Deck 6: Space Perception and Binocular Vision
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: Space Perception and Binocular Vision
1
The philosophical position arguing that there is a real world to sense is known as
A) Euclidean philosophy.
B) positivism.
C) materialism.
D) structuralism.
E) realism.
A) Euclidean philosophy.
B) positivism.
C) materialism.
D) structuralism.
E) realism.
realism.
2
In the movie The Matrix, what the main character Neo thought was real life instead turned out to be a computer simulation. Which philosophical position would most readily account for such a situation?
A) Realism
B) Positivism
C) Negativism
D) Stoicism
E) Existentialism
A) Realism
B) Positivism
C) Negativism
D) Stoicism
E) Existentialism
Positivism
3
According to Euclidean geometry, parallel lines _______ as they extend through space.
A) converge
B) diverge
C) bend
D) remain parallel
E) cross
A) converge
B) diverge
C) bend
D) remain parallel
E) cross
remain parallel
4
In humans, evolution may have favored two eyes facing forward because it statistically increases the chance of detecting a stimulus. The combination of signals from the two eyes that enhances performance on many tasks is called
A) binocular vision.
B) stereoacuity.
C) depth perception.
D) disparity.
E) binocular summation.
A) binocular vision.
B) stereoacuity.
C) depth perception.
D) disparity.
E) binocular summation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If you build a machine to detect an exotic particle, which principle explains why having two particle detectors in the machine are better than having just one?
A) Realism
B) Positivism
C) Particle physics
D) Probability summation
E) Euclidean geometry
A) Realism
B) Positivism
C) Particle physics
D) Probability summation
E) Euclidean geometry

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
_______ is the difference between the two retinal images of the same scene and is the basis of stereopsis.
A) Binocular disparity
B) Depth perception
C) Stereopsis
D) Binocular summation
E) Accommodation
A) Binocular disparity
B) Depth perception
C) Stereopsis
D) Binocular summation
E) Accommodation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Using the depth cue of _______ you can tell how far away something is based on how much detail is visible in the elements on the ground between you and the object.
A) occlusion
B) aerial perspective
C) linear perspective
D) relative height
E) texture gradient
A) occlusion
B) aerial perspective
C) linear perspective
D) relative height
E) texture gradient

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Refer to the figure.
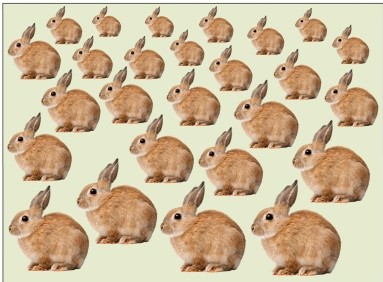 This figure depicts the _______ depth cue.
This figure depicts the _______ depth cue.
A) occlusion
B) linear perspective
C) texture gradient
D) haze/aerial perspective
E) anamorphic projection
 This figure depicts the _______ depth cue.
This figure depicts the _______ depth cue.A) occlusion
B) linear perspective
C) texture gradient
D) haze/aerial perspective
E) anamorphic projection

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure.
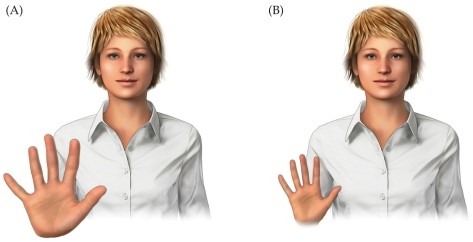 This figure depicts the depth cue of
This figure depicts the depth cue of
A) occlusion.
B) aerial perspective.
C) linear perspective.
D) relative height.
E) familiar size.
 This figure depicts the depth cue of
This figure depicts the depth cue ofA) occlusion.
B) aerial perspective.
C) linear perspective.
D) relative height.
E) familiar size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Refer to the image.
 The scene pictured demonstrates the _______ depth cue.
The scene pictured demonstrates the _______ depth cue.
A) motion parallax
B) haze/aerial perspective
C) linear perspective
D) accommodation
E) convergence
 The scene pictured demonstrates the _______ depth cue.
The scene pictured demonstrates the _______ depth cue.A) motion parallax
B) haze/aerial perspective
C) linear perspective
D) accommodation
E) convergence

