Deck 13: Earthquakes and Earth Structure
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Earthquakes and Earth Structure
1
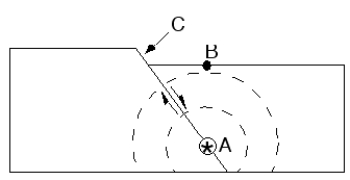
-Point A, where slip initiated during the earthquake, is called the __________.
A) dip
B) epicenter
C) focus
D) strike
C
2

-Point B is called the earthquake __________.
A) dip
B) epicenter
C) focus
D) strike
B
3
Where does slip initiate during an earthquake?
A) epicenter
B) focus
C) strike
A) epicenter
B) focus
C) strike
B
4
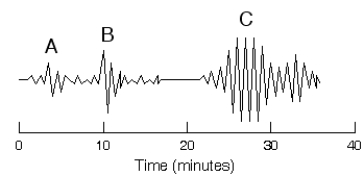
-What causes the up-and-down wiggles on the seismogram?
A) electromagnetic pulses
B) tsunami waves
C) ground vibrations
D) variations in air pressure

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5

-Which set(s) of waves travels through the Earth's interior?
A) set A
B) set B
C) sets A and B
D) sets A, B, and C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6

-Which set(s) of waves is/are most likely surface waves?
A) set A
B) set B
C) set C
D) Sets A, B, and C are all surface waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
What is the moment magnitude of an earthquake proportional to?
A) the area of the fault break
B) the seismic energy released during the rupture
C) both A and B
D) neither A nor B
A) the area of the fault break
B) the seismic energy released during the rupture
C) both A and B
D) neither A nor B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
What type of machine records the seismic waves generated by earthquakes?
A) gravimeter
B) compass
C) seismograph
A) gravimeter
B) compass
C) seismograph

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
At a seismograph station, what type of seismic waves arrive before the surface waves?
A) P waves but not S waves
B) S waves but not P waves
C) both P waves and S waves
A) P waves but not S waves
B) S waves but not P waves
C) both P waves and S waves

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
What type of information can be gained by examining the first motion (push or pull) of P waves arriving at different seismograph stations?
A) moment magnitude
B) type of faulting
C) amount of slip
A) moment magnitude
B) type of faulting
C) amount of slip

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
For two earthquakes located the same distance away, the ground shaking produced by a Richter magnitude 4 earthquake would be ___ times greater than the ground shaking produced by a magnitude 3 earthquake.
A) 1.33
B) 4
C) 10
A) 1.33
B) 4
C) 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
About how often do magnitude 8 earthquakes occur?
A) twice a year
B) once every 3 years
C) once every 30 to 100 years
A) twice a year
B) once every 3 years
C) once every 30 to 100 years

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
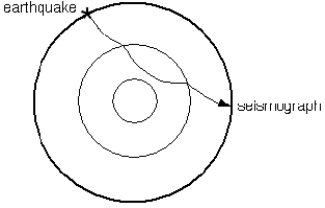
-What type of seismic wave is depicted by the ray path in the diagram?
A) a P wave
B) an S wave
C) a surface wave
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14

-The two kinks in the seismic wave path are examples of seismic __________.
A) isostasy
B) reflection
C) refraction
D) tomography

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
What causes the sharp increases in the velocity of S waves at 400 and 670 kilometers depth in the mantle?
A) changes in the composition of the mantle
B) changes in the mineral structures
C) changes in the pressure of the mantle
D) changes in the temperature of the mantle
A) changes in the composition of the mantle
B) changes in the mineral structures
C) changes in the pressure of the mantle
D) changes in the temperature of the mantle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The S wave shadow zone is caused by the
A) inner core.
B) lower mantle.
C) outer core.
A) inner core.
B) lower mantle.
C) outer core.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
P waves travel through peridotite at about ___ km/s.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The following question refers to the cross section of the Earth in the following figure.
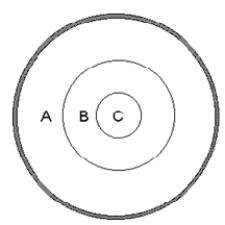
-Which region of the Earth does not transmit S waves?
A) region A
B) region B
C) region C

-Which region of the Earth does not transmit S waves?
A) region A
B) region B
C) region C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Seismic tomography can detect relatively warm regions of the mantle because S waves
A) do not pass through these regions.
B) travel more slowly through these regions.
C) travel more rapidly through these regions.
A) do not pass through these regions.
B) travel more slowly through these regions.
C) travel more rapidly through these regions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 19 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








