Deck 26: The Great Depression and World War II, 1929-1945
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 26: The Great Depression and World War II, 1929-1945
1
How did government actions to resolve the financial crisis that began in 1929 actually make conditions worse and extend the depression?
Answer would ideally include the following. Governments attempted to spur their economies by cutting their budgets and enacting huge tariffs against foreign goods. These actions only served to dampen trade and discourage consumer spending, which in turn led to enormous unemployment and underemployment. All of these factors extended the depression and made it more difficult for countries to recover.
2
How did Mohandas Gandhi challenge British rule in India, and how did the British government attempt to split his movement?
Answer would ideally include the following. Although Gandhi was privileged and had trained in England as a lawyer, he rejected the Western love of material wealth as part of his rejection of British rule in India. Gandhi adopted a life of Hindu self-denial. He advocated civil disobedience, the act of deliberately but peacefully breaking British laws, with the aim of ending Indian deference to the British. The British tried to undermine Gandhi's efforts by jailing him several times and by trying to split any movement for independence in India by pitting Muslims and Hindus against each other.
3
What were the Soviet purges of the 1930s, and how did they change society?
Answer would ideally include the following. The purges comprised widespread arrests, imprisonments in labor camps, and executions and were part of Stalin's effort to identify anti-communists, or "wreckers," and remove them from Soviet society. The purges were related in several ways to collectivization policies that aimed to seize private land from prosperous peasants and destroy anyone who opposed collectivization. The purge touched all segments of society, including engineers condemned for low productivity, prominent Bolshevik leaders, and military leaders. The spirit of the purge swept through society and demonstrated that the government was absolutely ruthless in removing anyone who opposed its policies, and had no qualms about killing and imprisoning millions in order to enforce Soviet government policy in the name of the revolution.
4
How did Adolf Hitler and the National Socialists use a combination of racism, violence, and propaganda to attract followers before 1932?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Although Ramsay MacDonald, Britain's prime minister at the time the Great Depression began, was the leader of the Labour Party, at least two of his government's early efforts to deal with the financial crisis suggested that the working people's welfare was not the British government's top priority. Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What was the subject of Pope Pius XI's address to the world in 1931, and how was it both similar to and different from the theology of Karl Barth?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Why did Italy invade Ethiopia in 1935, and how was the handling of this event by the League of Nations evidence of the league's ineffectiveness?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
How did the civil war in Spain start, and why did many people from a variety of countries go to Spain to fight for the republican cause?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Why was the situation at Dunkirk in the spring of 1940 both a symbol of disaster and a symbol of heroism for the Allies?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
How did housewives and other women participate in the resistance to the Nazis?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Discuss the reasons why Joseph Stalin and Adolf Hitler succeeded in implementing their domestic policies for modernization, industrialization, and economic recovery. Make sure you consider state-sanctioned violence, who benefited the most from their policies, and whether people had sufficient cause to believe that life was better under them than under the previous governments.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
How did culture, science, and religion respond to the conditions of the early twentieth century, as economies around the world suffered and international tensions escalated into global warfare?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Describe the steps Hitler took in the 1930s that violated the Treaty of Versailles that had ended World War I. How were these a part of his larger plans for Germany? Explain the steps France and Britain took in response to these actions. Why did they decide not to enforce the treaty provisions?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Describe the escalation of the Nazi persecution of the Jews from Hitler's rise to power until the end of World War II. In your answer, consider factors like the Nazi's use of legal means to discriminate against the Jews, the role of propaganda in garnering the support of the German population, and the creation and implementation of the "Final Solution."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In what ways was World War II a global war? What ties did Japan have to the other Axis powers? What role did the colonies play in the war?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Why did the U.S. stock market crash lead to a global economic depression?
A) The United States was unable to pay its war debts to European nations, which led to widespread economic collapse.
B) American lenders called in their international debts, which undermined banks and industry abroad.
C) American banks had borrowed so heavily from foreign lenders that the crash destabilized foreign currencies.
D) Most foreign companies traded their stock on the U.S. market, so they became weak and unstable.
A) The United States was unable to pay its war debts to European nations, which led to widespread economic collapse.
B) American lenders called in their international debts, which undermined banks and industry abroad.
C) American banks had borrowed so heavily from foreign lenders that the crash destabilized foreign currencies.
D) Most foreign companies traded their stock on the U.S. market, so they became weak and unstable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which eastern European country was able to increase industrial capacity, despite the depression and despite being far less economically developed than its Western neighbors?
A) Bulgaria
B) Romania
C) Serbia
D) Hungary
A) Bulgaria
B) Romania
C) Serbia
D) Hungary