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Refer to the figure.
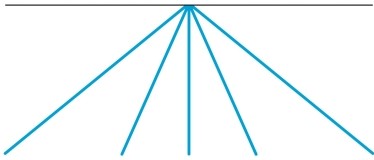 This figure illustrates the _______ depth cue.
This figure illustrates the _______ depth cue.
A) motion parallax
B) aerial perspective
C) linear perspective
D) accommodation
E) convergence
 This figure illustrates the _______ depth cue.
This figure illustrates the _______ depth cue.A) motion parallax
B) aerial perspective
C) linear perspective
D) accommodation
E) convergence

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Suppose you are looking at a road that recedes into the distance. Which depth cue describes the way the edges of the road seem to converge in the retinal image?
A) Motion parallax
B) Aerial perspective
C) Convergence
D) Accommodation
E) Linear perspective
A) Motion parallax
B) Aerial perspective
C) Convergence
D) Accommodation
E) Linear perspective

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Parallel lines in the world appear to meet at a single location called the
A) parallax.
B) singularity.
C) linear convergence.
D) vanishing point.
E) horopter.
A) parallax.
B) singularity.
C) linear convergence.
D) vanishing point.
E) horopter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
_______ is any sort of depth cue that can be depicted by an artist on a canvas.
A) A pictorial depth cue
B) Convergence
C) Motion parallax
D) An absolute metrical depth cue
E) Accommodation
A) A pictorial depth cue
B) Convergence
C) Motion parallax
D) An absolute metrical depth cue
E) Accommodation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
When an artist paints trees on a landscape extending into the distance, she distributes the trees vertically to simulate _______, and makes trees that are farther away smaller, simulating _______.
A) relative height; aerial perspective
B) aerial perspective; relative size
C) relative size; relative height
D) relative height; relative size
E) relative size; aerial perspective
A) relative height; aerial perspective
B) aerial perspective; relative size
C) relative size; relative height
D) relative height; relative size
E) relative size; aerial perspective

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A(n) _______ is an image that appears distorted unless viewed from a very specific angle.
A) random dot stereogram
B) anamorphic projection
C) horopter
D) stereoscope
E) Cyclopean image
A) random dot stereogram
B) anamorphic projection
C) horopter
D) stereoscope
E) Cyclopean image

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a metrical depth cue?
A) Motion parallax
B) Relative size
C) Relative height
D) Stereopsis
E) Occlusion
A) Motion parallax
B) Relative size
C) Relative height
D) Stereopsis
E) Occlusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
_______ provide(s) precise quantitative information about distance in the third dimension.
A) Relative height
B) Metrical depth cues
C) Nonmetrical depth cues
D) Aerial perspective
E) Occlusion
A) Relative height
B) Metrical depth cues
C) Nonmetrical depth cues
D) Aerial perspective
E) Occlusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which depth cue can provide information about precise distance from the observer?
A) Relative height
B) Aerial perspective
C) Occlusion
D) Linear perspective
E) Familiar size
A) Relative height
B) Aerial perspective
C) Occlusion
D) Linear perspective
E) Familiar size

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
As a depth cue, occlusion provides _______ information.
A) relative height
B) motion parallax
C) nonmetrical depth
D) relative metrical depth
E) absolute metrical depth
A) relative height
B) motion parallax
C) nonmetrical depth
D) relative metrical depth
E) absolute metrical depth

