Deck 25: World War I and Its Aftermath, 1914-1929
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 25: World War I and Its Aftermath, 1914-1929
1
How did the horrific nature of fighting in the Great War create bonds of camaraderie between soldiers (and even between enemies), while at the same time creating alienation from civilians back home?
Answer would ideally include the following. The horror of life in the trenches resulted in friendships that could ease the hardships and dangers of war; the desire to survive even led to a sense of camaraderie with enemy soldiers, who endured the same conditions and faced the same dangers. Some opposing units came to a tacit agreement not to fire upon each other. Many soldiers felt alienated from civilian life because those at home had not experienced the horrible conditions and supported the fighting. Many recruits even became disillusioned with civilization itself; they came to see this war as meaningless or as the triumph of machine over man.
2
Although women's work was necessary to the war effort in virtually every European country, many people opposed it. Why?
Answer would ideally include the following. The high mobilization of men coupled with the enormous demand for supplies to fight the war made it necessary for women to work. Many women were placed in higher-status jobs or professions from which they had formerly been excluded, causing men to fear that they would be unable to get their jobs back after the war. Others said that war work led women to become less feminine and that young women were learning to squander their money on frivolity. The general fear was that women's greater independence would overturn gender roles and contribute to social disorder.
3
Explain how the efforts of France and Belgium to secure reparations by seizing the Ruhr basin in 1923 led to the virtual economic collapse of Germany.
Answer would ideally include the following. France and Belgium seized the Ruhr basin in 1923 because Germany had defaulted on coal deliveries that were part of the war reparations agreement. In response, the German government encouraged its citizens in the territory to shut down industry and services. To support the German citizens in the Ruhr basin, to keep the closed industries afloat, and to continue to pay Germany's war debts, the German government printed trillions of marks, causing skyrocketing inflation and making the German currency practically worthless. At one point, a single U.S. dollar cost more than 4 trillion marks, which meant that people's life savings were wiped out, and the lives of many others were ruined.
4
In an effort to spur postwar economic recovery in the 1920s, many businesses turned to efficiency experts to increase productivity. How did their recommendations both threaten to worsen the lives of workers and promise to improve them?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
How did the Great War break down class and gender boundaries?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
How did postwar popular culture reflect the political and social tumult of the 1920s?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
What was the Bauhaus movement, and how was it a reaction to the carnage of the Great War?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
How did Lenin react to various revolts against Bolshevik rule in the 1920s?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
How were "hygiene" and "efficiency" promoted by the Soviet state?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
How did Benito Mussolini consolidate his power and protect himself from political attack after becoming prime minister?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
How did European governments mobilize the home front to sustain the war effort during World War I? How did wartime conditions affect the political, economic, and social landscape of European societies? What consequences did these conditions have on postwar society?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
What do historians mean when they refer to a war as a "total war"? How was World War I a total war? What would a total war look like today? In your opinion, would such a war be possible? Explain why or why not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
How did Lenin and the Bolsheviks use discontent in Russia to their advantage? Why were they able to overcome "White" resistance to their revolution?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Despite the intention of the Peace of Paris, which was to prevent future conflict in Europe, its resulting treaties actually made future conflicts more likely. Explain why this was the case and what factors played a role in the negotiation and implementation of the postwar settlement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Describe the various ways in which Europeans expressed both their rage and frustration with the war, which they saw as the failure of European civilization, and the sense of optimism and idea of postwar utopia that existed in the 1920s. In your answer, be sure to consider artistic, social, and political responses to these dual impulses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
At the outbreak of World War I, France, Great Britain, and which other country made up the Allied Powers?
A) Austria-Hungary
B) Russia
C) Germany
D) The Ottoman Empire
A) Austria-Hungary
B) Russia
C) Germany
D) The Ottoman Empire

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Although the combatants in the Great War had individual objectives, in the end they all had which common aim?
A) To secure wealth and power for the postwar era
B) To dominate Europe
C) To institute conservative governments that would resist socialism
D) To avoid any great losses of men or materiel on the battlefield
A) To secure wealth and power for the postwar era
B) To dominate Europe
C) To institute conservative governments that would resist socialism
D) To avoid any great losses of men or materiel on the battlefield

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which country initially sided with the Central Powers but ended up joining the Allies in 1915 in hopes of postwar gain?
A) Russia
B) The Ottoman Empire
C) Italy
D) Japan
A) Russia
B) The Ottoman Empire
C) Italy
D) Japan

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements regarding World War I is supported by this map?
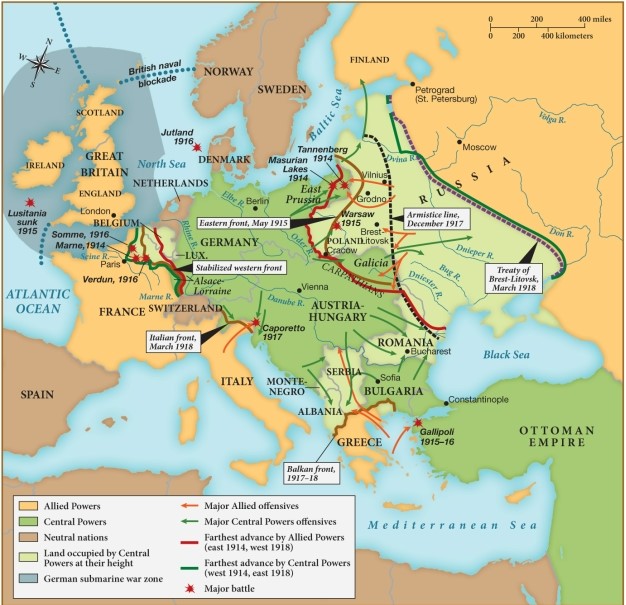
A) The Central Powers were unable to advance further east than Poland.
B) Great Britain had no use for its navy, as most battles were fought on mainland Europe.
C) The western front stabilized along the eastern border of France.
D) Italy remained neutral for most of the war.

