Deck 32: Foreign Exchange Markets
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 32: Foreign Exchange Markets
1
A _____ market is a complex, noncentralized market where currencies are traded.
A) derivatives
B) capital
C) foreign exchange
D) commodity
A) derivatives
B) capital
C) foreign exchange
D) commodity
C
2
A foreign exchange market is a:
A) market where equities are traded.
B) complex, noncentralized market where currencies are traded.
C) market where raw, homogeneous products are bought and sold.
D) market where future contracts and options are traded.
A) market where equities are traded.
B) complex, noncentralized market where currencies are traded.
C) market where raw, homogeneous products are bought and sold.
D) market where future contracts and options are traded.
B
3
A _____ market is a complex, noncentralized market where currencies are traded.
A) derivatives
B) capital
C) currency
D) commodity
A) derivatives
B) capital
C) currency
D) commodity
C
4
The foreign exchange market is located:
A) at the Intercontinental Exchange.
B) in the Chicago Mercantile Exchange.
C) at the New York stock exchange and the London stock exchange.
D) electronically and in many financial firms.
A) at the Intercontinental Exchange.
B) in the Chicago Mercantile Exchange.
C) at the New York stock exchange and the London stock exchange.
D) electronically and in many financial firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The foreign exchange market is _____ currency exchange can take place.
A) in New York city, where
B) in London, where
C) in Brussels, where
D) anywhere that
A) in New York city, where
B) in London, where
C) in Brussels, where
D) anywhere that

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The value of currency that is exchanged in one week:
A) cannot be determined.
B) exceeds the value of U.S. GDP in a year.
C) is always expressed in U.S. dollars.
D) is less than a trillion U.S. dollars.
A) cannot be determined.
B) exceeds the value of U.S. GDP in a year.
C) is always expressed in U.S. dollars.
D) is less than a trillion U.S. dollars.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Approximately _____ currencies are exchanged in the foreign exchange market.
A) 35
B) 115
C) 180
D) 300
A) 35
B) 115
C) 180
D) 300

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
_____ rate is the price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency.
A) A transfer
B) A value
C) A foreign
D) An exchange
A) A transfer
B) A value
C) A foreign
D) An exchange

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
If a Japanese firm does business with a firm in Italy, the Japanese firm must convert:
A) euros into yen.
B) yen into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.
A) euros into yen.
B) yen into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
If a Japanese firm does business with a firm in United States, the Japanese firm must convert:
A) euros into yen.
B) yen into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.
A) euros into yen.
B) yen into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If a U.S. firm does business with a firm in Japan, the U.S. firm must convert:
A) euros into yen.
B) yen into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.
A) euros into yen.
B) yen into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
If a U.S. firm does business with a firm in France, the U.S. firm must convert:
A) euros into yen.
B) dollars into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.
A) euros into yen.
B) dollars into euros.
C) yen into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If a German firm does business with a firm in the United States, the German firm must convert:
A) euros into yen.
B) dollars into euros.
C) euros into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.
A) euros into yen.
B) dollars into euros.
C) euros into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
If a German firm does business with a firm in Japan, the German firm must convert:
A) euros into yen.
B) dollars into euros.
C) euros into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.
A) euros into yen.
B) dollars into euros.
C) euros into dollars.
D) dollars into yen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
An exchange rate is the:
A) price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency.
B) standard notation that is used to express one currency in terms of another currency.
C) value of currency fluctuations.
D) appreciation of a currency.
A) price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency.
B) standard notation that is used to express one currency in terms of another currency.
C) value of currency fluctuations.
D) appreciation of a currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
An exchange rate has _____ currency and a _____ currency.
A) a front; back
B) an upper; lower
C) a base; counter
D) an appreciated; depreciated
A) a front; back
B) an upper; lower
C) a base; counter
D) an appreciated; depreciated