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following accurately describes one of the major sources of social tension during the Great Depression?
A) Many people fled the cities, overwhelming the ability of rural communities to support their own populations.
B) Even though the majority of people had jobs, they lived in constant fear that they would be replaced by cheaper laborers, like women or colonial workers.
C) Gender roles seemed to be reversed, as women often supported their families while their unemployed husbands remained at home.
D) Governments imposed restrictions on the number of children couples could have, as the burgeoning welfare states were weighed down by the burden of increased fertility.
A) Many people fled the cities, overwhelming the ability of rural communities to support their own populations.
B) Even though the majority of people had jobs, they lived in constant fear that they would be replaced by cheaper laborers, like women or colonial workers.
C) Gender roles seemed to be reversed, as women often supported their families while their unemployed husbands remained at home.
D) Governments imposed restrictions on the number of children couples could have, as the burgeoning welfare states were weighed down by the burden of increased fertility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In the 1930s, although the views of politicians varied, what was one belief that was shared by all?
A) Greater popular participation in politics would secure political stability by heightening the sense of shared responsibility.
B) Pump priming and government-sponsored job programs offered surefire solutions to the economic crisis.
C) Falling birthrates indicated a serious weakening or the imminent collapse of individual nations, if not of European society altogether.
D) An expansion of overseas markets would generate impressive revenues and lead to future prosperity.
A) Greater popular participation in politics would secure political stability by heightening the sense of shared responsibility.
B) Pump priming and government-sponsored job programs offered surefire solutions to the economic crisis.
C) Falling birthrates indicated a serious weakening or the imminent collapse of individual nations, if not of European society altogether.
D) An expansion of overseas markets would generate impressive revenues and lead to future prosperity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What effects did the economic depression have on Europe's overseas empires?
A) Economic distress spread throughout Europe's imperial possessions, fueling anger and discontent, which in turn led to action and the growth of anticolonial movements.
B) Europe was more dependent than ever on its colonies to produce greater revenue and invested heavily in industrial and infrastructure development.
C) The crisis in Europe drove up the prices of industrial goods and agricultural products in the colonies, increasing the standard of living in the empire while Europeans struggled.
D) Although the effects of the depression were felt across the globe, colonized peoples appreciated that their European colonizers had shielded them from the worst effects of the economic crisis.
A) Economic distress spread throughout Europe's imperial possessions, fueling anger and discontent, which in turn led to action and the growth of anticolonial movements.
B) Europe was more dependent than ever on its colonies to produce greater revenue and invested heavily in industrial and infrastructure development.
C) The crisis in Europe drove up the prices of industrial goods and agricultural products in the colonies, increasing the standard of living in the empire while Europeans struggled.
D) Although the effects of the depression were felt across the globe, colonized peoples appreciated that their European colonizers had shielded them from the worst effects of the economic crisis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
How did Mohandas Gandhi fight against British colonial rule of India?
A) He organized a vast network of resistance fighters.
B) He used his skills as a lawyer to marshal international support for Indian independence.
C) He encouraged Indians to practice civil disobedience.
D) He worked within the colonial system, campaigning for autonomy and self-government.
A) He organized a vast network of resistance fighters.
B) He used his skills as a lawyer to marshal international support for Indian independence.
C) He encouraged Indians to practice civil disobedience.
D) He worked within the colonial system, campaigning for autonomy and self-government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
How did Mustafa Kemal dramatically change Turkish society in the 1920s?
A) He created a quasi-Communist state that limited private ownership of property.
B) He developed an Islamic state that enforced traditional laws about all aspects of society.
C) He barred foreign banks and investments to make Turkey independent of outsiders.
D) He modernized Turkish society by adopting elements of Western economics and culture.
A) He created a quasi-Communist state that limited private ownership of property.
B) He developed an Islamic state that enforced traditional laws about all aspects of society.
C) He barred foreign banks and investments to make Turkey independent of outsiders.
D) He modernized Turkish society by adopting elements of Western economics and culture.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The term totalitarianism, as it is applied to the Fascist, Nazi, and Communist regimes of the 1930s, refers to
A) European states in which the leader came to power only after a rigged election.
B) a highly centralized system of government that attempts to control society and ensure obedience through a single party and police terror.
C) an economic and political system in which private property is abolished and all citizens are asked to devote their total allegiance to the state.
D) a political movement whose leaders believe in total economic and political equality for all citizens.
A) European states in which the leader came to power only after a rigged election.
B) a highly centralized system of government that attempts to control society and ensure obedience through a single party and police terror.
C) an economic and political system in which private property is abolished and all citizens are asked to devote their total allegiance to the state.
D) a political movement whose leaders believe in total economic and political equality for all citizens.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In 1929, Joseph Stalin implemented what ambitious industrial expansion program intended to end the Soviet Union's backwardness?
A) The New Economic Policy
B) The Struggle for Socialism
C) The first five-year plan
D) The Soviet Plan
A) The New Economic Policy
B) The Struggle for Socialism
C) The first five-year plan
D) The Soviet Plan

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Who was Stalin referring to when he called for a "liquidation of the kulaks"?
A) Prosperous peasants and anyone who opposed his plans to end independent farming
B) Coal miners from Siberia who went on strike just before the harsh winter of 1929
C) Russian bankers who resisted his plans to nationalize their holdings
D) Criminals who were making a profit by buying and selling black-market goods
A) Prosperous peasants and anyone who opposed his plans to end independent farming
B) Coal miners from Siberia who went on strike just before the harsh winter of 1929
C) Russian bankers who resisted his plans to nationalize their holdings
D) Criminals who were making a profit by buying and selling black-market goods