A) The Central Powers were unable to advance further east than Poland.
B) Great Britain had no use for its navy, as most battles were fought on mainland Europe.
C) The western front stabilized along the eastern border of France.
D) Italy remained neutral for most of the war.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The "cult of the offensive," a strategy that officers on both sides in World War I wholeheartedly adopted, was uniquely unsuited to
A) massive civilian armies, which were wholly unused to lightning-strike military tactics.
B) the two-front German battle plan developed by Alfred von Schlieffen.
C) the rain-soaked, uneven terrain of northeast France, where most of the war was fought.
D) the advanced weaponry and unprecedented new machinery developed by that time.
A) massive civilian armies, which were wholly unused to lightning-strike military tactics.
B) the two-front German battle plan developed by Alfred von Schlieffen.
C) the rain-soaked, uneven terrain of northeast France, where most of the war was fought.
D) the advanced weaponry and unprecedented new machinery developed by that time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What was the major tactical strategy at the heart of the German military's Schlieffen Plan?
A) To engage the British and French in trench warfare in the Belgian forest in order to keep them occupied while knocking out the Russian army on the eastern front
B) To engage Russia on the eastern front, distracting the British and French armies and allowing German forces to sneak in and attack France along its Italian border
C) To aim a concentrated blow against France that was expected to achieve that nation's defeat in six weeks, accompanied by a light holding action against Russia to the east
D) To engage Britain and France in skirmishes in their North African colonies while simultaneously planning land and sea invasions of their European territories
A) To engage the British and French in trench warfare in the Belgian forest in order to keep them occupied while knocking out the Russian army on the eastern front
B) To engage Russia on the eastern front, distracting the British and French armies and allowing German forces to sneak in and attack France along its Italian border
C) To aim a concentrated blow against France that was expected to achieve that nation's defeat in six weeks, accompanied by a light holding action against Russia to the east
D) To engage Britain and France in skirmishes in their North African colonies while simultaneously planning land and sea invasions of their European territories

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
In 1916, the battles at Verdun and the Somme not only accounted for more than two million soldiers dead and wounded, but they also reflected
A) France and Britain's confidence that the United States would enter the war.
B) the fact that the Schlieffen Plan had finally been discredited and abandoned.
C) Germany's determination to defend the industrial region along the Rhine River and the Saar basin.
D) military leaders' belief that the war could be won by persistent overwhelming assaults.
A) France and Britain's confidence that the United States would enter the war.
B) the fact that the Schlieffen Plan had finally been discredited and abandoned.
C) Germany's determination to defend the industrial region along the Rhine River and the Saar basin.
D) military leaders' belief that the war could be won by persistent overwhelming assaults.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What techniques did soldiers in the trenches adopt to manage the extreme conditions and miseries of prolonged trench warfare?
A) They attempted to maintain their physical and mental fitness through constant military drills and physical workouts, which led to more content and compliant soldiers.
B) They organized poetry readings and educational programs to distract themselves from the battlefront and educate the working-class men for their postwar lives.
C) They developed strong bonds of male camaraderie with their fellow soldiers.
D) They organized unions along class and race lines to protest the conditions at the front and to influence the military leadership's battle decisions.
A) They attempted to maintain their physical and mental fitness through constant military drills and physical workouts, which led to more content and compliant soldiers.
B) They organized poetry readings and educational programs to distract themselves from the battlefront and educate the working-class men for their postwar lives.
C) They developed strong bonds of male camaraderie with their fellow soldiers.
D) They organized unions along class and race lines to protest the conditions at the front and to influence the military leadership's battle decisions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Why was World War I called a "total war"?
A) All of the countries in Europe, their colonial possessions, and the United States were involved in it.
B) The entire industrial capacity of participating states and all civilian and military personnel were mobilized to fight the war.
C) The new weapons of war, including poison gas and machine guns, killed virtually everyone in their path.
D) Armies on both sides used a scorched-earth tactic to destroy all crops, livestock, buildings, and infrastructure in their paths.
A) All of the countries in Europe, their colonial possessions, and the United States were involved in it.
B) The entire industrial capacity of participating states and all civilian and military personnel were mobilized to fight the war.
C) The new weapons of war, including poison gas and machine guns, killed virtually everyone in their path.
D) Armies on both sides used a scorched-earth tactic to destroy all crops, livestock, buildings, and infrastructure in their paths.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following is an example of how European governments mobilized civilians on the home front to help fight World War I?
A) War ministries set up boards to draft both men and women to work in factories to keep industrial production moving.
B) Britain and France relocated women and children to their colonies and to the United States in order to have fewer people to feed.
C) Both Britain and Germany repealed laws restricting child labor, as there were not enough adult industrial workers to keep up with munitions needs.
D) As the war of attrition took its toll, Italy began drafting women to serve as soldiers in its fighting units on the front.
A) War ministries set up boards to draft both men and women to work in factories to keep industrial production moving.
B) Britain and France relocated women and children to their colonies and to the United States in order to have fewer people to feed.
C) Both Britain and Germany repealed laws restricting child labor, as there were not enough adult industrial workers to keep up with munitions needs.
D) As the war of attrition took its toll, Italy began drafting women to serve as soldiers in its fighting units on the front.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
How did women's participation in the war effort on the home front affect debates over gender roles?
A) Women were universally praised throughout Europe for their patriotism and rewarded with suffrage and expanded political rights.
B) Many saw women's assumption of men's jobs as a sign of social disorder and feared that women would remain in the workforce after the war, robbing men of jobs.
C) Only government officials who needed women's labor approved of their participation in the war effort; most Europeans believed they should return to the domestic sphere.
D) In most cases, women were punished politically for their participation in the war effort, as woman suffrage bills were soundly defeated in nearly every European country after the war.
A) Women were universally praised throughout Europe for their patriotism and rewarded with suffrage and expanded political rights.
B) Many saw women's assumption of men's jobs as a sign of social disorder and feared that women would remain in the workforce after the war, robbing men of jobs.
C) Only government officials who needed women's labor approved of their participation in the war effort; most Europeans believed they should return to the domestic sphere.
D) In most cases, women were punished politically for their participation in the war effort, as woman suffrage bills were soundly defeated in nearly every European country after the war.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
What was the single most significant aspect of German military policy in terms of its provocative effect on the United States and subsequent U.S. involvement in the war?
A) Unrestricted submarine warfare
B) The Germans' purported use of mass executions in Belgium
C) Germany's decision to wage a two-front war
D) The forced removal of entire European populations to labor camps in Germany
A) Unrestricted submarine warfare
B) The Germans' purported use of mass executions in Belgium
C) Germany's decision to wage a two-front war
D) The forced removal of entire European populations to labor camps in Germany

