Deck 20: Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System and Eyes
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 20: Microbial Diseases of the Nervous System and Eyes
1
Some microbes gain access to the normally axenic central nervous system by
A) damaging the blood-brain barrier.
B) axonal transport from infected peripheral neurons.
C) infecting macrophages which subsequently enter the CNS.
D) infecting lymph nodes in the cranium.
E) either damaging the blood-brain barrier or by axonal transport from infected peripheral neurons.
A) damaging the blood-brain barrier.
B) axonal transport from infected peripheral neurons.
C) infecting macrophages which subsequently enter the CNS.
D) infecting lymph nodes in the cranium.
E) either damaging the blood-brain barrier or by axonal transport from infected peripheral neurons.
E
2
Which of the following is TRUE of foodborne botulism?
A) It is an intoxication disorder.
B) It is not a life-threatening infection even when left untreated.
C) Large amounts of bacteria must be consumed to produce disease.
D) Normal food preparation methods can prevent it.
E) An effective vaccine is available.
A) It is an intoxication disorder.
B) It is not a life-threatening infection even when left untreated.
C) Large amounts of bacteria must be consumed to produce disease.
D) Normal food preparation methods can prevent it.
E) An effective vaccine is available.
A
3
A baby arrives at an emergency room suffering from violent muscles spasms and difficulty breathing. The baby's body is so rigid a proper exam is difficult, but the staff note the baby is only a few weeks old and the umbilicus has not healed properly. The signs are consistent with which of the following diseases?
A) infant botulism
B) acute bacterial meningitis
C) tetanus
D) rabies
E) listeriosis
A) infant botulism
B) acute bacterial meningitis
C) tetanus
D) rabies
E) listeriosis
C
4
Functions of the meninges include
A) support for the brain and spinal cord.
B) transmission of signals from the peripheral nervous system.
C) protection from external shock.
D) production of neurotransmitters.
E) support for the brain and spinal cord and protection from external shock.
A) support for the brain and spinal cord.
B) transmission of signals from the peripheral nervous system.
C) protection from external shock.
D) production of neurotransmitters.
E) support for the brain and spinal cord and protection from external shock.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The Gram-negative diplococcus ________ is resistant to phagocytosis and releases Lipid A to cause inflammation.
A) Clostridium botulinum
B) Haemophilus influenza
C) Streptococcus agalactiae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Listeria monocytogenes
A) Clostridium botulinum
B) Haemophilus influenza
C) Streptococcus agalactiae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Listeria monocytogenes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The Gram-positive diplococcus ________ is commonly found in the pharynx but may invade the central nervous system inside cells where it survives after endocytosis.
A) Streptococcus agalactiae
B) Listeria monocytogenes
C) Haemophilus influenzae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae
A) Streptococcus agalactiae
B) Listeria monocytogenes
C) Haemophilus influenzae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following diseases is the result of a bacterial infection of peripheral nerves?
A) botulism
B) acute bacterial meningitis
C) Hansen's disease
D) tetanus
E) rabies
A) botulism
B) acute bacterial meningitis
C) Hansen's disease
D) tetanus
E) rabies

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Voluntary muscle control is one of functions of the
A) cerebellum.
B) cerebrum.
C) spinal cord.
D) brain stem.
E) meninges.
A) cerebellum.
B) cerebrum.
C) spinal cord.
D) brain stem.
E) meninges.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The optic nerves are an example of which of the following?
A) motor nerves
B) spinal nerves
C) mixed nerves
D) synaptic nerves
E) sensory nerves
A) motor nerves
B) spinal nerves
C) mixed nerves
D) synaptic nerves
E) sensory nerves

