Deck 27: The Cold War and the Remaking of Europe, 1945-1960s
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 27: The Cold War and the Remaking of Europe, 1945-1960s
1
Why were many Russians surprised by Joseph Stalin's post-World War II domestic policies, and how did these policies affect industry, agriculture, the military, and women?
Answer would ideally include the following. While ordinary Russians expected the wartime relaxation of communism to continue, Stalin instead renewed political repression after 1945. In 1946, a new five-year plan was launched, with higher industrial production goals and more stringent agricultural collectivization. Low wartime birthrates were countered by intense propaganda urging women to continue their jobs while also fulfilling their "true nature" by producing more children.
2
What did the Allies do with Germany in the immediate postwar era (to 1949), and how was this a sign of the looming cold war?
Answer would ideally include the following. The Allies agreed to divide up Germany into four military-occupied blocs after the victory; these blocs were controlled by the Soviet Union, the United States, Great Britain, and France. The United States rigidly censored all media in its zone to repress any fascist or authoritarian resurgence, while the Soviet Union confiscated the wealth of German industrialists. The United States proposed that the Soviet-controlled sector and the Western-controlled sectors cooperate economically, but Stalin upset this plan by moving German industries and skilled workers by force into the USSR to aid the Soviet economy. The partition of Germany demonstrated the escalation of the cold war as the United States began an economic buildup of the now-unified western zone under the Marshall Plan in order to create a buffer zone against the Soviets. The Soviets retaliated in 1948 with the blockade of Berlin, and eventually Germany was partitioned into two entirely new countries.
3
How did western European states rebuild with some success in the decade or so after World War II?
Answer would ideally include the following. Reform-minded civilian governments emphasized democratic values and typically built broad-based coalitions. International assistance, particularly from the United States in the form of the Marshall Plan, and cooperation among the western European states positioned them to strengthen their economies and rebuild markets and industries disrupted by the conflict. The shift in focus from military to consumer needs also strengthened production, demand, and employment by the 1950s.
4
What advantages for the European Economic Community (the Common Market) were supposed to exist in using international "technocrats" to make expert decisions that would affect all member states?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
What were the causes of the "thaw" in the Soviet Union's internal policies in the mid-to-late 1950s, and what were some of the major political changes that reflected this new approach?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Describe the effects of the Algerian War on France.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Briefly describe the twentieth-century philosophy of existentialism. How did Simone de Beauvoir apply this philosophy to the condition of women?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Who was Rosa Parks, and why was her act of defiance so significant?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
How did the work of Christian Dior reflect the ideology of the return to normalcy advocated by popular culture following World War II?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Why did the United States and the Soviet Union turn so quickly from being allies to being "unofficial" enemies between 1945 and 1946? Be sure to consider differences in ideologies, tensions that may have existed before World War II, geographic considerations, and other factors that contributed to this breach.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Explain how the Marshall Plan, the establishment of NATO and the Warsaw Pact, and the founding of the European Economic Community all can be seen to reflect Europe's position between two nuclear superpowers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Discuss the role that the cold war played in the decolonization of European empires after World War II?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
How did Europeans experience what some called the "Americanization" of Europe in the postwar period?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Despite the emergence of new and fun pop culture icons and consumer goods, the 1950s were a time of emotional terror for those at the center of the cold war. Why was this? How did people cope with their fear? What role did Cuba play in the exacerbation of these fears?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which country remained mostly untouched by World War II?
A) Great Britain
B) Germany
C) The United States
D) France
A) Great Britain
B) Germany
C) The United States
D) France