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which of the following resulted from Stalin's use of terror tactics to assure fulfillment of production quotas in the 1930s?
A) Stalin received mass support, as his tactics were the same as those used by Lenin to inspire compliance with his New Economic Policy in the 1920s.
B) Uprisings among factory workers increased, and so many workers were imprisoned that the rate of production dropped some 20 percent by 1938.
C) Up to half a million skilled and semiskilled workers emigrated before Stalin effectively sealed the Russian borders in 1938.
D) Economic failure as workers were all too inexperienced with industry to meet quotas, as well as the murder of farmers, caused the grain harvest to drop dramatically.
A) Stalin received mass support, as his tactics were the same as those used by Lenin to inspire compliance with his New Economic Policy in the 1920s.
B) Uprisings among factory workers increased, and so many workers were imprisoned that the rate of production dropped some 20 percent by 1938.
C) Up to half a million skilled and semiskilled workers emigrated before Stalin effectively sealed the Russian borders in 1938.
D) Economic failure as workers were all too inexperienced with industry to meet quotas, as well as the murder of farmers, caused the grain harvest to drop dramatically.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
How did Stalin respond to economic failures such as the drop in grain harvest that resulted from the failure of the collectivization of agriculture?
A) He instituted new quotas and incentives to inspire workers to put in longer hours and to instill more efficient work habits.
B) He blamed failure on "wreckers" who deliberately plotted against communism and instituted violent purges to rid society of these imagined "villains."
C) He turned away from Marxist economic theory and began adopting American models of industrial efficiency and western European agricultural techniques.
D) He became increasingly isolated and allowed the Soviet economy to deteriorate further, leading to massive unrest within the Soviet population.
A) He instituted new quotas and incentives to inspire workers to put in longer hours and to instill more efficient work habits.
B) He blamed failure on "wreckers" who deliberately plotted against communism and instituted violent purges to rid society of these imagined "villains."
C) He turned away from Marxist economic theory and began adopting American models of industrial efficiency and western European agricultural techniques.
D) He became increasingly isolated and allowed the Soviet economy to deteriorate further, leading to massive unrest within the Soviet population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What was the name given to the extensive system of Soviet prison camps that stretched from Moscow to Siberia and housed millions of political prisoners in harsh conditions?
A) The kolkhoz
B) The kulaks
C) The Gulag
D) The Zhenotdel
A) The kolkhoz
B) The kulaks
C) The Gulag
D) The Zhenotdel

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following factors contributed to the growth in public support for the Nazi Party among the German population in the early 1930s?
A) Hitler and the Nazi Party received the endorsement of Joseph Stalin and the Third International, which drew the unemployed and working classes to the movement.
B) The economic depression paralyzed the parliamentary government, which discredited democracy and made Hitler look like a bold leader who was unafraid of confronting Germany's enemies.
C) Hitler was able to calm the violence in the streets and revitalize the stalled parliamentary democracy by promising to enact economic legislation that would provide jobs.
D) The influx of millions of refugees from the Soviet Union further weakened the economy and led more Germans to support Hitler's anti-Communist tactics.
A) Hitler and the Nazi Party received the endorsement of Joseph Stalin and the Third International, which drew the unemployed and working classes to the movement.
B) The economic depression paralyzed the parliamentary government, which discredited democracy and made Hitler look like a bold leader who was unafraid of confronting Germany's enemies.
C) Hitler was able to calm the violence in the streets and revitalize the stalled parliamentary democracy by promising to enact economic legislation that would provide jobs.
D) The influx of millions of refugees from the Soviet Union further weakened the economy and led more Germans to support Hitler's anti-Communist tactics.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Although every age group and class of people supported Hitler, what demographic did the Nazi Party especially attract?
A) The upper-middle class, most of whom were middle-aged and fairly conservative
B) Upper-class men and women of all ages and businessmen who appreciated Hitler's attacks on Communists
C) Young people under forty, the majority of whom were from the industrial working class or the lower-middle class
D) Women of all ages and social classes, and also the elderly, who thought Hitler reminded them of the kaiser
A) The upper-middle class, most of whom were middle-aged and fairly conservative
B) Upper-class men and women of all ages and businessmen who appreciated Hitler's attacks on Communists
C) Young people under forty, the majority of whom were from the industrial working class or the lower-middle class
D) Women of all ages and social classes, and also the elderly, who thought Hitler reminded them of the kaiser

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Hitler came to power in 1933 after
A) a successful coup d'état by the National Socialist (Nazi) Party.
B) he won an overwhelming majority of the vote in the 1932 election, beating his nearest rival by more than five million votes.
C) the military took over the government and chose Hitler as chancellor because he had long called for rearmament.
D) conservatives were forced to choose between Hitler and his Communist rival for chancellor and chose Hitler because they believed he would be easier to manipulate.
A) a successful coup d'état by the National Socialist (Nazi) Party.
B) he won an overwhelming majority of the vote in the 1932 election, beating his nearest rival by more than five million votes.
C) the military took over the government and chose Hitler as chancellor because he had long called for rearmament.
D) conservatives were forced to choose between Hitler and his Communist rival for chancellor and chose Hitler because they believed he would be easier to manipulate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Hitler used which of the following events as an excuse to suspend civil liberties and launch a brutal crackdown on his political opponents?
A) The burning of the Reichstag
B) A strike by mine workers that paralyzed coal production in the Ruhr basin
C) The assassination of the German president
D) Clashes between Nazi storm troopers and the German Communist Party in Berlin
A) The burning of the Reichstag
B) A strike by mine workers that paralyzed coal production in the Ruhr basin
C) The assassination of the German president
D) Clashes between Nazi storm troopers and the German Communist Party in Berlin