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
How does tetanospasmin affect motor control?
A) It blocks the secretion of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft.
B) It blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters in the CNS.
C) It triggers the endocytosis of skeletal muscle cells.
D) It induces nervous system proteins to fold into abnormal shapes.
E) It is a pyrogenic toxin.
A) It blocks the secretion of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft.
B) It blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters in the CNS.
C) It triggers the endocytosis of skeletal muscle cells.
D) It induces nervous system proteins to fold into abnormal shapes.
E) It is a pyrogenic toxin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The pleomorphic bacterium ________ is an obligate parasite due to its requirement for NAD⁺ and heme.
A) Neisseria meningitidis
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Haemophilus influenzae
E) Streptococcus agalactiae
A) Neisseria meningitidis
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae
C) Listeria monocytogenes
D) Haemophilus influenzae
E) Streptococcus agalactiae

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The highly destructive form of Hansen's disease is the result of
A) poor immune response to Mycobacterium leprae.
B) autoimmune disease triggered by Mycobacteriu leprae.
C) intracellular infection with Clostridium botulinum.
D) poor immune response to Streptococcus agalactiae.
E) infection with rabies virus.
A) poor immune response to Mycobacterium leprae.
B) autoimmune disease triggered by Mycobacteriu leprae.
C) intracellular infection with Clostridium botulinum.
D) poor immune response to Streptococcus agalactiae.
E) infection with rabies virus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Encephalitis is an infection of
A) the brain.
B) the meninges.
C) neurons of the peripheral nervous system.
D) the eye.
E) the cauda equina.
A) the brain.
B) the meninges.
C) neurons of the peripheral nervous system.
D) the eye.
E) the cauda equina.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Tetanus vaccine contains
A) antibodies against Clostridium tetani.
B) inactivated Clostridium tetani endospores.
C) antibodies against Clostridium tetani endospores.
D) fragments of Clostridium tetani cell walls.
E) inactivated tetanospasmin.
A) antibodies against Clostridium tetani.
B) inactivated Clostridium tetani endospores.
C) antibodies against Clostridium tetani endospores.
D) fragments of Clostridium tetani cell walls.
E) inactivated tetanospasmin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The type of bacterial meningitis that becomes epidemic among young adults is caused by
A) Streptococcus agalactiae.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Haemophilus influenzae.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
E) Listeria monocytogenes.
A) Streptococcus agalactiae.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Haemophilus influenzae.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
E) Listeria monocytogenes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Contaminated food is the source of ________, which causes meningitis in the elderly and susceptible persons.
A) Neisseria meningitidis
B) Streptococcus agalactiae
C) Haemophilus influenzae
D) Listeria monocytogenes
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae
A) Neisseria meningitidis
B) Streptococcus agalactiae
C) Haemophilus influenzae
D) Listeria monocytogenes
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Botulism toxin disrupts motor control by
A) blocking the release of acetylcholine by motor neurons.
B) causing demyelination of motor neurons.
C) blocking inhibitory signals to motor neurons.
D) killing motor neurons.
E) blocking acetylcholine receptors on muscle cells.
A) blocking the release of acetylcholine by motor neurons.
B) causing demyelination of motor neurons.
C) blocking inhibitory signals to motor neurons.
D) killing motor neurons.
E) blocking acetylcholine receptors on muscle cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Newborns exposed to the Gram-positive bacterium ________ during vaginal birth are at risk of developing neonatal meningitis.
A) Streptococcus agalactiae
B) Listeria monocytogenes
C) Haemophilus influenzae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae
A) Streptococcus agalactiae
B) Listeria monocytogenes
C) Haemophilus influenzae
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) Streptococcus pneumoniae

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Bacterial agents of meningitis which can survive phagocytosis include
A) Neisseria meningitidis.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Mycobacterium leprae.
D) both Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
E) Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Mycobacterium leprae.
A) Neisseria meningitidis.
B) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
C) Mycobacterium leprae.
D) both Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
E) Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Mycobacterium leprae.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the ________ to deliver nutrients to the brain and spinal cord.
A) dura mater
B) arachnoid villi
C) cranial sinuses
D) subarachnoid space
E) pia mater
A) dura mater
B) arachnoid villi
C) cranial sinuses
D) subarachnoid space
E) pia mater

