Deck 2: Near East Empires and the Reemergence of Civilization in Greece, 1000-500 B.C.E
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: Near East Empires and the Reemergence of Civilization in Greece, 1000-500 B.C.E
1
How did the Neo-Assyrian kings' treatment of both their own people and those they conquered contribute to the downfall of their empire?
Answer would ideally include the following. The Neo-Assyrians were among the most ruthless rulers in the Middle East. Many conquered persons were deported to Assyria and forced to help build the massive temples and palaces found in Assyrian cities. Those allowed to stay in their homelands were forced to pay annual payments to support the Neo-Assyrian army and the state. Neo-Assyrian kings used terror and brutality against ordinary people to instill fear and as a result were very much disliked, especially by their own social elite. Rebellions were frequent, and revolts greatly weakened the kingdom. A joint invasion by the Chaldeans and the Medes in the late seventh century B.C.E. ended the Neo-Assyrian Empire.
2
Who introduced the concept of moral dualism in Persian religious belief? What does this term mean?
Answer would ideally include the following. Zarathustra (also called Zoroaster), a Persian prophet, proposed that the world was the site of an ongoing struggle between the divine forces of good and evil. According to the concept of moral dualism, people were active participants in the conflict because when individuals chose to act morally, they were siding with good and were rewarded with salvation; when they were immoral, they were siding with evil and were condemned to damnation. This ideology stood in stark contrast to the belief that performing certain rituals was the only action necessary to attain the favor of the gods.
3
What moral code did the Hebrews have to follow according to the terms of their covenant with their deity?
Answer would ideally include the following. The covenant required human obedience to divine law and promised punishment for unrighteousness. The Ten Commandments required Israelites to worship their deity exclusively, make no idols, keep from misusing their deity's name, honor their parents, refrain from work on the seventh day of the week (the Sabbath), and abstain from murder, adultery, theft, lying, and covetousness.
4
How did trading contacts help Greece recover from its Dark Age, especially in terms of metallurgy and written culture?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Although the Olympic Games were held to display individual achievements, they also promoted a concept of collective Greek identity. Explain why this was so.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Why are some historians reluctant to use the word colonies to refer to settlements founded by Greeks in the Mediterranean and Black Seas during the Archaic Age?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
What is the hoplite revolution theory, and why do some scholars reject this hypothesis?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
According to the text, what does the myth of Pandora suggest about some Greeks' attitudes toward women?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which social, economic, and administrative aspects of the Spartan way of life most supported Sparta's primary goal of military preparedness and civil obedience?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Why was Solon's approach to the problem of debt slavery a clear break with the past?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Compare and contrast the Neo-Assyrian Empire with its Persian successor. Which elements of government style, social structure, and economic management explain Persia's greater success in establishing a far-flung empire and maintaining its cohesion?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
How did the Israelites develop a monotheistic religion? In your response, please discuss the stages in the evolution of Israelite monotheism as well as the meanings that the Israelites
attached to the covenant between them and their deity.
attached to the covenant between them and their deity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
How did the core ideas of Greek religion differ from those of the Israelites? What similarities did they show?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Why did Greece emerge as a nexus for philosophical thought by the seventh and sixth centuries B.C.E.? What questions did philosophers raise, and what answers did they propose?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What was a tyrant in the context of the Greek city-states from the 650s through about 585 B.C.E.? How do the tyrants of that time compare to tyrants as we know them today? Explain what event prompted Greeks to end tyrannical rule and what they replaced tyranny with.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Why do historians use the term Dark Age when speaking of the eastern Mediterranean region between 1200 and 1000 B.C.E.?
A) The previously existing civilizations had all permanently disintegrated.
B) The region was plagued by terrible natural disasters, including earthquakes, severe flooding, and tropical storms.
C) Previously existing systems of religion had collapsed, leaving a spiritual vacuum in their wake.
D) Economic conditions were poor, and historians' knowledge of the era is limited.
A) The previously existing civilizations had all permanently disintegrated.
B) The region was plagued by terrible natural disasters, including earthquakes, severe flooding, and tropical storms.
C) Previously existing systems of religion had collapsed, leaving a spiritual vacuum in their wake.
D) Economic conditions were poor, and historians' knowledge of the era is limited.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which new regional power had emerged in Mesopotamia by 900 B.C.E.?
A) The Neo-Assyrian Empire
B) The Babylonian Empire
C) The kingdom of Israel
D) The Persian Empire
A) The Neo-Assyrian Empire
B) The Babylonian Empire
C) The kingdom of Israel
D) The Persian Empire

