Deck 6: The Economic Efficiency of Markets
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/103
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: The Economic Efficiency of Markets
1
_____ is the maximum price of a good or service that the consumer puts on it.
A) Willingness to pay
B) Equilibrium
C) Utility
D) Rational self-interest
A) Willingness to pay
B) Equilibrium
C) Utility
D) Rational self-interest
A
2
Marta bids $15 for a shirt on an online auction site. She is the winning bid at $12. What is her willingness to pay?
A) $3
B) $12
C) $15
D) $27
A) $3
B) $12
C) $15
D) $27
C
3
Marta bids $15 for a shirt on an online auction site. She is the winning bid at $12. What is her consumer surplus?
A) $3
B) $12
C) $15
D) $27
A) $3
B) $12
C) $15
D) $27
A
4
(Figure: Willingness to Pay) The price is $15. In the table, what is Mabel's consumer surplus?
A) $0
B) $2
C) $5
D) $13
A) $0
B) $2
C) $5
D) $13

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
(Figure: Willingness to Pay) The price is $15. In the table, what is Hazel's consumer surplus?
A) $2
B) $5
C) $9
D) $13
A) $2
B) $5
C) $9
D) $13

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
(Figure: Willingness to Pay) The price is $15. In the table, what is Antoinette's consumer surplus?
A) $2
B) $5
C) $9
D) $13
A) $2
B) $5
C) $9
D) $13

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
(Figure: Consumer Surplus) The price is $15. In the table, what is Hazel's willingness to pay?
A) $6
B) $9
C) $15
D) $24
A) $6
B) $9
C) $15
D) $24

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
(Figure: Consumer Surplus) The price is $15. In the table, what is Mabel's willingness to pay?
A) $13
B) $15
C) $17
D) $20
A) $13
B) $15
C) $17
D) $20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
(Figure: Consumer Surplus) The price is $15. In the table, what is Antoinette's willingness to pay?
A) $10
B) $15
C) $20
D) $35
A) $10
B) $15
C) $20
D) $35

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
(Figure: Willingness to Pay) The price is $15. In the table, what is the total consumer surplus for the three women?
A) $14
B) $15
C) $16
D) $29
A) $14
B) $15
C) $16
D) $29

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Jim is willing to purchase a coffee mug for $20. The price of the mug is $15, but after the mug goes on sale, its new price is $12. What is Jim's consumer surplus based on the sale price?
A) $5
B) $8
C) $15
D) $20
A) $5
B) $8
C) $15
D) $20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Vijaya is willing to purchase a meal at her favorite restaurant for $30, which is the usual price. When she arrives at the restaurant, she learns that it is having a promotion and her meal is half-priced. Assuming that she was willing to pay the full price, what is Vijaya's consumer surplus?
A) $30
B) $25
C) $20
D) $15
A) $30
B) $25
C) $20
D) $15

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The minimum price that a seller will take for a good or service is called willingness to:
A) buy.
B) accept.
C) purchase.
D) demand.
A) buy.
B) accept.
C) purchase.
D) demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The minimum price that a seller is willing to accept for a good or service is called willingness to:
A) buy.
B) accept.
C) purchase.
D) demand.
A) buy.
B) accept.
C) purchase.
D) demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The seller's gain from a sale-measured as the difference between the seller's willingness to accept and the actual price received-is called:
A) item scarcity.
B) consumer surplus.
C) item value.
D) producer surplus.
A) item scarcity.
B) consumer surplus.
C) item value.
D) producer surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
(Figure: Producer Surplus 0) The price is $25. In the table, what is Mark's willingness to accept?
A) $5
B) $15
C) $20
D) $25
A) $5
B) $15
C) $20
D) $25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
(Figure: Producer Surplus 0) The price is $25. In the table, what is Hank's willingness to accept?
A) $5
B) $15
C) $20
D) $25
A) $5
B) $15
C) $20
D) $25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
(Figure: Producer Surplus 0) The price is $25. In the table, what is Andy's willingness to accept?
A) $5
B) $10
C) $20
D) $25
A) $5
B) $10
C) $20
D) $25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
(Figure: Willingness to Accept) The price is $25. In the table, what is Mark's producer surplus?
A) $5
B) $10
C) $20
D) $25
A) $5
B) $10
C) $20
D) $25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
(Figure: Willingness to Accept) The price is $25. In the table, what is Hank's producer surplus?
A) $5
B) $10
C) $20
D) $25
A) $5
B) $10
C) $20
D) $25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
(Figure: Willingness to Accept) The price is $25. In the table, what is Andy's producer surplus?
A) $5
B) $10
C) $15
D) $20
A) $5
B) $10
C) $15
D) $20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
(Figure: Willingness to Accept 0) The price is $30. In the table, what is the total producer surplus?
A) $10
B) $30
C) $44
D) $46
A) $10
B) $30
C) $44
D) $46

