Deck 8: Radiologic Evaluation of the Temporomandibular Joint
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Radiologic Evaluation of the Temporomandibular Joint
1
What can you see in a transcranial lateral radiograph?
A) Disk displacements
B) The shape of the articular eminence
C) Hyperplasia of the posterior ligament
D) The integrity of the articular cartilage
A) Disk displacements
B) The shape of the articular eminence
C) Hyperplasia of the posterior ligament
D) The integrity of the articular cartilage
The shape of the articular eminence
2
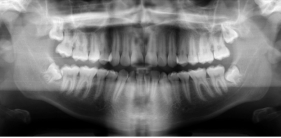
-Refer to the figure. What is the imaging method used in this image?
A) 3D scan
B) CT, soft tissue window
C) Panoramic radiograph
D) Transcranial radiograph
Panoramic radiograph
3

-How do cone beam CT (CBCT) and MRI compare for the evaluation of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)?
A) CBCT better demonstrates the intraarticular disk
B) MRI allows thinner slices
C) CBCT has better spatial resolution
D) MRI is better for evaluating cortical bone
CBCT has better spatial resolution
4

-The value of ultrasound imaging in the evaluation of the TMJ can be described in the following way:
A) It surpasses MRI for the evaluation of disk displacement
B) It can show, in real time, the position of the disk and condyle throughout the range of motion
C) It may show the subchondral bone of the condyle
D) For the detection of TMJ effusion, it does not match other imaging methods

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5

-What are the radiographic findings of osteoarthritis of the TMJ?
A) Subchondral osteoporosis
B) Abnormally smooth joint surfaces seen on CT scans
C) Osteophytes
D) Soft tissue edema and joint effusion, seen on T2 MRI

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
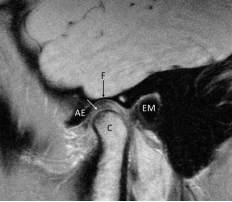
-Refer to the figure. This is a sagittal T1 MRI of a normal TMJ, made in in full occlusion. You can see the fossa (F), articular eminence (AE), external auditory meatus (EM), and the condyle (C). What is the structure the white arrow points to?
A) The superior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle
B) Articular capsule
C) Collateral ligament
D) Articular disk

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7

-What changes are associated with disk displacement?
A) Bone marrow edema seen on MRI
B) Thinning of the posterior ligament
C) Adhesion of the disk to the condyle
D) Thickening of the collateral ligaments

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
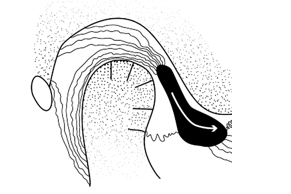
-This picture shows the articular disk (black) relative to the condyle and the articular eminence in the rest position of the TMJ. What is the position of the disk?
A) A normal position
B) A phase II displacement
C) A normal position but abnormal shape
D) A nonreducible displacement

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9

-Hypermobility of the TMJ:
A) May be present with a normal position of the articular disk relative to the condyle
B) Is diagnosed if the TMJ can open more than 30 mm
C) Can lead to impingement on the masseter muscle
D) May contribute to osteoarthritis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10

-A forward-head position cervical spine may influence the function of the TMJ because it:
A) Decreases activity in the masseter muscle
B) May lead anterior disk displacement relative to the condyle
C) Elevates the position of the hyoid bone
D) May decrease the angle of the mandible

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 10 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








