Deck 13: Energy and Thermochemistry
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Energy and Thermochemistry
1
Thermodynamics is the study of systems on the microscopic scale. It explains the interrelation of energy and chemistry and relies on information about individual molecular properties to do this.
False
2
Energy generated by a chemical reaction can be transferred as a result of motion against an opposing force as ____. .
work
3
Match the system name to its short description.
-Both matter and energy can be exchanged with its surroundings
A) Open
B) Closed
C) Isolated
-Both matter and energy can be exchanged with its surroundings
A) Open
B) Closed
C) Isolated
A
4
Match the system name to its short description.
-Only energy can be exchanged with its surroundings
A) Open
B) Closed
C) Isolated
-Only energy can be exchanged with its surroundings
A) Open
B) Closed
C) Isolated

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Match the system name to its short description.
-Neither energy or matter can be exchanged with its surroundings
A) Open
B) Closed
C) Isolated
-Neither energy or matter can be exchanged with its surroundings
A) Open
B) Closed
C) Isolated

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
What type of system is the Earth and its atmosphere?
A) Open.
B) Closed.
C) Isolated.
D) Not possible to define as a system.
A) Open.
B) Closed.
C) Isolated.
D) Not possible to define as a system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
What type of system is the Atlantic ocean?
A) Open.
B) Closed.
C) Isolated.
D) Not possible to define as a system.
A) Open.
B) Closed.
C) Isolated.
D) Not possible to define as a system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The term heat capacity, C, is used to quantify heat changes; it can be defined in different ways. Match the short definition with the correct heat capacity symbol.
-Specific heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance by 1 K
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv
-Specific heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance by 1 K
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The term heat capacity, C, is used to quantify heat changes; it can be defined in different ways. Match the short definition with the correct heat capacity symbol.
-Molar heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of substance by 1 K
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv
-Molar heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of substance by 1 K
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The term heat capacity, C, is used to quantify heat changes; it can be defined in different ways. Match the short definition with the correct heat capacity symbol.
-Molar heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of substance by 1 K, for a gas, measured at constant pressure
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv
-Molar heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of substance by 1 K, for a gas, measured at constant pressure
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The term heat capacity, C, is used to quantify heat changes; it can be defined in different ways. Match the short definition with the correct heat capacity symbol.
-Molar heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of substance by 1 K, for a gas, measured at constant volume
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv
-Molar heat capacity is the heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of substance by 1 K, for a gas, measured at constant volume
A) Cs
B) Cm
C) Cp
D) Cv

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The molar heat capacity, Cm of gold (Au(s)) is 25.4 J K-1 mol-1. Calculate the energy (in J) required to heat a 100 g bar of gold from 25 °C to 75 °C?
A) Not possible to calculate.
B) 645.
C) 127000.
D) 1.
A) Not possible to calculate.
B) 645.
C) 127000.
D) 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The specific heat capacity of liquid water is 4.18 J K-1 g-1. Calculate the temperature rise (in K) when 1050 J of heat is transferred to 5 mol of water.
A) 2.79
B) 50.24
C) 48.73
D) 2.79 × 10-3.
A) 2.79
B) 50.24
C) 48.73
D) 2.79 × 10-3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The specific heat capacity of Cu (s) is 0.38 J K-1 g-1 and that of Au (s) is 0.129 J K-1 g-1. When 100 J of heat is added to 100 g of sample of each of these substances, will one experience a larger increase in temperature?
A) Yes, gold.
B) No.
C) Yes, copper.
D) Not enough energy to increase the temperature of either substance.
A) Yes, gold.
B) No.
C) Yes, copper.
D) Not enough energy to increase the temperature of either substance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The specific heat capacity of iron (Fe(s)) is 0.45 J K-1 g-1, how much energy ( in J) must be added to raise the temperature of a 250 g iron bar by 30 ° C?
A) 34.104.
B) 34104.
C) 3375.
D) 6 × 10-5.
A) 34.104.
B) 34104.
C) 3375.
D) 6 × 10-5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Match the definition with the quantity it is describing.
-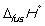
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure
-
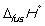
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Match the definition with the quantity it is describing.
-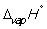
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure
-
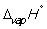
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Match the definition with the quantity it is describing.
-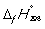
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure
-
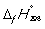
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Match the definition with the quantity it is describing.
-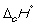
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure
-
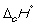
A) Energy required to melt one mol of a pure substance at its melting point, Tm, at 1 bar pressure
B) Energy required to vaporize one mole of a pure liquid at its boiling point, Tb, at 1 bar pressure
C) Enthalpy change at 298 K when 1 mol of a compound is formed under standard conditions from its constituent elements in their standard states
D) Enthalpy change when 1 mol of a substance reacts completely with oxygen gas at 1 bar pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The standard enthalpy change of formation is the energy released when 1 mol of compound is formed from its constituent elements under which set of conditions?