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Upon conquering foreign regions, Neo-Assyrian kings
A) exterminated the indigenous populations to make it easier for them to rule.
B) deported many of the conquered peoples to Assyria to work as slaves on building projects.
C) established colonies in the newly acquired territories to ease overpopulation back home.
D) treated the conquered peoples with a remarkable degree of benevolence.
A) exterminated the indigenous populations to make it easier for them to rule.
B) deported many of the conquered peoples to Assyria to work as slaves on building projects.
C) established colonies in the newly acquired territories to ease overpopulation back home.
D) treated the conquered peoples with a remarkable degree of benevolence.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Why were Assyrian women unlikely to rise to positions of political power?
A) The pursuits most admired by the Assyrian elite were warfare and hunting, which were exclusively male occupations.
B) The Assyrians believed that only women who were secluded from public life were capable of bearing strong children.
C) The Assyrians believed that Egypt had fallen because it had allowed women to hold positions of power, and they did not want to imitate such a flawed state.
D) The Assyrians' religion taught that if the natural purity of women were defiled by allowing them to hold public office, the gods would punish the people of Assyria.
A) The pursuits most admired by the Assyrian elite were warfare and hunting, which were exclusively male occupations.
B) The Assyrians believed that only women who were secluded from public life were capable of bearing strong children.
C) The Assyrians believed that Egypt had fallen because it had allowed women to hold positions of power, and they did not want to imitate such a flawed state.
D) The Assyrians' religion taught that if the natural purity of women were defiled by allowing them to hold public office, the gods would punish the people of Assyria.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What precipitated the collapse of the Neo-Assyrian Empire?
A) An invasion by the Egyptians, who sought to reconquer their territory
B) A series of natural disasters, including droughts, floods, and earthquakes
C) A seventh-century B.C.E. rebellion and a subsequent invasion by the Medes and Chaldeans
D) The death of the heir to the imperial throne, which triggered a civil war
A) An invasion by the Egyptians, who sought to reconquer their territory
B) A series of natural disasters, including droughts, floods, and earthquakes
C) A seventh-century B.C.E. rebellion and a subsequent invasion by the Medes and Chaldeans
D) The death of the heir to the imperial throne, which triggered a civil war

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
During the Neo-Babylonian Empire, the Chaldeans rebuilt the great temple of their chief god,
A) Ahura Mazda.
B) Zoroaster.
C) Ishtar.
D) Marduk.
A) Ahura Mazda.
B) Zoroaster.
C) Ishtar.
D) Marduk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which strategy did early Persian rulers adopt to rule over their newly conquered peoples?
A) They enacted a code of law based on Hammurabi's law code, which the Persian kings personally enforced.
B) They held lavish banquets for everyone in the conquered territories in dozens of cities.
C) They allowed local people to keep their own beliefs and customs.
D) They segregated ethnic groups in order to minimize quarrels between them.
A) They enacted a code of law based on Hammurabi's law code, which the Persian kings personally enforced.
B) They held lavish banquets for everyone in the conquered territories in dozens of cities.
C) They allowed local people to keep their own beliefs and customs.
D) They segregated ethnic groups in order to minimize quarrels between them.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
How did Darius I change Persia during his rule?
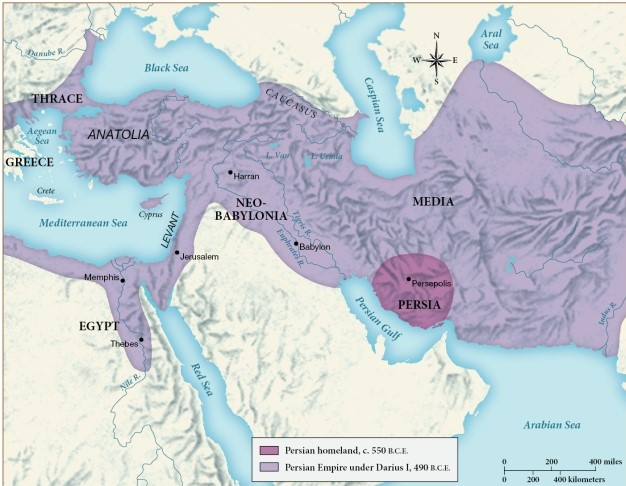
A) The Neo-Babylonian Empire overcame Persia.
B) Persia shrank in size due to Darius I's failure to protect the region from invasion.
C) Persia expanded from an area surrounding Persepolis to a massive Persian Empire.
D) The Persian Empire lost many of its important territories along water for trading.