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
An intracellular parasite primarily transmitted as an STD is the agent of ________, which may cause enough damage to result in blindness.
A) primary amebic meningoencephalopathy
B) trachoma
C) rabies
D) tetanus
E) cryptococcal meningitis
A) primary amebic meningoencephalopathy
B) trachoma
C) rabies
D) tetanus
E) cryptococcal meningitis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Slow deterioration of muscle function occurring over many years occurs in
A) West Nile encephalitis.
B) postpolio syndrome.
C) African sleeping sickness.
D) minor polio.
E) leprosy.
A) West Nile encephalitis.
B) postpolio syndrome.
C) African sleeping sickness.
D) minor polio.
E) leprosy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The condition known as "pinkeye" may be the result of infection with
A) Haemophilus influenzae.
B) Trypanosoma brucei.
C) Acanthamoeba.
D) Clostridium botulinum.
E) Chlamydia trachomatis.
A) Haemophilus influenzae.
B) Trypanosoma brucei.
C) Acanthamoeba.
D) Clostridium botulinum.
E) Chlamydia trachomatis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
One summer, bird watchers and zookeepers in a major city notice that more birds than usual are dying. At the same time reports of human encephalitis cases increase sharply. The cerebrospinal fluid of human patients is clear. Similar enveloped RNA virus particles are detected in samples from both birds and humans. Which of the following might be responsible for this outbreak?
A) an arbovirus
B) coxsackie A virus
C) Cryptococcus neoformans
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) rabies virus
A) an arbovirus
B) coxsackie A virus
C) Cryptococcus neoformans
D) Neisseria meningitidis
E) rabies virus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease can be prevented by avoiding
A) contact with mosquitoes.
B) contaminated waterways.
C) consumption of contaminated meat.
D) contact with bird droppings.
E) consumption of undercooked meat.
A) contact with mosquitoes.
B) contaminated waterways.
C) consumption of contaminated meat.
D) contact with bird droppings.
E) consumption of undercooked meat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Poliovirus is most often transmitted via
A) contaminated water.
B) household pets.
C) mosquitoes.
D) droplets.
E) endospores.
A) contaminated water.
B) household pets.
C) mosquitoes.
D) droplets.
E) endospores.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The normal hosts for St. Louis encephalitis virus are
A) birds.
B) small mammals.
C) horses.
D) humans.
E) horses and humans.
A) birds.
B) small mammals.
C) horses.
D) humans.
E) horses and humans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A child is brought to the hospital with high fever and headache. During examination a stiff neck is noted. What sign indicates the child has viral meningitis instead of bacterial meningitis?
A) blood in the CSF.
B) cloudy CSF.
C) paralysis.
D) clear CSF.
E) peripheral nerve pain.
A) blood in the CSF.
B) cloudy CSF.
C) paralysis.
D) clear CSF.
E) peripheral nerve pain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A child is brought to the hospital with a high fever, nausea, and vomiting, and complaining of headache. The cerebrospinal fluid collected by spinal tap is cloudy and contains spherical cells which stain Gram-positive. These signs and symptoms are consistent with
A) primary amebic encephalitis caused by Naegleria.
B) cryptococcal meningitis due to infection with Cryptococcus neoformans.
C) bacterial meningitis probably due to Streptococcus.
D) tetanus resulting from infection with Clostridium botulinum.
E) aseptic meningitis from infection with Neisseria meningitidis.
A) primary amebic encephalitis caused by Naegleria.
B) cryptococcal meningitis due to infection with Cryptococcus neoformans.
C) bacterial meningitis probably due to Streptococcus.
D) tetanus resulting from infection with Clostridium botulinum.
E) aseptic meningitis from infection with Neisseria meningitidis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The least common type of polio is
A) nonparalytic polio.
B) an asymptomatic infection.
C) minor polio.
D) paralytic polio.
E) postpolio syndrome.
A) nonparalytic polio.
B) an asymptomatic infection.
C) minor polio.
D) paralytic polio.
E) postpolio syndrome.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Nasal or ocular contact with water containing ________ may result in primary amebic meningoencephalitis.
A) Acanthamoeba
B) Naegleria
C) Trypanosoma brucei
D) both Acanthomoeba and Naegleria
E) Acanthamoeba, Naegleria and Trypanosoma brucei
A) Acanthamoeba
B) Naegleria
C) Trypanosoma brucei
D) both Acanthomoeba and Naegleria
E) Acanthamoeba, Naegleria and Trypanosoma brucei

