Deck 12: The Environment
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 12: The Environment
1
FIGURE 12-1
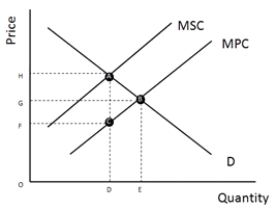
Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. At the socially optimal output level, what are internal costs equal to?
A) OG
B) AC
C) OH
D) OF

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. At the socially optimal output level, what are internal costs equal to?
A) OG
B) AC
C) OH
D) OF
OH
2
Which of the following is NOT an externality associated with the production of steel?
A) soot that is deposited on the cars of nearby homeowners
B) dead fish as a result of chemical discharge into river systems
C) respiratory disease caused by air pollution
D) higher wages as a result of the increase in demand for labour
A) soot that is deposited on the cars of nearby homeowners
B) dead fish as a result of chemical discharge into river systems
C) respiratory disease caused by air pollution
D) higher wages as a result of the increase in demand for labour
higher wages as a result of the increase in demand for labour
3
FIGURE 12-1

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. What represents the socially optimal price and output combination?
A) OG; OD
B) OG; OE
C) OH; OD
D) OF; OD

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. What represents the socially optimal price and output combination?
A) OG; OD
B) OG; OE
C) OH; OD
D) OF; OD
OH; OD
4
FIGURE 12-1

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. To internalize the externality, what is the total amount that the firms have to pay society equal to?
A) AC
B) ACB
C) OHAD
D) FHAC

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. To internalize the externality, what is the total amount that the firms have to pay society equal to?
A) AC
B) ACB
C) OHAD
D) FHAC

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
FIGURE 12-2
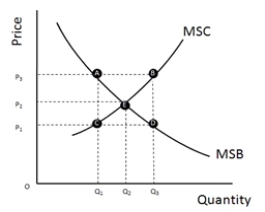
Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. In the absence of pollution control legislation, at what point will firms spend on pollution-control measures?
A) P1Q1
B) P3Q1
C) P3Q3
D) P1Q3

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. In the absence of pollution control legislation, at what point will firms spend on pollution-control measures?
A) P1Q1
B) P3Q1
C) P3Q3
D) P1Q3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
FIGURE 12-1

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. What represents the price and output combination that the industry would produce?
A) OG; OE
B) OH; OD
C) OG; OD
D) OF; OD

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. What represents the price and output combination that the industry would produce?
A) OG; OE
B) OH; OD
C) OG; OD
D) OF; OD

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
At what point does the optimal level of pollution abatement in the steel industry occur?
A) where the total cost of abatement is equal to the total benefit from abatement
B) where the marginal social cost of producing steel is equal to the demand for steel
C) where the marginal social cost of abatement is equal to the marginal social benefit from abatement
D) where the marginal private cost of abatement is equal to the marginal social benefit from abatement
A) where the total cost of abatement is equal to the total benefit from abatement
B) where the marginal social cost of producing steel is equal to the demand for steel
C) where the marginal social cost of abatement is equal to the marginal social benefit from abatement
D) where the marginal private cost of abatement is equal to the marginal social benefit from abatement

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following is an externality associated with owning a dog?
A) the noise your neighbours hear when your dog barks
B) protection from burglars
C) time spent walking the dog
D) dog hair in the carpet
A) the noise your neighbours hear when your dog barks
B) protection from burglars
C) time spent walking the dog
D) dog hair in the carpet

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
When does a negative externality exist?
A) whenever marginal social cost exceed marginal private costs
B) whenever marginal social costs exceed marginal social benefits
C) whenever marginal social benefits exceed marginal private benefits
D) whenever marginal private costs exceed marginal private benefits
A) whenever marginal social cost exceed marginal private costs
B) whenever marginal social costs exceed marginal social benefits
C) whenever marginal social benefits exceed marginal private benefits
D) whenever marginal private costs exceed marginal private benefits