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Why was World War II more destructive in Europe than World War I?
A) World War II was a war that for the first time involved all sectors of society, not just the military and munitions manufacturers.
B) Nazi policies fanaticized the German army, leading it to wreak far greater material destruction than the army of the German kaiser during World War I.
C) Armies in World War II had fought a war of movement on the ground and in the air, and massive bombing campaigns leveled thousands of square miles of territory.
D) The Allies in World War II were much more bent on punishing Germany in an effort to avenge the victims of Nazi aggression.
A) World War II was a war that for the first time involved all sectors of society, not just the military and munitions manufacturers.
B) Nazi policies fanaticized the German army, leading it to wreak far greater material destruction than the army of the German kaiser during World War I.
C) Armies in World War II had fought a war of movement on the ground and in the air, and massive bombing campaigns leveled thousands of square miles of territory.
D) The Allies in World War II were much more bent on punishing Germany in an effort to avenge the victims of Nazi aggression.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements best describes the movement of Russians after World War II?
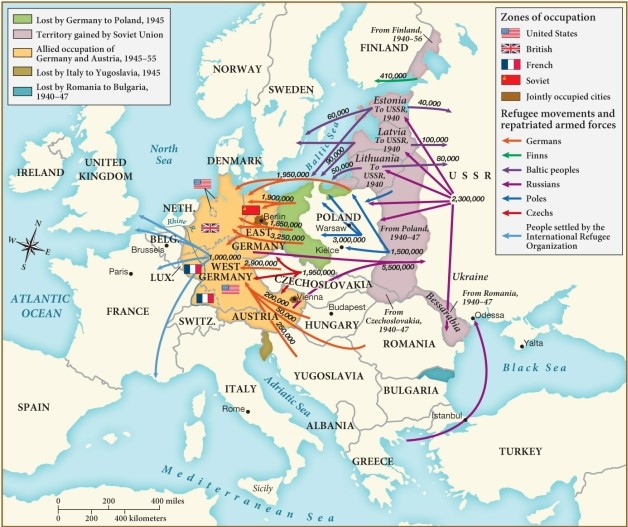
A) Many Russians migrated south into Turkey and Greece to seek freedom.
B) Many Russians migrated west out of the USSR as refugees.
C) Many Russians migrated north to Finland and Sweden for better job opportunities.
D) Many Russians migrated to China in search of cultural variety.

A) Many Russians migrated south into Turkey and Greece to seek freedom.
B) Many Russians migrated west out of the USSR as refugees.
C) Many Russians migrated north to Finland and Sweden for better job opportunities.
D) Many Russians migrated to China in search of cultural variety.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Many Jewish concentration camp survivors returned to their countries in Europe to find that
A) the Jewish populations that had stayed behind welcomed them home with open arms.
B) anti-Semitism was still present in popular attitudes, and very little help was offered them in returning to postwar life.
C) guilt over the Holocaust led to a drastic decline in anti-Semitism, so postwar life was easier than prewar life.
D) governments were eager to redress the injustices of the Holocaust, so Jewish property was returned and state programs were established to aid reintegration.
A) the Jewish populations that had stayed behind welcomed them home with open arms.
B) anti-Semitism was still present in popular attitudes, and very little help was offered them in returning to postwar life.
C) guilt over the Holocaust led to a drastic decline in anti-Semitism, so postwar life was easier than prewar life.
D) governments were eager to redress the injustices of the Holocaust, so Jewish property was returned and state programs were established to aid reintegration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The demands of total war in the Soviet Union had encouraged independent initiative and led to relaxed Communist oversight, a development that Stalin
A) encouraged in his five-year plan of 1946 through a series of decentralization measures designed to increase production levels.
B) praised as proof of worker flexibility and self-empowerment, two linchpins of socialism.
C) ruthlessly reversed through increased repression, aggressive production goals, and a still more radical collectivization of agriculture.
D) reversed with the gradual adoption of the command and control procedures regularly exercised in the ever-growing Soviet army.
A) encouraged in his five-year plan of 1946 through a series of decentralization measures designed to increase production levels.
B) praised as proof of worker flexibility and self-empowerment, two linchpins of socialism.
C) ruthlessly reversed through increased repression, aggressive production goals, and a still more radical collectivization of agriculture.
D) reversed with the gradual adoption of the command and control procedures regularly exercised in the ever-growing Soviet army.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following characterized U.S. president Harry Truman's policies toward the Soviet Union?
A) He erred on the side of caution, seeking to cooperate as much as possible.
B) He was tougher than Roosevelt, cutting off aid as soon as the war ended.
C) He attempted to cooperate closely with Churchill and de Gaulle in crafting a common policy.
D) He attempted to continue the wartime alliance and offered joint security guarantees.
A) He erred on the side of caution, seeking to cooperate as much as possible.
B) He was tougher than Roosevelt, cutting off aid as soon as the war ended.
C) He attempted to cooperate closely with Churchill and de Gaulle in crafting a common policy.
D) He attempted to continue the wartime alliance and offered joint security guarantees.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The U.S. strategy of using military and economic aid to block the expansion of communism became known as the
A) Marshall Plan.
B) North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
C) Truman Doctrine.
D) Warsaw Pact.
A) Marshall Plan.
B) North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
C) Truman Doctrine.
D) Warsaw Pact.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What was the Marshall Plan designed to provide?
A) Food, equipment, and services to war-devastated Europe
B) Military aid to the Japanese to assist them in holding off Russian and Chinese threats
C) Aid to rebuild Britain and France's badly damaged military establishments
D) Exchange students and scholars to lessen the distrust that many countries felt after the war
A) Food, equipment, and services to war-devastated Europe
B) Military aid to the Japanese to assist them in holding off Russian and Chinese threats
C) Aid to rebuild Britain and France's badly damaged military establishments
D) Exchange students and scholars to lessen the distrust that many countries felt after the war