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Among all the combatants the world over, which country suffered the greatest number of casualties, with some 7.5 million dead during World War I?
A) Germany
B) France
C) Great Britain
D) Russia
A) Germany
B) France
C) Great Britain
D) Russia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The abdication of Tsar Nicholas II in March 1917 and the collapse of the Romanov dynasty in Russia led to
A) the immediate end of Russia's engagement in World War I through a treaty signed with the German high command.
B) the creation of the Provisional Government, made up of aristocratic and middle-class politicians from the old Duma.
C) the invasion of Russia by German forces who no longer had to fight a unified Russian army, instead confronting disorganized bands of fighters.
D) the formation of a peasant-led revolutionary committee that put the tsar and his family on trial for treason and ordered their immediate execution.
A) the immediate end of Russia's engagement in World War I through a treaty signed with the German high command.
B) the creation of the Provisional Government, made up of aristocratic and middle-class politicians from the old Duma.
C) the invasion of Russia by German forces who no longer had to fight a unified Russian army, instead confronting disorganized bands of fighters.
D) the formation of a peasant-led revolutionary committee that put the tsar and his family on trial for treason and ordered their immediate execution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In April 1917, the Germans moved to destabilize Russia by
A) sending agents to blow up railway tracks, provoking a tsarist crackdown on dissidents.
B) using submarines to cut off the Russian supply lines in the Baltic Sea.
C) distributing leaflets and forged documents in Russia that purportedly proved that Nicholas II planned to reimpose serfdom.
D) providing safe rail transportation back to Russia for V. I. Lenin and other Bolsheviks.
A) sending agents to blow up railway tracks, provoking a tsarist crackdown on dissidents.
B) using submarines to cut off the Russian supply lines in the Baltic Sea.
C) distributing leaflets and forged documents in Russia that purportedly proved that Nicholas II planned to reimpose serfdom.
D) providing safe rail transportation back to Russia for V. I. Lenin and other Bolsheviks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Why did Russia's Provisional Government lose popular support?
A) It failed to win any military victories.
B) It prevented an election that would have brought the Bolsheviks to power.
C) It gave up enormous territories to Germany in exchange for peace.
D) It began seizing farm produce from peasants in order to feed the Russian army.
A) It failed to win any military victories.
B) It prevented an election that would have brought the Bolsheviks to power.
C) It gave up enormous territories to Germany in exchange for peace.
D) It began seizing farm produce from peasants in order to feed the Russian army.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
What changes did Lenin and the Bolshevik government institute in Russia after the Bolshevik Revolution in the fall of 1917?
A) They reorganized the collapsed Russian army to fight off the German invasion, organized elections for local and national offices, and restructured the economy.
B) They used troops to take over the government, limited elected candidates to members of the Communist Party, abolished private property, and nationalized factories.
C) They first secured the food supply to prevent peasant uprisings and keep supplies moving to the front and then reorganized the economy and political system.
D) They instituted universal suffrage for both men and women, abolished all political parties except for the Communist Party, and instituted mandatory primary schooling for all peasants.
A) They reorganized the collapsed Russian army to fight off the German invasion, organized elections for local and national offices, and restructured the economy.
B) They used troops to take over the government, limited elected candidates to members of the Communist Party, abolished private property, and nationalized factories.
C) They first secured the food supply to prevent peasant uprisings and keep supplies moving to the front and then reorganized the economy and political system.
D) They instituted universal suffrage for both men and women, abolished all political parties except for the Communist Party, and instituted mandatory primary schooling for all peasants.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, signed by Germany and Russia early in 1918,
A) required Germany and Russia to cede territory for the reconstruction of Poland.
B) withdrew Russia from the war in exchange for German withdrawal from Ukraine.
C) pulled Russia out of the war and changed the balance of World War I.
D) created the Third International and promoted its aggressive Marxist agenda.
A) required Germany and Russia to cede territory for the reconstruction of Poland.
B) withdrew Russia from the war in exchange for German withdrawal from Ukraine.
C) pulled Russia out of the war and changed the balance of World War I.
D) created the Third International and promoted its aggressive Marxist agenda.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The Russian civil war pitted which two groups against each other?
A) Russian peasants ("Whites") against urban Bolsheviks ("Reds") who wanted to nationalize farms and turn peasants into factory workers
B) Russian soldiers ("Reds"), many of whom were on the verge of starvation, against peasants ("Whites"), who believed the soldiers were treasonous deserters
C) Bolsheviks ("Reds") against the Russian army ("Whites"), many of whom supported the tsar and believed the Bolsheviks had betrayed them in signing the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
D) The pro-Bolshevik "Reds" against the "Whites," who were made up of an array of forces that wanted to turn back the revolution, including the tsarist military leadership
A) Russian peasants ("Whites") against urban Bolsheviks ("Reds") who wanted to nationalize farms and turn peasants into factory workers
B) Russian soldiers ("Reds"), many of whom were on the verge of starvation, against peasants ("Whites"), who believed the soldiers were treasonous deserters
C) Bolsheviks ("Reds") against the Russian army ("Whites"), many of whom supported the tsar and believed the Bolsheviks had betrayed them in signing the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
D) The pro-Bolshevik "Reds" against the "Whites," who were made up of an array of forces that wanted to turn back the revolution, including the tsarist military leadership

