Deck 9: Male and Female Urinary Tract and Male Genital Tract
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 9: Male and Female Urinary Tract and Male Genital Tract
1
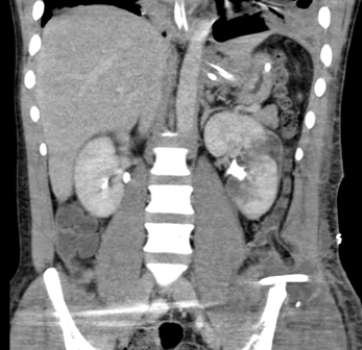 This enhanced CT image is consistent with:
This enhanced CT image is consistent with:A) a history of painless obstructive jaundice.
B) a patient with colicky left flank pain suspicious for ureteral calculus.
C) a trauma patient with a lacerated kidney.
D) an alcoholic with cirrhosis.
a trauma patient with a lacerated kidney.
2
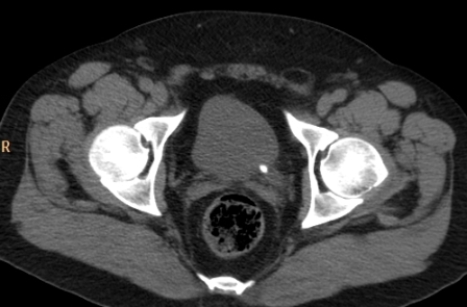 This unenhanced axial CT was performed on a patient with:
This unenhanced axial CT was performed on a patient with:A) left renal colic.
B) bloody stools.
C) infertility.
D) diarrhea.
left renal colic.
3
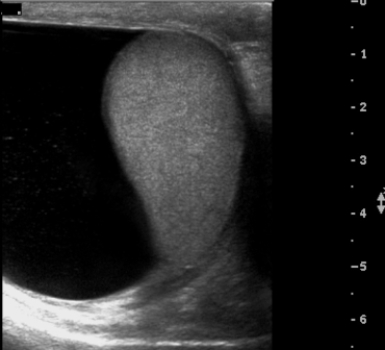 This scrotal ultrasound confirms the clinical diagnosis of:
This scrotal ultrasound confirms the clinical diagnosis of:A) varicocele.
B) epididymal cyst.
C) large hydrocele.
D) testicular tumor.
large hydrocele.
4
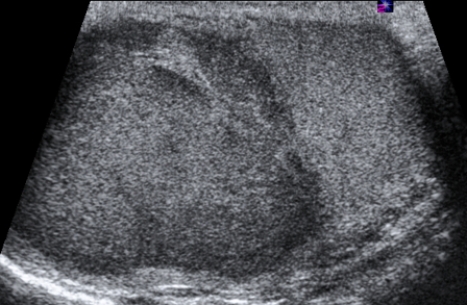 The scrotal ultrasound image illustrates which pathology?
The scrotal ultrasound image illustrates which pathology?A) Varicocele
B) Testicular tumor
C) Hydrocele
D) Microlithiasis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
When CT on a trauma patient reveals pubic diastasis and/or pubic fracture and the status of the urethra is not clearly shown on CT:
A) retrograde urethrography is typically done before attempted bladder catheterization.
B) intravenous urography is scheduled.
C) suprapubic bladder catheterization is immediately performed.
D) routine bladder catheterization is performed with ultrasound guidance.
A) retrograde urethrography is typically done before attempted bladder catheterization.
B) intravenous urography is scheduled.
C) suprapubic bladder catheterization is immediately performed.
D) routine bladder catheterization is performed with ultrasound guidance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Gadolinium-based contrast material (GBCM):
A) is potentially more nephrotoxic than iodinated contrast agents in patients with moderate renal failure.
B) cannot be used in patients with mildly compromised renal function.
C) has less risk of systemic complication than iodinated contrast material in patients with advanced renal failure and acute illness.
D) can be avoided in dialysis patients by performing CTA, rather than MRA, because the renal toxicity of iodinated contrast agents is not clinically relevant in these patients.
A) is potentially more nephrotoxic than iodinated contrast agents in patients with moderate renal failure.
B) cannot be used in patients with mildly compromised renal function.
C) has less risk of systemic complication than iodinated contrast material in patients with advanced renal failure and acute illness.
D) can be avoided in dialysis patients by performing CTA, rather than MRA, because the renal toxicity of iodinated contrast agents is not clinically relevant in these patients.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following is NOT true of renovascular hypertension?
A) Doppler measurement of peak systolic renal artery velocity above 180 cm/sec and renal artery/aorta velocity ratio above 3.5 has been considered diagnostic of hemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis.
B) CTA can directly demonstrate potentially hemodynamically significant stenoses.
C) MRA can directly demonstrate potentially hemodynamically significant stenoses.
D) renal artery stenosis greater than 50% always causes hypertension.