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Matt is selling a footstool in an online auction and is willing to accept $21 for the footstool. When the auction ends, the winning bid is $25. What is Matt's producer surplus?
A) $4
B) $21
C) $25
D) $46
A) $4
B) $21
C) $25
D) $46

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Enid is selling a dress in an online auction and would be happy to get $15 for the dress. When the auction ends, the high bid is $18. What is Enid's willingness to accept?
A) $15
B) $18
C) $26
D) $33
A) $15
B) $18
C) $26
D) $33

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Producer surplus increases when:
A) consumer surplus increases.
B) consumer surplus decreases.
C) prices fall.
D) prices rise.
A) consumer surplus increases.
B) consumer surplus decreases.
C) prices fall.
D) prices rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When price increases, producer surplus could increase because:
A) price decreases.
B) new sellers enter the market.
C) consumer surplus increases.
D) consumer surplus decreases.
A) price decreases.
B) new sellers enter the market.
C) consumer surplus increases.
D) consumer surplus decreases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The sum of producer and consumer surplus along with any tax revenue is called:
A) total utility.
B) deadweight loss.
C) deadweight gain.
D) total surplus.
A) total utility.
B) deadweight loss.
C) deadweight gain.
D) total surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Reduction in total surplus resulting from a market distortion is called:
A) total utility.
B) deadweight loss.
C) deadweight gain.
D) total surplus.
A) total utility.
B) deadweight loss.
C) deadweight gain.
D) total surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The total benefit to society for having a market to buy and sell goods is called:
A) total utility.
B) deadweight loss.
C) deadweight gain.
D) total surplus.
A) total utility.
B) deadweight loss.
C) deadweight gain.
D) total surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Another name for a market that is not in equilibrium is:
A) equal equilibrium.
B) deadweight loss.
C) government failure.
D) market distortion.
A) equal equilibrium.
B) deadweight loss.
C) government failure.
D) market distortion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Market distortions that prevent price from reaching equilibrium generally cause:
A) an unequal equilibrium.
B) a deadweight loss.
C) a government failure.
D) a sunk cost.
A) an unequal equilibrium.
B) a deadweight loss.
C) a government failure.
D) a sunk cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
_____ is a concept that can be used to evaluate whether government policies are beneficial.
A) Unequal equilibrium
B) Market distortion
C) Government failure
D) Deadweight loss
A) Unequal equilibrium
B) Market distortion
C) Government failure
D) Deadweight loss

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Minimizing production costs for any given output is called:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) productive efficiency.
C) market failure.
D) deadweight loss.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) productive efficiency.
C) market failure.
D) deadweight loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
_____ is obtaining output for the lowest possible cost.
A) Productive efficiency
B) Allocative efficiency
C) Market failure
D) Deadweight loss
A) Productive efficiency
B) Allocative efficiency
C) Market failure
D) Deadweight loss

