Deck 6: Imperfect Competition
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: Imperfect Competition
1
Imperfectly competitive markets include monopolistic competition and oligopoly.
True
2
When the Top 4 concentration ratio approaches zero, the market is generally regarded as monopolistic.
False
3
Oligopoly is the market structure that is closest to perfect competition.
False
4
Because a monopolistically competitive firm faces competition from substitute products sold by rivals, its demand curve is more elastic than the demand curve of a pure monopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A monopolistically competitive firm always realizes an economic profit in the short run, but realizes only a normal profit in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The difference between the output corresponding to minimum average total cost and the output produced by a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run is called excess capacity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
An objective of persuasive advertising is to increase the demand for a firm's product and make it more elastic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
By informing potential customers about alternative sources of supply and pricing policies, advertising forces sellers to maintain relatively low prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Price discrimination is the practice of charging some buyers a higher price than others for an identical good, even though there is no difference in the cost to the firm of supplying these buyers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A firm practicing price discrimination would charge a higher price to buyers with relatively elastic demand curves and a lower price to buyers with relatively inelastic demand curves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The Liberty Theater would engage in price discrimination by charging higher prices to nonstudents, who have less elastic demand curves, and lower prices to students, who have more elastic demand curves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
A firm engaging in successful price discrimination can reduce its total cost without increasing total revenue, thereby increasing total profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In oligopoly, a small number of firms compete with each other and each firm has significant price-making ability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The quantity sold by an oligopolist depends not only on that firm's product price, but also on the other firms' prices and quantities sold.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Relatively low barriers to entry and modest economies of scale help explain why markets are oligopolistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The merger of Miller and Anheuser-Busch in the beer industry would be an example of a conglomerate merger.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The merger of Ford Motors and General Motors would be an example of a vertical merger.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The products produced by oligopolies can be either differentiated or standardized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Diseconomies of scale is one explanation for why an oligopoly exists.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
By the 1980s, competition by foreign automakers reduced the market share and price-making abilities of the "Big Three" U.S. automakers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The purpose of a cartel is to increase output and reduce price in order to increase the group profits of its members.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Among the obstacles that a cartel faces are a large number of sellers in the market and differences in cost and demand conditions among members of the cartel.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The steel and pharmaceutical industries are generally regarded as momopolistic competition industries, rather than oligopolies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Federal regulators carefully scrutinize horizontal mergers because they result in the uniting of formerly competing firms and increase the monopoly power of the newly formed firm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
According to the theory of contestable markets, a market can be dominated by a single firm without exhibiting the inefficiencies of monopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When the four largest firms control less than 40 percent of industry output, the industry is generally regarded as oligopolistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Batteries are considered to be a high-concentration industry, while bakeries are a low-concentration industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Product differentiation is a fundamental characteristic of perfect competition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A monopolistic competitive firm produces at the lowest point on its average total cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In order for price discrimination to take place, the firm must be able to subdivide the market into groups of people with different price elasticities of demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Based on the notes of one voyager, it's possible that the Pilgrims landed at Plymouth Rock because they were running out of beer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Sam Walton, the founder of Wal-Mart, earned his undergraduate degree in economics.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Game theory is a field of economics that relates to the behavior of individual firms operating in perfectly competitive markets.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Economic prosperity is an obstacle to the successful operation of a cartel.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Grocery stores in a large city provide an example of
A) pure monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) oligopoly
D) monopolistic competition
A) pure monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) oligopoly
D) monopolistic competition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following is not a characteristic of oligopoly?
A) profit maximization according to the MR = MC rule
B) sizable barriers to entry
C) firm's horizontal demand curve
D) firms being price makers rather than price takers
A) profit maximization according to the MR = MC rule
B) sizable barriers to entry
C) firm's horizontal demand curve
D) firms being price makers rather than price takers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Cartels tend to encounter difficulties when
A) there is a relatively large number of sellers in the market
B) demand and cost conditions among sellers are similar
C) market demand is strong and profits are sizable
D) there are barriers that prevent potential competitors from entering the industry
A) there is a relatively large number of sellers in the market
B) demand and cost conditions among sellers are similar
C) market demand is strong and profits are sizable
D) there are barriers that prevent potential competitors from entering the industry