A) Doppler measurement of peak systolic renal artery velocity above 180 cm/sec and renal artery/aorta velocity ratio above 3.5 has been considered diagnostic of hemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis.
B) CTA can directly demonstrate potentially hemodynamically significant stenoses.
C) MRA can directly demonstrate potentially hemodynamically significant stenoses.
D) renal artery stenosis greater than 50% always causes hypertension.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements regarding imaging for ureterolithiasis is NOT true?
A) Ultrasound can demonstrate the presence of and the exact position of a ureteral calculus.
B) When a patient has a history of urinary tract calculi or a known acute ureteral calculus (diagnosed on CT), a supine abdominal radiograph (KUB) can be useful.
C) MR urography can be used in a pregnant patient to avoid radiation exposure.
D) Unenhanced CT of the abdomen and pelvis is the modality of choice in most adult cases of suspected ureteral calculus.
A) Ultrasound can demonstrate the presence of and the exact position of a ureteral calculus.
B) When a patient has a history of urinary tract calculi or a known acute ureteral calculus (diagnosed on CT), a supine abdominal radiograph (KUB) can be useful.
C) MR urography can be used in a pregnant patient to avoid radiation exposure.
D) Unenhanced CT of the abdomen and pelvis is the modality of choice in most adult cases of suspected ureteral calculus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Phleboliths:
A) are large ureteral stones that constrict surrounding veins.
B) are spherical calcifications in pelvic veins that can mimic ureteral calculi.
C) are calculi that cause hydronephrosis.
D) indicate the presence of acute pelvic thrombophlebitis.
A) are large ureteral stones that constrict surrounding veins.
B) are spherical calcifications in pelvic veins that can mimic ureteral calculi.
C) are calculi that cause hydronephrosis.
D) indicate the presence of acute pelvic thrombophlebitis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Transillumination:
A) is a modality useful for diagnosing a hydrocele.
B) is the most reliable modality for diagnosing scrotal abnormalities.
C) can accurately determine if a scrotal mass is intratesticular.
D) can determine if a testicular mass is malignant.
A) is a modality useful for diagnosing a hydrocele.
B) is the most reliable modality for diagnosing scrotal abnormalities.
C) can accurately determine if a scrotal mass is intratesticular.
D) can determine if a testicular mass is malignant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Doppler sonography:
A) is used to differentiate benign from malignant testicular masses.
B) is used for the differential diagnosis of acute epididymitis versus testicular torsion.
C) is important for the diagnosis of a hydrocele.
D) cannot determine whether a scrotal mass represents a varicocele.
A) is used to differentiate benign from malignant testicular masses.
B) is used for the differential diagnosis of acute epididymitis versus testicular torsion.
C) is important for the diagnosis of a hydrocele.
D) cannot determine whether a scrotal mass represents a varicocele.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The intravenous urogram (IVU):
A) is superior to CT for depicting renal cortical masses.
B) involves a series of radiographs obtained after the IV injection of contrast material.
C) is the procedure of choice for diagnosing urinary tract calculi.
D) is the ideal procedure for the diagnosis of bladder masses.
A) is superior to CT for depicting renal cortical masses.
B) involves a series of radiographs obtained after the IV injection of contrast material.
C) is the procedure of choice for diagnosing urinary tract calculi.
D) is the ideal procedure for the diagnosis of bladder masses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
When a renal cyst is diagnosed with CT or MRI as a Bosniak Category I lesion:
A) the patient should be told that it has malignant potential and must be investigated further.
B) the patient can be reassured that it is completely benign and requires no further follow-up imaging.
C) the patient needs to provide a complete family medical history for possible adult polycystic kidney disease (APKD).
D) the patient should be told that it is probably benign; follow-up MRI in 6 months should be scheduled.
A) the patient should be told that it has malignant potential and must be investigated further.
B) the patient can be reassured that it is completely benign and requires no further follow-up imaging.
C) the patient needs to provide a complete family medical history for possible adult polycystic kidney disease (APKD).
D) the patient should be told that it is probably benign; follow-up MRI in 6 months should be scheduled.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements regarding ultrasonography of the male urinary system is NOT true?
A) It can provide a measurement of residual bladder volume.
B) It can be used to diagnosis BPH.
C) It can identify urethral strictures.
D) It can be used to guide transrectal needle biopsy of the prostate.
A) It can provide a measurement of residual bladder volume.
B) It can be used to diagnosis BPH.
C) It can identify urethral strictures.
D) It can be used to guide transrectal needle biopsy of the prostate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In a patient with a markedly elevated PSA and symptoms suspicious for metastatic disease, you might request any of the following imaging studies EXCEPT:
A) a radionuclide bone scan.
B) CT of the abdomen and pelvis.
C) MRI of the pelvis.
D) transabdominal pelvic sonography.
A) a radionuclide bone scan.
B) CT of the abdomen and pelvis.
C) MRI of the pelvis.
D) transabdominal pelvic sonography.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 15 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