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Obtaining the maximum possible output with a given set of resources is called:
A) productive efficiency.
B) allocative efficiency.
C) market failure.
D) deadweight loss.
A) productive efficiency.
B) allocative efficiency.
C) market failure.
D) deadweight loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The optimal mix of goods and services produced is called:
A) productive efficiency.
B) allocative efficiency.
C) market failure.
D) deadweight loss.
A) productive efficiency.
B) allocative efficiency.
C) market failure.
D) deadweight loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
When markets in equilibrium maximize total surplus, the result is called:
A) productive efficiency.
B) total utility.
C) allocative efficiency.
D) deadweight loss.
A) productive efficiency.
B) total utility.
C) allocative efficiency.
D) deadweight loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
On a graph, total surplus would be depicted in the area:
A) above the demand curve and above the supply curve.
B) below the demand curve and above the supply curve.
C) above the demand curve and below the supply curve.
D) below the demand curve and below the supply curve.
A) above the demand curve and above the supply curve.
B) below the demand curve and above the supply curve.
C) above the demand curve and below the supply curve.
D) below the demand curve and below the supply curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
(Figure: Consumer, Producer, and Total Surplus) In the above figure, which area represents consumer surplus?
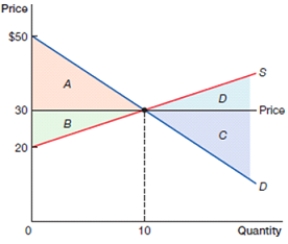
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
(Figure: Consumer, Producer, and Total Surplus) In the above figure, which area represents producer surplus?
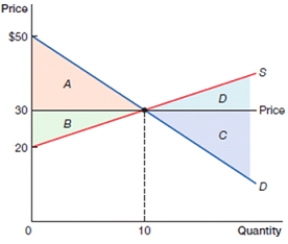
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
(Figure: Consumer, Producer, and Total Surplus) In the above figure, which area represents total surplus?
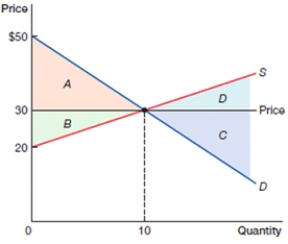
A) A + B + C + D
B) A + B
C) B + C
D) C + D

A) A + B + C + D
B) A + B
C) B + C
D) C + D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
When allocative efficiency is achieved, _____ is maximized.
A) deadweight loss
B) consumer surplus
C) producer surplus
D) total surplus
A) deadweight loss
B) consumer surplus
C) producer surplus
D) total surplus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
At _____, there is no other price or quantity that would result in a higher total surplus.
A) deadweight loss
B) consumer surplus
C) producer surplus
D) equilibrium
A) deadweight loss
B) consumer surplus
C) producer surplus
D) equilibrium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Jerome bought a shirt for $15. He would have paid $20. Michael, the seller, would have sold it for $12. What is the total surplus resulting from the transaction?
A) $3
B) $8
C) $20
D) $27
A) $3
B) $8
C) $20
D) $27

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Kerrie sold a footstool to Alan for $21. She would have taken $15. Alan was willing to pay $30. What is the total surplus resulting from the transaction?
A) $6
B) $9
C) $15
D) $21
A) $6
B) $9
C) $15
D) $21

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
From a recent transaction, Alfred's consumer surplus was $20. What does this mean?
A) The seller gave Alfred $20 in change.
B) The item cost Alfred $20 more than he was willing to pay.
C) Alfred would have paid $20 more than he did for the item.
D) Alfred was $20 short.
A) The seller gave Alfred $20 in change.
B) The item cost Alfred $20 more than he was willing to pay.
C) Alfred would have paid $20 more than he did for the item.
D) Alfred was $20 short.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
From a recent transaction, Anton's producer surplus was $5. What does this mean?
A) Anton gave the purchaser $5 in change.
B) The price of the item was $5 more than the purchaser was willing to pay.
C) Anton received $5 less than he wanted.
D) Anton would have accepted $5 less.
A) Anton gave the purchaser $5 in change.
B) The price of the item was $5 more than the purchaser was willing to pay.
C) Anton received $5 less than he wanted.
D) Anton would have accepted $5 less.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
When a government intervenes in a market, generally the result is:
A) a move toward equilibrium.
B) equilibrium.
C) greater competition.
D) deadweight loss.
A) a move toward equilibrium.
B) equilibrium.
C) greater competition.
D) deadweight loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
_____ generally occurs when a market fails to reach equilibrium.
A) Allocative efficiency
B) Productive efficiency
C) Deadweight loss
D) Market utility
A) Allocative efficiency
B) Productive efficiency
C) Deadweight loss
D) Market utility