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which depth cue gives you the most precise metrical information about object distance?
A) Relative height
B) Relative size
C) Texture gradient
D) Haze/aerial perspective
E) Stereopsis
A) Relative height
B) Relative size
C) Texture gradient
D) Haze/aerial perspective
E) Stereopsis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
_______ is an important depth cue that comes into play during head movements or while moving through an environment.
A) Motion parallax
B) Familiar size
C) Convergence
D) Vanishing point
E) Stereopsis
A) Motion parallax
B) Familiar size
C) Convergence
D) Vanishing point
E) Stereopsis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
When driving in a car, the fact that light posts by the side of the road move faster across your eye than do distant buildings is the visual cue known as
A) relative height.
B) occlusion.
C) linear perspective.
D) stereo disparity.
E) motion parallax.
A) relative height.
B) occlusion.
C) linear perspective.
D) stereo disparity.
E) motion parallax.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Turning the two eyes inward to place the two images of a feature in the world on corresponding locations in the two retinal images is known as
A) accommodation.
B) divergence.
C) convergence.
D) disparity.
E) linear perspective.
A) accommodation.
B) divergence.
C) convergence.
D) disparity.
E) linear perspective.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If a fly lands on your nose and you turn your eyes inward to look at it, what kind of eye movement are you making?
A) Convergent
B) Divergent
C) Saccadic
D) Reflexive
E) Smooth pursuit
A) Convergent
B) Divergent
C) Saccadic
D) Reflexive
E) Smooth pursuit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The process by which the eye changes its focus by adjusting the lens is called
A) accommodation.
B) divergence.
C) convergence.
D) disparity.
E) linear perspective.
A) accommodation.
B) divergence.
C) convergence.
D) disparity.
E) linear perspective.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If a camera judges the distance of an object based on the lens setting that causes the object to appear in focus, then the camera is using the depth cue of
A) aerial perspective.
B) motion parallax.
C) stereo vision.
D) accommodation.
E) convergence.
A) aerial perspective.
B) motion parallax.
C) stereo vision.
D) accommodation.
E) convergence.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure.
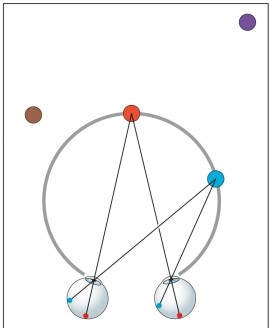 The imaginary (gray) circle in the figure is known as
The imaginary (gray) circle in the figure is known as
A) the vanishing point.
B) the horopter.
C) Panum's circle.
D) the convergence point.
E) the stereo circle.
 The imaginary (gray) circle in the figure is known as
The imaginary (gray) circle in the figure is known asA) the vanishing point.
B) the horopter.
C) Panum's circle.
D) the convergence point.
E) the stereo circle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure.
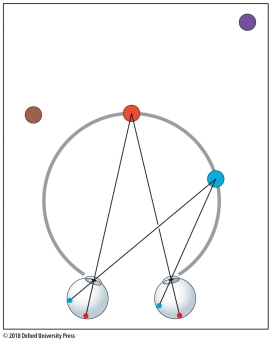 In this figure, what do the red and blue circles have in common?
In this figure, what do the red and blue circles have in common?
A) They have the same retinal sizes.
B) They have the same linear perspective.
C) They both have the same disparity.
D) They both have uncrossed disparity.
E) They both have crossed disparity.
 In this figure, what do the red and blue circles have in common?
In this figure, what do the red and blue circles have in common?A) They have the same retinal sizes.
B) They have the same linear perspective.
C) They both have the same disparity.
D) They both have uncrossed disparity.
E) They both have crossed disparity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
_______ is the surface of zero disparity, or the location of objects whose images lie on corresponding points in the two eyes.
A) The vanishing point
B) The Vieth-Müller circle
C) Panum's circle
D) The convergence point
E) The stereo circle
A) The vanishing point
B) The Vieth-Müller circle
C) Panum's circle
D) The convergence point
E) The stereo circle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The difference between crossed disparity and uncrossed disparity is that crossed disparity involves objects that are _______ the plane of fixation, while uncrossed disparity involves objects that are _______ the plane of fixation.
A) below; above
B) above; below
C) behind; in front of
D) in front of; behind
E) exactly at; in front of
A) below; above
B) above; below
C) behind; in front of
D) in front of; behind
E) exactly at; in front of

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Refer to the figure.
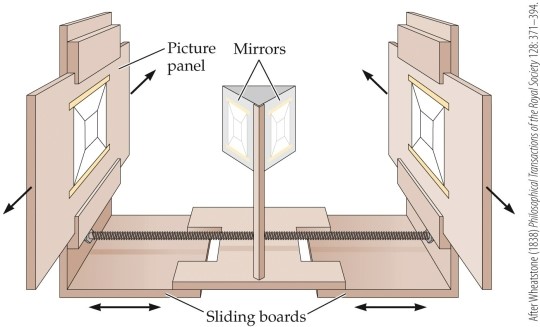 This figure depicts a(n)
This figure depicts a(n)
A) convergence test.
B) occluder.
C) metronome.
D) stereoscope.
E) accommodation test.
 This figure depicts a(n)
This figure depicts a(n)A) convergence test.
B) occluder.
C) metronome.
D) stereoscope.
E) accommodation test.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Virtual reality headsets have a separate display for each eye. What is another technical name for such a device?
A) Heads up display
B) Stereoscope
C) Corrective lenses
D) Random dot stereogram
E) Autostereogram
A) Heads up display
B) Stereoscope
C) Corrective lenses
D) Random dot stereogram
E) Autostereogram