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Successful persuasive advertising by Coca Cola
A) increases its demand and make it more elastic
B) increases its demand and makes it less elastic
C) decreases its demand and makes it more elastic
D) decreases its demand and makes it less elastic
A) increases its demand and make it more elastic
B) increases its demand and makes it less elastic
C) decreases its demand and makes it more elastic
D) decreases its demand and makes it less elastic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following industries is best described as an oligopoly?
A) commercial fishing
B) grocery stores
C) automobiles
D) agriculture
A) commercial fishing
B) grocery stores
C) automobiles
D) agriculture

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The merger of Boeing and McDonnell Douglas in the commercial jetliner industry is an example of a(n)
A) vertical merger
B) horizontal merger
C) conglomerate merger
D) integrative merger
A) vertical merger
B) horizontal merger
C) conglomerate merger
D) integrative merger

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The merger of Pizza Hut and General Motors would be an example of a(n)
A) vertical merger
B) horizontal merger
C) conglomerate merger
D) integrative merger
A) vertical merger
B) horizontal merger
C) conglomerate merger
D) integrative merger

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The merger of Johnson's Dairy Farm and Peterman's Milk Store would be an example of a(n)
A) vertical merger
B) horizontal merger
C) conglomerate merger
D) integrative merger
A) vertical merger
B) horizontal merger
C) conglomerate merger
D) integrative merger

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Informative advertising tends to
A) shift a firm's average total cost curve downward
B) shift a firm's total cost curve downward
C) make a firm's demand curve more elastic
D) make a firm's demand curve more inelastic
A) shift a firm's average total cost curve downward
B) shift a firm's total cost curve downward
C) make a firm's demand curve more elastic
D) make a firm's demand curve more inelastic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Persuasive advertising tends to
A) shift a firm's average total cost curve downward
B) shift a firm's total cost curve downward
C) make a firm's demand curve more elastic
D) make a firm's demand curve more inelastic
A) shift a firm's average total cost curve downward
B) shift a firm's total cost curve downward
C) make a firm's demand curve more elastic
D) make a firm's demand curve more inelastic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Monopolistically competitive firms tend to realize normal profits in the long run because
A) barriers to entry into the industry are relatively low
B) firms produce under conditions of diseconomies of scale
C) advertising increases the firm's costs and thus decreases profits
D) sales promotion makes the firm's demand curve more inelastic
A) barriers to entry into the industry are relatively low
B) firms produce under conditions of diseconomies of scale
C) advertising increases the firm's costs and thus decreases profits
D) sales promotion makes the firm's demand curve more inelastic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The two broad categories of imperfect competition are
A) perfect competition and monopolistic competition
B) monopolistic competition and oligopoly
C) oligopoly and monopoly
D) perfect competition and monopoly
A) perfect competition and monopolistic competition
B) monopolistic competition and oligopoly
C) oligopoly and monopoly
D) perfect competition and monopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A payoff matrix is used to analyze the behavior of firms operating in
A) perfect competition
B) monopolistic competition
C) oligopoly
D) pure monopoly
A) perfect competition
B) monopolistic competition
C) oligopoly
D) pure monopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If Southwest Airlines engages in successful price discrimination, it will charge
A) a relatively high price to travelers with more elastic demand curves
B) a relatively high price to travelers with more inelastic demand curves
C) the same price to all travelers regardless of their elasticities of demand
D) a higher price in markets in markets where costs are higher
A) a relatively high price to travelers with more elastic demand curves
B) a relatively high price to travelers with more inelastic demand curves
C) the same price to all travelers regardless of their elasticities of demand
D) a higher price in markets in markets where costs are higher

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
By practicing successful price discrimination, Northwest Airlines will realize
A) lower unit costs and thus increased profit
B) higher revenue and thus increased profit
C) a rightward shift in its demand curve and thus increased profit
D) a leftward shift in its demand curve and thus increased profit
A) lower unit costs and thus increased profit
B) higher revenue and thus increased profit
C) a rightward shift in its demand curve and thus increased profit
D) a leftward shift in its demand curve and thus increased profit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
What is true of cooperative price-fixing agreements in the long run?
A) they work well when the number of members is large
B) they only work in perfectly competitive markets
C) they get stronger over time and result in even higher profits for members
D) they tend to break down as members cheat
A) they work well when the number of members is large
B) they only work in perfectly competitive markets
C) they get stronger over time and result in even higher profits for members
D) they tend to break down as members cheat

