Deck 6: The Economics of Environmental Regulation Ii: Transferable Emission Credits, and the Macroeconomic Effects of Environmental Regulation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: The Economics of Environmental Regulation Ii: Transferable Emission Credits, and the Macroeconomic Effects of Environmental Regulation
1
The purpose for creating a tradable emission credit system is to substitute the
market for pollution rights.
market for pollution rights.
False
2
A system of transferable credits operates on the basis that there is a legally
sanctioned right to pollute.
sanctioned right to pollute.
True
3
Transferable credits work better when the number of parties involved in the
exchange of credit are limited or capped.
exchange of credit are limited or capped.
False
4
A bubble policy is generally used by a firm that has only one source of pollution
so that it remains in compliance with a set emission standard.
so that it remains in compliance with a set emission standard.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The benefit of pooling together all of a firm's emissions as one source is that the
firm does not need to meet standards for each source.
firm does not need to meet standards for each source.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The banking policy allows firms to use their initial credit allotment over time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The offset policy is used can only be used when the level of a given pollutant
exceeds the level permitted by the federal standards.
exceeds the level permitted by the federal standards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
There has been considerable resistance in the application of emission trading
program particularly in the member states of the European Union (EU) and some Latin American countries.
program particularly in the member states of the European Union (EU) and some Latin American countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
In the presence of uncertainty, when control costs that are higher than expected, a
regulatory scheme based on transferable pollution credits can result in a cleanup
costing more than the socially optimal level.
regulatory scheme based on transferable pollution credits can result in a cleanup
costing more than the socially optimal level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Hot-spots are any areas that contain high local concentration of any pollutant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In the United States, the acid rain program (ARP), was established under Title IV
of the 2009 Clean Air Act Amendment which requires major emission reduction
of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxide (nox).
of the 2009 Clean Air Act Amendment which requires major emission reduction
of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxide (nox).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Although not a human health issue, the accumulation over time of sulfur dioxide
(SO2) and acid rain depositions on lakes, streams, and forests are believed to
cause substantial damage to aquatic organisms and trees.
(SO2) and acid rain depositions on lakes, streams, and forests are believed to
cause substantial damage to aquatic organisms and trees.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Most findings since the 1980s show that environmental regulations have actually
contributed to productivity slow-downs in the US and other countries.
contributed to productivity slow-downs in the US and other countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Strictly enforced environmental policy could, in effect, force firms to adopt
efficient pollution abatement technology, which will lead to a competitive
advantage in the long-term.
efficient pollution abatement technology, which will lead to a competitive
advantage in the long-term.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Underestimation of the cost of environmental regulations remains a serious
concern.
concern.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which one of the following statements about a system of tradable carbon permits is false?
A) An advantage of carbon permits is that greenhouse gases could be reduced at the lowest
cost.
B) Nations can emit more carbon if they purchase additional permits.
C) The equilibrium price of a carbon permit depends on the willingness to pay for carbon
emissions.
D) A carbon permit system would require each country to meet their emissions targets.
E) Nations which exceed their targets can sell permits to other countries.
A) An advantage of carbon permits is that greenhouse gases could be reduced at the lowest
cost.
B) Nations can emit more carbon if they purchase additional permits.
C) The equilibrium price of a carbon permit depends on the willingness to pay for carbon
emissions.
D) A carbon permit system would require each country to meet their emissions targets.
E) Nations which exceed their targets can sell permits to other countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following is true about the first large-scale use of tradable pollution credits in the United States?
A) They were introduced with the passage of the 2010 Clean Air Act Amendments.
B) The Act introducing them made use of market-based approaches.
C) The credits were primarily designed to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions
from power plants.
D) The credits were primarily designed to reduce methane (CH4) emissions from
power plants.
E) All of the above are true.
A) They were introduced with the passage of the 2010 Clean Air Act Amendments.
B) The Act introducing them made use of market-based approaches.
C) The credits were primarily designed to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions
from power plants.
D) The credits were primarily designed to reduce methane (CH4) emissions from
power plants.
E) All of the above are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a (are) characteristic(s) of the US acid rain program?
A) There is total annual emissions goal set for the nation.
B) The EPA limits individual electric utility plants by issuing a fixed number of
Tradable allowances on the basis of projected emissions.
C) The EPA limits individual electric utility plants by issuing a fixed number of
Tradable allowances on the basis of historical emissions.
D) Both a and b .
E) Both a and c .
A) There is total annual emissions goal set for the nation.
B) The EPA limits individual electric utility plants by issuing a fixed number of
Tradable allowances on the basis of projected emissions.
C) The EPA limits individual electric utility plants by issuing a fixed number of
Tradable allowances on the basis of historical emissions.
D) Both a and b .
E) Both a and c .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
What does the empirical evidence, on the whole, concerning the relationships between environmental protection, the economy, and jobs reveal?
A) The impact of environmental regulations on jobs is a net loss.
B) The impact of environmental regulations on jobs is a net gain.
C) The impact of environmental regulations on jobs is a zero.
D) There is no evidence to link job losses with state environmentalism.
E) There is no empirical evidence available.
A) The impact of environmental regulations on jobs is a net loss.
B) The impact of environmental regulations on jobs is a net gain.
C) The impact of environmental regulations on jobs is a zero.
D) There is no evidence to link job losses with state environmentalism.
E) There is no empirical evidence available.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What is the basis for the Porter Hypothesis?
A) The recognition that the market for pollution abatement technology is expanding
Everywhere.
B) Firms that save costs by not adopting new pollution technologies will have
Competitive advantages.
C) Strictly enforced environmental policy would have the effect of forcing firms to
Adopt efficient pollution abatement technology, but there will be long-term costs
That reduce competitive advantage.
D) Strictly enforced environmental policy would have the effect of forcing firms to
Adopt efficient pollution abatement technology, but there will be short-term costs
That reduce competitive advantage.
E) All of the above are applicable.
A) The recognition that the market for pollution abatement technology is expanding
Everywhere.
B) Firms that save costs by not adopting new pollution technologies will have
Competitive advantages.
C) Strictly enforced environmental policy would have the effect of forcing firms to
Adopt efficient pollution abatement technology, but there will be long-term costs
That reduce competitive advantage.
D) Strictly enforced environmental policy would have the effect of forcing firms to
Adopt efficient pollution abatement technology, but there will be short-term costs
That reduce competitive advantage.
E) All of the above are applicable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Clearly define property rights are important because…
A) Emission trading programs cannot work without them.
B) Governments cannot set limits for pollution levels without them.
C) Polluters will pollute less without them.
D) The Porter Hypothesis calls for them.
E) All of the above.
A) Emission trading programs cannot work without them.
B) Governments cannot set limits for pollution levels without them.
C) Polluters will pollute less without them.
D) The Porter Hypothesis calls for them.
E) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following would allow a polluter to treat all its different types of sources of pollution as a single source?
A) Bubble policy.
B) Banking policy.
C) Porter Hypothesis policy.
D) Offset policy.
E) All of the above.
A) Bubble policy.
B) Banking policy.
C) Porter Hypothesis policy.
D) Offset policy.
E) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which of the following would relieves polluters from making impulsive decisions on what to do about their emission credits immediately upon the retirement of an existing source of pollution?
A) Bubble policy.
B) Banking policy.
C) Porter Hypothesis policy.
D) Offset policy.
E) All of the above.
A) Bubble policy.
B) Banking policy.
C) Porter Hypothesis policy.
D) Offset policy.
E) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Figure 6A
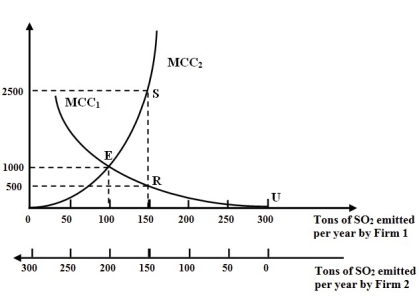
-Refer to Figure 6A. Assume that government regulation limits sulfur dioxide emissions to 150 tons per year. Also assume that Firm 1 cannot reduce its emissions below 100 tons per year. Which of the following would apply in this situation?
A) The government would necessarily increase the emission limits to over 150 tons to be
fair.
B) The marginal control costs for firm 1 will be higher than those for firm 2.
C) The marginal control costs for firm 2 will be infinitely high.
D) The marginal control costs for firm 2 will be less than $500.
E) The marginal control costs for firm 2 will be $1000.