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
According to this map, which of the following territories did Russia lose after the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk?
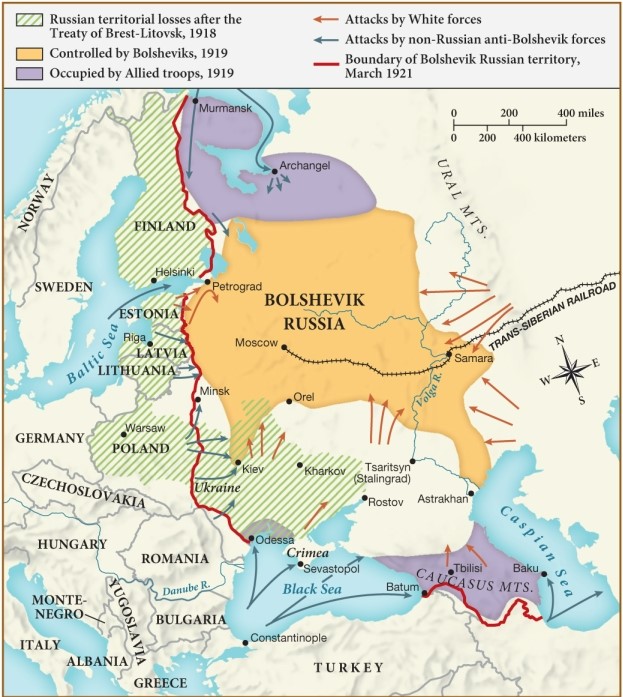
A) Moscow
B) Poland
C) Italy
D) Turkey