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
An exception to the rule in eastern Europe, the Communist ruler Tito (Josip Broz, 1892-1980) established a fairly independent, non-Soviet Communist state in
A) Yugoslavia.
B) Poland.
C) Bulgaria.
D) Albania.
A) Yugoslavia.
B) Poland.
C) Bulgaria.
D) Albania.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
How did the agreements reached at the Yalta and Potsdam conferences in 1945 shape the future of postwar Germany?
A) The United States and the Soviet Union divided Germany into two halves, with the Soviets occupying the eastern half and the United States occupying the western half.
B) The four major Allied powers agreed to a vast anti-fascism project to reprogram German attitudes and help remake Germany into a functioning democracy.
C) The Allies divided Germany into four zones, each of which was controlled by one of the four principal victors in the war and occupied by troops from those nations.
D) Stalin ceded control of Germany to the United States, Britain, and France in return for having free reign over nearly all of eastern Europe.
A) The United States and the Soviet Union divided Germany into two halves, with the Soviets occupying the eastern half and the United States occupying the western half.
B) The four major Allied powers agreed to a vast anti-fascism project to reprogram German attitudes and help remake Germany into a functioning democracy.
C) The Allies divided Germany into four zones, each of which was controlled by one of the four principal victors in the war and occupied by troops from those nations.
D) Stalin ceded control of Germany to the United States, Britain, and France in return for having free reign over nearly all of eastern Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
How did Stalin violate the agreement made among the Soviet Union, France, Great Britain, and the United States regarding postwar Germany?
A) He took control of the eastern half of Berlin in 1945.
B) He dismantled and sent a significant percentage of the German industrial infrastructure in the Soviet zone of occupation to the Soviet Union.
C) He failed to prosecute top Nazi officials who had fled east to escape imminent arrest.
D) He permitted the rearmament of the German Democratic Republic, or East Germany, upon the new country's founding in 1949.
A) He took control of the eastern half of Berlin in 1945.
B) He dismantled and sent a significant percentage of the German industrial infrastructure in the Soviet zone of occupation to the Soviet Union.
C) He failed to prosecute top Nazi officials who had fled east to escape imminent arrest.
D) He permitted the rearmament of the German Democratic Republic, or East Germany, upon the new country's founding in 1949.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
How did the United States respond when, in 1948, the Soviets blockaded Berlin, which was situated more than one hundred miles inside the Soviet zone?
A) It threatened to rescind the Allied agreement concluded at Yalta over the Soviet's role in Korea and Manchuria.
B) It cut off negotiations with Stalin over the Soviet Union's possible inclusion in the Marshall Plan.
C) It expelled Soviet diplomats from Washington, D.C., and mobilized U.S. forces in the American zone of occupation in western Germany.
D) It staged Operation Vittles, an ongoing airlift that supplied the residents of Berlin with food and fuel into the spring of 1949.
A) It threatened to rescind the Allied agreement concluded at Yalta over the Soviet's role in Korea and Manchuria.
B) It cut off negotiations with Stalin over the Soviet Union's possible inclusion in the Marshall Plan.
C) It expelled Soviet diplomats from Washington, D.C., and mobilized U.S. forces in the American zone of occupation in western Germany.
D) It staged Operation Vittles, an ongoing airlift that supplied the residents of Berlin with food and fuel into the spring of 1949.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
How did the Soviet Union retaliate after the United States forced Britain and France to invite West Germany to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1955?
A) By expelling all diplomats from NATO member states from the Soviet Union and seizing embassy property
B) By installing missiles in East Germany and spreading the word that they were armed with atomic bombs
C) By forming a parallel military organization with Soviet satellite countries, commonly called the Warsaw Pact
D) By forming an alliance with China's leader Mao Zedong in an attempt to create a global Communist alliance more powerful than the West
A) By expelling all diplomats from NATO member states from the Soviet Union and seizing embassy property
B) By installing missiles in East Germany and spreading the word that they were armed with atomic bombs
C) By forming a parallel military organization with Soviet satellite countries, commonly called the Warsaw Pact
D) By forming an alliance with China's leader Mao Zedong in an attempt to create a global Communist alliance more powerful than the West