A) The Neo-Babylonian Empire overcame Persia.
B) Persia shrank in size due to Darius I's failure to protect the region from invasion.
C) Persia expanded from an area surrounding Persepolis to a massive Persian Empire.
D) The Persian Empire lost many of its important territories along water for trading.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
By 490 B.C.E., which of the following regions had the Persian Empire expanded to control?
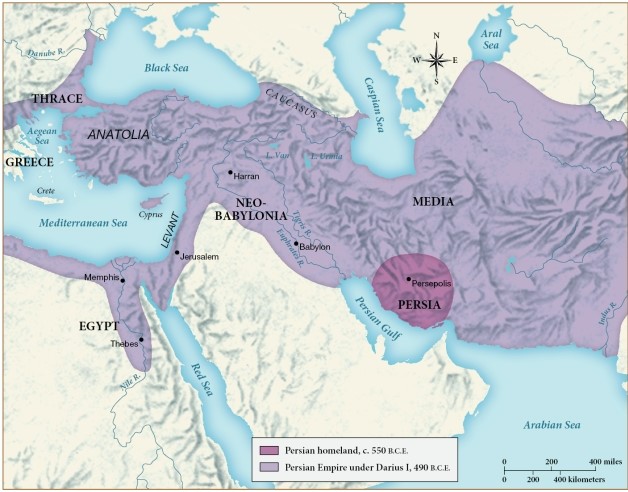
A) The land to the north of the Caucasus mountains
B) Anatolia
C) The land west of the Danube River
D) Crete

A) The land to the north of the Caucasus mountains
B) Anatolia
C) The land west of the Danube River
D) Crete

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following Persian rulers expanded the boundaries of the empire all the way to the edges of India and Greece?
A) Cyrus
B) Marduk
C) Darius I
D) Zarathustra
A) Cyrus
B) Marduk
C) Darius I
D) Zarathustra

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Zarathustra made a significant contribution to Western thought when he proposed which of the following?
A) That God was pure thought, not a physical individual
B) That human behavior was influenced both by the environment and by upbringing
C) That a person's gender had no bearing on his or her intellectual capabilities
D) That individuals determined their own eternal fate through the moral choices they made while on earth
A) That God was pure thought, not a physical individual
B) That human behavior was influenced both by the environment and by upbringing
C) That a person's gender had no bearing on his or her intellectual capabilities
D) That individuals determined their own eternal fate through the moral choices they made while on earth

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Why did the ancient Israelites have such a powerful influence on Western civilization, when their kingdom never enjoyed the same level of political and military power as the other great empires in the Near East?
A) Their monotheism directly influenced the monotheism practiced by the Egyptian pharaohs, who in turn passed it on to the Christians.
B) When the Israelite kingdoms were conquered by the Neo-Assyrians and the Babylonians, their citizens in exile rose to high positions in both empires.
C) Their monotheism and sacred scripture made the Israelites a fundamental building block in the foundations of Western civilization.
D) The Israelites established themselves as leading merchants and traders, founding colonies throughout the Mediterranean world.
A) Their monotheism directly influenced the monotheism practiced by the Egyptian pharaohs, who in turn passed it on to the Christians.
B) When the Israelite kingdoms were conquered by the Neo-Assyrians and the Babylonians, their citizens in exile rose to high positions in both empires.
C) Their monotheism and sacred scripture made the Israelites a fundamental building block in the foundations of Western civilization.
D) The Israelites established themselves as leading merchants and traders, founding colonies throughout the Mediterranean world.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What did the covenant established between the Israelites and their deity require the Israelites to do?
A) Worship their deity as their only god and live according to his laws
B) Move from Canaan to Mesopotamia
C) Sign treaties with the leading empires of the Near East
D) Punish their sons and grandsons to the third and fourth generation for their own criminal offenses
A) Worship their deity as their only god and live according to his laws
B) Move from Canaan to Mesopotamia
C) Sign treaties with the leading empires of the Near East
D) Punish their sons and grandsons to the third and fourth generation for their own criminal offenses