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If Microsoft is in a(n)_____ market for computer software, it will not behave as though it is a monopoly even though it is the only firm in the market.
A) oligopolistic
B) monopolistically competitive
C) contestable
D) industrial
A) oligopolistic
B) monopolistically competitive
C) contestable
D) industrial

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
If the Liberty Movie Theater operates in a monopolistically competitive market, in the long run the firm will
A) always operate at output levels associated with diseconomies of scale
B) always operate at output levels associated with economies of scale
C) realize an economic profit
D) realize a normal profit
A) always operate at output levels associated with diseconomies of scale
B) always operate at output levels associated with economies of scale
C) realize an economic profit
D) realize a normal profit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A low concentration ratio in an industry suggests that the
A) industry is oligopolistic
B) industry is monopolistic
C) dominant firms in the industry have modest price-making ability
D) dominant firms in the industry have sizable price-making ability
A) industry is oligopolistic
B) industry is monopolistic
C) dominant firms in the industry have modest price-making ability
D) dominant firms in the industry have sizable price-making ability

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistically competitive markets?
A) only normal profits in the long run
B) price-taking firms
C) excess productive capacity in the long run
D) many firms of relatively small size
A) only normal profits in the long run
B) price-taking firms
C) excess productive capacity in the long run
D) many firms of relatively small size

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Proponents of advertising maintain that advertising can eventually result in decreased unit costs of production by
A) increasing the level of output, thus enabling firms to take advantage of economies of scale
B) increasing the level of output, which results in a downward shift in a firm's long-run average total cost curve
C) reducing sales, thus enabling firms to avoid diseconomies of scale
D) reducing sales, thus allowing firms to downsize their production operations
A) increasing the level of output, thus enabling firms to take advantage of economies of scale
B) increasing the level of output, which results in a downward shift in a firm's long-run average total cost curve
C) reducing sales, thus enabling firms to avoid diseconomies of scale
D) reducing sales, thus allowing firms to downsize their production operations

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Because there is significant freedom of entry and exit of firms in the retail sale of gasoline,
A) firms tend to realize normal profits in the long run
B) firms engage in wasteful advertising expenditures
C) firms always operate at the low point on their average total cost curves
D) consumers receive low-quality gasoline and are charged high prices
A) firms tend to realize normal profits in the long run
B) firms engage in wasteful advertising expenditures
C) firms always operate at the low point on their average total cost curves
D) consumers receive low-quality gasoline and are charged high prices

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The demand curve and marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm are downward sloping because
A) the firm is a price taker rather than a price maker
B) high barriers prevent potential competitors from entering the industry
C) the firm's product is differentiated
D) all consumers have identical tastes and preferences
A) the firm is a price taker rather than a price maker
B) high barriers prevent potential competitors from entering the industry
C) the firm's product is differentiated
D) all consumers have identical tastes and preferences

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
A monopolistically competitive firm hopes to
A) make an economic profit, but realizes economic losses in the long run
B) make an economic profit, but realizes normal profits in the long run
C) minimize its losses in the short run, but realizes economic profits in the long run
D) minimize its losses in the short run, but realizes economic losses in the long run
A) make an economic profit, but realizes economic losses in the long run
B) make an economic profit, but realizes normal profits in the long run
C) minimize its losses in the short run, but realizes economic profits in the long run
D) minimize its losses in the short run, but realizes economic losses in the long run

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If existing fast-food firms realize sizable economic profits in the short run, which of the following will take place in the long run?
A) The demand curves of existing firms will decrease and become more elastic.
B) The demand curves of existing firms will decrease and become less elastic.
C) The demand curves of existing firms will increase and become more elastic.
D) The demand curves of existing firms will increase and become less elastic.
A) The demand curves of existing firms will decrease and become more elastic.
B) The demand curves of existing firms will decrease and become less elastic.
C) The demand curves of existing firms will increase and become more elastic.
D) The demand curves of existing firms will increase and become less elastic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm produces an output where
A) average total cost is at a minimum
B) marginal cost is at a minimum
C) price equals average total cost
D) price equals marginal cost
A) average total cost is at a minimum
B) marginal cost is at a minimum
C) price equals average total cost
D) price equals marginal cost