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Hitler's order for the assassination of Ernst Roehm, which also resulted in the deaths of hundreds of SA leaders and innocent civilians, is known as the
A) Anschluss.
B) Final Solution.
C) Night of the Long Knives.
D) Volksgemeinschaft.
A) Anschluss.
B) Final Solution.
C) Night of the Long Knives.
D) Volksgemeinschaft.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What economic policy did the Nazi Party pursue that centered on stimulating the economy through government spending on tanks and airplanes and on public works programs such as the building of the Autobahn?
A) Laissez-faire economics
B) Pump priming
C) Money creation
D) Credit deflation
A) Laissez-faire economics
B) Pump priming
C) Money creation
D) Credit deflation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
What name was given to the 1935 legislation that deprived German Jews of citizenship, defined Jewishness according to ancestry rather than religious belief, and prohibited marriages between Jews and other Germans?
A) The Aryan Protection Act
B) The Munich Decrees
C) The Nuremberg Laws
D) The Anti-Semitic Defense Laws
A) The Aryan Protection Act
B) The Munich Decrees
C) The Nuremberg Laws
D) The Anti-Semitic Defense Laws

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following was a 1938 event in which the Nazis publicly persecuted Jews in Germany by burning synagogues, destroying Jewish property, and imprisoning Jews in retaliation for the murder of a German official by a Jewish teenager?
A) Volksgemeinschaft
B) The Night of the Long Knives
C) The Anschluss
D) Kristallnacht
A) Volksgemeinschaft
B) The Night of the Long Knives
C) The Anschluss
D) Kristallnacht

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What was U.S. president Franklin Delano Roosevelt's "New Deal"?
A) A new political party developed with a coalition of former Communists who were disillusioned with Stalin and liberal Democrats
B) A program of economic legislation designed to provide relief and recovery from the Great Depression
C) A movement to assist Jewish refugees from Nazi Germany that gained momentum after Kristallnacht in 1938
D) A political platform based around a policy of nonintervention in European wars
A) A new political party developed with a coalition of former Communists who were disillusioned with Stalin and liberal Democrats
B) A program of economic legislation designed to provide relief and recovery from the Great Depression
C) A movement to assist Jewish refugees from Nazi Germany that gained momentum after Kristallnacht in 1938
D) A political platform based around a policy of nonintervention in European wars