A) Elements in their standard states and 1 bar pressure.
B) Elements in their standard states and 1 atm pressure.
C) Elements in their standard states at 101325 Pa pressure.
D) Elements in their standard states at any temperature and pressure.
A) Elements in their standard states and 1 bar pressure.
B) Elements in their standard states and 1 atm pressure.
C) Elements in their standard states at 101325 Pa pressure.
D) Elements in their standard states at any temperature and pressure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The standard enthalpy change of fusion and vaporization for water are +6.01 kJ mol-1 and +40.7 kJ mol-1 respectively. Why is the value for vaporization so much larger than fusion?
A) Because it is measured at a higher temperature.
B) Because the pressure has increased.
C) Because gas is released into the surroundings.
D) Because overcoming all intermolecular forces that hold a liquid together needs a lot of energy.
A) Because it is measured at a higher temperature.
B) Because the pressure has increased.
C) Because gas is released into the surroundings.
D) Because overcoming all intermolecular forces that hold a liquid together needs a lot of energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The standard enthalpy change of vaporization of water is + 40.7 kJ mol-1. Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ) when 15 g of water vaporizes at its boiling point at 1 bar.
A) 611.
B) 49.
C) + 34.
D) 3.
A) 611.
B) 49.
C) + 34.
D) 3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Calculate the enthalpy change (in kJ mol-1) when 1 mol of solid ethanol is melted at 155.8 K and heated to 298 K. (Take the molar heat capacity of liquid ethanol to be 112 J K-1 mol-1), 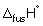 (ethanol) = + 4.60 kJ mol-1 and
(ethanol) = + 4.60 kJ mol-1 and 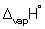 (ethanol) = + 43.5 kJ mol-1.
(ethanol) = + 43.5 kJ mol-1.
A) + 64.0
B) + 20.5
C) + 15.9
D) + 38
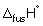 (ethanol) = + 4.60 kJ mol-1 and
(ethanol) = + 4.60 kJ mol-1 and 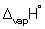 (ethanol) = + 43.5 kJ mol-1.
(ethanol) = + 43.5 kJ mol-1.A) + 64.0
B) + 20.5
C) + 15.9
D) + 38

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Calculate the standard enthalpy change (in kJ mol-1) for the hydrogenation of propene to propane at 298 K. The standard enthalpy change at 298 K for reactions of graphite and hydrogen gas to form 1 mol of each of these compounds is + 20.4 kJ mol-1 and - 103.9 kJ mol-1 respectively.
A) + 83.5
B) + 124.3
C) - 83.5
D) - 124.3
A) + 83.5
B) + 124.3
C) - 83.5
D) - 124.3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Calculate the standard enthalpy change (in kJ mol-1) for the hydrogenation of ethyne to ethene at 298 K. The standard enthalpy change at 298 K for reactions of graphite and hydrogen gas to form 1 mol of each of these compounds is + 226.7 kJ mol-1 and + 52.5 kJ mol-1 respectively.
A) + 279.2
B) - 279.2
C) + 174.2
D) - 174.2
A) + 279.2
B) - 279.2
C) + 174.2
D) - 174.2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Calculate the enthalpy change at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure for the following reaction, using 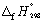 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:
SiCl4 (l) + 2H2O (l) → SiO2 (s) + 4 HCl (g)
A) + 30.4 kJ mol-1.
B) - 30.4 kJ mol-1.
C) + 21.5 kJ mol-1.
D) - 21.5 kJ mol-1.
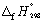 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:SiCl4 (l) + 2H2O (l) → SiO2 (s) + 4 HCl (g)
A) + 30.4 kJ mol-1.
B) - 30.4 kJ mol-1.
C) + 21.5 kJ mol-1.
D) - 21.5 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Calculate the enthalpy change at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure for the following reaction, using 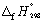 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:
CH4 (g) + Cl2 (g) → CH3Cl (g) + HCl (g)
A) - 101.2 kJ mol-1.
B) + 101.2 kJ mol-1.
C) - 250.8 kJ mol-1.
D) 250.8 kJ mol-1.
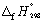 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:CH4 (g) + Cl2 (g) → CH3Cl (g) + HCl (g)
A) - 101.2 kJ mol-1.
B) + 101.2 kJ mol-1.
C) - 250.8 kJ mol-1.
D) 250.8 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Calculate the enthalpy change at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure for the following reaction, using 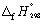 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:
2 Cl (g) → Cl2 (g)
A) - 121.7 kJ mol-1.
B) 0 kJ mol-1.
C) - 243.4 kJ mol-1.
D) + 243.4 kJ mol-1.
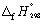 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:2 Cl (g) → Cl2 (g)
A) - 121.7 kJ mol-1.
B) 0 kJ mol-1.