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
According to this map, which of the following European nations was part of the Warsaw Pact?
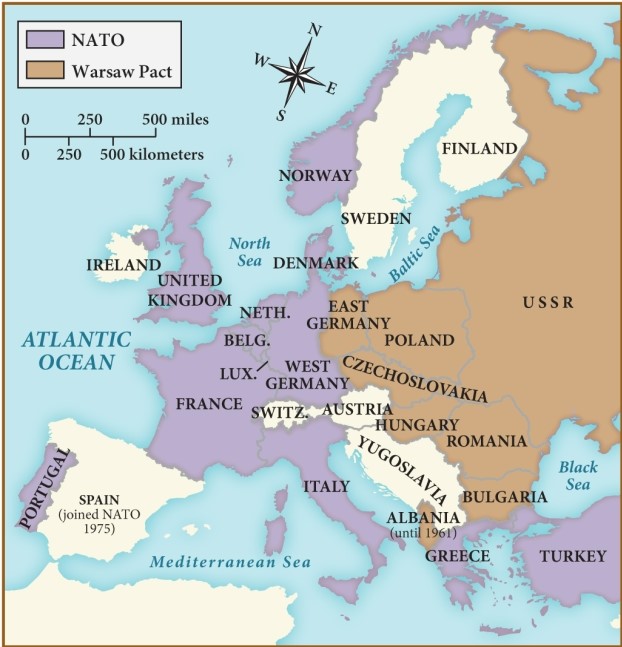
A) France
B) Italy
C) Poland
D) Yugoslavia

A) France
B) Italy
C) Poland
D) Yugoslavia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The Nuremberg trials of Nazi war criminals, held in the fall of 1945, led to either execution or long-term prison terms for
A) three hundred senior Nazi SS, Gestapo, and military officers.
B) twenty-four senior Nazi officials.
C) more than one thousand Nazi officials and concentration camp administrators.
D) one hundred defendants, including thirty-five Nazi judges.
A) three hundred senior Nazi SS, Gestapo, and military officers.
B) twenty-four senior Nazi officials.
C) more than one thousand Nazi officials and concentration camp administrators.
D) one hundred defendants, including thirty-five Nazi judges.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The Allied victors all believed that one of their tasks in occupied Germany was ideological reorientation, a task that they accomplished through
A) a program of "denazification."
B) the confiscation and redistribution of land, particularly the estates of former Nazis.
C) the exile of hundreds of thousands of former Nazi officials.
D) a treaty that forced the Germans to pay for the reconstruction of postwar Europe.
A) a program of "denazification."
B) the confiscation and redistribution of land, particularly the estates of former Nazis.
C) the exile of hundreds of thousands of former Nazi officials.
D) a treaty that forced the Germans to pay for the reconstruction of postwar Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The Christian Democrats who took power in several countries after World War II descended from what prewar political movements?
A) Popular Front coalitions
B) Traditional Catholic centrist parties
C) An alliance of reformed protofascists and traditional conservative parties
D) Anti-Communist socialist parties and labor unions
A) Popular Front coalitions
B) Traditional Catholic centrist parties
C) An alliance of reformed protofascists and traditional conservative parties
D) Anti-Communist socialist parties and labor unions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In 1949, German centrist politicians came to power in the new state of the German Federal Republic, whose first chancellor was which Catholic politician?
A) Charles de Gaulle
B) Joseph McCarthy
C) Konrad Adenauer
D) Ludwig Erhard
A) Charles de Gaulle
B) Joseph McCarthy
C) Konrad Adenauer
D) Ludwig Erhard

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
From 1949 to 1954, a wave of anti-Communist hysteria that included book burnings and investigations of over six million people spread across which country?
A) France
B) Great Britain
C) The United States
D) Vietnam
A) France
B) Great Britain
C) The United States
D) Vietnam

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What European country experienced a stunning revival in the 1960s that was labeled the "economic miracle"?
A) France
B) West Germany
C) Great Britain
D) East Germany
A) France
B) West Germany
C) Great Britain
D) East Germany

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
According to one of the founders of the European Economic Community (EEC), known popularly as the Common Market, which of the following was one of its stated aims?
A) To "prevent the race of nationalism, which is the true curse of the modern world"
B) To "encourage the spread of capitalism and prevent the expansion of communism"
C) To "maintain trading partnerships with the empire and Europe's global partners"
D) To "provide an economic counterbalance to the United States"
A) To "prevent the race of nationalism, which is the true curse of the modern world"
B) To "encourage the spread of capitalism and prevent the expansion of communism"
C) To "maintain trading partnerships with the empire and Europe's global partners"
D) To "provide an economic counterbalance to the United States"

