Deck 26: The Chemistry of the Aromatic Heterocycles and Nucleic Acids
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 26: The Chemistry of the Aromatic Heterocycles and Nucleic Acids
1
Name the heterocycle.
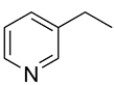

The heterocycle is 3-ethylpyridine.
2
Name the heterocycle.
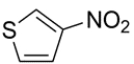

The heterocycle is 3-nitrothiophene.
3
Draw a structure for each of the compounds.
a. 4-methoxyindole
b. thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
a. 4-methoxyindole
b. thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
a.
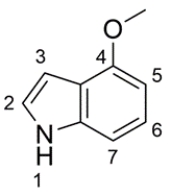
b.
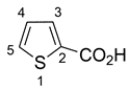

b.

4
Draw a structure for each of the compounds.
a. oxazole-5-carbaldehyde
b. 4-methoxypyridine
a. oxazole-5-carbaldehyde
b. 4-methoxypyridine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The structure of indole is shown below. Unlike most amines, indole is difficult to protonate. Its conjugate acid has a pKa of -3.5. Explain why indole is difficult to protonate.
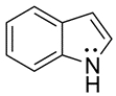


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
An imidazole ring is an important heterocycle found in the amino acid histidine. Draw an orbital configuration of imidazole, showing the 2p orbitals and electrons in each orbital. Use the diagram to explain which electrons are part of the aromatic system and which can be protonated in the presence of an acid.
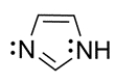


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Purine is a bicyclic ring found in DNA. The structure for purine is shown below. For each lone pair of nitrogen, determine whether the lone pair resides on a 2p orbital or sp2 orbital.
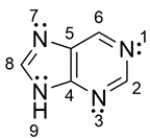


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
For each heterocycle, label as aromatic, anti-aromatic, or nonaromatic.
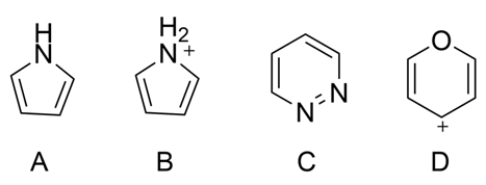


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
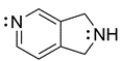
9
Circle the nitrogen that is more basic and explain why.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Rank the reactivity of these compounds towards electrophilic aromatic substitution, from most reactive to least.
benzene, furan, thiophene, pyrrole, pyridine
benzene, furan, thiophene, pyrrole, pyridine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
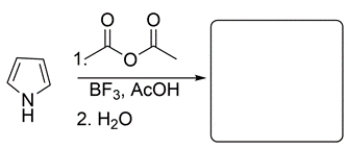
11
Predict the major organic product for the reaction.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Thiophene undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) with bromine to give two possible regioisomers, A and

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
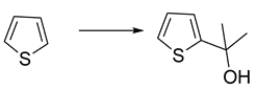
13
Outline a synthesis for the transformation:


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Outline a synthesis for the transformation:



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Identify the missing reagent(s) for the transformation:



فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
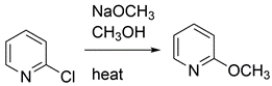
16
2-Halopyridines undergo substitution under milder conditions than the Chichibabin reaction. Write a curved-arrow mechanism for this substitution.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Predict the major organic product for this synthetic sequence.
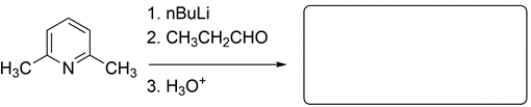


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In biological systems, pyridoxal phosphate is a cofactor that aids in the decarboxylation of glutamic acid to 4-aminobutanoic acid. The key intermediate is shown below. Draw curved arrows to show the decarboxylation step.
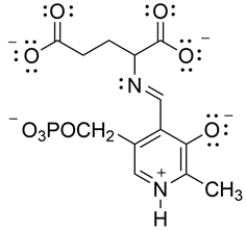


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Identify the correct name or abbreviation of the given nucleoside or nucleotide:
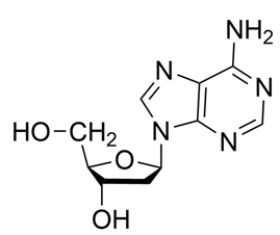
A) 2ʹ-deoxyadenosine
B) adenine
C) adenosine
D) dATP

A) 2ʹ-deoxyadenosine
B) adenine
C) adenosine
D) dATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Shown below are the two types of base pairs in DNA, with the bases in the same relative alignments that they are in DNA.
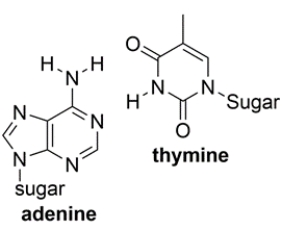
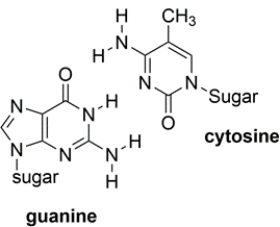 a. Show all the relevant hydrogen bonds with dotted lines and include the unshared pairs on the acceptor atoms, within each pair.
a. Show all the relevant hydrogen bonds with dotted lines and include the unshared pairs on the acceptor atoms, within each pair.
b. Which base pair has the strongest intermolecular interaction and why?

 a. Show all the relevant hydrogen bonds with dotted lines and include the unshared pairs on the acceptor atoms, within each pair.
a. Show all the relevant hydrogen bonds with dotted lines and include the unshared pairs on the acceptor atoms, within each pair.b. Which base pair has the strongest intermolecular interaction and why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The nitrogen mustard mustine is toxic to cells because it reacts with two DNA bases on opposite strands of the double helix. Representing the two reacting bases of DNA as R3N: and Rʹ3N: show the products of the reaction of mustine with DNA in a manner that would crosslink the two DNA strands. Your mechanism should account for the very high reactivity of mustine. Show all charges and unshared pairs.
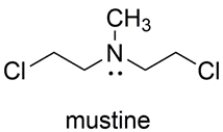


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Give the complementary sequence to the DNA strand.
5ʹ-TATGAC-3ʹ
5ʹ-TATGAC-3ʹ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Give the complementary sequence to the DNA strand.
5ʹ-ACTGAC-3ʹ
5ʹ-ACTGAC-3ʹ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The heterocyclic base 7-aminopropargyl-7-deaza-2,6-diaminopurine has been incorporated into a short sequence of nucleotides. The structure is shown below. Compare it to the other nucleotides and determine which nucleotide base is it likely to pair with. Draw the matching nucleotide with hydrogen bonds as dotted lines.
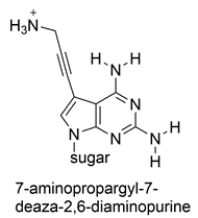


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Omeprazole is a drug used for the treatment of acid-reflux disease. The structure is shown below. Highlight the aromatic heterocycles in the structure and name the heterocycles.
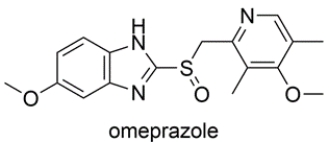


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