C) - 243.4 kJ mol-1.
D) + 243.4 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Calculate the enthalpy change 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure for the following reaction, using 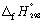 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:
NH3 (g) + HNO3 (l) → NH4NO3 (s)
A) + 585.8 kJ mol-1.
B) + 145.4 kJ mol-1.
C) - 585.8 kJ mol-1.
D) - 145.4 kJ mol-1.
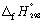 data in Appendix 7:
data in Appendix 7:NH3 (g) + HNO3 (l) → NH4NO3 (s)
A) + 585.8 kJ mol-1.
B) + 145.4 kJ mol-1.
C) - 585.8 kJ mol-1.
D) - 145.4 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The symbol 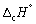 conveys which of the following information? Select all that apply.
conveys which of the following information? Select all that apply.
A) Standard enthalpy change of combustion.
B) Standard enthalpy change measured at 273.15 K.
C) Enthalpy change measured at 1 bar pressure.
D) Enthalpy change measured for 1 gram of substance.
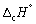 conveys which of the following information? Select all that apply.
conveys which of the following information? Select all that apply.A) Standard enthalpy change of combustion.
B) Standard enthalpy change measured at 273.15 K.
C) Enthalpy change measured at 1 bar pressure.
D) Enthalpy change measured for 1 gram of substance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The combustion of glucose (C6H12O6) at 1 bar and 298 K releases 2802.5 kJ mol-1 of heat.
C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2 (g) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) Calculate the standard enthalpy change of formation of glucose (in kJ mol-1). Use data in Appendix 7.
A) + 2123.2
B) - 1273.3
C) + 1273.3
D) - 6878.3
C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2 (g) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) Calculate the standard enthalpy change of formation of glucose (in kJ mol-1). Use data in Appendix 7.
A) + 2123.2
B) - 1273.3
C) + 1273.3
D) - 6878.3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The combustion of ethanol (C2H5OH) at 1 bar and 298 K releases 1367 kJ mol-1 of heat.
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l) Calculate the standard enthalpy change of formation of ethanol (in kJ mol-1). Use data in Appendix 7.
A) - 277.4
B) + 277.4
C) - 3011.4
D) + 3011.4
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l) Calculate the standard enthalpy change of formation of ethanol (in kJ mol-1). Use data in Appendix 7.
A) - 277.4
B) + 277.4
C) - 3011.4
D) + 3011.4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Values of bond dissociation enthalpies D(A-B) are always positive because they are measured in the gas phase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Calculate for the following reaction:
C5H12 (g)+ 8 O2 (g) 5 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g), using the following bond enthalpies given (in kJ mol-1):
C-H = + 412
C=O = + 742
C-O = + 358
C-C = + 347
O=O = + 498
O-H = + 464
A) + 2325 kJ mol-1.
B) - 2672 kJ mol-1.
C) + 2672 kJ mol-1
D) - 2325 kJ mol-1.
C5H12 (g)+ 8 O2 (g) 5 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g), using the following bond enthalpies given (in kJ mol-1):
C-H = + 412
C=O = + 742
C-O = + 358
C-C = + 347
O=O = + 498
O-H = + 464
A) + 2325 kJ mol-1.
B) - 2672 kJ mol-1.
C) + 2672 kJ mol-1
D) - 2325 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction :
C2H6O (g)+ 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (g), using the bond enthalpies given (in kJ mol-1):
C-H = + 412
C=O = + 742
C-O = + 358
C-C = + 347
O=O = + 498
O-H = + 464
A) - 1081 kJ mol-1.
B) + 1081 kJ mol-1.
C) + 1029 kJ mol-1.
D) - 1029 kJ mol-1.
C2H6O (g)+ 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (g), using the bond enthalpies given (in kJ mol-1):
C-H = + 412
C=O = + 742
C-O = + 358
C-C = + 347
O=O = + 498
O-H = + 464
A) - 1081 kJ mol-1.
B) + 1081 kJ mol-1.
C) + 1029 kJ mol-1.
D) - 1029 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The enthalpy change for the complete combustion of 1 mol of methane at 1 bar and 298 K is - 890.3 kJ mol-1.
Calculate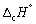 at 335 K.
at 335 K.
Mean Cp / J K-1 mol-1: CH4 (g) 35.7; O2 (g) 29.4; CO2 (g) 37.1; H2O (l) 75.3.
A) - 890.3 kJ mol-1.
B) - 859.1 kJ mol-1.
C) - 888.8 kJ mol-1.
D) - 886.9 kJ mol-1.
Calculate
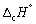 at 335 K.
at 335 K.Mean Cp / J K-1 mol-1: CH4 (g) 35.7; O2 (g) 29.4; CO2 (g) 37.1; H2O (l) 75.3.
A) - 890.3 kJ mol-1.
B) - 859.1 kJ mol-1.