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
During free fusion, the eyes _______ in order to view a stereogram without a stereoscope.
A) converge or diverge
B) are half closed
C) use the motion parallax
D) use the pictorial depth cue
E) glaze over
A) converge or diverge
B) are half closed
C) use the motion parallax
D) use the pictorial depth cue
E) glaze over

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Virtual reality headsets display a different image to each eye, which is technically a form of _______ presentation.
A) biopic
B) monoptic
C) stereoptic
D) chronoptic
E) dichoptic
A) biopic
B) monoptic
C) stereoptic
D) chronoptic
E) dichoptic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A random dot stereogram contains
A) many monocular cues.
B) a horopter.
C) no monocular cues.
D) a vanishing point.
E) occlusion cues.
A) many monocular cues.
B) a horopter.
C) no monocular cues.
D) a vanishing point.
E) occlusion cues.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure.
 This figure is an example of
This figure is an example of
A) a random dot stereogram.
B) motion parallax.
C) strabismus.
D) stereoblindness.
E) diplopia.
 This figure is an example of
This figure is an example ofA) a random dot stereogram.
B) motion parallax.
C) strabismus.
D) stereoblindness.
E) diplopia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The theoretical significance of random dot stereograms is that they show that
A) accommodation and convergence cannot be uncoupled.
B) stereo vision can be achieved only with identifiable shapes.
C) stereo vision can be achieved without identifiable shapes.
D) the parvocellular system cannot perceive stereo.
E) the magnocellular system cannot perceive stereo.
A) accommodation and convergence cannot be uncoupled.
B) stereo vision can be achieved only with identifiable shapes.
C) stereo vision can be achieved without identifiable shapes.
D) the parvocellular system cannot perceive stereo.
E) the magnocellular system cannot perceive stereo.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The problem of determining which bit of the image in the left eye should be matched with which bit of image in the right eye is known as the
A) Cyclopean problem.
B) correspondence problem.
C) motion paradox.
D) disparity paradox.
E) convergence problem.
A) Cyclopean problem.
B) correspondence problem.
C) motion paradox.
D) disparity paradox.
E) convergence problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Which of the following cannot be used to solve the correspondence problem?
A) A low spatial frequency version of the image
B) The uniqueness constraint
C) The continuity constraint
D) The disparity constraint
E) Binocular neurons in primary visual cortex.
A) A low spatial frequency version of the image
B) The uniqueness constraint
C) The continuity constraint
D) The disparity constraint
E) Binocular neurons in primary visual cortex.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Stereoblindness usually results from
A) stroke.
B) visual neglect.
C) childhood disorders.
D) agnosia.
E) glaucoma.
A) stroke.
B) visual neglect.
C) childhood disorders.
D) agnosia.
E) glaucoma.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following is evidence for neurons that encode the horopter?
A) Binocular neurons that respond best when retinal images are on corresponding points in the two retinas.
B) Binocular neurons that respond best when retinal images are on different points in the two retinas.
C) Binocular neurons that respond best to the right eye.
D) Binocular neurons that respond best to the left eye.
E) Binocular neurons that respond best when a feature is seen in one eye but not the other.
A) Binocular neurons that respond best when retinal images are on corresponding points in the two retinas.
B) Binocular neurons that respond best when retinal images are on different points in the two retinas.
C) Binocular neurons that respond best to the right eye.
D) Binocular neurons that respond best to the left eye.
E) Binocular neurons that respond best when a feature is seen in one eye but not the other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
If you are able to free-fuse a display and get it to appear in focus but not perceive any apparent depth, then you might be
A) esotropic.
B) exotropic.
C) strabismic.
D) stereoblind.
E) an object agnostic.
A) esotropic.
B) exotropic.
C) strabismic.
D) stereoblind.
E) an object agnostic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
_______ is based on the idea that prior knowledge could influence the estimates of the probability of a current event.
A) Binocular rivalry philosophy
B) Euclidean philosophy
C) The Bayesian approach
D) The uniqueness constraint
E) The correspondence problem
A) Binocular rivalry philosophy
B) Euclidean philosophy
C) The Bayesian approach
D) The uniqueness constraint
E) The correspondence problem