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
If a market's concentration ratio is near zero, the market tends to be
A) perfectly competitive
B) monopolistically competitive
C) oligopolistic
D) monopolistic
A) perfectly competitive
B) monopolistically competitive
C) oligopolistic
D) monopolistic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
There will be a tendency for cheating to take place with a cartel if
A) the number of firms in the market is relatively small
B) the firms produce standardized products
C) the costs of production differ among firms
D) economic profits are being earned by the cartel
A) the number of firms in the market is relatively small
B) the firms produce standardized products
C) the costs of production differ among firms
D) economic profits are being earned by the cartel

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Table 6.1 Hypothetical Profit Matrix for Boeing and Airbus
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer to Table 6.1. If Boeing and Airbus behave competitively, the most likely profit is
A) $500 million for Boeing and $500 million for Airbus
B) $400 million for Boeing and $650 million for Airbus
C) $650 million for Boeing and $400 million for Airbus
D) $350 million for Boeing and $350 million for Airbus
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer to Table 6.1. If Boeing and Airbus behave competitively, the most likely profit is
A) $500 million for Boeing and $500 million for Airbus
B) $400 million for Boeing and $650 million for Airbus
C) $650 million for Boeing and $400 million for Airbus
D) $350 million for Boeing and $350 million for Airbus

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Table 6.1 Hypothetical Profit Matrix for Boeing and Airbus
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer to Table 6.1. If Boeing and Airbus form a collusive pact to maximize joint profits, the firms will realize profits totaling
A) $700 million
B) $900 million
C) $1,000 million
D) $1,050 million
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer to Table 6.1. If Boeing and Airbus form a collusive pact to maximize joint profits, the firms will realize profits totaling
A) $700 million
B) $900 million
C) $1,000 million
D) $1,050 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Table 6.1 Hypothetical Profit Matrix for Boeing and Airbus
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer to Table 6.1. Assume that Boeing adopts a low?price strategy and Airbus adopts a high?price strategy. Compared to what is realized when both firms adopt a high?price strategy,
A) Boeing's profits will rise by $100 and Airbus' profits will fall by $150
B) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
C) Boeing's profits will rise by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
D) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will fall by $150
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer to Table 6.1. Assume that Boeing adopts a low?price strategy and Airbus adopts a high?price strategy. Compared to what is realized when both firms adopt a high?price strategy,
A) Boeing's profits will rise by $100 and Airbus' profits will fall by $150
B) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
C) Boeing's profits will rise by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
D) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will fall by $150

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Table 6.1 Hypothetical Profit Matrix for Boeing and Airbus
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer Table 6.1. Assume that Boeing adopts a high?price strategy and Airbus adopts a low?price strategy. Compared to what is realized when both firms adopt a high?price strategy,
A) Boeing's profits will rise by $150 and Airbus' profits will fall by $100
B) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
C) Boeing's profits will rise by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
D) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will fall by $150
(millions of dollars in profits for high-price and low-price strategies)
-Refer Table 6.1. Assume that Boeing adopts a high?price strategy and Airbus adopts a low?price strategy. Compared to what is realized when both firms adopt a high?price strategy,
A) Boeing's profits will rise by $150 and Airbus' profits will fall by $100
B) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
C) Boeing's profits will rise by $100 and Airbus' profits will rise by $150
D) Boeing's profits will fall by $100 and Airbus' profits will fall by $150

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
A pure monopoly differs from a monopolistically competitive firm in that a monopoly
A) has a downward-sloping demand curve
B) has a downward-sloping marginal revenue curve
C) can earn economic profits in the short run
D) can earn economic profits in the long run
A) has a downward-sloping demand curve
B) has a downward-sloping marginal revenue curve
C) can earn economic profits in the short run
D) can earn economic profits in the long run

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
In a long run, freedom of entry into a market forces a ______ to charge a price equal to average total cost, but average total cost exceeds its minimum level.
A) perfectly competitive firm
B) monopolistically competitive firm
C) oligopolistic firm
D) pure monopoly
A) perfectly competitive firm
B) monopolistically competitive firm
C) oligopolistic firm
D) pure monopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A fundamental characteristic of monopolistic competition is
A) strong barriers to entry
B) that each firm considers its rivals reactions
C) product differentiation
D) the existence of just a few firms producing all the output
A) strong barriers to entry
B) that each firm considers its rivals reactions
C) product differentiation
D) the existence of just a few firms producing all the output