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
______ occurs when government intervention keeps the price above or below the free-market equilibrium price.
A) Allocative efficiency
B) Productive efficiency
C) Deadweight loss
D) Market utility
A) Allocative efficiency
B) Productive efficiency
C) Deadweight loss
D) Market utility

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A law that sets a maximum price generally below equilibrium is called a price:
A) ceiling.
B) floor.
C) point.
D) equilibrium.
A) ceiling.
B) floor.
C) point.
D) equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Maria owns several apartments that she rents for $800 per month. The local government decides that $800 is too high and passes an ordinance stating that property owners cannot charge more than $600 per month. This is an example of a price:
A) ceiling.
B) floor.
C) point.
D) equilibrium.
A) ceiling.
B) floor.
C) point.
D) equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Maria owns several apartments that she rents for $800 per month. The local government decides that $800 is too high and passes an ordinance stating that property owners cannot charge more than $600 per month. What will most likely happen to the quantity supplied of apartments in the area in the long run?
A) Quantity supplied will increase.
B) Quantity supplied will decrease.
C) Quantity supplied will not be affected.
D) Quantity supplied will equal quantity demanded.
A) Quantity supplied will increase.
B) Quantity supplied will decrease.
C) Quantity supplied will not be affected.
D) Quantity supplied will equal quantity demanded.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which of the following is a reason that governments may institute price ceilings?
A) to raise money for local government operations
B) to support worthwhile charities
C) to make a product more affordable to low income individuals
D) to increase the cost of the product or service
A) to raise money for local government operations
B) to support worthwhile charities
C) to make a product more affordable to low income individuals
D) to increase the cost of the product or service

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
(Figure: Price Ceiling 0) In the above figure, what is the equilibrium price?
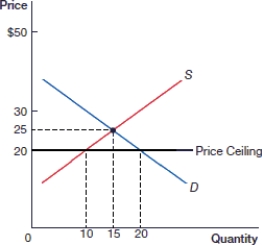
A) $25
B) $30
C) $35
D) $50

A) $25
B) $30
C) $35
D) $50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
(Figure: Price Ceiling 0) In the above figure, what is the equilibrium quantity?
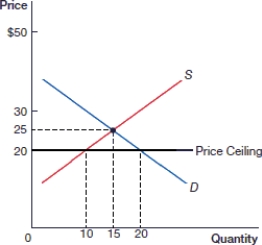
A) 15
B) 20
C) 10
D) 30

A) 15
B) 20
C) 10
D) 30

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
(Figure: Price Ceiling 0) In the above figure, what is the price after the price ceiling is instituted?
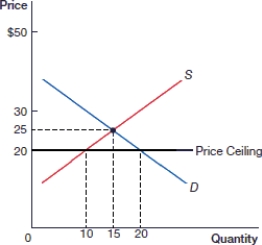
A) $15
B) $20
C) $25
D) $30

A) $15
B) $20
C) $25
D) $30

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
(Figure: Price Ceiling 0) In the above figure, what is the quantity demanded after the price ceiling is instituted?
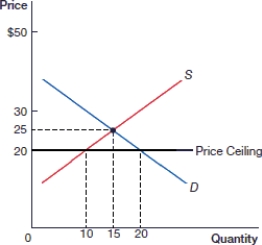
A) 15
B) 30
C) 10
D) 20

A) 15
B) 30
C) 10
D) 20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
(Figure: Price Ceiling 0) In the above figure, after the price ceiling is instituted, there is:

A) an equilibrium.
B) a shortage.
C) a surplus.
D) an efficient market.

