Deck 24: Carbohydrates
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 24: Carbohydrates
1
Classify the carbohydrate, then indicate the chiral carbons with an asterisk. How many possible stereoisomers can exist for this carbohydrate?
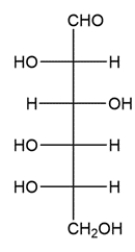

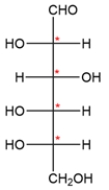
A carbohydrate with an aldehyde group is called an aldose, and carbohydrates are classified by the number of carbons they contain. The carbohydrate shows six carbons and has an aldehyde on carbon 1, so it is an aldohexose. There are four stereocenters, so there will be 24 or 16 stereoisomers.

2
Classify the carbohydrate, then indicate the chiral carbons with an asterisk. How many possible stereoisomers can exist for this carbohydrate?
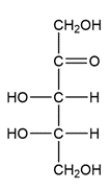

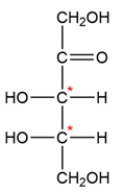
A carbohydrate with a ketone group is called a ketose, and carbohydrates are classified by the number of carbons they contain. The structure is a ketopentose since it has five carbons and a ketone. There are two chiral carbons, so there are four total stereoisomers possible.

3
Assign the R/S configuration for each of the asymmetric carbons in the carbohydrate.
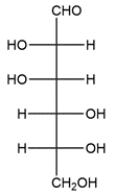

Recall in a Fischer projection that the vertical bonds are receding from view and the horizontal bonds are coming toward the viewer. In each case, the lowest priority hydrogen is on a horizontal bond, so a shortcut would be to assign priorities and note the direction of increasing priority. Then simply reverse the R/S assignment.


4
Convert the line-and-wedge structure into a Fischer projection, then assign as a D- or L-carbohydrate.
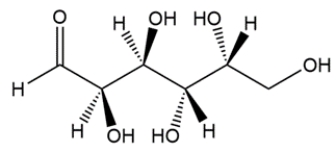


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Draw an enantiomer of the carbohydrate. Assign the D- or L-configuration to each.
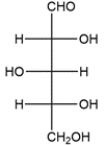


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Most hexoses found in nature are D-carbohydrates. Comparing a D-carbohydrate with the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system of nomenclature, select the true statement.
A) A D-carbohydrate will have R configuration.
B) A D-carbohydrate will have S configuration.
C) There is no relationship between the D,L system and the R/S configuration.
A) A D-carbohydrate will have R configuration.
B) A D-carbohydrate will have S configuration.
C) There is no relationship between the D,L system and the R/S configuration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Identify the relationship between the two carbohydrates. Select all that apply.
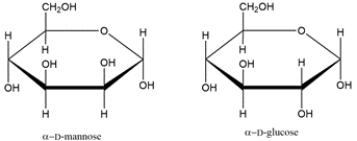
A) enantiomer
B) diastereomer
C) anomer
D) epimer

A) enantiomer
B) diastereomer
C) anomer
D) epimer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Identify the relationship between the two carbohydrates. Select all that apply.
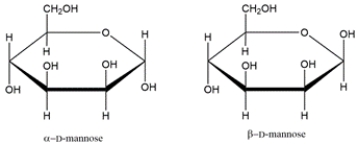
A) enantiomer
B) diastereomer
C) anomer
D) epimer

A) enantiomer
B) diastereomer
C) anomer
D) epimer

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Given the Fischer projection, draw both anomers of the corresponding pyranose ring in a Haworth projection, then label each anomer.
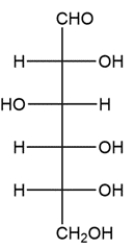


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Given the chair conformation of a monosaccharide, provide the open-chain form.
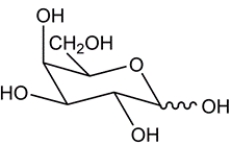


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Ribose is cyclized to the hemiacetal -D-ribofuranose. Draw a curved-arrow mechanism to show the cyclization step.
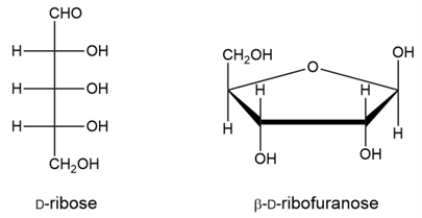