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Why did Great Britain initially refuse to join the European Economic Community (EEC) established by Italy, France, Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands in 1957?
A) The other countries refused to base the EEC's administration in London.
B) It did not want to join in the establishment of a single European currency.
C) It opposed German membership.
D) It flinched at the prospect of losing status through absorption into the European continent.
A) The other countries refused to base the EEC's administration in London.
B) It did not want to join in the establishment of a single European currency.
C) It opposed German membership.
D) It flinched at the prospect of losing status through absorption into the European continent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following characterized postwar European welfare states?
A) An emphasis on limiting overpopulation by encouraging smaller families
B) The provision of pensions and various programs for veterans and programs aimed at improving health and well-being
C) Policies designed to make it much easier for women to work outside the home, and equal benefits for married women in particular
D) A focus on private provision of health care, while other benefits came from the state
A) An emphasis on limiting overpopulation by encouraging smaller families
B) The provision of pensions and various programs for veterans and programs aimed at improving health and well-being
C) Policies designed to make it much easier for women to work outside the home, and equal benefits for married women in particular
D) A focus on private provision of health care, while other benefits came from the state

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What characterized the Soviet Union's treatment of eastern bloc countries?
A) A military occupation where troops were quartered on civilian property
B) A "light hand" policy that encouraged eastern European states to promote their own "national communist cultures"
C) Policies of "Russification" and aggressive de-Christianization
D) The direct rule of these societies by Russian officials
A) A military occupation where troops were quartered on civilian property
B) A "light hand" policy that encouraged eastern European states to promote their own "national communist cultures"
C) Policies of "Russification" and aggressive de-Christianization
D) The direct rule of these societies by Russian officials

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
In 1949, the Soviet Union created regional economic organizations in order to
A) increase Russian production so as to stay ahead of production in eastern Europe.
B) place high tariffs on goods coming into the USSR from eastern Europe.
C) prevent western European goods from swamping socialist markets in eastern Europe and the USSR.
D) coordinate economic relations between the Soviet Union and its satellite countries.
A) increase Russian production so as to stay ahead of production in eastern Europe.
B) place high tariffs on goods coming into the USSR from eastern Europe.
C) prevent western European goods from swamping socialist markets in eastern Europe and the USSR.
D) coordinate economic relations between the Soviet Union and its satellite countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
When Stalin died in 1953, the situation in the Soviet Union and its satellites
A) became even more repressive because Communist officials feared potential unrest as citizens saw an opportunity for freedom in regime change.
B) turned extremely tense as the Western powers prepared to invade the Soviet bloc and take advantage of the power vacuum to break down the Communist system.
C) shifted as political prisoners and workers protested the repressive conditions under Stalinism and the Communist power structure, leading to political reforms.
D) turned anxious as hundreds of thousands prepared to seize the opportunity to flee to the West and escape the repression of the Soviet system.
A) became even more repressive because Communist officials feared potential unrest as citizens saw an opportunity for freedom in regime change.
B) turned extremely tense as the Western powers prepared to invade the Soviet bloc and take advantage of the power vacuum to break down the Communist system.
C) shifted as political prisoners and workers protested the repressive conditions under Stalinism and the Communist power structure, leading to political reforms.
D) turned anxious as hundreds of thousands prepared to seize the opportunity to flee to the West and escape the repression of the Soviet system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
In 1956, the Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev (1894-1971) criticized
A) what he called an excessive focus on heavy industry at the expense of consumer goods and other facets of everyday life, a distortion he planned to rectify.
B) the incipient spread of Western cultural values through illegal radio and television broadcasts and other Western attempts to corrupt socialist youth.
C) Stalin's misguided political and economic policies and his "cult of personality."
D) Western-inspired "reformist elements" and signaled his intention to crack down on popular insurrections within the Soviet Union.
A) what he called an excessive focus on heavy industry at the expense of consumer goods and other facets of everyday life, a distortion he planned to rectify.
B) the incipient spread of Western cultural values through illegal radio and television broadcasts and other Western attempts to corrupt socialist youth.
C) Stalin's misguided political and economic policies and his "cult of personality."
D) Western-inspired "reformist elements" and signaled his intention to crack down on popular insurrections within the Soviet Union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What event in Hungary in 1956 precipitated an invasion by Soviet forces?
A) The Hungarian leader Imre Nagy announced that Hungary might leave the Warsaw Pact.
B) Hungary's leaders expanded what had been purely economic demands to include the establishment of a multiparty system.
C) The Hungarian army ignored orders from Moscow and refused to repress a rebellion led by Hungarian railroad workers.
D) Marshal Zhukov overthrew Communist premier Imre Nagy.
A) The Hungarian leader Imre Nagy announced that Hungary might leave the Warsaw Pact.
B) Hungary's leaders expanded what had been purely economic demands to include the establishment of a multiparty system.
C) The Hungarian army ignored orders from Moscow and refused to repress a rebellion led by Hungarian railroad workers.
D) Marshal Zhukov overthrew Communist premier Imre Nagy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Why did Yuri Gagarin cause great concern in the United States?
A) He organized the Soviet missile program and threatened to "bury" the West during a visit to the United States.
B) He was the first man to orbit the earth, thus demonstrating that the Soviet Union was ahead of the United States in space technology.
C) He was the chief scientist on the Soviet nuclear weapons program during the cold war.
D) He was the director of the KGB, the Soviet intelligence agency responsible for spying on the United States.
A) He organized the Soviet missile program and threatened to "bury" the West during a visit to the United States.
B) He was the first man to orbit the earth, thus demonstrating that the Soviet Union was ahead of the United States in space technology.
C) He was the chief scientist on the Soviet nuclear weapons program during the cold war.
D) He was the director of the KGB, the Soviet intelligence agency responsible for spying on the United States.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
In 1947, what two independent countries emerged out of a former British colony as the result of a political and religious conflict incited by the British?
A) Kenya and Tanzania
B) Ireland and Northern Ireland
C) India and Pakistan
D) North and South Vietnam
A) Kenya and Tanzania
B) Ireland and Northern Ireland
C) India and Pakistan
D) North and South Vietnam