A) an equilibrium.
B) a shortage.
C) a surplus.
D) an efficient market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
(Figure: Price Ceiling 0) In the above figure, there is a _____ of _____ as a result of the price ceiling.
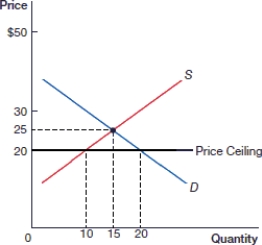
A) surplus; 10
B) surplus; 5
C) shortage; 5
D) shortage; 10

A) surplus; 10
B) surplus; 5
C) shortage; 5
D) shortage; 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
(Figure: Price Ceiling A) In the above figure, what is the price after the price ceiling is instituted?
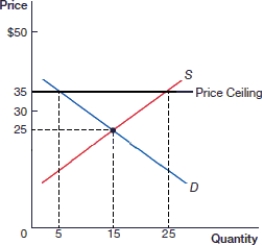
A) $20
B) $25
C) $30
D) $35

A) $20
B) $25
C) $30
D) $35

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
(Figure: Price Ceiling A) In the above figure, what is the quantity supplied after the price ceiling is instituted?
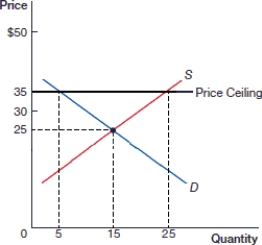
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 5

A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
When a price ceiling is above equilibrium:
A) market price rises.
B) market price falls.
C) the price ceiling is illegal.
D) the market remains at equilibrium.
A) market price rises.
B) market price falls.
C) the price ceiling is illegal.
D) the market remains at equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The equilibrium price for travel by taxi is $1 per mile. The local government sets a price ceiling of $3 per mile. What is the effect on the market for travel by taxi?
A) Market price rises to $4 per mile.
B) Market price rises to $3 per mile.
C) Market price rises to $2 per mile.
D) Market price remains at $1 per mile.
A) Market price rises to $4 per mile.
B) Market price rises to $3 per mile.
C) Market price rises to $2 per mile.
D) Market price remains at $1 per mile.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
According to most economists, the best way to eliminate shortages is to:
A) lower a price ceiling.
B) lower a price floor.
C) eliminate price controls.
D) raise a price ceiling.
A) lower a price ceiling.
B) lower a price floor.
C) eliminate price controls.
D) raise a price ceiling.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
(Figure: DWL0) In the figure, what is the total consumer surplus with the price ceiling?
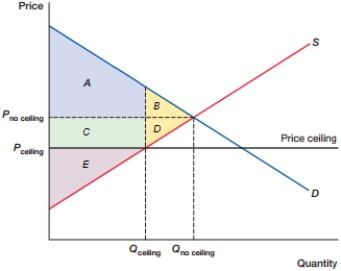
A) A + B
B) A + C
C) B + D
D) C + E

A) A + B
B) A + C
C) B + D
D) C + E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
(Figure: DWL0) In the figure, what is the total consumer surplus at equilibrium?
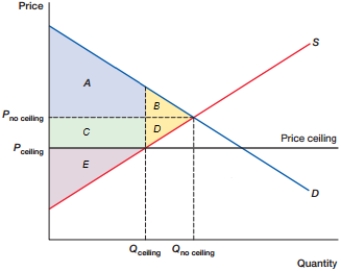
A) A + B
B) A + C
C) B + D
D) C + E

A) A + B
B) A + C
C) B + D
D) C + E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
(Figure: DWL0) In the figure, what is the total producer surplus with the price ceiling?
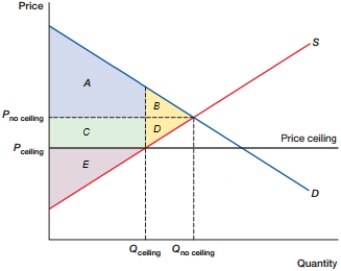
A) B + D
B) C + D + E
C) C + E
D) E