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
When -D-glucopyranose is dissolved in water, mutarotation occurs. What has happened?
A) The carbohydrate has converted completely to -D-glucopyranose.
B) The carbohydrate has converted to a mixture of -D-glucopyranose and -D-glucopyranose.
C) The carbohydrate has converted to its enantiomer.
D) The carbohydrate has changed from D- to L-configuration.
A) The carbohydrate has converted completely to -D-glucopyranose.
B) The carbohydrate has converted to a mixture of -D-glucopyranose and -D-glucopyranose.
C) The carbohydrate has converted to its enantiomer.
D) The carbohydrate has changed from D- to L-configuration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
D-Altrose can be transformed to another aldose and 2-ketose upon treatment with base. Draw the structure of the aldose and 2-ketose.
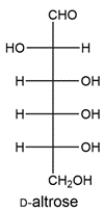


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A methyl D-glucopyranoside contains a methoxy group on which carbon of glucose? Explain the difference between a pyranoside and a pyranose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Predict the major organic product for the reaction. If more than one isomer is formed, just draw one.
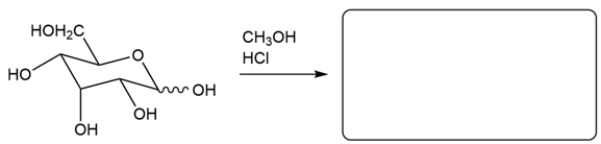


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Devise a two-step synthesis for the transformation.
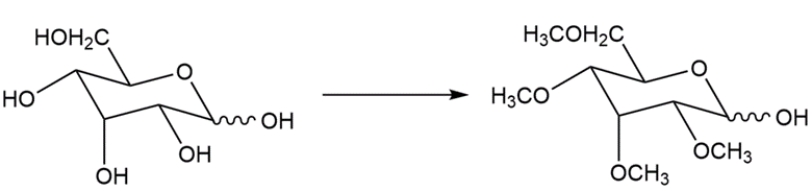


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Devise a two-step synthesis for the transformation.
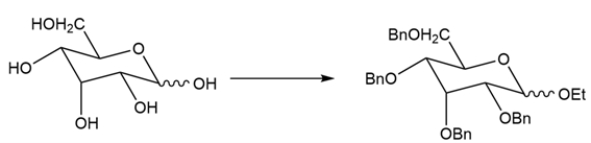


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A D-aldohexose is treated with HNO3 to give an optically inactive aldaric acid. Deduce the Fischer projection of the D-aldohexose. There is more than one correct answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A D-aldotetrose reacts with NaBH4 to give an optically active product. Deduce the structure of the D-aldotetrose and the product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Two aldohexoses (D-galactose and D-talose) are formed from a Kiliani-Fischer synthesis. Deduce the starting material.
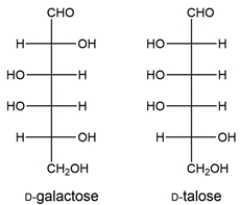


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The Ruff degradation of two aldohexoses gives D-xylose. Deduce the structures of the two aldohexoses.
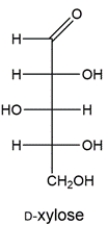


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The Ruff degradation of two aldopentoses gives D-threose. Deduce the structures of the two aldopentoses.
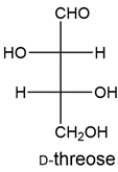


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The disaccharide maltose is shown below.
a. Classify the disaccharide as a reducing or nonreducing sugar and explain why.
b. Identify the glucoside linkage in maltose and classify each as either alpha or beta.
c. Name the monosaccharides formed when maltose is hydrolyzed in aqueous acid.
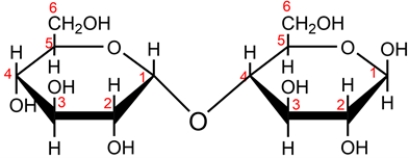
a. Classify the disaccharide as a reducing or nonreducing sugar and explain why.
b. Identify the glucoside linkage in maltose and classify each as either alpha or beta.
c. Name the monosaccharides formed when maltose is hydrolyzed in aqueous acid.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
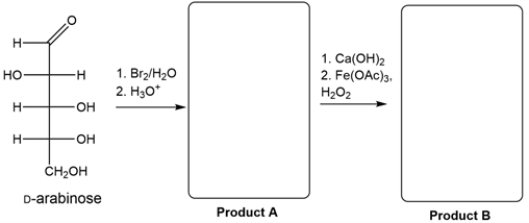
24
Identify products A and B from the synthesis.


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A D-aldopentose forms two aldohexoses, A and B, after a Kiliani-Fisher synthesis. Aldohexose A is oxidized to an optically inactive aldaric acid, while aldohexose B is oxidized to an optically active aldaric acid. The aldopentose can also be oxidized to an optically inactive aldaric acid. Deduce the structures of the aldopentose and the two aldohexoses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