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
How did Israelite law differ from the legal codes previously established in Mesopotamia?
A) It was significantly harsher, as it called for the death penalty for almost all property crimes.
B) It created a new standard of punishment based on the principle of "an eye for an eye."
C) It increased punishments for slaves.
D) It applied the same rules and punishments to all, without regard to social standing or rank.
A) It was significantly harsher, as it called for the death penalty for almost all property crimes.
B) It created a new standard of punishment based on the principle of "an eye for an eye."
C) It increased punishments for slaves.
D) It applied the same rules and punishments to all, without regard to social standing or rank.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The term Diaspora describes the experience of those Jews who
A) died for their faith while under the yoke of foreign rule.
B) lived outside the Jewish homeland but still followed Jewish law.
C) suffered from a shortage of food and severe depredation while under foreign rule.
D) gave up their Jewish identity and assimilated into foreign cultures.
A) died for their faith while under the yoke of foreign rule.
B) lived outside the Jewish homeland but still followed Jewish law.
C) suffered from a shortage of food and severe depredation while under foreign rule.
D) gave up their Jewish identity and assimilated into foreign cultures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of the following was one of the few aspects of the former Mycenaean civilization to survive the Dark Age in Greece?
A) The writing script known as Linear B, originally developed by palace scribes to keep track of the flow of goods
B) The economic system used by local rulers to redistribute goods from better endowed regions to the poorest communities
C) The tradition of decorating pottery with images of humans and animals
D) The oral transmission of Greek cultural traditions
A) The writing script known as Linear B, originally developed by palace scribes to keep track of the flow of goods
B) The economic system used by local rulers to redistribute goods from better endowed regions to the poorest communities
C) The tradition of decorating pottery with images of humans and animals
D) The oral transmission of Greek cultural traditions

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
When the Greeks began writing again about 800 B.C.E., they adopted and adapted an alphabet they received from the
A) Egyptians.
B) Hebrews.
C) Babylonians.
D) Phoenicians.
A) Egyptians.
B) Hebrews.
C) Babylonians.
D) Phoenicians.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
How did the Greeks significantly improve the quality of their farm implements and weaponry following their Dark Age?
A) They rediscovered the lost art of bronze metallurgy by smelting tin and copper.
B) They learned the skill of iron metallurgy from their eastern trading partners and went on to mine their own iron ore deposits.
C) They raided the farms and armories on the edges of Near Eastern empires for tools and weapons they could not construct themselves.
D) They used the advanced mathematics of Ionia to achieve the precise measurements needed to create new alloys, such as iron.
A) They rediscovered the lost art of bronze metallurgy by smelting tin and copper.
B) They learned the skill of iron metallurgy from their eastern trading partners and went on to mine their own iron ore deposits.
C) They raided the farms and armories on the edges of Near Eastern empires for tools and weapons they could not construct themselves.
D) They used the advanced mathematics of Ionia to achieve the precise measurements needed to create new alloys, such as iron.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The Greek word aretê signified "excellence," a concept that historians insist led the Greeks to do which of the following?
A) Compete fiercely with one another in all fields of endeavor, from the arts to politics, athletics, science, and war, for the public honor that achieving excellence bestowed
B) Seek harmony in their relations with other Greek city-states, so as to perpetuate the state of peace needed to cultivate excellence in such arenas as the arts, philosophy, and commerce
C) Avoid prolonged contact with outside powers, whom the Greeks considered culturally inferior and potentially damaging to the purity of Greek aretê
D) Develop a consuming preoccupation with physical fitness, devoting inordinate amounts of time to athletic games at the expense of other aspects of culture
A) Compete fiercely with one another in all fields of endeavor, from the arts to politics, athletics, science, and war, for the public honor that achieving excellence bestowed
B) Seek harmony in their relations with other Greek city-states, so as to perpetuate the state of peace needed to cultivate excellence in such arenas as the arts, philosophy, and commerce
C) Avoid prolonged contact with outside powers, whom the Greeks considered culturally inferior and potentially damaging to the purity of Greek aretê
D) Develop a consuming preoccupation with physical fitness, devoting inordinate amounts of time to athletic games at the expense of other aspects of culture

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
What is recounted in Homer's epic poem The Iliad?
A) The events of the Trojan War
B) Odysseus's return from the Trojan War
C) The creation of the universe
D) The founding of Athens
A) The events of the Trojan War
B) Odysseus's return from the Trojan War
C) The creation of the universe
D) The founding of Athens