A) Moscow
B) Poland
C) Italy
D) Turkey

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What did the German high command do in October 1918 to deflect blame for Germany's total defeat away from the military?
A) They helped create an inexperienced civilian government and then claimed that weak-willed civilians had dealt the military a "stab in the back" by forcing a surrender.
B) They hired agitators to encourage strikes and sabotage at munitions plants and then claimed they did not have access to enough weapons to win the war.
C) They launched a propaganda campaign, calling the army "undefeated" and promising to rebuild and "give the world" a German victory.
D) They accused Kaiser Wilhelm II and his aristocratic advisers of having forced the military into waging a foolhardy two-front war against the advice of the generals.
A) They helped create an inexperienced civilian government and then claimed that weak-willed civilians had dealt the military a "stab in the back" by forcing a surrender.
B) They hired agitators to encourage strikes and sabotage at munitions plants and then claimed they did not have access to enough weapons to win the war.
C) They launched a propaganda campaign, calling the army "undefeated" and promising to rebuild and "give the world" a German victory.
D) They accused Kaiser Wilhelm II and his aristocratic advisers of having forced the military into waging a foolhardy two-front war against the advice of the generals.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Following the official end of hostilities on November 11, 1918, the world experienced another devastating blow with the death of some one hundred million more people as a result of
A) a typhus epidemic.
B) famine.
C) an influenza epidemic.
D) colonial uprisings.
A) a typhus epidemic.
B) famine.
C) an influenza epidemic.
D) colonial uprisings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What major issue challenged the stability of the Weimar Republic from the beginning?
A) The Weimar government refused to grant women the right to vote, so more than half the population of Germany never supported the government.
B) The Weimar government relied on street violence, paramilitary groups, and protests rather than parliaments to solve political problems.
C) The Weimar government was made up of many former military leaders, but the German population deeply distrusted the military and did not see the new government as a legitimate authority.
D) Weimar leaders refused to sign the Treaty of Versailles, which angered the vast number of Germans who just wanted to end the war, whatever the cost.
A) The Weimar government refused to grant women the right to vote, so more than half the population of Germany never supported the government.
B) The Weimar government relied on street violence, paramilitary groups, and protests rather than parliaments to solve political problems.
C) The Weimar government was made up of many former military leaders, but the German population deeply distrusted the military and did not see the new government as a legitimate authority.
D) Weimar leaders refused to sign the Treaty of Versailles, which angered the vast number of Germans who just wanted to end the war, whatever the cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The Peace of Paris, which was composed of a cluster of individual treaties negotiated between 1919 and 1920, redrew the map of Europe in which of the following ways?
A) Primarily focused on punishing Germany, the treaties diminished German lands by nearly half, with France, Italy, and Russia gaining large chunks of territory.
B) Building on the concept of self-determination, Austria, Germany, and all German-speaking peoples in the Habsburg Empire were combined into a single German state.
C) Italy took over the Balkans and part of Hungary, while the Habsburg Empire was greatly diminished and Russia gained access to Poland and to land on Austria's eastern border.
D) The treaties broke up the Ottoman and Habsburg Empires, separating Austria and Hungary and creating several weak, independent states in central Europe, such as Czechoslovakia and a reconstructed Poland.
A) Primarily focused on punishing Germany, the treaties diminished German lands by nearly half, with France, Italy, and Russia gaining large chunks of territory.
B) Building on the concept of self-determination, Austria, Germany, and all German-speaking peoples in the Habsburg Empire were combined into a single German state.
C) Italy took over the Balkans and part of Hungary, while the Habsburg Empire was greatly diminished and Russia gained access to Poland and to land on Austria's eastern border.
D) The treaties broke up the Ottoman and Habsburg Empires, separating Austria and Hungary and creating several weak, independent states in central Europe, such as Czechoslovakia and a reconstructed Poland.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
According to this map, which of the following countries was negatively impacted by the peace settlements reached after World War I in terms of territorial control?
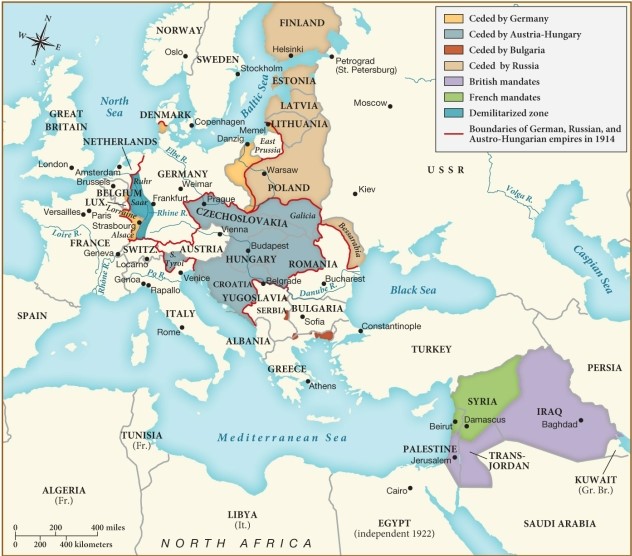
A) France
B) Russia
C) Great Britain
D) Romania