-Refer to Figure 6A. Assume that government regulation limits sulfur dioxide emissions to 150 tons per year. Also assume that Firm 1 cannot reduce its emissions below 100 tons per year. Which of the following would apply in this situation?
A) The government would necessarily increase the emission limits to over 150 tons to be
fair.
B) The marginal control costs for firm 1 will be higher than those for firm 2.
C) The marginal control costs for firm 2 will be infinitely high.
D) The marginal control costs for firm 2 will be less than $500.
E) The marginal control costs for firm 2 will be $1000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Figure 6A

-Refer to Figure 6A. Why do the two firms not pollute at points R and S respectively when pollution credits and regulations exist ?
A) They do because the points R and S are Pareto optimal.
B) They do not because only point R is Pareto optimal.
C) They do not because only point S is Pareto optimal.
D) They do not because point E is Pareto optimal.
E) They do because their marginal control costs are minimized at points R and S.

-Refer to Figure 6A. Why do the two firms not pollute at points R and S respectively when pollution credits and regulations exist ?
A) They do because the points R and S are Pareto optimal.
B) They do not because only point R is Pareto optimal.
C) They do not because only point S is Pareto optimal.
D) They do not because point E is Pareto optimal.
E) They do because their marginal control costs are minimized at points R and S.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 25 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