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following nervous system diseases is treated with both passive and active immunization?
A) arboviral encephalitis
B) botulism
C) primary amebic meningoencephalopathy
D) rabies
E) West Nile encephalitis
A) arboviral encephalitis
B) botulism
C) primary amebic meningoencephalopathy
D) rabies
E) West Nile encephalitis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which of the following is classified as a spongiform encephalopathy?
A) botulism
B) variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
C) Hansen's disease
D) arboviral encephalitis
E) African sleeping sickness
A) botulism
B) variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
C) Hansen's disease
D) arboviral encephalitis
E) African sleeping sickness

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements concerning rabies is FALSE?
A) It is caused by an ssRNA virus.
B) Transmission is usually via a bite from a rabid animal.
C) Treatment includes vaccination.
D) Bats are the source of most cases of rabies in humans.
E) All mammals can serve as a reservoir for the disease.
A) It is caused by an ssRNA virus.
B) Transmission is usually via a bite from a rabid animal.
C) Treatment includes vaccination.
D) Bats are the source of most cases of rabies in humans.
E) All mammals can serve as a reservoir for the disease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The disease known as cryptococcal meningitis
A) begins as a lung infection.
B) is caused by a Gram-negative coccus.
C) results from exposure to bird droppings.
D) is transmitted in respiratory aerosols.
E) results from exposure to bird droppings and begins as a lung infection.
A) begins as a lung infection.
B) is caused by a Gram-negative coccus.
C) results from exposure to bird droppings.
D) is transmitted in respiratory aerosols.
E) results from exposure to bird droppings and begins as a lung infection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A young man is experiencing fever and severe headaches, and is having difficulty staying awake. He reports having spent time in Africa on a missionary trip several months ago. Recently he spent time in a park where he went swimming in the lake and was bitten by a bat he attempted to catch. His cerebrospinal fluid is nearly clear, and contains long, slender, mobile cells. This description indicates infection with
A) Acanthamoeba.
B) an enterovirus.
C) rabies virus.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
E) Trypanosoma brucei.
A) Acanthamoeba.
B) an enterovirus.
C) rabies virus.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
E) Trypanosoma brucei.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Viral meningitis is also called "aseptic meningitis"
A) to indicate no bacteria are involved.
B) because it is frequently a nosocomial infection.
C) since it is treatable with antiviral medications.
D) because it is vaccine-preventable.
E) to distinguish it from encephalitis.
A) to indicate no bacteria are involved.
B) because it is frequently a nosocomial infection.
C) since it is treatable with antiviral medications.
D) because it is vaccine-preventable.
E) to distinguish it from encephalitis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis is directly related to its ability to
A) produce a powerful toxin.
B) form endospores.
C) produce a polysaccharide capsule.
D) live and reproduce inside its host's cells.
E) resist most antimicrobial agents.
A) produce a powerful toxin.
B) form endospores.
C) produce a polysaccharide capsule.
D) live and reproduce inside its host's cells.
E) resist most antimicrobial agents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
African sleeping sickness is fatal if not treated because the parasite
A) evades destruction by the immune system by changing surface antigens.
B) produces a toxin which binds irreversibly to neurons.
C) is an intracellular parasite in RBC's, where they are not detected by the immune system.
D) reproduces so fast there is no time for an immune response to develop.
E) produces a non-immunogenic toxin the immune system cannot neutralize.
A) evades destruction by the immune system by changing surface antigens.
B) produces a toxin which binds irreversibly to neurons.
C) is an intracellular parasite in RBC's, where they are not detected by the immune system.
D) reproduces so fast there is no time for an immune response to develop.
E) produces a non-immunogenic toxin the immune system cannot neutralize.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following causes of viral meningitis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route?
A) Eastern equine encephalitis virus
B) California encephalitis virus
C) West Nile virus
D) echovirus
E) rabies
A) Eastern equine encephalitis virus
B) California encephalitis virus
C) West Nile virus
D) echovirus
E) rabies