A) France
B) Russia
C) Great Britain
D) Romania

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
U.S. president Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points called for
A) harsh penalties to be directed toward Germany, since he believed it bore all responsibility for the war.
B) a fair settlement for Germany and a restructuring of the European system that emphasized open diplomacy, arms reduction, and self-determination for national groups.
C) an end to communism and the threat of socialist uprisings through the suppression of trade unions and an economic embargo on the Bolsheviks.
D) an end to colonialism, suffrage for all men and women regardless of their race or social class, and support for ethnic minorities in eastern Europe.
A) harsh penalties to be directed toward Germany, since he believed it bore all responsibility for the war.
B) a fair settlement for Germany and a restructuring of the European system that emphasized open diplomacy, arms reduction, and self-determination for national groups.
C) an end to communism and the threat of socialist uprisings through the suppression of trade unions and an economic embargo on the Bolsheviks.
D) an end to colonialism, suffrage for all men and women regardless of their race or social class, and support for ethnic minorities in eastern Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Why was the League of Nations weakened at the outset?
A) The United States, the Soviet Union, and Germany did not or could not participate.
B) Germany refused to join the league because France was involved.
C) England and France agreed to partition the former territories of the Ottoman Empire.
D) France and Britain disagreed over the issue of admitting the former Central Powers.
A) The United States, the Soviet Union, and Germany did not or could not participate.
B) Germany refused to join the league because France was involved.
C) England and France agreed to partition the former territories of the Ottoman Empire.
D) France and Britain disagreed over the issue of admitting the former Central Powers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
One of the main tasks of the League of Nations was the administration of the mandate system, which entailed
A) supervising elections and political matters in the newly formed states of eastern Europe, as these countries were inexperienced in democracy and self-government.
B) acting as a sort of international court to settle conflicts between ethnic minorities and the countries in which they lived.
C) exercising political control over the former colonies and territories of Germany and the Ottoman Empire, which the Europeans claimed were not yet capable of self-governance.
D) setting up international arms treaties to regulate the manufacture, sale, and deployment of weapons in the hopes of preventing another war like World War I.
A) supervising elections and political matters in the newly formed states of eastern Europe, as these countries were inexperienced in democracy and self-government.
B) acting as a sort of international court to settle conflicts between ethnic minorities and the countries in which they lived.
C) exercising political control over the former colonies and territories of Germany and the Ottoman Empire, which the Europeans claimed were not yet capable of self-governance.
D) setting up international arms treaties to regulate the manufacture, sale, and deployment of weapons in the hopes of preventing another war like World War I.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Of all the penalties imposed by the Treaty of Versailles, the one that generated the most outrage in Germany was the
A) so-called war guilt clause.
B) demand for 132 billion gold marks in reparations.
C) French occupation of the western bank of the Rhine and the coal-rich Saar basin.
D) loss of Alsace and Lorraine.
A) so-called war guilt clause.
B) demand for 132 billion gold marks in reparations.
C) French occupation of the western bank of the Rhine and the coal-rich Saar basin.
D) loss of Alsace and Lorraine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What did the Dawes Plan (1924), the Treaty of Locarno (1925), and the Young Plan (1929) attempt to accomplish?
A) The creation of a balance of power in Europe by limiting the number of battleships each country could build
B) The correction of some of the more punitive provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
C) The avoidance of an economic depression by establishing a single currency standard
D) Strengthening the League of Nations by establishing a set of goals for each member nation to achieve
A) The creation of a balance of power in Europe by limiting the number of battleships each country could build
B) The correction of some of the more punitive provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
C) The avoidance of an economic depression by establishing a single currency standard
D) Strengthening the League of Nations by establishing a set of goals for each member nation to achieve

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What was one of the lasting effects of World War I?
A) International negotiations and peace conferences were abandoned because they had not prevented the war.
B) Certain military terms and soldiers' slang entered common usage, such as lousy, trench coat, and basket case.
C) The horror of mechanized war caused many munitions manufacturers to question continued innovation in arms making.
D) The 1920s were a gloomy decade of retrenchment and cultural stagnation.
A) International negotiations and peace conferences were abandoned because they had not prevented the war.
B) Certain military terms and soldiers' slang entered common usage, such as lousy, trench coat, and basket case.
C) The horror of mechanized war caused many munitions manufacturers to question continued innovation in arms making.
D) The 1920s were a gloomy decade of retrenchment and cultural stagnation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
In many European countries, women were "rewarded" for their efforts in World War I with which of the following new rights?
A) The right to join labor unions
B) The right to sue for custody of their children after divorce
C) The right to vote
D) The right to control their own wages
A) The right to join labor unions
B) The right to sue for custody of their children after divorce
C) The right to vote
D) The right to control their own wages

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following best describes the new republics of eastern Europe during the 1920s?
A) They flourished economically, as they were better able to industrialize and regulate agricultural production as individual countries than as subject nations under vast empires.
B) They struggled to accommodate the arrival of hundreds of thousands of postwar refugees, most of whom had neither land nor jobs.
C) They attracted Europe's greatest cultural and intellectual leaders, who saw the new republics as spaces for democratic and artistic experimentation.
D) They became some of the most stable democracies in Europe, as the postwar concept of reorganizing eastern Europe along "nationality" lines turned out to be a success.
A) They flourished economically, as they were better able to industrialize and regulate agricultural production as individual countries than as subject nations under vast empires.
B) They struggled to accommodate the arrival of hundreds of thousands of postwar refugees, most of whom had neither land nor jobs.
C) They attracted Europe's greatest cultural and intellectual leaders, who saw the new republics as spaces for democratic and artistic experimentation.
D) They became some of the most stable democracies in Europe, as the postwar concept of reorganizing eastern Europe along "nationality" lines turned out to be a success.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The recreation of Poland after World War I, as evidenced by this map, brought with it
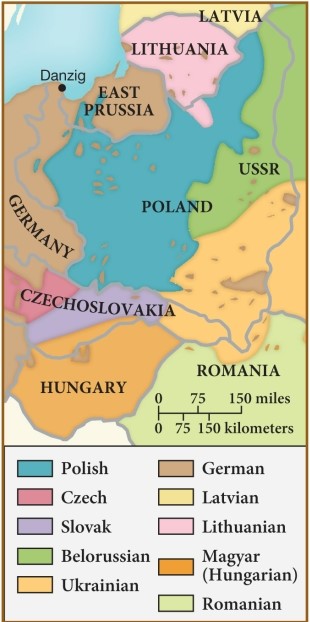
A) economic prosperity.
B) an end to Russian intrigue.
C) ethnic tensions.
D) a landlocked nation.