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The Olympic Games were open to any socially elite
A) Greek man or woman sponsored by a city-state.
B) Greek man good enough to compete.
C) Greek man or woman without a family.
D) Greek or foreign man old enough to compete.
A) Greek man or woman sponsored by a city-state.
B) Greek man good enough to compete.
C) Greek man or woman without a family.
D) Greek or foreign man old enough to compete.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The Greek concept of divine justice is illustrated in Hesiod's epic poems,
A) which were derived from the creation myths of the Near East.
B) and can also be seen in Homer's poems.
C) but it was not applied to commoners.
D) though not in his Theogony.
A) which were derived from the creation myths of the Near East.
B) and can also be seen in Homer's poems.
C) but it was not applied to commoners.
D) though not in his Theogony.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What did the Greeks establish as they began to recover from two centuries of economic devastation and population decimation?
A) Independent monarchies modeled on the Mycenaean political system of earlier centuries
B) A new form of political and social organization known as the polis, or independent city-state
C) Popular democracies based on an unprecedented system of universal suffrage
D) A single, centralized state ruled by a powerful monarch, who was able to marshal the resources to reaffirm Greek economic hegemony over the Aegean area.
A) Independent monarchies modeled on the Mycenaean political system of earlier centuries
B) A new form of political and social organization known as the polis, or independent city-state
C) Popular democracies based on an unprecedented system of universal suffrage
D) A single, centralized state ruled by a powerful monarch, who was able to marshal the resources to reaffirm Greek economic hegemony over the Aegean area.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following best describes ancient Greece's natural resources?
A) Greece had a mountainous, rocky terrain that was suitable for the cultivation of olives, grapes, and barley but little else.
B) Greece was mountainous in the north, where there was little rainfall, but very flat and fertile in the south.
C) Greece was rich in both farmland and in deposits of highly prized stones such as marble, lapis lazuli, alabaster, and obsidian.
D) Ancient Greece has often been called the breadbasket of the West because its warm, fertile valleys produced an abundance of grains and other foodstuffs.
A) Greece had a mountainous, rocky terrain that was suitable for the cultivation of olives, grapes, and barley but little else.
B) Greece was mountainous in the north, where there was little rainfall, but very flat and fertile in the south.
C) Greece was rich in both farmland and in deposits of highly prized stones such as marble, lapis lazuli, alabaster, and obsidian.
D) Ancient Greece has often been called the breadbasket of the West because its warm, fertile valleys produced an abundance of grains and other foodstuffs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Magna Graecia ("Great Greece") was the name the ancient Greeks used to describe which region?
A) The southern peninsula of Greece called the Peloponnese, which was home to Sparta-militarily the most powerful of all the Greek city-states
B) The western coast of Anatolia, site of the greatest number of overseas Greek settlements
C) Southern Italy and Sicily, sites of some of the largest and most powerful overseas Greek settlements, including Naples and Syracuse
D) The northern region of Macedonia, future home of the Greek conqueror Alexander the Great
A) The southern peninsula of Greece called the Peloponnese, which was home to Sparta-militarily the most powerful of all the Greek city-states
B) The western coast of Anatolia, site of the greatest number of overseas Greek settlements
C) Southern Italy and Sicily, sites of some of the largest and most powerful overseas Greek settlements, including Naples and Syracuse
D) The northern region of Macedonia, future home of the Greek conqueror Alexander the Great

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
How did Greek settlement in the eastern Mediterranean abroad influence the development of Greek culture during the Archaic Age (c. 750-500 B.C.E.)?
A) It allowed the Greeks to borrow directly from Roman architecture and sculpture.
B) It paved the way for the Greeks to imitate Near Eastern and Egyptian statuary.
C) It introduced the Greeks to the Hebrew concept of monotheism and altered Greek religion.
D) It introduced the Greeks to Assyrian models of warfare and led to their use of chariots in military campaigns.
A) It allowed the Greeks to borrow directly from Roman architecture and sculpture.
B) It paved the way for the Greeks to imitate Near Eastern and Egyptian statuary.
C) It introduced the Greeks to the Hebrew concept of monotheism and altered Greek religion.
D) It introduced the Greeks to Assyrian models of warfare and led to their use of chariots in military campaigns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following best characterizes developments during the era of Greek "colonization"?
A) Greek city-states officially founded colonies abroad.
B) Greek settlers sought new wealth through trade and agriculture.
C) Greek emigrants found religious freedom by settling new territories.
D) Private Greek entrepreneurs built settlements that became colonies.
A) Greek city-states officially founded colonies abroad.
B) Greek settlers sought new wealth through trade and agriculture.
C) Greek emigrants found religious freedom by settling new territories.
D) Private Greek entrepreneurs built settlements that became colonies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Based on this map, who did Greek city-states tend to trade with from 750 to 500 B.C.E.?
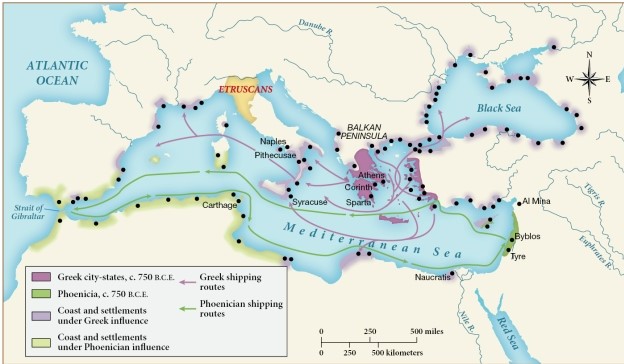
A) Other Greek city-states and settlements under Greek influence
B) Phoenicia
C) Settlements under Phoenician rule
D) The Etruscans