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In 1950, the UN Security Council approved a "police action" that deployed troops in
A) Korea.
B) the Philippines.
C) Uganda.
D) Japan.
A) Korea.
B) the Philippines.
C) Uganda.
D) Japan.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Why were the French forced to withdraw from Indochina in 1954?
A) The United States refused to support them in putting down a rebellion.
B) Ho Chi Minh's peasant army defeated them.
C) Soviet assistance to Vietnamese rebels meant that French forces were outgunned.
D) China intervened in a nationalist rebellion against French colonial rule.
A) The United States refused to support them in putting down a rebellion.
B) Ho Chi Minh's peasant army defeated them.
C) Soviet assistance to Vietnamese rebels meant that French forces were outgunned.
D) China intervened in a nationalist rebellion against French colonial rule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
How was Vietnam divided by 1954?

A) East and west along a prominent river
B) Evenly among Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand
C) North and south at the 17th Parallel
D) Evenly among France, Great Britain, and Germany

A) East and west along a prominent river
B) Evenly among Cambodia, Laos, and Thailand
C) North and south at the 17th Parallel
D) Evenly among France, Great Britain, and Germany

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In 1947, Britain ceded its control of Palestine to
A) Israel.
B) the United Nations.
C) Jordan.
D) the United States.
A) Israel.
B) the United Nations.
C) Jordan.
D) the United States.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Based on the data appearing on this map, what contributing factor to later Middle Eastern tensions is evident?
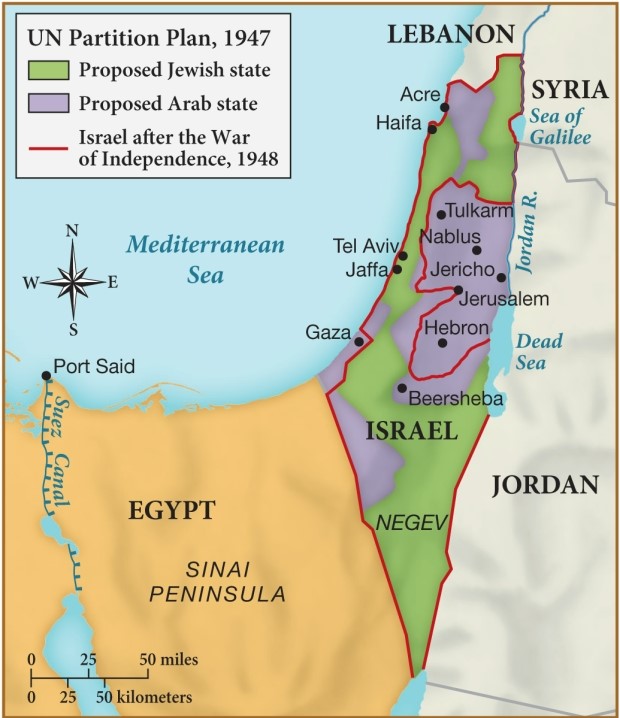
A) Before 1948, Israel controlled lands beyond the Jordan River.
B) Upon its creation, Israel absconded lands not proposed for it in 1947.
C) Israel assumed sovereignty over the Sinai peninsula.
D) The holy city of Tel Aviv was controlled by Palestinians.