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
In the currency pair, USD/EUR .87, the base currency is _____, and the counter currency is:
A) EUR; unknown.
B) unknown; EUR.
C) USD; EUR.
D) EUR; USD.
A) EUR; unknown.
B) unknown; EUR.
C) USD; EUR.
D) EUR; USD.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In the currency pair, EUR/JPY 130, the base currency is _____, and the counter currency is:
A) EUR; unknown.
B) unknown; EUR.
C) JPY; EUR.
D) EUR; JPY.
A) EUR; unknown.
B) unknown; EUR.
C) JPY; EUR.
D) EUR; JPY.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In the currency pair USD/EUR, _____ the currency is being considered.
A) neither the USD nor the EUR is
B) the JPY is
C) the USD is
D) the EUR is
A) neither the USD nor the EUR is
B) the JPY is
C) the USD is
D) the EUR is

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
_____ of a currency is an adjustment in the exchange rate that makes a country's currency more valuable relative to another country's currency.
A) Appreciation
B) Depreciation
C) Manipulation
D) Maneuvering
A) Appreciation
B) Depreciation
C) Manipulation
D) Maneuvering

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
_____ of a currency is an adjustment in the exchange rate that makes a country's currency less valuable relative to another country's currency.
A) Appreciation
B) Depreciation
C) Manipulation
D) Maneuvering
A) Appreciation
B) Depreciation
C) Manipulation
D) Maneuvering

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
_____ occurs when the euro rises in value against the dollar.
A) A manipulation of the dollar
B) A maneuvering of the dollar
C) An appreciation of the euro
D) A depreciation of the euro
A) A manipulation of the dollar
B) A maneuvering of the dollar
C) An appreciation of the euro
D) A depreciation of the euro

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
When the euro falls against the yen, the euro has _____, and the yen has:
A) depreciated; appreciated.
B) depreciated; depreciated.
C) appreciated; depreciated.
D) appreciated; appreciated.
A) depreciated; appreciated.
B) depreciated; depreciated.
C) appreciated; depreciated.
D) appreciated; appreciated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
If USD/JPY 111.24 changes to USD/JPY 114.2, the dollar has _____, and the yen has:
A) depreciated; appreciated.
B) depreciated; depreciated.
C) appreciated; depreciated.
D) appreciated; appreciated.
A) depreciated; appreciated.
B) depreciated; depreciated.
C) appreciated; depreciated.
D) appreciated; appreciated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If USD/EUR .86 changes to USD/EUR .82, the dollar has _____, and the euro has:
A) depreciated; appreciated.
B) depreciated; depreciated.
C) appreciated; depreciated.
D) appreciated; appreciated.
A) depreciated; appreciated.
B) depreciated; depreciated.
C) appreciated; depreciated.
D) appreciated; appreciated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When the yen _____ against the euro, the price of goods and services that are produced in Japan are generally _____ in Europe.
A) depreciates; not affected
B) depreciates; less expensive
C) appreciates; not affected
D) appreciates; less expensive
A) depreciates; not affected
B) depreciates; less expensive
C) appreciates; not affected
D) appreciates; less expensive

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
When the yen _____ against the euro, the price of goods and services produced in Japan are generally _____ in Europe.
A) depreciates; not affected
B) depreciates; more expensive
C) appreciates; not affected
D) appreciates; more expensive
A) depreciates; not affected
B) depreciates; more expensive
C) appreciates; not affected
D) appreciates; more expensive

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
If the USD/EUR .86 changes to USD/EUR .89, the USD has _____, and the EUR has:
A) appreciated; depreciated.
B) depreciated; appreciated.
C) appreciated; appreciated.
D) depreciated; depreciated.
A) appreciated; depreciated.
B) depreciated; appreciated.
C) appreciated; appreciated.
D) depreciated; depreciated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The demand for a currency is derived from the _____ for products and financial investments that require that currency.
A) price
B) cost
C) supply
D) demand
A) price
B) cost
C) supply
D) demand

