Deck 33: Electromagnetic Waves
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 33: Electromagnetic Waves
1
The Maxwell-Ampere Law can be written as . The term in the equation that relates to the magnetic field produced by the so-called displacement current is
A)
B)
C)
D) No term in this equation is related to the displacement current.
A)
B)
C)
D) No term in this equation is related to the displacement current.
2
The Maxwell-Ampere Law can be written as; . The term in the equation that relates to the magnetic field produced by an electric current is
A)
B)
C)
D) No term in this equation is related to the displacement current.
A)
B)
C)
D) No term in this equation is related to the displacement current.
3
Maxwell's equations are a compilation of the fundamental laws needed for a complete mathematical description of the behavior of electric and magnetic fields. The equation that mathematically reflects that there are no isolated magnetic poles is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)
4
Maxwell's equations are a compilation of the fundamental laws needed for a complete mathematical description of the behavior of electric and magnetic fields. The equation that mathematically reflects that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A 4.0-A current is charging a 10.0-mF capacitor. The total displacement current between the capacitor plates is
A) 4.0 A.
B) -4.0 A.
C) 0 A.
D) Not enough information is given to solve this problem.
A) 4.0 A.
B) -4.0 A.
C) 0 A.
D) Not enough information is given to solve this problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A current is used to charge a capacitor. After the capacitor has been charged, the magnetic field between the plates is
A) given by
B) given by
C) given by
D) zero.
A) given by
B) given by
C) given by
D) zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Given that the sun's intensity at the Earth's surface is 1350 W/m2, the amount of electrical energy in a cubic meter at the Earth's surface is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A parallel-plate capacitor consists of circular plates with a radius of one unit. During the charging process the magnitude of the magnetic field as a function of radius is
A)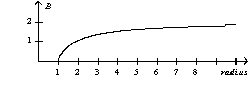
B)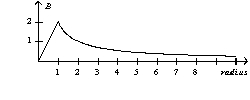
C)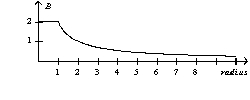
D)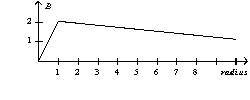
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A charge undergoes an acceleration. The tangential component of the electric field produced during the acceleration is
A) a maximum in the direction of the acceleration.
B) larger than the radial component.
C) decreasing in a manner that is proportional to 1/r2 from the source.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
E) None of the above answers is correct.
A) a maximum in the direction of the acceleration.
B) larger than the radial component.
C) decreasing in a manner that is proportional to 1/r2 from the source.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
E) None of the above answers is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The functional dependence of the transverse component of the radiation field produced by an accelerating charge as a function of distance from the charge is proportional to
A) r.
B) 1/r.
C) r2.
D) 1/r2.
E) none of the above.
A) r.
B) 1/r.
C) r2.
D) 1/r2.
E) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The functional dependence of the radial component of the field produced by an accelerating charge as a function of distance from the charge is proportional to
A) r.
B) 1/r.
C) r2.
D) 1/r2.
E) none of the above.
A) r.
B) 1/r.
C) r2.
D) 1/r2.
E) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Given a wave pulse that is traveling in the direction while its electric field is in the direction, the magnetic field is in the
A) direction.
B)
direction.
C) direction.
D) direction.
A) direction.
B)
direction.
C) direction.
D) direction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A wave pulse is traveling in the direction while its magnetic field is in the direction. The electric field is in the
A) direction.
B) direction.
C) direction.
D) direction.
A) direction.
B) direction.
C) direction.
D) direction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The Maxwell-Ampere Law can be written as . The term in the equation that does not contribute to the theoretical description of the propagation of an electromagnetic wave pulse is
A)
B)
C)
D) No term in this equation is related to the propagation of the electromagnetic wave pulse.
A)
B)
C)
D) No term in this equation is related to the propagation of the electromagnetic wave pulse.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is . The wavelength of this wave is
A) 150 nm.
B) 67 mm.
C) 1500 nm.
D) 670 nm.
A) 150 nm.
B) 67 mm.