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
How did parliamentary leader Alva Myrdal address the problem of the population decline in Sweden?
A) She worked to pass legislation that discouraged women from working outside the home and made it legal for businesses to discriminate based on gender.
B) She campaigned for the criminalization of abortion and of the use of birth control.
C) She worked with leading eugenicists to identify the healthiest couples to promote strong breeding practices, while also promoting sterilization for those who were deemed "unfit."
D) She promoted government-sponsored prenatal care, free childbirth in a hospital, a food relief program, and subsidized housing for large families.
A) She worked to pass legislation that discouraged women from working outside the home and made it legal for businesses to discriminate based on gender.
B) She campaigned for the criminalization of abortion and of the use of birth control.
C) She worked with leading eugenicists to identify the healthiest couples to promote strong breeding practices, while also promoting sterilization for those who were deemed "unfit."
D) She promoted government-sponsored prenatal care, free childbirth in a hospital, a food relief program, and subsidized housing for large families.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Why would an antifascist coalition government such as the French Popular Front have been impossible in democratic countries before 1936?
A) Stalin had just reversed his ban on international Communists participating in coalition governments.
B) That year saw the defeat of the antifascist republicans in Spain.
C) That was the year that the League of Nations agreed to allow the formation of multiparty coalitions.
D) No one recognized that fascism was a growing danger until that year, when Hitler unveiled his new army and air force.
A) Stalin had just reversed his ban on international Communists participating in coalition governments.
B) That year saw the defeat of the antifascist republicans in Spain.
C) That was the year that the League of Nations agreed to allow the formation of multiparty coalitions.
D) No one recognized that fascism was a growing danger until that year, when Hitler unveiled his new army and air force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
In his 1931 address, Pope Pius XI (r. 1922-1939)
A) condemned the rising tide of ethnic tensions in eastern Europe as well as political extremism in countries such as Italy, Germany, and Russia.
B) blamed the decline in European fertility rates on the modern neglect of the family, the emancipation of women, and the spread of contraception.
C) condemned the failure of modern societies to provide their citizens with the moral and material conditions necessary for a decent life.
D) called upon Europeans to return to their religious faith in this time of economic distress and to focus on family, thrift, and hard work.
A) condemned the rising tide of ethnic tensions in eastern Europe as well as political extremism in countries such as Italy, Germany, and Russia.
B) blamed the decline in European fertility rates on the modern neglect of the family, the emancipation of women, and the spread of contraception.
C) condemned the failure of modern societies to provide their citizens with the moral and material conditions necessary for a decent life.
D) called upon Europeans to return to their religious faith in this time of economic distress and to focus on family, thrift, and hard work.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The Japanese justified their expansionist practices in Asia by claiming they were
A) restoring ancient religious beliefs and practices, especially Confucianism.
B) freeing the region from the domination of Western imperialism.
C) establishing democratic governments in place of the ancient monarchies of Asia.
D) creating a Communist-style state run from a central government located in Japan.
A) restoring ancient religious beliefs and practices, especially Confucianism.
B) freeing the region from the domination of Western imperialism.
C) establishing democratic governments in place of the ancient monarchies of Asia.
D) creating a Communist-style state run from a central government located in Japan.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
How did Western leaders respond to Japanese aggression in China in 1931-1937?
A) The League of Nations condemned Japan's actions but imposed no sanctions, while the United States drastically cut the flow of raw materials to Japanese industry.
B) Western leaders universally condemned it, and the League of Nations imposed harsh sanctions and fines on Japan and threatened military intervention in the event of further incursions.
C) Western leaders gave their tacit support, as Japan was seen as a more "civilized" society, and its invasion of China could potentially open the country to Western investment.
D) Western leaders did nothing, as both Japan and China were seen as far-off countries that held little interest for Europe or the United States and posed no major threat.
A) The League of Nations condemned Japan's actions but imposed no sanctions, while the United States drastically cut the flow of raw materials to Japanese industry.
B) Western leaders universally condemned it, and the League of Nations imposed harsh sanctions and fines on Japan and threatened military intervention in the event of further incursions.
C) Western leaders gave their tacit support, as Japan was seen as a more "civilized" society, and its invasion of China could potentially open the country to Western investment.
D) Western leaders did nothing, as both Japan and China were seen as far-off countries that held little interest for Europe or the United States and posed no major threat.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In 1936, how did both France and Britain lead Mussolini to believe that they would do little to stop fascist aggression?
A) They thwarted an attempt by some members of the League of Nations to impose a rigorous embargo on Italy following Mussolini's invasion of Ethiopia.
B) They forcibly repatriated Italian refugees fleeing arrest by Mussolini's Fascist police force.
C) They agreed to lower import duties on Italian goods despite Italy's seizure of Abyssinia two weeks earlier.
D) They failed to protest or otherwise respond to the virulent rhetoric that accompanied Mussolini's declaration of a "Rome-Berlin Axis."
A) They thwarted an attempt by some members of the League of Nations to impose a rigorous embargo on Italy following Mussolini's invasion of Ethiopia.
B) They forcibly repatriated Italian refugees fleeing arrest by Mussolini's Fascist police force.
C) They agreed to lower import duties on Italian goods despite Italy's seizure of Abyssinia two weeks earlier.
D) They failed to protest or otherwise respond to the virulent rhetoric that accompanied Mussolini's declaration of a "Rome-Berlin Axis."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Why did the republican forces lose the Spanish Civil War despite the popular outpouring of support for the cause of democracy from around the globe?
A) Although the republicans had strong support from European governments, squabbling among British and French military leaders led to poor strategic decisions that cost republicans the war.
B) Once Stalin pledged his support to the republican cause, anti-Communist members of the republican forces abandoned the coalition and joined the rebel forces.
C) As their appeals for material aid went unheeded by European democracies, republican troops floundered in the face of Franco's army, which was supported by Hitler and Mussolini.
D) Despite global support for the cause of democracy, the legendary atrocities committed by republican forces eroded support for their cause among the Spanish population.
A) Although the republicans had strong support from European governments, squabbling among British and French military leaders led to poor strategic decisions that cost republicans the war.
B) Once Stalin pledged his support to the republican cause, anti-Communist members of the republican forces abandoned the coalition and joined the rebel forces.
C) As their appeals for material aid went unheeded by European democracies, republican troops floundered in the face of Franco's army, which was supported by Hitler and Mussolini.
D) Despite global support for the cause of democracy, the legendary atrocities committed by republican forces eroded support for their cause among the Spanish population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
According to this map, which of the following statements supports why the Nationalists were successful during the Spanish Civil War?
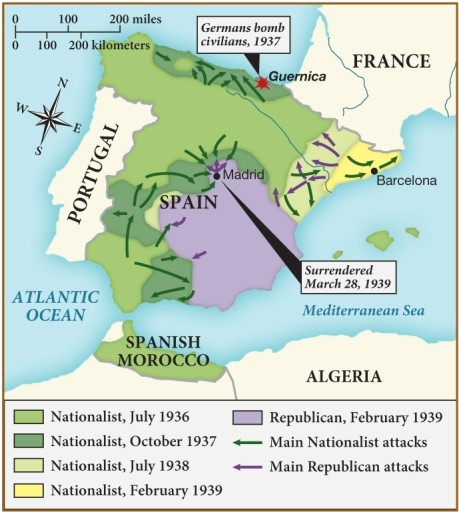
A) They were able to use strategic positions to launch naval attacks.
B) They had control over key cities like Madrid and Barcelona.
C) They were able to mobilize and expand more easily than the Republicans could.
D) They had the assistance of neighboring Portugal.