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When Europeans visit Disney World in Florida, they:
A) demand euros in exchange for dollars.
B) supply euros in exchange for dollars.
C) supply dollars in exchange for euros.
D) demand dollars in exchange for euros.
A) demand euros in exchange for dollars.
B) supply euros in exchange for dollars.
C) supply dollars in exchange for euros.
D) demand dollars in exchange for euros.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
If Europeans no longer desire U.S. clothing, the demand for dollars will _____, and the dollar will:
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
If Europe is experiencing inflation, the demand for euros will _____, and the euro will:
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If prices are falling in Japan, the demand for yen will _____, and the yen will:
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
An increase in tariffs on European goods _____ the demand for euros, and the euro will:
A) decreases; depreciate.
B) decreases; appreciate.
C) increases; depreciate.
D) increases; appreciate.
A) decreases; depreciate.
B) decreases; appreciate.
C) increases; depreciate.
D) increases; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A decrease in tariffs on U.S. goods _____ the demand for dollars, and the dollar will:
A) decreases; depreciate.
B) decreases; appreciate.
C) increases; depreciate.
D) increases; appreciate.
A) decreases; depreciate.
B) decreases; appreciate.
C) increases; depreciate.
D) increases; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
If banks in Europe are paying a higher rate of interest on savings accounts, the demand for euros will _____, and the euro will:
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If a Japanese bank is paying 2% interest on savings and an American bank is paying 4% interest, the demand for dollars will _____, and the dollar will:
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.
A) decrease; depreciate.
B) decrease; appreciate.
C) increase; depreciate.
D) increase; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A fall in a country's interest rate will generally cause the currency to _____, and a rise in interest rates will cause the currency to:
A) depreciate; depreciate.
B) depreciate; appreciate.
C) appreciate; depreciate.
D) appreciate; appreciate.
A) depreciate; depreciate.
B) depreciate; appreciate.
C) appreciate; depreciate.
D) appreciate; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
(Figure: Currency Shift) In the above figure, the dollar _____, while the euro _____.
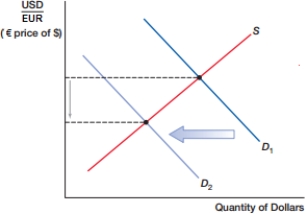
A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
(Figure: Currency Shift 0) In the above figure, the dollar _____, while the euro _____.
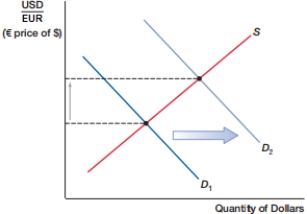
A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
When a central bank _____ the supply of dollars on the foreign exchange market, the dollar will:
A) floats; depreciate.
B) floats; appreciate.
C) decreases; depreciate.
D) decreases; appreciate.
A) floats; depreciate.
B) floats; appreciate.
C) decreases; depreciate.
D) decreases; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
When a central bank _____ the supply of dollars on the foreign exchange market, the dollar will:
A) floats; depreciate.
B) floats; appreciate.
C) increases; depreciate.
D) increases; appreciate.
A) floats; depreciate.
B) floats; appreciate.
C) increases; depreciate.
D) increases; appreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
_____ in the exchange rate market is what occurs when the quantity demanded for a country's currency is the same as the quantity supplied of the country's currency.
A) Floating
B) Equilibrium
C) Appreciation
D) Depreciation
A) Floating
B) Equilibrium
C) Appreciation
D) Depreciation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Equilibrium in the exchange rate market occurs when:
A) two currencies equal each other.
B) three currencies equal each other.
C) the quantity demanded for a country's currency is the same as the quantity supplied of the country's currency.
D) the quantity demanded for a country's currency is greater than the quantity supplied of the country's currency.
A) two currencies equal each other.
B) three currencies equal each other.
C) the quantity demanded for a country's currency is the same as the quantity supplied of the country's currency.
D) the quantity demanded for a country's currency is greater than the quantity supplied of the country's currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
(Figure: Shifts in the Supply of Dollars) 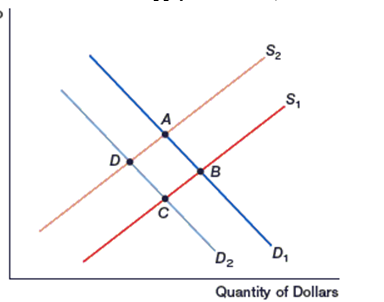
-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
(Figure: Shifts in the Supply of Dollars) 
-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) move to point
B) move to point
C) move to point
D) not move.