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
In the last 30 years, what has happened to environmental legislation and pollution levels?
A) Legislation has been getting weaker, and pollution levels have been getting higher.
B) Legislation has been getting tougher, and pollution levels have been getting lower.
C) Legislation has been getting tougher, and pollution levels have been getting higher.
D) Legislation has been getting weaker, and pollution levels have been getting lower.
A) Legislation has been getting weaker, and pollution levels have been getting higher.
B) Legislation has been getting tougher, and pollution levels have been getting lower.
C) Legislation has been getting tougher, and pollution levels have been getting higher.
D) Legislation has been getting weaker, and pollution levels have been getting lower.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
FIGURE 12-1

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. What is the marginal external cost equal to?
A) FG
B) FH
C) GH
D) OF

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. What is the marginal external cost equal to?
A) FG
B) FH
C) GH
D) OF

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Why are negative externalities difficult to measure in practice?
A) because most external costs are nonpecuniary in nature
B) because the marginal value of cleaner air is close to zero
C) because the effects of pollution are subjective in nature
D) because some resources are owned by society and therefore have no opportunity cost
A) because most external costs are nonpecuniary in nature
B) because the marginal value of cleaner air is close to zero
C) because the effects of pollution are subjective in nature
D) because some resources are owned by society and therefore have no opportunity cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following best describes the impact of increased concerns regarding the environment and climate change?
A) It has likely caused the marginal social cost curve to shift to the right.
B) It has likely caused the marginal social benefit curve to shift to the right.
C) It has likely caused the marginal social cost curve to shift to the left.
D) It has likely caused the marginal social benefit curve to shift to the left.
A) It has likely caused the marginal social cost curve to shift to the right.
B) It has likely caused the marginal social benefit curve to shift to the right.
C) It has likely caused the marginal social cost curve to shift to the left.
D) It has likely caused the marginal social benefit curve to shift to the left.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
People that choose to live near airports must put up with the noise associated with aircrafts arriving and departing. Which of the following best describes how those people are compensated for the negative externality that they face?
A) They have been compensated for the externality by the airlines.
B) They have been compensated for the externality with easier access to the airport.
C) They have been compensated for the externality with lower housing costs.
D) They have been compensated for the externality by the government.
A) They have been compensated for the externality by the airlines.
B) They have been compensated for the externality with easier access to the airport.
C) They have been compensated for the externality with lower housing costs.
D) They have been compensated for the externality by the government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
FIGURE 12-1

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. At the private market output level, what is the deadweight loss associated with the overallocation of resources equal to?
A) ABGH
B) FHAC
C) ACB
D) OHAD

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. At the private market output level, what is the deadweight loss associated with the overallocation of resources equal to?
A) ABGH
B) FHAC
C) ACB
D) OHAD

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
FIGURE 12-1

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. To internalize the externality, what is the per unit amount that the firms would have to pay society equal to?
A) OH
B) ACB
C) FHAC
D) HF

Refer to Figure 12-1, which represents a hypothetical market for steel. To internalize the externality, what is the per unit amount that the firms would have to pay society equal to?
A) OH
B) ACB
C) FHAC
D) HF

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following is NOT a policy option for dealing with environmental pollution?
A) requiring that firms that pollute locate away from populated areas
B) prohibiting activities that generate pollution
C) requiring firms to adopt pollution-control technology
D) dictating maximum permissible levels of output
A) requiring that firms that pollute locate away from populated areas
B) prohibiting activities that generate pollution
C) requiring firms to adopt pollution-control technology
D) dictating maximum permissible levels of output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Why are negative externalities difficult to internalize in practice?
A) because the cost of cleaning up the effects of pollution is overstated
B) because the marginal cost of socially owned resources is zero
C) because no markets exist to measure the cost of the externality
D) because the deadweight loss is subjective in nature
A) because the cost of cleaning up the effects of pollution is overstated
B) because the marginal cost of socially owned resources is zero
C) because no markets exist to measure the cost of the externality
D) because the deadweight loss is subjective in nature