C) - 888.8 kJ mol-1.
D) - 886.9 kJ mol-1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The enthalpy change for the complete combustion of 1 mol of hydrogen at 1 bar and 298 K is - 286 kJ mol-1.
Calculate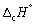 at 323 K (in kJ mol-1).
at 323 K (in kJ mol-1).
Mean Cp / J K-1 mol-1: H2 (g) 28.8; O2 (g) 29.4; CO2 (g) 37.1; H2O (l) 75.3.
A) + 1304.
B) - 286.
C) - 284.
D) - 265.
Calculate
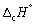 at 323 K (in kJ mol-1).
at 323 K (in kJ mol-1).Mean Cp / J K-1 mol-1: H2 (g) 28.8; O2 (g) 29.4; CO2 (g) 37.1; H2O (l) 75.3.
A) + 1304.
B) - 286.
C) - 284.
D) - 265.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
When 1 mole of gas expands from a volume of 2.5 dm3 to 5 dm3 against a constant pressure of 1 atm, which of the following are true? Select all that apply.
A) Work is done by the system.
B) Work is done on the system.
C) Energy is gained by the system.
D) Energy is lost by the system.
A) Work is done by the system.
B) Work is done on the system.
C) Energy is gained by the system.
D) Energy is lost by the system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A reaction produces hydrogen gas. A balloon attached to the reaction vessel expands against a constant pressure of 1 atm and at the end of the reaction it is calculated that 1.5 dm3 of H2 (g) has been produced. Calculate the energy transferred as work, w, (in J).
A) - 152.
B) + 152.
C) - 1.5.
D) - 1.5 × 10-3.
A) - 152.
B) + 152.
C) - 1.5.
D) - 1.5 × 10-3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
When 1 mol of gas expands from a volume of 2.5 dm3 to 5 dm3 against a constant pressure of 1 atm, calculate the energy transferred as work, w, (in J).
A) - 2.5 × 10-3.
B) + 253.
C) - 253.
D) - 2.5.
A) - 2.5 × 10-3.
B) + 253.
C) - 253.
D) - 2.5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The First Law of thermodynamics states the principle of conservation of energy that the total quantity of energy in the Universe is ________.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
One mole of gas is heated with 1.75 kJ of energy; it expands doing 250 J of work. Calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
A) + 1500 J.
B) + 2000 J.
C) - 1500 J.
D) - 2000 J.
A) + 1500 J.
B) + 2000 J.
C) - 1500 J.
D) - 2000 J.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
For a reaction conducted at constant pressure and at 298 K the change in number of moles of gas (Δngas) is + 2. Calculate the difference (in kJ mol-1) between ΔH (enthalpy change) and ΔU (internal energy).
A) - 4.96
B) + 4.96.
C) + 2.
D) - 2.
A) - 4.96
B) + 4.96.
C) + 2.
D) - 2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
For a reaction conducted at constant pressure and at 298 K the change in number of moles of gas (Δngas) is - 1. Calculate the difference (in kJ mol-1) between ΔH (enthalpy change) and ΔU (internal energy).
A) + 2.48.
B) - 2.48.
C) + 1.
D) - 1.
A) + 2.48.
B) - 2.48.
C) + 1.
D) - 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The combustion of ethanol (C2H5OH) at 1 bar and 298 K releases 1367 kJ mol-1 of heat.
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l) Calculate (in kJ mol-1) for ethanol.
A) + 1110.
B) - 3845.
C) - 1369.
D) -1365.
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l) Calculate (in kJ mol-1) for ethanol.
A) + 1110.
B) - 3845.
C) - 1369.
D) -1365.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following correctly characterise a bomb calorimeter? Select all that apply.
A) It measures the internal energy change of a reaction.
B) It measures the enthalpy change of a reaction.
C) It is a reaction chamber where the temperature is kept constant.
D) It can measure many different reactions.
A) It measures the internal energy change of a reaction.
B) It measures the enthalpy change of a reaction.
C) It is a reaction chamber where the temperature is kept constant.
D) It can measure many different reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The calibration factor of a bomb calorimeter was calculated to be 10.27 kJ K-1. Calculate the internal energy change of combustion 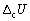 for glucose (Mr = 180.16) if the combustion at 298 K of 1.228 g caused a temperature rise of 1.847 K.
for glucose (Mr = 180.16) if the combustion at 298 K of 1.228 g caused a temperature rise of 1.847 K.
A) - 2783.
B) + 19.
C) - 19.
D) + 2783.
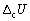 for glucose (Mr = 180.16) if the combustion at 298 K of 1.228 g caused a temperature rise of 1.847 K.
for glucose (Mr = 180.16) if the combustion at 298 K of 1.228 g caused a temperature rise of 1.847 K.A) - 2783.
B) + 19.
C) - 19.
D) + 2783.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 47 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