-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) move to point
B) move to point
C) move to point
D) not move.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
(Figure: Shifts in the Supply of Dollars) 
-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
(Figure: Shifts in the Supply of Dollars) 
-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

-In the figure, the dollar is currently at point
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
(Figure: Currency Shift A) In the figure, the dollar _____, while the euro _____.
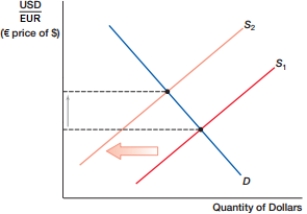
A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
(Figure: Currency Shift I) In the figure, the dollar _____, while the euro _____.
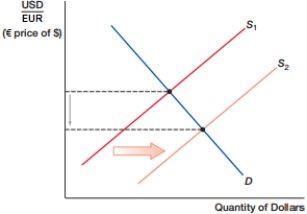
A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

A) depreciates; depreciates.
B) depreciates; appreciates.
C) appreciates; depreciates.
D) appreciates; appreciates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
XYZ Corporation, a major exporter of tires, would generally prefer _____ dollar.
A) an unstable
B) a variable
C) a stronger
D) a weaker
A) an unstable
B) a variable
C) a stronger
D) a weaker

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
When the dollar _____, U.S. products are _____ expensive to the rest of the world.
A) appreciates; less
B) appreciates; more
C) depreciates; more
D) depreciates; equally
A) appreciates; less
B) appreciates; more
C) depreciates; more
D) depreciates; equally

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
When the dollar _____, U.S. products are _____ expensive to the rest of the world.
A) appreciates; less
B) appreciates; equally
C) depreciates; more
D) depreciates; less
A) appreciates; less
B) appreciates; equally
C) depreciates; more
D) depreciates; less

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
U.S. exports will increase when the dollar depreciates if the depreciation is caused by a decrease in demand for:
A) U.S. goods and services.
B) international trade.
C) financial assets.
D) the other country's currency.
A) U.S. goods and services.
B) international trade.
C) financial assets.
D) the other country's currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
U.S. exports will decrease when the dollar depreciates if the depreciation is caused by a decrease in demand for:
A) U.S. goods and services.
B) international trade.
C) financial assets.
D) the other country's currency.
A) U.S. goods and services.
B) international trade.
C) financial assets.
D) the other country's currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When the supply of a domestic currency increases while demand simultaneously decreases, that currency tends to _____ against other currencies.
A) stabilize
B) equal out
C) appreciate
D) depreciate
A) stabilize
B) equal out
C) appreciate
D) depreciate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if interest rates increase in Europe.