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Why might zero pollution NOT be the optimal objective?
A) It is difficult to determine which firms are doing the polluting.
B) There is no marginal benefit to a clean environment.
C) A clean environment comes with an opportunity cost.
D) Some people may not be affected by the pollution.
A) It is difficult to determine which firms are doing the polluting.
B) There is no marginal benefit to a clean environment.
C) A clean environment comes with an opportunity cost.
D) Some people may not be affected by the pollution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What is the most likely outcome when trying to eliminate pollution?
A) Abatement will exhibit diminishing returns.
B) Abatement will be subject to diminishing average cost.
C) Firms will increase output in the short run.
D) Public opinion will matter more to firms than profit maximization.
A) Abatement will exhibit diminishing returns.
B) Abatement will be subject to diminishing average cost.
C) Firms will increase output in the short run.
D) Public opinion will matter more to firms than profit maximization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
In a cap and trade system, who has the most incentive to develop pollution abatement technologies?
A) The polluters, since they will have to buy permits to pollute over a certain amount.
B) The government, since they are responsible for setting up the system.
C) The people that directly suffer from the pollution, since they are the ones who are negatively affected.
D) The consumers, since they are the final users of the product.
A) The polluters, since they will have to buy permits to pollute over a certain amount.
B) The government, since they are responsible for setting up the system.
C) The people that directly suffer from the pollution, since they are the ones who are negatively affected.
D) The consumers, since they are the final users of the product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Since it is nearly impossible to measure negative externalities, it is better to ignore them and allow the market solution to continue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What is an advantage of using a transferable pollution right over a pollution tax?
A) The government can legislate the method of abatement.
B) The government receives less revenue from the tax.
C) Consumer prices won't rise.
D) Governments don't need information on the cheapest abatement strategy.
A) The government can legislate the method of abatement.
B) The government receives less revenue from the tax.
C) Consumer prices won't rise.
D) Governments don't need information on the cheapest abatement strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following firms is most likely to be the first to implement pollution control technologies if the government implements a system of transferable pollution rights?
A) the firm with the lowest marginal cost of production
B) the firm with the lowest marginal cost of implementation
C) the firm with the lowest level of pollution
D) the firm with the highest level of pollution
A) the firm with the lowest marginal cost of production
B) the firm with the lowest marginal cost of implementation
C) the firm with the lowest level of pollution
D) the firm with the highest level of pollution

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
FIGURE 12-3
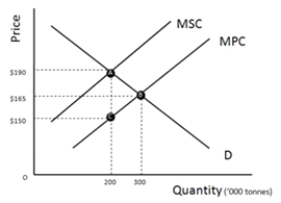
Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. Suppose the market is currently producing at the profit maximizing point and the government wishes to impose a tax to correct the overallocation of resources caused by the externality. What per unit tax would accomplish this goal?
A) $15
B) $25
C) $40
D) $190

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. Suppose the market is currently producing at the profit maximizing point and the government wishes to impose a tax to correct the overallocation of resources caused by the externality. What per unit tax would accomplish this goal?
A) $15
B) $25
C) $40
D) $190

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The Coase theorem suggests that a private transaction can compensate for an externality when private property rights exist. In practice, why doesn't it work when large numbers of people are involved?
A) because marginal costs are higher than marginal benefits
B) because too many politicians get involved
C) because marginal benefits are higher than marginal costs
D) because transaction costs are too high
A) because marginal costs are higher than marginal benefits
B) because too many politicians get involved
C) because marginal benefits are higher than marginal costs
D) because transaction costs are too high

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following is more likely to result in better pollution reduction technologies?
A) environmental subsidies to nonpolluters
B) transferable pollution rights
C) media attention directed at the worst polluters
D) pollution tax
A) environmental subsidies to nonpolluters
B) transferable pollution rights
C) media attention directed at the worst polluters
D) pollution tax

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What is environmental damage, as a market failure, caused by?
A) the absence of prices for the use of the atmosphere and waterways
B) firms' relentless pursuit of profits
C) apathy on the part of consumers
D) globalization
A) the absence of prices for the use of the atmosphere and waterways
B) firms' relentless pursuit of profits
C) apathy on the part of consumers
D) globalization

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
FIGURE 12-3

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. What is the externality per tonne of pulp?
A) $15
B) $25
C) $40
D) $190

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. What is the externality per tonne of pulp?
A) $15
B) $25
C) $40
D) $190

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When a negative externality is present, the socially optimal level is less than the private market equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
FIGURE 12-2

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. What is the optimal amount of spending on pollution control?
A) P3Q1
B) P1Q1
C) P3Q3
D) P2Q2