A) Other Greek city-states and settlements under Greek influence
B) Phoenicia
C) Settlements under Phoenician rule
D) The Etruscans

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
According to this map, the Phoenician shipping routes were primarily within the
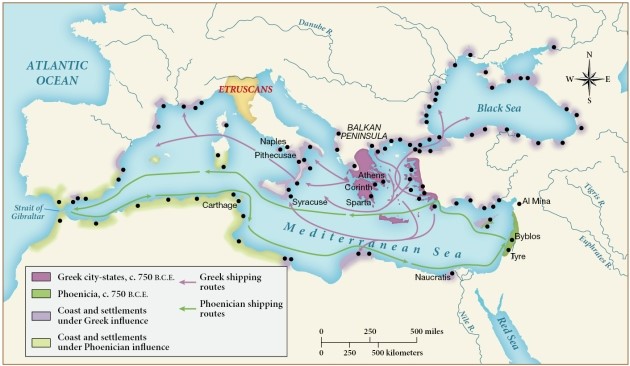
A) Nile River.
B) Black Sea.
C) Red Sea.
D) Mediterranean Sea.

A) Nile River.
B) Black Sea.
C) Red Sea.
D) Mediterranean Sea.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Why were the political forms of the Greek city-states and the Greek concept of citizenship so unprecedented and unique?
A) They allowed all the inhabitants of a city-state, irrespective of race or gender, to vote equally.
B) They represented a radical departure from long-held communal values, as the rights of the individual henceforth took precedence.
C) They affirmed the right of all Greek inhabitants to an equal share in the state's governance.
D) They were based on the concept of citizenship for all free inhabitants and allowed for some degree of shared governing, except in tyrannies.
A) They allowed all the inhabitants of a city-state, irrespective of race or gender, to vote equally.
B) They represented a radical departure from long-held communal values, as the rights of the individual henceforth took precedence.
C) They affirmed the right of all Greek inhabitants to an equal share in the state's governance.
D) They were based on the concept of citizenship for all free inhabitants and allowed for some degree of shared governing, except in tyrannies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Ancient Greek religion was based on a pantheon of gods, each representing different strengths or forces, and the Greeks believed that
A) they had to try to please the gods through prayers, ritual offerings, and the avoidance of offensive behavior.
B) the gods would reward them whenever they excelled or attained aretê.
C) the gods demanded that humans conduct their lives according to a strict moral code that forbade transgressions like theft, murder, dishonesty, greed, and cruelty.
D) the gods had chosen Greece as a favored land, and that the Greeks were destined to conquer other peoples and achieve worldly glory.
A) they had to try to please the gods through prayers, ritual offerings, and the avoidance of offensive behavior.
B) the gods would reward them whenever they excelled or attained aretê.
C) the gods demanded that humans conduct their lives according to a strict moral code that forbade transgressions like theft, murder, dishonesty, greed, and cruelty.
D) the gods had chosen Greece as a favored land, and that the Greeks were destined to conquer other peoples and achieve worldly glory.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The concept of miasma-the ritual contamination suffered by the members of a group who failed to punish a criminal in their midst-reflected which of the following?
A) A sense of communal responsibility for upholding divine law
B) The influence of Egyptian religious thought on the Greeks
C) The belief that people cannot influence the actions of the gods
D) The power of priests to interfere in public life
A) A sense of communal responsibility for upholding divine law
B) The influence of Egyptian religious thought on the Greeks
C) The belief that people cannot influence the actions of the gods
D) The power of priests to interfere in public life