A) economic prosperity.
B) an end to Russian intrigue.
C) ethnic tensions.
D) a landlocked nation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Future German leader Adolf Hitler first gained attention in Germany for what political event?
A) The Beer Hall Putsch in Munich
B) The murder of Spartacists Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht
C) The Night of the Long Knives
D) His meeting with Benito Mussolini in Venice
A) The Beer Hall Putsch in Munich
B) The murder of Spartacists Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht
C) The Night of the Long Knives
D) His meeting with Benito Mussolini in Venice

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Why did right-wing parties have less influence in France and Britain than elsewhere in Europe?
A) The French and British governments were experienced at clamping down on opposition parties.
B) Socialist leaders were in power in both France and Britain after the war.
C) The economies of France and Britain were much stronger than those throughout the rest of Europe in 1918, so right-wing policies had little public appeal.
D) Parliamentary institutions were better established in France and Britain, and their upper classes were not plotting to restore authoritarian monarchies.
A) The French and British governments were experienced at clamping down on opposition parties.
B) Socialist leaders were in power in both France and Britain after the war.
C) The economies of France and Britain were much stronger than those throughout the rest of Europe in 1918, so right-wing policies had little public appeal.
D) Parliamentary institutions were better established in France and Britain, and their upper classes were not plotting to restore authoritarian monarchies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In 1921, after three years of fighting Irish republicans, the British drew up a treaty that
A) made Ireland a self-governing dominion and let Northern Ireland retain seats in the British Parliament.
B) thoroughly ignored the distribution of religious minorities in Ireland.
C) finally recognized the Irish Free State, only to see the treaty rejected by the northern counties that contained Protestant majorities.
D) called for a cessation of hostilities and established a twenty-year timetable for Irish independence.
A) made Ireland a self-governing dominion and let Northern Ireland retain seats in the British Parliament.
B) thoroughly ignored the distribution of religious minorities in Ireland.
C) finally recognized the Irish Free State, only to see the treaty rejected by the northern counties that contained Protestant majorities.
D) called for a cessation of hostilities and established a twenty-year timetable for Irish independence.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What impact did World War I have on European colonialism?
A) The huge cost of the war and of maintaining empires convinced the majority of Europeans that they should give up their colonies and focus on domestic issues.
B) It convinced Europeans of the necessity of their colonies but also pushed colonized peoples who had fought in the war to demand more rights and even independence.
C) Colonized peoples came to understand how reliant they were on European military and economic support, so they pushed for closer ties with their metropolitan colonizers.
D) Just as the postwar settlement spread democracy across eastern Europe, European colonizers encouraged political reform and nationalism throughout their colonies.
A) The huge cost of the war and of maintaining empires convinced the majority of Europeans that they should give up their colonies and focus on domestic issues.
B) It convinced Europeans of the necessity of their colonies but also pushed colonized peoples who had fought in the war to demand more rights and even independence.
C) Colonized peoples came to understand how reliant they were on European military and economic support, so they pushed for closer ties with their metropolitan colonizers.
D) Just as the postwar settlement spread democracy across eastern Europe, European colonizers encouraged political reform and nationalism throughout their colonies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which of the following was true of post-World War I European economies?
A) They collapsed under the weight of war debt and reconstruction costs and never managed to recover.
B) Since western European economies were destroyed, new industrial growth in eastern Europe became the major competition for the United States and Japan.
C) Although the European economies were weakened, the war forced industry to become more productive and efficient.
D) They quickly regained their prewar strength, and by 1925 Britain and Germany once again surpassed the United States in industrial production.
A) They collapsed under the weight of war debt and reconstruction costs and never managed to recover.
B) Since western European economies were destroyed, new industrial growth in eastern Europe became the major competition for the United States and Japan.
C) Although the European economies were weakened, the war forced industry to become more productive and efficient.
D) They quickly regained their prewar strength, and by 1925 Britain and Germany once again surpassed the United States in industrial production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Throughout Europe, the efforts of governments to support veterans who returned home after World War I were
A) nonexistent, as most civilians sought to return life to "normal."
B) varied, as soldiers were welcomed as heroes in the victor countries and viewed as mutinous traitors in countries like Germany.
C) very limited, as governments were bound by liberal ideology from interfering in the marketplace or privileging certain citizens.
D) extensive, as governments attempted to reduce the appeal of communism and reintegrate men into society.
A) nonexistent, as most civilians sought to return life to "normal."
B) varied, as soldiers were welcomed as heroes in the victor countries and viewed as mutinous traitors in countries like Germany.
C) very limited, as governments were bound by liberal ideology from interfering in the marketplace or privileging certain citizens.
D) extensive, as governments attempted to reduce the appeal of communism and reintegrate men into society.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What impact did the total war have on gender roles?
A) Women became shockingly liberated and promiscuous as a result of their newfound freedom from male chaperones, guardians, and even husbands.
B) The majority of women became dedicated pacifists who were largely out of sympathy with their government and with military men.
C) Convinced of veterans' need for a secure family life, many women retreated from feminism and women's social gains to cultivate a nurturing domesticity.
D) Women were more independent, joined formerly male occupations, adopted practical hairstyles and clothing, and sought greater political and social freedoms.
A) Women became shockingly liberated and promiscuous as a result of their newfound freedom from male chaperones, guardians, and even husbands.
B) The majority of women became dedicated pacifists who were largely out of sympathy with their government and with military men.
C) Convinced of veterans' need for a secure family life, many women retreated from feminism and women's social gains to cultivate a nurturing domesticity.
D) Women were more independent, joined formerly male occupations, adopted practical hairstyles and clothing, and sought greater political and social freedoms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which development of the 1920s made it easier for ordinary people to obtain new consumer goods such as refrigerators, washing machines, and stoves?
A) Warehouses sold electrical appliances directly to the consumer at dramatically reduced prices.
B) Lower-priced manufactured goods from the colonies, produced by low-paid native labor, were introduced.
C) Installment buying allowed families to pay for goods over time.
D) The government sponsored loans that were intended to improve veterans' standard of living.
A) Warehouses sold electrical appliances directly to the consumer at dramatically reduced prices.
B) Lower-priced manufactured goods from the colonies, produced by low-paid native labor, were introduced.
C) Installment buying allowed families to pay for goods over time.
D) The government sponsored loans that were intended to improve veterans' standard of living.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In the 1920s, radio broadcasts
A) were still too expensive and cumbersome for most private citizens.
B) were reserved largely for emergency messages, ship-to-shore communications, and weather reports for farmers.
C) were nothing but news reports, which consisted of announcers reading from major newspapers of the day.
D) quickly became common in private homes.
A) were still too expensive and cumbersome for most private citizens.
B) were reserved largely for emergency messages, ship-to-shore communications, and weather reports for farmers.
C) were nothing but news reports, which consisted of announcers reading from major newspapers of the day.
D) quickly became common in private homes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The novels of James Joyce and Virginia Woolf
A) focused on careful description of natural phenomena.
B) illuminated the fast-moving inner lives of their characters.
C) vividly portrayed a utopian future.
D) offered a dark and negative portrayal of modern life.
A) focused on careful description of natural phenomena.
B) illuminated the fast-moving inner lives of their characters.
C) vividly portrayed a utopian future.
D) offered a dark and negative portrayal of modern life.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
How did Lenin's New Economic Policy (NEP) break with his war communism policy?
A) It reversed the policy of absolute nationalization and allowed some free-market activity.
B) It gave soldiers and sailors their first raise in pay in over four years.
C) It set up essential trade with Germany.
D) It brought all economic activity under a centralized planning commission.
A) It reversed the policy of absolute nationalization and allowed some free-market activity.
B) It gave soldiers and sailors their first raise in pay in over four years.
C) It set up essential trade with Germany.
D) It brought all economic activity under a centralized planning commission.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
In his last will and testament, Lenin asked his comrades to find a way to remove which Communist Party leader from power?
A) Leon Trotsky
B) Joseph Stalin
C) Aleksandra Kollontai
D) Aleksandr Kerensky
A) Leon Trotsky
B) Joseph Stalin
C) Aleksandra Kollontai
D) Aleksandr Kerensky