C) 1500 nm.
D) 670 nm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A gamma ray has a wavelength of . The frequency of this wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The amplitude of the electric field of an electromagnetic wave is 6.0 10 -3 V/m. The amplitude of the magnetic field of this wave is
A) 1.8
106 T.
B) 1.8
10-11 T.
C) 1.8
10-10 T.
D) 2.0
10-11 T.
A) 1.8
106 T.
B) 1.8
10-11 T.
C) 1.8
10-10 T.
D) 2.0
10-11 T.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Unpolarized light with an intensity of I0 is traveling in the + x direction. The light is incident on a polarizer whose axis is aligned along the y axis. The light that passes through the polarizer has an intensity that is
A) (1/2)I0 with a polarization along the z axis.
B) (1/2)I0 with a polarization along the y axis.
C) I0 with a polarization along the z axis.
D) I0 with a polarization along the y axis.
A) (1/2)I0 with a polarization along the z axis.
B) (1/2)I0 with a polarization along the y axis.
C) I0 with a polarization along the z axis.
D) I0 with a polarization along the y axis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Initially polarized light is incident on a polarizer. If the intensity of the light after passing through the polarizer is (3/4) of the initial intensity, the angle between the polarizer axis and the original polarization axis of the light is
A) 41.4°.
B) 30°.
C) 48.6°.
D) 60°.
A) 41.4°.
B) 30°.
C) 48.6°.
D) 60°.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Unpolarized light of intensity I0 is incident upon the first of two polarizers. The second polarizer has its preferential direction at 50° with respect to the first polarizer. The final transmitted intensity is
A) (0.21) I0.
B) (0.41) I0.
C) (0.044) I0.
D) (0.59) I0.
A) (0.21) I0.
B) (0.41) I0.
C) (0.044) I0.
D) (0.59) I0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Unpolarized light of intensity I0 is incident upon the first of two polarizers. The final transmitted intensity is (3/8)I0. With respect to the first polarizer, the second polarizer has its preferential direction at
A) 52°.
B) 41°.
C) 38°.
D) 30°.
A) 52°.
B) 41°.
C) 38°.
D) 30°.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The following electromagnetic radiation has a wavelength that is closest to the size of automobile:
A) Radio waves
B) Infrared radiation
C) Visible radiation
D) Ultraviolet radiation
A) Radio waves
B) Infrared radiation
C) Visible radiation
D) Ultraviolet radiation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The unit associated with an energy flux is
A) joule.
B) watt/meter.
C) watt/meter2.
D) joule/meter2.
A) joule.
B) watt/meter.
C) watt/meter2.
D) joule/meter2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
At a given point the electric field is 0.25 V/m. The energy flux at this point is
A) 1.7
10-4 W/m2.
B) 2.8
10-4 W/m2.
C) 8.2
10-4 W/m2.
D) 8.2
10-5 W/m2.
A) 1.7
10-4 W/m2.
B) 2.8
10-4 W/m2.
C) 8.2
10-4 W/m2.
D) 8.2
10-5 W/m2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The direction the wave is traveling in is
A)
B)
C) -
D)
A)
B)
C) -
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The axis of polarization of the wave is
A)
B)
C) -
D)
A)
B)
C) -
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The frequency of the wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The wavelength of the wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The wave number of the magnetic field associated with this wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The magnitude of the magnetic field associated with this wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
An electromagnetic wave has an electric field given by . The direction of the polarization of the magnetic field associated with this wave is
A)
B)
C)
D) Hold on. The wave is not polarized.
A)
B)
C)
D) Hold on. The wave is not polarized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The speed of radio waves traveling in a vacuum depends on
A) the wavelength of the waves.
B) the frequency of the waves.
C) the polarization of the waves.
D) none of the above.
A) the wavelength of the waves.
B) the frequency of the waves.
C) the polarization of the waves.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A pressure of is due to sunlight being reflected from a surface of a "solar sail." The energy flux incident on the surface is
A) 1125 W/m2.
B) 2250 W/m2.
C) 4500 W/m2.
D) 9000 W/m2.
A) 1125 W/m2.
