beta-oxidation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Bacteriochlorophyll a absorbs ________ light.
A) 350 nm, ultraviolet
B) 425 nm, violet
C) 660 nm, red
D) both 425 & 660 nm (violet and red)
E) all visible
A) 350 nm, ultraviolet
B) 425 nm, violet
C) 660 nm, red
D) both 425 & 660 nm (violet and red)
E) all visible

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Noncyclic photophosphorylation produces
A) ATP only.
B) oxygen.
C) NADPH only.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) water and ATP.
A) ATP only.
B) oxygen.
C) NADPH only.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) water and ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl-CoA can be described as ________, because a molecule of CO₂ is produced as a by-product.
A) decarboxylation
B) amination
C) respiration
D) oxidation
E) phosphorylation
A) decarboxylation
B) amination
C) respiration
D) oxidation
E) phosphorylation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
When a cell forms an amino acid by adding an amine group derived from ammonia to a precursor metabolite, this process is called
A) amination.
B) transamination.
C) reduction.
D) polymerization.
E) deamination.
A) amination.
B) transamination.
C) reduction.
D) polymerization.
E) deamination.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Enzymes known as lyases participate in ________ reactions.
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) both anabolic and catabolic
D) neither anabolic nor catabolic
E) oxidation-reduction
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) both anabolic and catabolic
D) neither anabolic nor catabolic
E) oxidation-reduction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Beta-oxidation of fatty acids produces a substrate of the
A) pentose phosphate pathway.
B) protein synthesis pathways.
C) Embden-Meyerhof pathway.
D) Krebs cycle.
E) Calvin-Benson cycle.
A) pentose phosphate pathway.
B) protein synthesis pathways.
C) Embden-Meyerhof pathway.
D) Krebs cycle.
E) Calvin-Benson cycle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
During the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from pyruvic acid, ________ is produced.
A) ATP
B) NADH
C) FADH₂
D) H₂O
E) acetic acid
A) ATP
B) NADH
C) FADH₂
D) H₂O
E) acetic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
During reactions catalyzed by oxidoreductases an electron donor is
A) oxidized.
B) reduced.
C) synthesized.
D) degraded.
E) unaltered.
A) oxidized.
B) reduced.
C) synthesized.
D) degraded.
E) unaltered.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Hydrolases are generally involved in ________ reactions.
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) both anabolic and catabolic
D) neither anabolic nor catabolic
E) oxidation-reduction
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) both anabolic and catabolic
D) neither anabolic nor catabolic
E) oxidation-reduction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If a cell reverses the process of beta-oxidation, which of the following molecules will it make?
A) glycerol
B) amino acids
C) fatty acids
D) nucleotides
E) starch
A) glycerol
B) amino acids
C) fatty acids
D) nucleotides
E) starch

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which of the following is associated with the Calvin-Benson cycle?
A) acetyl-CoA
B) TMAO
C) RuBP
D) FADH₂
E) PABA
A) acetyl-CoA
B) TMAO
C) RuBP
D) FADH₂
E) PABA

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The reactions of photosynthesis take place in the ________ of prokaryotes.
A) thylakoids
B) cytoplasm
C) nucleoid
D) cristae
E) outer membrane
A) thylakoids
B) cytoplasm
C) nucleoid
D) cristae
E) outer membrane

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following is TRUE concerning the structure and function of enzymes?
A) All enzymes bind cofactors necessary for their function.
B) An apoenzyme is a combination of a cofactor bound to a holoenzyme.
C) Enzymes can function at a wide range of pH.
D) Competitive inhibition of an enzyme occurs when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme.
E) After an enzyme has catalyzed a reaction, it resumes its original shape and can interact with a new substrate molecule.
A) All enzymes bind cofactors necessary for their function.
B) An apoenzyme is a combination of a cofactor bound to a holoenzyme.
C) Enzymes can function at a wide range of pH.
D) Competitive inhibition of an enzyme occurs when an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme.
E) After an enzyme has catalyzed a reaction, it resumes its original shape and can interact with a new substrate molecule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The conversion of amino acids to carbohydrates is an example of
A) amination.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) substrate-level phosphorylation.
D) beta-oxidation.
E) electron transport.
A) amination.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) substrate-level phosphorylation.
D) beta-oxidation.
E) electron transport.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following metabolic processes is commonly used to identify bacteria?
A) carbohydrate fermentation
B) lipid catabolism
C) Krebs cycle products
D) lipid synthesis
E) pentose phosphate pathway products
A) carbohydrate fermentation
B) lipid catabolism
C) Krebs cycle products
D) lipid synthesis
E) pentose phosphate pathway products