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What allowed Benito Mussolini, the leader of the Fascists in Italy, to become prime minister in 1922?
A) Mussolini's party ran unopposed in national elections.
B) The middle classes voted him into power to block the working-class Communist Party.
C) His followers marched on Rome and forced the king to make him prime minister.
D) His followers intimidated voters, cast false ballots, and destroyed voting booths in order to secure his election in 1922.
A) Mussolini's party ran unopposed in national elections.
B) The middle classes voted him into power to block the working-class Communist Party.
C) His followers marched on Rome and forced the king to make him prime minister.
D) His followers intimidated voters, cast false ballots, and destroyed voting booths in order to secure his election in 1922.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The Italian Fascist movement led by Benito Mussolini (1883-1945) placed its greatest emphasis on which of the following principles?
A) Male violence and nationalist opposition to undesirable groups and ways of life
B) Individual dedication to an understanding of Fascist theory
C) Economic equality between the poor agrarian south and the rich industrial north
D) Liberation from ties to the past, especially the Italian parliament and the Catholic church
A) Male violence and nationalist opposition to undesirable groups and ways of life
B) Individual dedication to an understanding of Fascist theory
C) Economic equality between the poor agrarian south and the rich industrial north
D) Liberation from ties to the past, especially the Italian parliament and the Catholic church

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Adolf Hitler's rise to power in Germany was slowed in the 1920s by
A) political pressure on the Weimar regime from Britain and France to ban his Nazi Party.
B) popular disgust in Germany for his over-the-top autobiography, Mein Kampf.
C) his failure to develop a united following.
D) the better functioning of the Weimar regime.
A) political pressure on the Weimar regime from Britain and France to ban his Nazi Party.
B) popular disgust in Germany for his over-the-top autobiography, Mein Kampf.
C) his failure to develop a united following.
D) the better functioning of the Weimar regime.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Which of the following countries was an original member of the League of Nations?
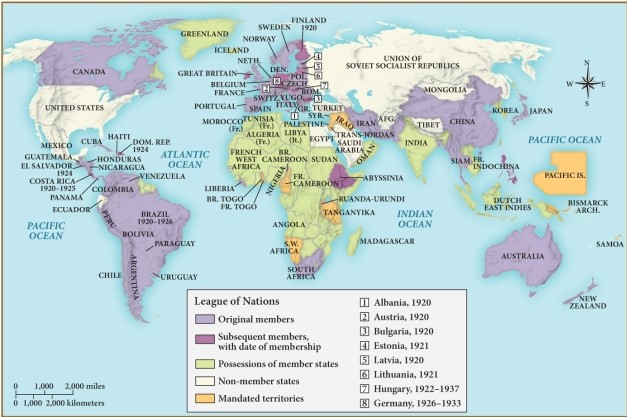
A) The USSR
B) Mexico
C) The United States
D) Canada

A) The USSR
B) Mexico
C) The United States
D) Canada

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 65 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