A) They were able to use strategic positions to launch naval attacks.
B) They had control over key cities like Madrid and Barcelona.
C) They were able to mobilize and expand more easily than the Republicans could.
D) They had the assistance of neighboring Portugal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What term was used for Hitler's annexation of (or merger with) Austria?
A) The Aryan March
B) The Anschluss
C) The Fourth Reich
D) The Volksgemeinschaft
A) The Aryan March
B) The Anschluss
C) The Fourth Reich
D) The Volksgemeinschaft

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
How did Nazi propaganda justify the German invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1938?
A) The Nazis fabricated a plot in which Czech Jews, with the support of Czechoslovakia's democratic government, had threatened to assassinate Hitler.
B) Nazi propaganda showed the German population newsreels of the Czech army mobilizing on the Austrian front in preparation for avenging the German annexation of Austria.
C) The Nazis accused Czechoslovakia of persecuting its German minority and warned the Czechs that they would have to grant autonomy to the German-populated Sudetenland or face invasion.
D) The Nazis claimed that the Czech government had asked for assistance in stabilizing its discredited parliamentary democracy.
A) The Nazis fabricated a plot in which Czech Jews, with the support of Czechoslovakia's democratic government, had threatened to assassinate Hitler.
B) Nazi propaganda showed the German population newsreels of the Czech army mobilizing on the Austrian front in preparation for avenging the German annexation of Austria.
C) The Nazis accused Czechoslovakia of persecuting its German minority and warned the Czechs that they would have to grant autonomy to the German-populated Sudetenland or face invasion.
D) The Nazis claimed that the Czech government had asked for assistance in stabilizing its discredited parliamentary democracy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Why have many historians criticized the Munich Pact of 1938?
A) It gave Germany more time to build its military and gave Hitler the idea that western European nations would not try to stop further aggression.
B) It did not go far enough; German grievances about Czechoslovakia and the Versailles Treaty were legitimate and needed to be recognized.
C) It gave Hitler complete reign in eastern Europe, including Poland and Romania.
D) The Western powers were given too much influence in Germany's affairs, including the ability to restrict its militarization, along the lines of the Versailles Treaty.
A) It gave Germany more time to build its military and gave Hitler the idea that western European nations would not try to stop further aggression.
B) It did not go far enough; German grievances about Czechoslovakia and the Versailles Treaty were legitimate and needed to be recognized.
C) It gave Hitler complete reign in eastern Europe, including Poland and Romania.
D) The Western powers were given too much influence in Germany's affairs, including the ability to restrict its militarization, along the lines of the Versailles Treaty.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
According to this map, which of the following regions was annexed by Germany in 1939?
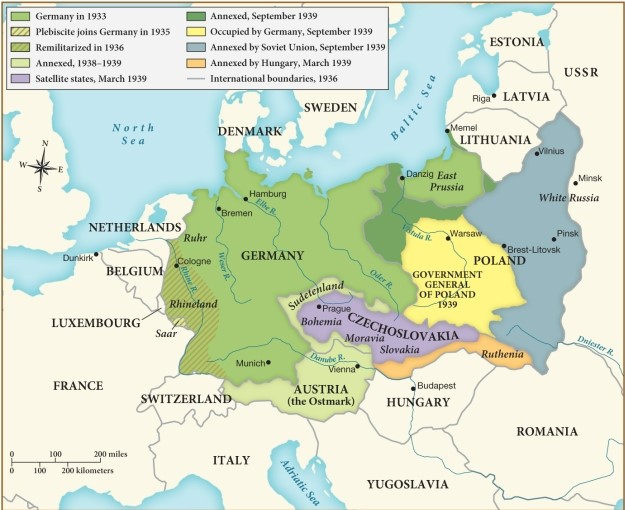
A) Hungary
B) Ruthenia
C) Lithuania
D) Poland

A) Hungary
B) Ruthenia
C) Lithuania
D) Poland

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Why did the Nazi-Soviet Pact signed on August 23, 1939, stun the Western world?
A) It gave Mussolini the pope's specific endorsement in exchange for increased financial support for the Catholic church.
B) It allied the Soviet Union with China, creating the world's geographically largest alliance.
C) It created a nonaggression agreement between fascist Germany and the Communist Soviet Union, despite their ideological hatred of each other.
D) It reflected Britain's decision to side with Germany regarding the partition of Poland in hopes of avoiding war.
A) It gave Mussolini the pope's specific endorsement in exchange for increased financial support for the Catholic church.
B) It allied the Soviet Union with China, creating the world's geographically largest alliance.
C) It created a nonaggression agreement between fascist Germany and the Communist Soviet Union, despite their ideological hatred of each other.
D) It reflected Britain's decision to side with Germany regarding the partition of Poland in hopes of avoiding war.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What did the Germans call their strategy of capturing Poland by launching an overpowering, concentrated attack using airplanes, tanks, and motorized infantry?
A) The Anschluss
B) Blitzkrieg
C) The Schlieffen Plan
D) Volksgemeinschaft
A) The Anschluss
B) Blitzkrieg
C) The Schlieffen Plan
D) Volksgemeinschaft

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The relentless German bombing of British cities in the summer of 1940 is known as the
A) battle of Britain.
B) Summer of Bombs.
C) Great Air War.
D) battle of the Atlantic.
A) battle of Britain.
B) Summer of Bombs.
C) Great Air War.
D) battle of the Atlantic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What event persuaded the previously isolationist United States to enter the war on the side of the Allies?
A) The German bombing of Britain in the summer of 1940
B) The German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941
C) The Japanese attacks on Pearl Harbor and the Philippines in December 1941
D) The Nazi meeting in Wannsee in January 1942, at which the "Final Solution" was formalized
A) The German bombing of Britain in the summer of 1940
B) The German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941
C) The Japanese attacks on Pearl Harbor and the Philippines in December 1941
D) The Nazi meeting in Wannsee in January 1942, at which the "Final Solution" was formalized