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if inflation increases in Europe.
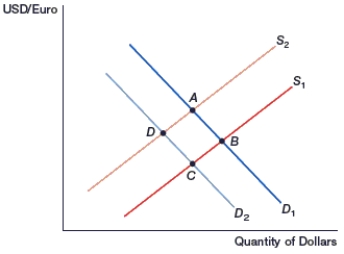
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if interest rates decrease in the U.S.
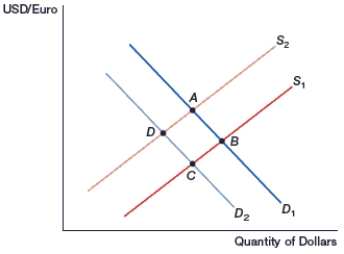
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if inflation decreases in the U.S.
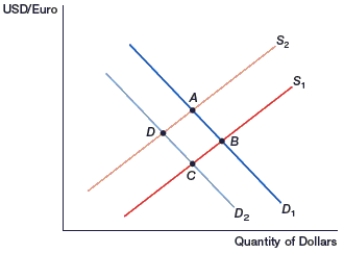
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if interest rates decrease in Europe.
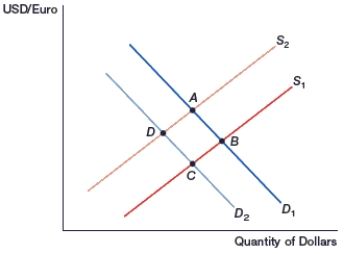
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if inflation decreases in Europe.
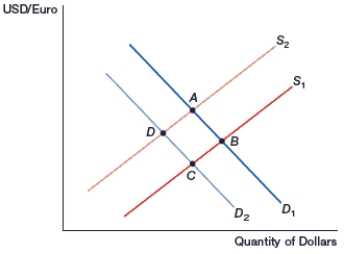
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if interest rates increase in the U.S.
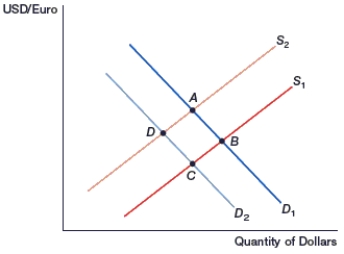
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, movement from _____ occurs if inflation increases in the U.S.
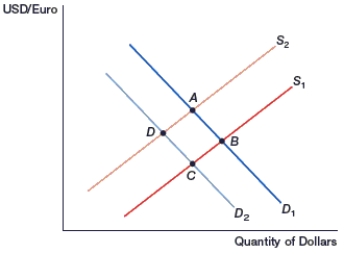
A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

A) D to B
B) B to D
C) C to A
D) A to C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
When supply decreases while demand of a domestic currency simultaneously increases, that currency tends to:
A) stabilize.
B) equal out.
C) appreciate.
D) depreciate.
A) stabilize.
B) equal out.
C) appreciate.
D) depreciate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, if the domestic currency is at point D, its supply increases, and demand decreases, the domestic currency will move to point:
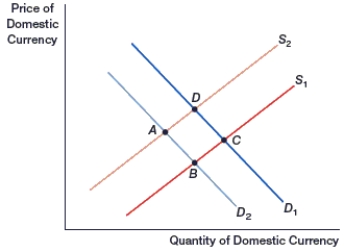
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, if the domestic currency is at point B, its supply decreases, and demand increases, the domestic currency will move to point:
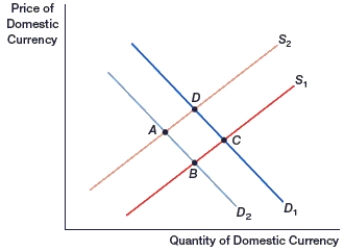
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, if the yen is the domestic currency and interest rates fall in Japan, the yen will move from point D to point:
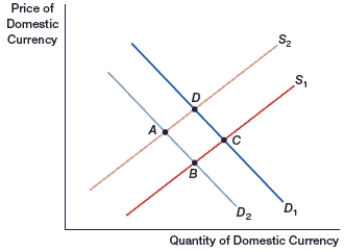
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
(Figure: Generalized Exchange Rate Model) In the figure, if the yen is the domestic currency and interest rates rise in Japan, the yen will move from point B to point:
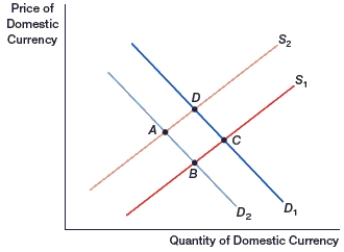
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
When exchange rates are expressed as their reciprocals, _____ reversed.
A) the numerator and denominator are
B) supply and demand are
C) currency risk is
D) equilibrium is
A) the numerator and denominator are
B) supply and demand are
C) currency risk is
D) equilibrium is