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Chemical reactions that can proceed toward either anabolism or catabolism are called
A) glycolytic.
B) light-independent.
C) synthetic.
D) cyclic.
E) amphibolic.
A) glycolytic.
B) light-independent.
C) synthetic.
D) cyclic.
E) amphibolic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Where is the majority of ATP generated in prokaryotic cells?
A) in the cytoplasmic membrane
B) in the cytosol
C) in the thylakoids
D) in the inner mitochondrial membrane
E) on ribosomes
A) in the cytoplasmic membrane
B) in the cytosol
C) in the thylakoids
D) in the inner mitochondrial membrane
E) on ribosomes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Another term for a protein catalyst is a(n) (enzyme/ribozyme).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A(n) (oxidation/reduction/transport) reaction is one in which a molecule accepts an electron.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The production of NADH takes place during the ________ stage(s) of glycolysis.
A) energy-conservation
B) energy-investment
C) lysis
D) lysis and energy-investment
E) energy-investment and energy-conservation
A) energy-conservation
B) energy-investment
C) lysis
D) lysis and energy-investment
E) energy-investment and energy-conservation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
During chemiosmosis, electrons are pumped across a membrane to produce ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
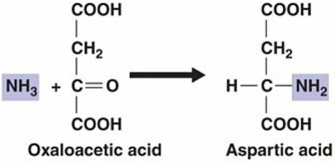 The process illustrated in the figure above is an example of a(n) ________ reaction.
The process illustrated in the figure above is an example of a(n) ________ reaction.A) amination
B) reduction
C) oxidation
D) transamination
E) transferase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The conversion of phosphoenol pyruvic acid (PEP) to pyruvic acid results in the production of an ATP. This reaction is an example of (substrate-level/oxidative/reductive) phosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
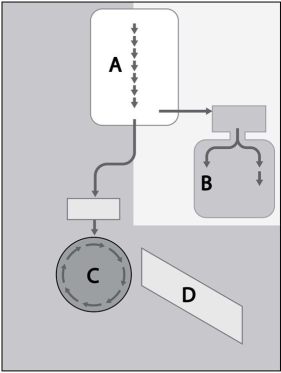
Identify the processes of glucose metabolism represented in Figure 5.1.
A) A = electron transport chain, B = Krebs cycle, C = glycolysis, D = fermentation
B) A = glycolysis, B = fermentation, C = Krebs cycle, D = electron transport chain
C) A = fermentation, B = glycolysis, C = Krebs cycle, D = electron transport chain
D) A = glycolysis, B = Krebs cycle, C = fermentation, D = electron transport chain
E) A = glycolysis, B = Krebs cycle, C = electron transport chain, D = fermentation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
As the concentration of substrate increases, the activity of the enzyme decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
All the precursors of amino acids are intermediates of glycolytic and fermentation pathways.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The (activation /inhibition/saturation) point of an enzyme is reached when all active sites have bound substrate molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Essential amino acids are amino acids that cannot be synthesized by an organism and so must be provided as nutrients.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs during which of the following stage(s) of glucose catabolism?
A) formation of acetyl-CoA
B) lysis stage of glycolysis
C) energy-conservation stage of glycolysis
D) Krebs cycle
E) formation of acetyl-CoA and the Krebs cycle
A) formation of acetyl-CoA
B) lysis stage of glycolysis
C) energy-conservation stage of glycolysis
D) Krebs cycle
E) formation of acetyl-CoA and the Krebs cycle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Accumulation of a metabolic pathway product may result in decreased activity of the pathway enzymes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The pentose phosphate pathway generates all the necessary precursors for nucleotide biosynthesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Reactions that are both catabolic and anabolic are amphibolic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
All substrates for ribozymes are RNA molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The amount of energy required for a reaction to occur is its activation energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is an intermediate in the Calvin-Benson cycle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of stages in glycolysis?
A) energy-conservation, energy-investment, lysis
B) lysis, energy-investment, energy-conservation
C) energy-investment, lysis, energy-conservation
D) lysis,energy-conservation, energy-investment
E) energy-investment, energy-conservation, lysis
A) energy-conservation, energy-investment, lysis
B) lysis, energy-investment, energy-conservation
C) energy-investment, lysis, energy-conservation
D) lysis,energy-conservation, energy-investment
E) energy-investment, energy-conservation, lysis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Reactions involving ligases are typically ________ reactions.
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) both anabolic and catabolic
D) neither anabolic nor catabolic
E) exergonic
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) both anabolic and catabolic
D) neither anabolic nor catabolic
E) exergonic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Some bacteria use (acetyl-CoA/DHAP/TMAO) as a final electron receptor, resulting in a detectable odor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The discussion of carbohydrate catabolism includes some of the many metabolic variations microbes are capable of. Devise a set of biochemical tests to identify the Gram-negative bacteria mentioned. Assume you can detect various organic compounds. Prepare a dichotomous key of your identification scheme.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Laboratory fermentation tests often include a pH indicator because many bacteria produce (O₂/bases/acids) as they ferment carbohydrates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Cells can use (active/allosteric/substrate) sites to regulate enzyme activity and thereby control their metabolism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Beta-oxidation of fatty acids produces (acetic acid/acetyl-CoA/glycerol).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Anaerobic respiration involves the use of molecules other than oxygen as the final electron (acceptor/donor) in an electron transport chain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Discuss the interrelationships between anabolic and catabolic pathways. Provide specific examples in your answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Significant amounts of the NADPH required for the Calvin-Benson cycle are produced during the (cyclic/noncyclic) photophosphorylation reactions of photosynthesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Compare and contrast cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Amino acids are converted to substrates of the Krebs cycle by (beta-oxidation/deamination/transamination).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Explain why the ATP yield from processes such as cellular respiration is generally given as a theoretical number.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Describe the mechanism of feedback inhibition and the role this process plays in controlling enzyme activity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Anoxygenic photosynthesis typically results in the production of (oxygen/sulfur/ammonia) as a waste product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Electrons are transferred in the Krebs cycle in the form of (oxygen/hydrogen) atoms to NAD+ and FAD.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Only Photosystem I is required for (anoxygenic/cyclic/noncyclic) photophosphorylation to occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The purpose of electron transport is to create a proton (concentration/gradient/pump) across a membrane that can then be used to make ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
When a noncompetitive inhibitor molecule binds to a(n) (active/allosteric/substrate) site on an enzyme, the shape of the active site changes so that the substrate molecules can no longer bind.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 77 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