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. What is the optimal amount of spending on pollution control?
A) P3Q1
B) P1Q1
C) P3Q3
D) P2Q2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
FIGURE 12-2

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. What might overly stringent pollution-control legislation result in the marginal social benefit being equal to?
A) 0
B) P1
C) P2
D) P3

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. What might overly stringent pollution-control legislation result in the marginal social benefit being equal to?
A) 0
B) P1
C) P2
D) P3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The presence of a negative externality such as pollution causes an underallocation of resources.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The socially optimal level of pollution is none at all.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Which of the following is NOT one of the three objectives of a pollution control policy?
A) motivating advances in abatement technology
B) requiring polluting firms to bear all the costs of pollution abatement
C) achieving the efficient level of pollution
D) achieving pollution reduction at least cost
A) motivating advances in abatement technology
B) requiring polluting firms to bear all the costs of pollution abatement
C) achieving the efficient level of pollution
D) achieving pollution reduction at least cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
An externality exists when an individual other than the demander receives part of the benefits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
FIGURE 12-2

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. What is the optimal amount of pollution control?
A) 0
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3

Refer to Figure 12-2, which represents the costs and benefits of pollution control. What is the optimal amount of pollution control?
A) 0
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
FIGURE 12-3

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. Suppose the market is currently producing at the profit maximizing point and the government wishes to impose a tax to correct the overallocation of resources caused by the externality. Once the tax is imposed, what will the per unit price of pulp be?
A) $110
B) $150
C) $165
D) $190

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. Suppose the market is currently producing at the profit maximizing point and the government wishes to impose a tax to correct the overallocation of resources caused by the externality. Once the tax is imposed, what will the per unit price of pulp be?
A) $110
B) $150
C) $165
D) $190

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
FIGURE 12-3

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. Suppose the market is currently producing at the profit maximizing point and the government wishes to impose a tax to correct the overallocation of resources caused by the externality. How much revenue would the government receive?
A) $4 million
B) $8 million
C) $12 million
D) $16 million

Refer to Figure 12-3, which represents the market for pulp, the production of which creates dioxin emissions. Suppose the market is currently producing at the profit maximizing point and the government wishes to impose a tax to correct the overallocation of resources caused by the externality. How much revenue would the government receive?
A) $4 million
B) $8 million
C) $12 million
D) $16 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Your neighbour's dog barks and disturbs your sleep. According to the Coase theorem, in which of the following scenarios can you and your neighbour NOT come to a resolution?
A) when your marginal benefit of sleep is exactly equal to your neighbour's marginal benefit of owning a dog
B) when your marginal benefit of sleep is greater than your neighbour's marginal benefit of owning a dog
C) when your marginal benefit of sleep is greater than your neighbour's marginal cost of owning a dog
D) when your marginal benefit of sleep is less than your neighbour's marginal benefit of owning a dog
A) when your marginal benefit of sleep is exactly equal to your neighbour's marginal benefit of owning a dog
B) when your marginal benefit of sleep is greater than your neighbour's marginal benefit of owning a dog
C) when your marginal benefit of sleep is greater than your neighbour's marginal cost of owning a dog
D) when your marginal benefit of sleep is less than your neighbour's marginal benefit of owning a dog

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The Province of Ontario has recently banned the use of cellular telephones in automobiles. Do cellular phones create a negative externality?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The marginal social benefit of pollution abatement is likely to be lower in rural areas than it is in urban areas.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The Coase theorem suggests that the optimal solution to pollution may be independent of the initial property rights.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Intervention when a negative externality exists can move the market output closer to the socially optimal level and reduce the size of the deadweight loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Car owners in some metropolitan areas must subject their vehicles to annual emissions testing while car owners in rural areas do not. Why might this be socially optimal?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Why do tradable pollution permits provide an incentive to reduce pollution?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The government must determine the optimal method of reducing pollution when transferable pollution rights are implemented.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Suppose that your neighbour's dog barks every morning and wakes you up. The marginal benefit of the sleep that you lost is $100. Your neighbour's marginal benefit from owning the dog is $120. Suggest how a private transaction might make you both better off. What if the marginal benefit of your sleep was $120 and your neighbour's marginal benefit from owning the dog was $100.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Governments should always attempt to solve externality problems that cannot be solved through private actions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