A) B + D
B) C + D + E
C) C + E
D) E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
(Figure: DWL0) In the figure, what is the deadweight loss caused by the price ceiling?
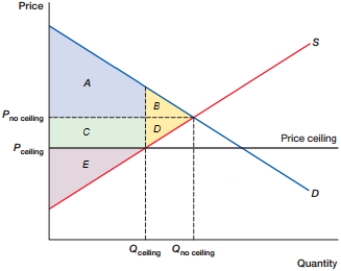
A) B + D
B) C + D
C) C + B + D
D) D

A) B + D
B) C + D
C) C + B + D
D) D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
A law that sets a minimum price, usually above equilibrium, is a:
A) price ceiling.
B) price floor.
C) price point.
D) price equilibrium.
A) price ceiling.
B) price floor.
C) price point.
D) price equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A price floor is intended to benefit:
A) consumers.
B) suppliers.
C) only the poor.
D) only the wealthy.
A) consumers.
B) suppliers.
C) only the poor.
D) only the wealthy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A price ceiling is intended to benefit:
A) consumers.
B) suppliers.
C) only the poor.
D) only the wealthy.
A) consumers.
B) suppliers.
C) only the poor.
D) only the wealthy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Farmer Jones raises wheat. The equilibrium market price for wheat is $5.15 per bushel. However, government is requiring Farmer Jones to sell his wheat at $5.50 per bushel. This is an example of a:
A) price ceiling.
B) price floor.
C) market equilibrium.
D) new equilibrium price.
A) price ceiling.
B) price floor.
C) market equilibrium.
D) new equilibrium price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
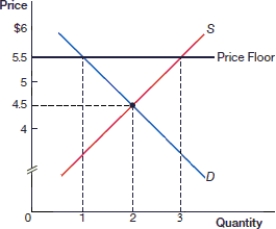
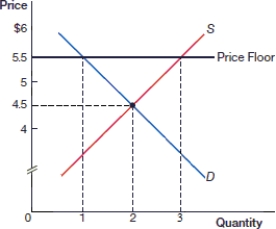
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, what is the equilibrium price?
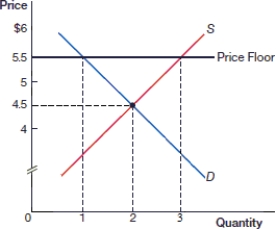
A) $4
B) $4.50
C) $5
D) $5.50

A) $4
B) $4.50
C) $5
D) $5.50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, what is the equilibrium quantity?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
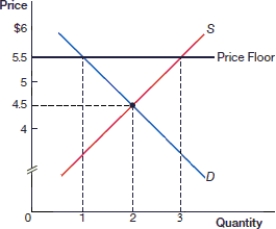
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, what is the price after the price floor is instituted?
A) $4
B) $4.5
C) $5
D) $5.5

A) $4
B) $4.5
C) $5
D) $5.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, what is the quantity demanded after the price floor is instituted?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
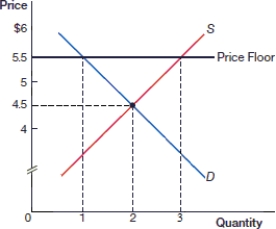
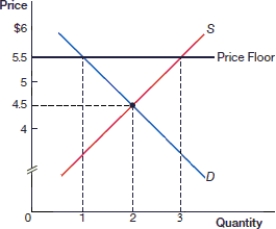
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, after the price floor is instituted there is:
A) an equilibrium.
B) a shortage.
C) a surplus.
D) an efficient market.

A) an equilibrium.
B) a shortage.
C) a surplus.
D) an efficient market.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, there is a _____ of _____ as a result of the price floor.
A) surplus; 1
B) surplus; 2
C) shortage; 1
D) shortage; 2

A) surplus; 1
B) surplus; 2
C) shortage; 1
D) shortage; 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
(Figure: Price Floor 0) In the above figure, what is the quantity supplied after the price floor is instituted?
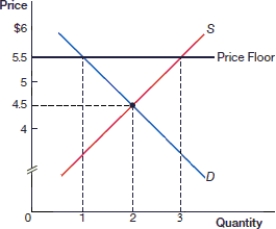
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 103 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