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Why was the notion of citizenship such a radical innovation in ancient Greece?
A) The ancient world was otherwise characterized by monarchies and legal inequality.
B) Learning of the new rights for citizens, slaves rose up to demand citizenship as well.
C) It promoted a movement toward direct democracy in most Greek city-states, including Athens, Corinth, and Sparta.
D) All citizens were endowed with the right to hold political office.
A) The ancient world was otherwise characterized by monarchies and legal inequality.
B) Learning of the new rights for citizens, slaves rose up to demand citizenship as well.
C) It promoted a movement toward direct democracy in most Greek city-states, including Athens, Corinth, and Sparta.
D) All citizens were endowed with the right to hold political office.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Greek slaves who attained their freedom
A) became citizens of the city-state in which they had labored.
B) joined the sizable group of noncitizens allowed to live in the city-state.
C) could become citizens only if they accumulated a legally specified amount of property.
D) were forced to relocate outside the city-state in special areas called demes.
A) became citizens of the city-state in which they had labored.
B) joined the sizable group of noncitizens allowed to live in the city-state.
C) could become citizens only if they accumulated a legally specified amount of property.
D) were forced to relocate outside the city-state in special areas called demes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Women in Greek city-states could also be citizens, an honor that
A) did not, however, grant them political rights, such as the right to vote or otherwise participate in political life.
B) bestowed on them unprecedented political rights, such as the right to vote.
C) enabled them to attain equal legal status with men with regard to such things as property ownership, but not equal political status.
D) was reserved, however, for only the wealthiest women.
A) did not, however, grant them political rights, such as the right to vote or otherwise participate in political life.
B) bestowed on them unprecedented political rights, such as the right to vote.
C) enabled them to attain equal legal status with men with regard to such things as property ownership, but not equal political status.
D) was reserved, however, for only the wealthiest women.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which form of family life was the general rule in ancient Greece?
A) Polygamy, with men being permitted to take multiple wives
B) Monogamy, except when men took their slaves and concubines as wives
C) Monogamy, in which men were permitted only one wife
D) Polygamy, with men being permitted to marry both women and other men
A) Polygamy, with men being permitted to take multiple wives
B) Monogamy, except when men took their slaves and concubines as wives
C) Monogamy, in which men were permitted only one wife
D) Polygamy, with men being permitted to marry both women and other men

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following is a form of social and political organization in which a small group of men dominated policymaking in an assembly of male citizens?
A) Democracy
B) Tyranny
C) Oligarchy
D) Monarchy
A) Democracy
B) Tyranny
C) Oligarchy
D) Monarchy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The Spartan governmental structure can best be described as which of the following?
A) An oligarchy, consisting of a council of twenty-eight elders; five annually elected magistrates, or ephors; and two hereditary military and religious leaders, referred to as kings but sharing a status similar to that of the other members of the oligarchy
B) A democracy headed by an annually elected magistrate who had primary control over military and religious affairs and who ruled in conjunction with an appointed council of elders
C) A tyranny controlled by the strongest and most popular general, who typically exercised supreme control over all military, religious, and economic matters
D) An oligarchy consisting of a council of ten of the best generals, known as ephors, elected every two years by an assembly of adult male citizens
A) An oligarchy, consisting of a council of twenty-eight elders; five annually elected magistrates, or ephors; and two hereditary military and religious leaders, referred to as kings but sharing a status similar to that of the other members of the oligarchy
B) A democracy headed by an annually elected magistrate who had primary control over military and religious affairs and who ruled in conjunction with an appointed council of elders
C) A tyranny controlled by the strongest and most popular general, who typically exercised supreme control over all military, religious, and economic matters
D) An oligarchy consisting of a council of ten of the best generals, known as ephors, elected every two years by an assembly of adult male citizens

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The term Helot was used to designate which of the following?
A) A foreigner who moved to Greece
B) A slave in Sparta who was of Greek origin
C) Any Greek colonist who had settled in Sicily
D) A non-Greek who ruled over Greeks elsewhere in the Mediterranean
A) A foreigner who moved to Greece
B) A slave in Sparta who was of Greek origin
C) Any Greek colonist who had settled in Sicily
D) A non-Greek who ruled over Greeks elsewhere in the Mediterranean