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What advantages did the Allied powers have over the Axis powers that allowed them to win the war?
A) Vastly superior weapons and technology as well as a strong industrial base
B) Greater manpower and resources and access to goods from their global empires
C) The support of their civilian populations, which the Axis leaders never had
D) A more sophisticated understanding of propaganda and mass media as well as the tools to use it more effectively
A) Vastly superior weapons and technology as well as a strong industrial base
B) Greater manpower and resources and access to goods from their global empires
C) The support of their civilian populations, which the Axis leaders never had
D) A more sophisticated understanding of propaganda and mass media as well as the tools to use it more effectively

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Why were literate civilians in the conquered areas of eastern Europe the most vulnerable?
A) Hitler and Stalin saw them as leading members of the civil society they were trying to destroy.
B) They were able to read the execution orders of the German and Soviet army officers and warn other civilians.
C) Hitler and Stalin wanted to prevent local populations from documenting the atrocities that their soldiers were committing in eastern Europe.
D) They were suspected of being spies for the Allies, as most civilians would not have had access to education.
A) Hitler and Stalin saw them as leading members of the civil society they were trying to destroy.
B) They were able to read the execution orders of the German and Soviet army officers and warn other civilians.
C) Hitler and Stalin wanted to prevent local populations from documenting the atrocities that their soldiers were committing in eastern Europe.
D) They were suspected of being spies for the Allies, as most civilians would not have had access to education.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When did the "Final Solution"-the Nazis' plan to systematically murder all the Jews of Europe-begin?
A) In 1933 when Hitler became chancellor of Germany
B) In 1939 when Germany invaded Poland and World War II began
C) In 1942 at a meeting in Wannsee
D) In 1943 after the Warsaw ghetto uprising
A) In 1933 when Hitler became chancellor of Germany
B) In 1939 when Germany invaded Poland and World War II began
C) In 1942 at a meeting in Wannsee
D) In 1943 after the Warsaw ghetto uprising

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which statement about the Final Solution is justified by this map?
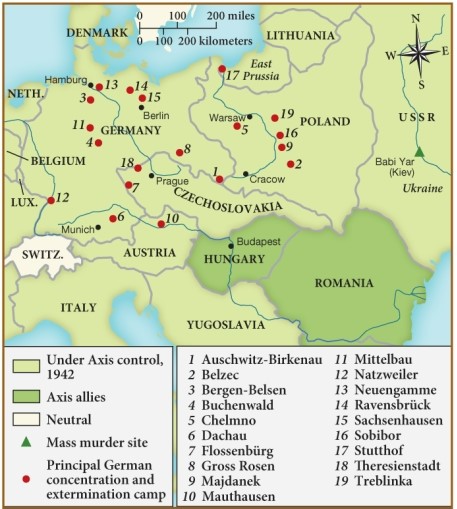
A) Switzerland participated in the Final Solution.
B) Camps were established in Denmark and Italy.
C) Poland was the site of the most camps outside German territory.
D) All German camps were established along rivers.

A) Switzerland participated in the Final Solution.
B) Camps were established in Denmark and Italy.
C) Poland was the site of the most camps outside German territory.
D) All German camps were established along rivers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Why were Allied governments more successful in mobilizing civilian women than the Axis powers were?
A) In Germany and Italy, government policy had particularly exalted motherhood and discouraged women from taking jobs outside the home.
B) Allied governments provided women with better incentives, including promises of equal pay and equal rights with men.
C) Allied governments offered social benefits to women, like free child care and access to government subsidies for large families, that the Axis governments did not provide.
D) The Allied powers had all given women the right to vote and allowed them to participate in politics, whereas the Axis powers denied women this privilege.
A) In Germany and Italy, government policy had particularly exalted motherhood and discouraged women from taking jobs outside the home.
B) Allied governments provided women with better incentives, including promises of equal pay and equal rights with men.
C) Allied governments offered social benefits to women, like free child care and access to government subsidies for large families, that the Axis governments did not provide.
D) The Allied powers had all given women the right to vote and allowed them to participate in politics, whereas the Axis powers denied women this privilege.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Which of the following was an indication of the prevalence of racial thinking in the United States during World War II?
A) All legislators of German descent were forced to resign.
B) German, Italian, and Japanese language classes were banned at every university.
C) Citizens of Japanese descent were forced to give up their homes and businesses and relocate to internment camps.
D) All citizens of German descent had to take an oath of loyalty to the United States, even if they were American-born citizens.
A) All legislators of German descent were forced to resign.
B) German, Italian, and Japanese language classes were banned at every university.
C) Citizens of Japanese descent were forced to give up their homes and businesses and relocate to internment camps.
D) All citizens of German descent had to take an oath of loyalty to the United States, even if they were American-born citizens.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Civilian resistance to Nazism and fascism in Europe
A) was almost nonexistent due to the totalitarian nature of those regimes and their strict control of civilian populations.
B) could be seen in areas where Germans and Italians did not have direct authority.
C) was largely the work of men who joined armed paramilitary movements in the countryside.
D) was widespread and involved both men and women who fought back in both dramatic and subtle ways.
A) was almost nonexistent due to the totalitarian nature of those regimes and their strict control of civilian populations.
B) could be seen in areas where Germans and Italians did not have direct authority.
C) was largely the work of men who joined armed paramilitary movements in the countryside.
D) was widespread and involved both men and women who fought back in both dramatic and subtle ways.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Based on this map, the first major battle that helped to kick off World War II occurred in
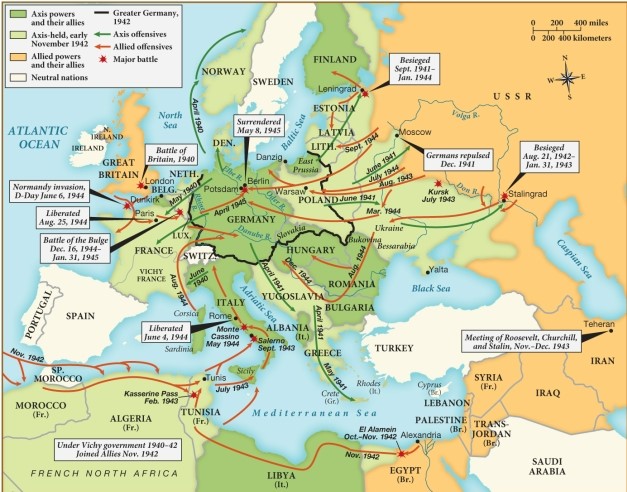
A) Great Britain.
B) France.
C) Italy.
D) Greece.