A) Before 1948, Israel controlled lands beyond the Jordan River.
B) Upon its creation, Israel absconded lands not proposed for it in 1947.
C) Israel assumed sovereignty over the Sinai peninsula.
D) The holy city of Tel Aviv was controlled by Palestinians.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
What 1956 event in Egypt sparked an international crisis that inspired colonized peoples around the world in their fight for independence from their colonizers?
A) Egyptian nationalists declared Egypt's independence from British rule and began organizing democratic elections.
B) A member of the Muslim Brotherhood was elected as the first president of independent Egypt.
C) The Egyptian president decided to expel all British and French citizens from Egyptian territory.
D) Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalized the British-owned Suez Canal.
A) Egyptian nationalists declared Egypt's independence from British rule and began organizing democratic elections.
B) A member of the Muslim Brotherhood was elected as the first president of independent Egypt.
C) The Egyptian president decided to expel all British and French citizens from Egyptian territory.
D) Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalized the British-owned Suez Canal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In 1960, Niger, Chad, and Mali gained independence from which country?
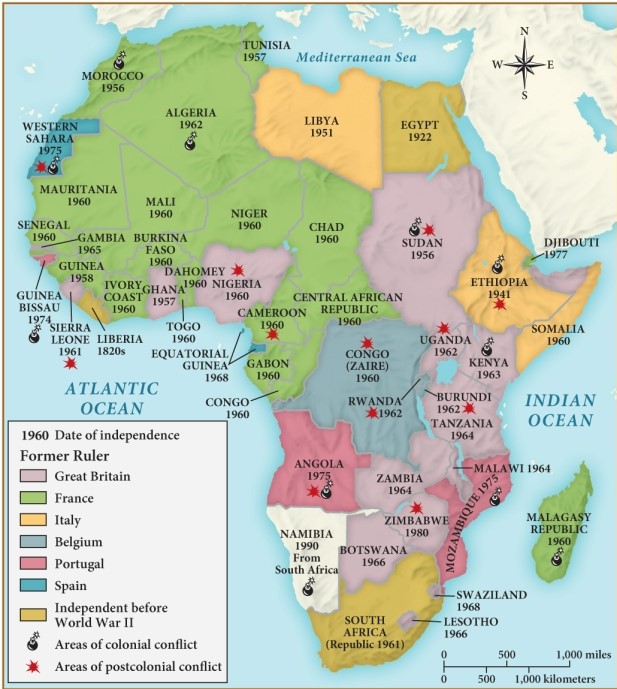
A) Great Britain
B) Italy
C) Belgium
D) France

A) Great Britain
B) Italy
C) Belgium
D) France

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Protests erupted in Paris and around the world in the late 1950s as a result of which of the following?
A) The British granting independence to Tunisia
B) The ascension to power of Charles de Gaulle in 1958
C) The French army's brutal actions toward Algerians seeking independence
D) The British maintaining control over Morocco and West Africa
A) The British granting independence to Tunisia
B) The ascension to power of Charles de Gaulle in 1958
C) The French army's brutal actions toward Algerians seeking independence
D) The British maintaining control over Morocco and West Africa

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What notable change ensured the United Nations a greater chance of success than its predecessor, the League of Nations?
A) The United Nations drafted a global constitution that unified all member nations in a global government.
B) All countries in the world received equal membership and had equal say in all United Nations decisions.
C) Both the United States and the Soviet Union were active members from the outset.
D) The finances, working space, and bureaucracy of the United Nations were entirely independent from any member nation, having been underwritten by endowments from many wealthy families and organizations.
A) The United Nations drafted a global constitution that unified all member nations in a global government.
B) All countries in the world received equal membership and had equal say in all United Nations decisions.
C) Both the United States and the Soviet Union were active members from the outset.
D) The finances, working space, and bureaucracy of the United Nations were entirely independent from any member nation, having been underwritten by endowments from many wealthy families and organizations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Starting relatively soon after World War II, western European countries received a large number of immigrant workers from their former
A) enemy, the Soviet Union.
B) colonies.
C) allies, the United States and Canada.
D) trading rivals in eastern Europe.
A) enemy, the Soviet Union.
B) colonies.
C) allies, the United States and Canada.
D) trading rivals in eastern Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
In 1955, the Indonesian president Sukarno sponsored the Bandung Convention, which
A) set a common policy among nonaligned African and Asian nations for achieving modernization and facing the superpowers.
B) established the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) to compete in the global marketplace.
C) called for a nuclear-free zone in an area spanning the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
D) set up a cartel of oil-producing Asian countries, giving more power to the member producers.
A) set a common policy among nonaligned African and Asian nations for achieving modernization and facing the superpowers.
B) established the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) to compete in the global marketplace.
C) called for a nuclear-free zone in an area spanning the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
D) set up a cartel of oil-producing Asian countries, giving more power to the member producers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Which of the following was the Catholic Council convened by Pope John XXIII in 1962 in response to what he saw as a crisis in faith caused by affluence and secularism?
A) The Ecumenical Movement
B) The Catholic Reformation
C) The Second Vatican Council, or Vatican II
D) De-Christianization
A) The Ecumenical Movement
B) The Catholic Reformation
C) The Second Vatican Council, or Vatican II
D) De-Christianization

