Deck 17: Least Cost Path and Network Analysis
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 17: Least Cost Path and Network Analysis
1
Link impedance for network applications can be measured by:
A) physical length
B) travel time
C) both of these are correct
A) physical length
B) travel time
C) both of these are correct
both of these are correct
2
What is the main objective of the "vehicle routing problem"?
No Answer
3
Explain the difference between a network and a line shapefile.
No Answer
4
A shortest-path analysis can include intermediate stops between the origin and destination.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A ____ link connects a cell to one of its immediate neighbors, and a ____ link connects the cell to one of its corner neighbors.
A) lateral, diagonal
B) diagonal, lateral
A) lateral, diagonal
B) diagonal, lateral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
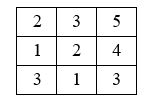
The diagram below represents a cost raster, with the origin at the upper left corner. (1) What is the cost for moving from (col. 1, row. 1) to (col. 2, row 1)? (2) What is the cost for moving from (col. 1, row. 1) to (col. 2, row 2)? (3) What is the least accumulative cost from (col. 1, row. 1) to (col. 2, row 3)?


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Least-cost path analysis is _____based, and network analysis is _____based.
A) vector, vector
B) raster, raster
C) vector, raster
D) raster, vector
A) vector, vector
B) raster, raster
C) vector, raster
D) raster, vector

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Explain the role of a source raster in least cost path analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
How does the surface distance differ from the regular (planimetric) cost distance?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Explain the difference between the minimum impedance model and the maximum coverage model for location-allocation analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The surface distance measure is calculated from a(n):
A) path raster
B) allocation raster
C) elevation raster
D) cost raster
A) path raster
B) allocation raster
C) elevation raster
D) cost raster

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In ArcGIS a network dataset can be built from:
A) a shapefile
B) a geodatabase
C) both of these are correct
A) a shapefile
B) a geodatabase
C) both of these are correct

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A raster that assigns each cell to its closest source cell on the basis of cost distance measures is called a(n):
A) allocation raster
B) none of these are correct
C) direction raster
D) shortest path raster
A) allocation raster
B) none of these are correct
C) direction raster
D) shortest path raster

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Define "allocation analysis."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In an allocation analysis, the service area of a fire station will _____ if the response time increases:
A) increase
B) decrease
A) increase
B) decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Explain the difference between the physical distance and the cost distance in distance measure operations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
One-way streets are treated as ______in network analysis:
A) link impedance
B) turn impedance
C) none of these is correct
D) restriction
A) link impedance
B) turn impedance
C) none of these is correct
D) restriction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The surface distance _______ when the elevation difference between two cells _______.
A) increases, decreases
B) increases, increases
A) increases, decreases
B) increases, increases

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The cost in a cost raster usually represents the sum of a number of cost factors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
If the speed limits are lowered (e.g., from 30 miles/hour to 20 miles/hour) on a network, then the service areas of a fire station will ________ in an allocation analysis:
A) decrease
B) increase
A) decrease
B) increase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which of the following is a common data source for building a road network in the United States?
A) Satellite imagery
B) DEM
C) DOQ
D) TIGER/Line files
A) Satellite imagery
B) DEM
C) DOQ
D) TIGER/Line files

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true about location-allocation analysis?
A) Both a location-allocation analysis requires inputs in supply, demand, and distance measures and a a model or algorithm for problem solving.
B) A location-allocation analysis requires inputs in supply, demand, and distance measures.
C) Distances may represent shortest-path distances on a road network or straight-line distances.
D) A location-allocation analysis requires a model or algorithm for problem solving.
E) All of these are correct
A) Both a location-allocation analysis requires inputs in supply, demand, and distance measures and a a model or algorithm for problem solving.
B) A location-allocation analysis requires inputs in supply, demand, and distance measures.
C) Distances may represent shortest-path distances on a road network or straight-line distances.
D) A location-allocation analysis requires a model or algorithm for problem solving.
E) All of these are correct

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What is turn impedance?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Provide an example to support the statement that a road network must have the topological relationship of connectivity before it can be used for network analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Name three network attributes that are normally needed for traffic analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Shortest-path analysis is used to solve the closest facility problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Use an example to explain how a "cost raster" is put together by using different factors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Both raster-based least cost path analysis and vector-based shortest path analysis use Dijkstra's algorithm. Explain in general terms how Dijkstra's algorithm works.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Cost distance measure operations are based on the node-link cell representation. Explain this representation with a diagram.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 29 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