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The presence of (cocci/diplococci/coccobacilli/streptococci) in the CSF is consistent with infection with Listeria monocytogenes. (Describe the appearance of the cells.)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Cryptococcal meningitis can affect both healthy and immunocompromised individuals.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Tetanospasmin blocks the release of stimulatory neurotransmitters.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
West Nile virus is transmitted by (food/mosquitoes/water).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A diagnostic indicator of bacterial meningitis is (clear/milky/dark) cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
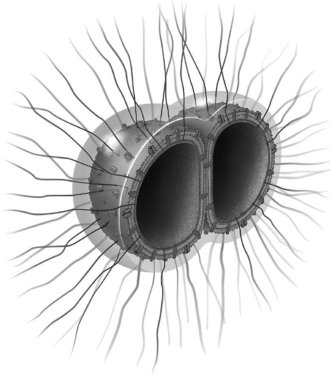 The illustration is of a Gram-negative bacterium frequently responsible for meningitis. What virulence factor(s) of the bacterium is/are illustrated?
The illustration is of a Gram-negative bacterium frequently responsible for meningitis. What virulence factor(s) of the bacterium is/are illustrated?A) a capsule
B) fimbriae
C) a membrane containing LOS
D) a capsule and fimbriae
E) a capsule, fimbriae, and a membrane containing LOS

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
All arboviruses are members of the same virus family.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Rabies is a rare zoonosis in humans but common in many other species of mammal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The neurotoxins of Clostridium botulinum produce (paralysis/spasms/weakness) by interfering with acetylcholine secretion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The only natural hosts for infection with the microbe Mycobacterium leprae are humans and (armadillos/birds/pigs).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Viral meningitis is usually more serious than bacterial meningitis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The form of botulism known as (foodborne/infant/wound) is an intoxication disorder.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Small subcutaneous hemorrhages called (granulations/macules/petechiae) are sometimes present in cases of meningitis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Children in the United States are vaccinated with the (IPV/OPV/PEP) to prevent polio. (Use all uppercase in your answer.)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Rodents are a major reservoir for rabies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Horses and humans are considered "dead-end" hosts for arboviruses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Fungi rarely infect the central nervous system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Trypanosoma brucei is transmitted to animals and people by a bloodsucking fly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Clostridium botulinum can grow in the intestinal tracts of both infants and adults.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Infant botulism is the result of (inhalation/ingestion/inoculation) of bacterial endospores.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A one-year-old child is brought to the hospital with high fever and limited range of motion of the head. The child frequently rubs her head. A recent history is not immediately available due to a language barrier on the part of the parent. The attending physician suspects meningitis and orders a sample of CFS be collected. Describe the various diagnoses possible based on the results with the CSF.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Compare and contrast the pathogenicity of Clostridium botulinum and Clostridium tetani, including mechanisms of action of their toxins and disease manifestations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast African sleeping sickness and primary amebic meningoencephalopathy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Discuss the two types of poliovirus vaccines available, including the advantages and disadvantages of each.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Negri bodies are a characteristic microscopic finding in the diagnosis of (encephalitis/leprosy/rabies).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The (eyes/intestines/lungs) are the initial site of infection with Cryptococcus neoformans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The normal habitat for Naegleria is (birds/mammals/water).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The condition called (conjunctivitis/keratitis/trachoma) is the result of infection of the cornea.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The presence of the pathogen in the blood called (bacteremia/parasitemia/viremia) is a defining feature of African sleeping sickness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Spongiform encephalopathy diseases develop as a result of infection with (parasites/prions/rabies).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Describe the pathogenesis associated with Trypanosoma brucei that makes it nearly impossible for infected individuals to become immune to the pathogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