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
When the numerator and denominator in a currency pair are reversed, the exchange rate is expressed:
A) in terms of currency risk.
B) with the dollar first.
C) at equilibrium.
D) as its reciprocal.
A) in terms of currency risk.
B) with the dollar first.
C) at equilibrium.
D) as its reciprocal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
To calculate payments in an alternative currency:
A) divide the domestic currency by the foreign currency.
B) multiply the currency being swapped by the exchange rate or its reciprocal.
C) multiply the domestic currency by the foreign currency.
D) multiply the numerator by the denominator.
A) divide the domestic currency by the foreign currency.
B) multiply the currency being swapped by the exchange rate or its reciprocal.
C) multiply the domestic currency by the foreign currency.
D) multiply the numerator by the denominator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Mandy is visiting Japan and wants to purchase a pair of earrings. They are priced at 14,000 yen, and one U.S dollar is equal to 111 yen. If Mandy converts her U.S. dollars into yen, she will need about ____ dollars to pay for the earrings.
A) $111
B) $126
C) $140
D) $1,554
A) $111
B) $126
C) $140
D) $1,554

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Gunther is visiting Japan and wants to purchase a set of Japanese knives. They are priced at 24,000 yen, and one euro is equal to 129 yen. If Gunther converts his euros into yen, he will need about ____ euros to pay for the knives.
A) 129
B) 186
C) 240
D) 3,000,000
A) 129
B) 186
C) 240
D) 3,000,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Aimi is visiting the United States and wants to purchase some Indian pottery from Arizona. The pottery is priced at $36.00. If $1 is equal to ¥111, Aimi will need about:
A) ¥0.32.
B) ¥3,360.
C) ¥4,000.
D) ¥4,360.
A) ¥0.32.
B) ¥3,360.
C) ¥4,000.
D) ¥4,360.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Gaspard is visiting the United States, and his hotel bill for one week is $1,500. The hotel insists on being paid in U.S. dollars. Gaspard will need to convert _____ euros into dollars to pay the bill because €1 equals $1.16.
A) 116
B) 1,116
C) 1,291
D) 1,740
A) 116
B) 1,116
C) 1,291
D) 1,740

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Aaron is visiting Europe and wishes to take a tour of southern Italy for €2,000. If the exchange rate is USD/EUR .86, Aaron will need to exchange about _____ dollars for euros to pay for the tour.
A) 1,720
B) 2,000
C) 2,172
D) 2,325
A) 1,720
B) 2,000
C) 2,172
D) 2,325

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Assume that EUR/USD 1.16. A $36 shirt would cost _____ euros, and a €20 hat would be _____ dollars.
A) 31; 23
B) 23; 31
C) 42; 17
D) 136; 149
A) 31; 23
B) 23; 31
C) 42; 17
D) 136; 149

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Assume that EUR/YEN 129. A ¥6,470 shirt would cost about _____ euros, and a €20 hat would be about _____ yen.
A) 50; 2,580
B) 2,580; 50
C) 26; 3,328
D) 3,328; 26
A) 50; 2,580
B) 2,580; 50
C) 26; 3,328
D) 3,328; 26

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Assume that USD/YEN 111. A ¥6,470 shirt would cost about _____ dollars, and a $30 hat would be about _____ yen.
A) 3,350; 58
B) 58; 3,350
C) 7,180; 33
D) 33; 7,180
A) 3,350; 58
B) 58; 3,350
C) 7,180; 33
D) 33; 7,180

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 110 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