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Homosexual relationships between men in Sparta
A) were punished with a painful and drawn-out death or with permanent banishment from Sparta.
B) were accepted only if both partners were unmarried men over the age of thirty who no longer actively served in the military.
C) usually took place between an older man and an adolescent boy as a form of social and political education.
D) were lasting bonds that were recognized as legal marriages if each man had previously married a woman and that union had produced at least one child.
A) were punished with a painful and drawn-out death or with permanent banishment from Sparta.
B) were accepted only if both partners were unmarried men over the age of thirty who no longer actively served in the military.
C) usually took place between an older man and an adolescent boy as a form of social and political education.
D) were lasting bonds that were recognized as legal marriages if each man had previously married a woman and that union had produced at least one child.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Tyrants in Archaic Greece were most likely to do which of the following?
A) Proclaim their semidivine origins and set up temples for the worship of themselves and their families
B) Ignore the demands of the masses in order to enrich only the social elite
C) Organize wars of conquest against neighboring states in order to enrich their followers
D) Cultivate the goodwill of the people through public works projects and other policies that favored the interests of the masses
A) Proclaim their semidivine origins and set up temples for the worship of themselves and their families
B) Ignore the demands of the masses in order to enrich only the social elite
C) Organize wars of conquest against neighboring states in order to enrich their followers
D) Cultivate the goodwill of the people through public works projects and other policies that favored the interests of the masses

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which Greek city-state is renowned for having established the first democracy ("rule by the people") based on voting rights and full political participation for all male citizens?
A) Sparta
B) Athens
C) Corinth
D) Thebes
A) Sparta
B) Athens
C) Corinth
D) Thebes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Who were the archons in Athens?
A) Poets and playwrights
B) Athletes
C) Philosophers and teachers
D) Magistrates and judges
A) Poets and playwrights
B) Athletes
C) Philosophers and teachers
D) Magistrates and judges

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
As a result of Solon's reforms, council members who prepared the agenda for the assembly were chosen by
A) direct election.
B) an assembly of all property owners.
C) the decision of the archons.
D) lottery.
A) direct election.
B) an assembly of all property owners.
C) the decision of the archons.
D) lottery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
What change in Athens's democracy did Cleisthenes implement by about 500 B.C.E.?
A) He established a four-hundred-man ruling council whose members ran for election annually and represented the entire citizenry.
B) He organized popularly elected neighborhood advisory groups who could be called on to decide on important legislation when the appointed legislature was deadlocked.
C) He instituted political rights, including the right to vote, for all female citizens who could trace their genealogy back two generations.
D) He established a ruling council of five hundred individuals chosen annually by lottery and representing the demes in proportion to the size of their populations.
A) He established a four-hundred-man ruling council whose members ran for election annually and represented the entire citizenry.
B) He organized popularly elected neighborhood advisory groups who could be called on to decide on important legislation when the appointed legislature was deadlocked.
C) He instituted political rights, including the right to vote, for all female citizens who could trace their genealogy back two generations.
D) He established a ruling council of five hundred individuals chosen annually by lottery and representing the demes in proportion to the size of their populations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Who was the lyric poet who wrote about intense emotions, especially love?
A) Penelope
B) Homer
C) Sappho
D) Peisistratus
A) Penelope
B) Homer
C) Sappho
D) Peisistratus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Where did most of the rationalist philosophers of the Greek Archaic Age originate?
A) Athens
B) Ionia
C) Corinth
D) The Peloponnese
A) Athens
B) Ionia
C) Corinth
D) The Peloponnese

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which of the following was proposed by Thales and Anaximander?
A) The universe was governed not by the gods' wishes but by unchanging laws of nature.
B) Humans were capable of understanding divine wisdom through intense meditation and study.
C) The study of human history showed that people were not rational beings, which meant that their behavior could not be predicted.
D) The actions of animals proved that they had souls, just as humans did.
A) The universe was governed not by the gods' wishes but by unchanging laws of nature.
B) Humans were capable of understanding divine wisdom through intense meditation and study.
C) The study of human history showed that people were not rational beings, which meant that their behavior could not be predicted.
D) The actions of animals proved that they had souls, just as humans did.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
By 500 B.C.E., most of the Phoenician settlements were located
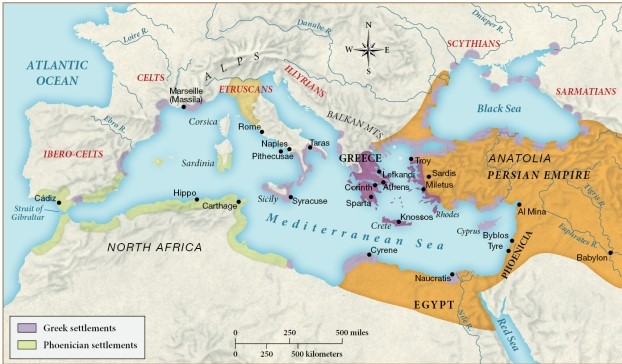
A) within the Persian Empire.
B) north of Greece.
C) in North Africa.
D) along the Red Sea.

A) within the Persian Empire.
B) north of Greece.
C) in North Africa.
D) along the Red Sea.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