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Figure 6.1 Demand and Cost Conditions for a Monopolistically Competitive Firm
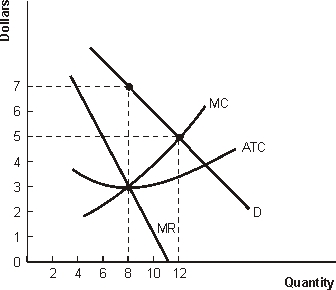
-Refer to Figure 6.1. How much output should this monopolistic competitive firm produce in order to maximize profits?
A) 0
B) 3
C) 8
D) 12

-Refer to Figure 6.1. How much output should this monopolistic competitive firm produce in order to maximize profits?
A) 0
B) 3
C) 8
D) 12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Figure 6.1 Demand and Cost Conditions for a Monopolistically Competitive Firm

-Refer to Figure 6.1. What price should this monopolistic competitive firm charge in order to maximize profits?
A) $10
B) $7
C) $5
D) $3

-Refer to Figure 6.1. What price should this monopolistic competitive firm charge in order to maximize profits?
A) $10
B) $7
C) $5
D) $3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Figure 6.1 Demand and Cost Conditions for a Monopolistically Competitive Firm

-Refer to Figure 6.1. When the firm does its best to maximize profits, it experiences
A) economic profits
B) economic losses
C) normal profits
D) breakeven profits

-Refer to Figure 6.1. When the firm does its best to maximize profits, it experiences
A) economic profits
B) economic losses
C) normal profits
D) breakeven profits

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Cartels could be present in which type of market structure?
A) monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) monopolistic competition
D) oligopoly
A) monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) monopolistic competition
D) oligopoly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Three of the following are types of mergers covered in the text. Which one is not a type of merger?
A) horizontal
B) contestable
C) vertical
D) conglomerate
A) horizontal
B) contestable
C) vertical
D) conglomerate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
An oligopolist may be reluctant to lower its price because
A) its competitors may lower their prices, too
B) this will encourage the development of new technology
C) other firms will go out of business
D) it will keep other potential competitors from entering the market
A) its competitors may lower their prices, too
B) this will encourage the development of new technology
C) other firms will go out of business
D) it will keep other potential competitors from entering the market

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which of the following is not a necessary condition for price discrimination?
A) The seller can prevent re-sale of products.
B) The market can be subdivided into groups with different sensitivities to price.
C) The seller has different costs of supplying the product to different customers.
D) The seller can control the price of the product.
A) The seller can prevent re-sale of products.
B) The market can be subdivided into groups with different sensitivities to price.
C) The seller has different costs of supplying the product to different customers.
D) The seller can control the price of the product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Barriers to entry for oligopolistic industries include all of the following except
A) ownership of key resources
B) patents
C) product differentiation and advertising
D) economic downturn and cheating
A) ownership of key resources
B) patents
C) product differentiation and advertising
D) economic downturn and cheating

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
When tickets to a rock concert are sold to students at half price, while the general public must pay full price for the same seats, this is an example of
A) price discrimination
B) game theory
C) collusion
D) monopolistic competition
A) price discrimination
B) game theory
C) collusion
D) monopolistic competition

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Suppose that a movie theater is practicing price discrimination. If students must show a college ID to get a discounted movie admission ticket, this is done in order to
A) charge a higher price to the group with more elastic demand
B) benefit the local colleges and universities
C) decrease its profit so as to prevent the entry of other movie theaters
D) prevent the resale of the movie tickets to nonstudents
A) charge a higher price to the group with more elastic demand
B) benefit the local colleges and universities
C) decrease its profit so as to prevent the entry of other movie theaters
D) prevent the resale of the movie tickets to nonstudents

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
One major reason why airline profits are falling is because the airlines
A) are engaging in price discrimination and the passengers are angry about it
B) charge vacation travelers higher prices than business travelers
C) are experiencing a decline in business travelers as electronic communication increases
D) are no longer allowed to practice price discrimination because it has been declared illegal
A) are engaging in price discrimination and the passengers are angry about it
B) charge vacation travelers higher prices than business travelers
C) are experiencing a decline in business travelers as electronic communication increases
D) are no longer allowed to practice price discrimination because it has been declared illegal

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 90 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