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If you want to know the probability that the world is in a particular state given a particular observation, which formal approach should you use?
A) Binocular summation
B) Bayesian approach
C) Probability summation
D) Critical period analysis
E) Positivism
A) Binocular summation
B) Bayesian approach
C) Probability summation
D) Critical period analysis
E) Positivism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure.
 In this figure, the viewer mistakes the two horizontal lines to be
In this figure, the viewer mistakes the two horizontal lines to be
A) not parallel to one another.
B) closer to each other than they actually are.
C) farther away from each other than they actually are.
D) the same length.
E) of different lengths.
 In this figure, the viewer mistakes the two horizontal lines to be
In this figure, the viewer mistakes the two horizontal lines to beA) not parallel to one another.
B) closer to each other than they actually are.
C) farther away from each other than they actually are.
D) the same length.
E) of different lengths.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Refer to the figure.
 In this figure, why might the top horizontal line appear to be longer than the bottom line?
In this figure, why might the top horizontal line appear to be longer than the bottom line?
A) Relative height makes the top line appear closer, which means it must be longer.
B) Linear perspective makes the top line appear farther away, which means it must be longer.
C) Relative size makes the top line appear closer, which means it must be longer.
D) Binocular disparity makes the top line appear farther away, which means it must be longer.
E) Motion parallax makes the top line appear farther away, which means it must be longer.
 In this figure, why might the top horizontal line appear to be longer than the bottom line?
In this figure, why might the top horizontal line appear to be longer than the bottom line?A) Relative height makes the top line appear closer, which means it must be longer.
B) Linear perspective makes the top line appear farther away, which means it must be longer.
C) Relative size makes the top line appear closer, which means it must be longer.
D) Binocular disparity makes the top line appear farther away, which means it must be longer.
E) Motion parallax makes the top line appear farther away, which means it must be longer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure.
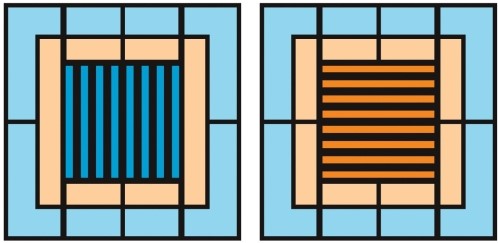 If these two images are free-fused, it leads to
If these two images are free-fused, it leads to
A) stereoblindness.
B) absolute disparity.
C) relative disparity.
D) binocular rivalry.
E) stereopsis.
 If these two images are free-fused, it leads to
If these two images are free-fused, it leads toA) stereoblindness.
B) absolute disparity.
C) relative disparity.
D) binocular rivalry.
E) stereopsis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
_______ is a measure of the smallest binocular disparity that can generate a sensation of depth.
A) Minimum disparity
B) Stereoacuity
C) Stereo sensitivity
D) Disparity threshold
E) Stereo parallax
A) Minimum disparity
B) Stereoacuity
C) Stereo sensitivity
D) Disparity threshold
E) Stereo parallax

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
_______ refers to the presentation of two stimuli, one to each eye.
A) Biopic
B) Monoptic
C) Dichoptic
D) Stereoptic
E) Chronoptic
A) Biopic
B) Monoptic
C) Dichoptic
D) Stereoptic
E) Chronoptic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If normal binocular visual stimulation is not experienced during _______, then proper stereo vision might not develop.
A) gestation
B) adulthood
C) adolescence
D) the critical period
E) the early period
A) gestation
B) adulthood
C) adolescence
D) the critical period
E) the early period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
_______ disrupts binocular vision because one or both eyes are not aligned properly.
A) Strabismus
B) Hyperopia
C) Emmetropia
D) Presbyopia
E) Free fusion
A) Strabismus
B) Hyperopia
C) Emmetropia
D) Presbyopia
E) Free fusion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
If the two eyes are not aligned properly the brain tends to ignore information from one eye. This phenomenon is known as
A) esotropia.
B) exotropia.
C) suppression.
D) strabismus.
E) Cyclopean vision.
A) esotropia.
B) exotropia.
C) suppression.
D) strabismus.
E) Cyclopean vision.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
What is the difference between metrical and nonmetrical depth cues?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What is a random dot stereogram and why is it theoretically important?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
What is the correspondence problem in stereo vision?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
What happens when two different images are presented to the two eyes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Define and compare the following monocular depth cues: occlusion, relative height, relative size, texture gradient, and familiar size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What is the Bayesian approach and why is it important for visual perception?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
What is a critical period and how does it relate to the development of stereo vision?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 60 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