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which of the following was argued by the philosophy of existentialism, which was championed by Albert Camus and Jean-Paul Sartre and became fashionable in the 1950s?
A) Human existence is the result not of divine creation but of natural birth, and human morality derives itself from nature.
B) Human (and personal) existence is not the result of divine creation or natural birth but is created through action and choice.
C) The question of human existence, although ultimately unanswerable, is the most pressing intellectual concern for the modern postwar world.
D) The question of human existence must be returned to its divine origins, but religion should also change its emphasis to humans rather than gods.
A) Human existence is the result not of divine creation but of natural birth, and human morality derives itself from nature.
B) Human (and personal) existence is not the result of divine creation or natural birth but is created through action and choice.
C) The question of human existence, although ultimately unanswerable, is the most pressing intellectual concern for the modern postwar world.
D) The question of human existence must be returned to its divine origins, but religion should also change its emphasis to humans rather than gods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In Black Skin, White Masks (1952) and The Wretched of the Earth (1961), Frantz Fanon, a Black psychiatrist from the French colony of Martinique, proposed that
A) Western nations should focus on education and health care in newly decolonized nations, not on economic development.
B) Islam was the only force capable of creating unified states south of the Sahara.
C) liberation movements used violence to attain their ends because their members had been traumatized by the violence used to colonize their countries.
D) the International Monetary Fund was incapable of dealing with poverty in Africa.
A) Western nations should focus on education and health care in newly decolonized nations, not on economic development.
B) Islam was the only force capable of creating unified states south of the Sahara.
C) liberation movements used violence to attain their ends because their members had been traumatized by the violence used to colonize their countries.
D) the International Monetary Fund was incapable of dealing with poverty in Africa.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
How did the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in the case of Brown v. Board of Education (1954) affect the civil rights movement in the United States?
A) It upheld the legality of segregation in education, social services, and all public spaces, setting back the civil rights movement by decades.
B) It upheld the concept of "separate but equal" in education throughout the United States.
C) It mandated that the U.S. education curriculum include the history of slavery and African American history.
D) It declared that segregated education violated the U.S. Constitution, setting off a mass movement of civil disobedience within the African American community.
A) It upheld the legality of segregation in education, social services, and all public spaces, setting back the civil rights movement by decades.
B) It upheld the concept of "separate but equal" in education throughout the United States.
C) It mandated that the U.S. education curriculum include the history of slavery and African American history.
D) It declared that segregated education violated the U.S. Constitution, setting off a mass movement of civil disobedience within the African American community.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Youth culture in postwar Europe took its inspiration from what American style?
A) Rock-and-roll
B) Wild West
C) New York high fashion
D) Ivy League prep school
A) Rock-and-roll
B) Wild West
C) New York high fashion
D) Ivy League prep school

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Which of the following icons of popular culture was one of the most recognizable products of the post-World War II world?
A) Albert Camus
B) Elvis Presley
C) Simone de Beauvoir
D) Marlene Dietrich
A) Albert Camus
B) Elvis Presley
C) Simone de Beauvoir
D) Marlene Dietrich

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What consumer brand epitomized to many Europeans the "Americanization" of Europe in the postwar period?
A) Disney
B) Coca-Cola
C) Ford automobiles
D) Colgate toothpaste
A) Disney
B) Coca-Cola
C) Ford automobiles
D) Colgate toothpaste

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
What was the Voice of America?
A) The official in-house publication of the Federal Communications Commission
B) A series of inspirational radio addresses by President John F. Kennedy
C) A radio station that used culture as a weapon in the cold war
D) The forerunner of public television
A) The official in-house publication of the Federal Communications Commission
B) A series of inspirational radio addresses by President John F. Kennedy
C) A radio station that used culture as a weapon in the cold war
D) The forerunner of public television

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The Cuban missile crisis began in 1962 immediately after the
A) United States launched an invasion of Cuba with the intention of overthrowing the Communist leader Fidel Castro.
B) launch of a Soviet satellite that was mistakenly perceived to be a nuclear missile aimed at the United States.
C) Soviet Union sent soldiers to a military base in Cuba, which the United States interpreted as a preliminary to a Soviet invasion of U.S. territory.
D) CIA reported the installation of silos to house Soviet medium-range missiles in Cuba.
A) United States launched an invasion of Cuba with the intention of overthrowing the Communist leader Fidel Castro.
B) launch of a Soviet satellite that was mistakenly perceived to be a nuclear missile aimed at the United States.
C) Soviet Union sent soldiers to a military base in Cuba, which the United States interpreted as a preliminary to a Soviet invasion of U.S. territory.
D) CIA reported the installation of silos to house Soviet medium-range missiles in Cuba.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