A) Great Britain.
B) France.
C) Italy.
D) Greece.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
In the face of total military defeat by late 1944, Hitler continued to beseech the Germans to fight on, believing that
A) the Germans, having failed to secure victory, deserved to die.
B) they could at least wrest a partial victory from the Allies by holding on to territory in the east.
C) such resolve would intimidate the Allies into agreeing to a less punishing peace.
D) divine providence was on the German side and that a turnaround was still possible.
A) the Germans, having failed to secure victory, deserved to die.
B) they could at least wrest a partial victory from the Allies by holding on to territory in the east.
C) such resolve would intimidate the Allies into agreeing to a less punishing peace.
D) divine providence was on the German side and that a turnaround was still possible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
What was the purpose of the Manhattan Project?
A) To make America the financial capital of the postwar world
B) To create a postwar alliance between Britain and the United States
C) To break German wartime codes using advanced mathematics
D) To develop the atomic bomb
A) To make America the financial capital of the postwar world
B) To create a postwar alliance between Britain and the United States
C) To break German wartime codes using advanced mathematics
D) To develop the atomic bomb

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Why did the results of Churchill's meeting with Stalin in October 1944 on the postwar distribution of territories disturb Roosevelt?
A) He felt that U.S. interests in Europe were being ignored.
B) Their agreements violated the U.S. government's promotion of collective security, self-determination, and free trade.
C) He did not trust Stalin and did not believe that Western powers could negotiate with him in good faith.
D) Churchill had at least tacitly agreed to allow the Soviets free reign to expand their influence over Korea, Manchuria, and the Sakhalin and Kurile Islands.
A) He felt that U.S. interests in Europe were being ignored.
B) Their agreements violated the U.S. government's promotion of collective security, self-determination, and free trade.
C) He did not trust Stalin and did not believe that Western powers could negotiate with him in good faith.
D) Churchill had at least tacitly agreed to allow the Soviets free reign to expand their influence over Korea, Manchuria, and the Sakhalin and Kurile Islands.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Which of the following European nations experienced the lowest percentage of population loss by the end of World War II in 1945?
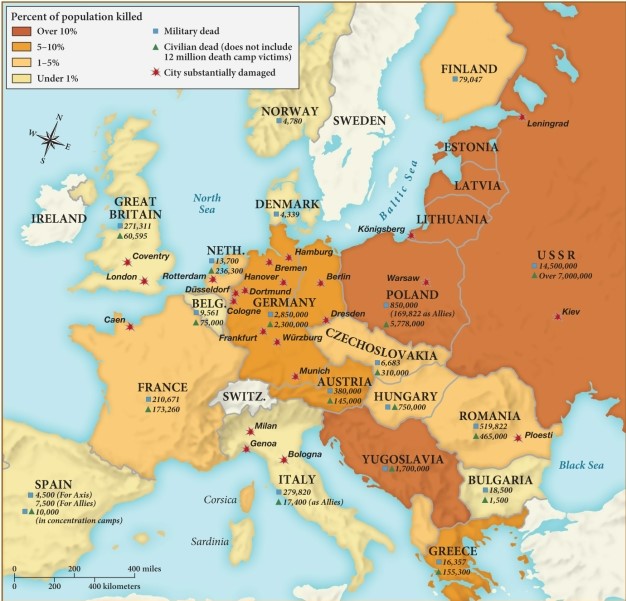
A) France
B) Germany
C) Poland
D) Italy

A) France
B) Germany
C) Poland
D) Italy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