B) 2250 W/m2.
C) 4500 W/m2.
D) 9000 W/m2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A pressure of is due to sunlight being absorbed by a surface of a "solar sail." The energy flux incident on the surface is
A) 1125 W/m2.
B) 2250 W/m2.
C) 4500 W/m2.
D) 9000 W/m2.
A) 1125 W/m2.
B) 2250 W/m2.
C) 4500 W/m2.
D) 9000 W/m2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A wave has double the amplitude of a second wave. The energy density of the second wave is
A) four times that of the first wave.
B) double that of the first wave.
C) equal to that of the first wave.
D) half that of the first wave.
E) one-quarter that of the first wave.
A) four times that of the first wave.
B) double that of the first wave.
C) equal to that of the first wave.
D) half that of the first wave.
E) one-quarter that of the first wave.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
An electromagnetic wave with an electric field amplitude of 0.15 V/m has an intensity of
A)
B)
C) .
D) .
A)
B)
C) .
D) .

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A spherical wave spreads out from a source, and the total power at a distance of R0 is P0. At a distance of 2R0 the power is
A) P0/8.
B) P0/4.
C) P0/2.
D) P0.
A) P0/8.
B) P0/4.
C) P0/2.
D) P0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A spherical wave spreads out from a source, and the energy flux at a distance of R0 is S0. At a distance of 2R0 the energy flux is
A) S0/8.
B) S0/4.
C) S0/2.
D) S0.
A) S0/8.
B) S0/4.
C) S0/2.
D) S0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An electromagnetic wave consists of
A) only an electric field.
B) only a magnetic field.
C) an electric field and a magnetic field oriented parallel to each other.
D) an electric field and a magnetic field oriented perpendicular to each other.
A) only an electric field.
B) only a magnetic field.
C) an electric field and a magnetic field oriented parallel to each other.
D) an electric field and a magnetic field oriented perpendicular to each other.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The direction of propagation of an electromagnetic wave is given by
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Stationary charges produce
A) electromagnetic waves.
B) only magnetic fields.
C) only electric fields.
D) both electric and magnetic fields.
A) electromagnetic waves.
B) only magnetic fields.
C) only electric fields.
D) both electric and magnetic fields.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Accelerating charges produce
A) electromagnetic standing waves.
B) only magnetic fields.
C) only electric fields.
D) both electric and magnetic fields.
A) electromagnetic standing waves.
B) only magnetic fields.
C) only electric fields.
D) both electric and magnetic fields.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
is related to the speed of light and the permeability of free space through the relation
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A satellite 300 km above the surface of the Earth emits a radio wave pulse ( = 25m). The transit time for the wave to reach the surface of the Earth is
A) 1 s.
B) 10 s.
C) 100 s.
D) 1 ms.
A) 1 s.
B) 10 s.
C) 100 s.
D) 1 ms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Consider a 150-W incandescent lightbulb that radiates light in all directions. At a distance of 1.5 m the time-averaged energy flux emitted by the bulb is
A) 7.9 W/m2.
B) 5.3 W/m2.
C) 100 W/m2.
D) 67 W/m2.
A) 7.9 W/m2.
B) 5.3 W/m2.
C) 100 W/m2.
D) 67 W/m2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Consider a 150-W incandescent lightbulb that radiates light in all directions. At a distance of 1.5 m the amplitude of the oscillating electric field E0 is
A) 77 V/m.
B) 63 V/m.
C) 225 V/m.
D) 39 V/m.
A) 77 V/m.
B) 63 V/m.
C) 225 V/m.
D) 39 V/m.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Consider a 150-W incandescent lightbulb that radiates light in all directions. At a distance of 1.5 m the amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field B0 is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The electric field component of an electromagnetic wave is 130 V/m. The electric energy density of the wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The magnetic field component of an electromagnetic wave is 25 . The electric energy density of the wave is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Radiation from a source is striking a surface at a rate of 50 W/m2. The peak value of the electric field is
A) 110 V/m.
B) 150 V/m.
C) 190 V/m.
D) 250 V/m.
A) 110 V/m.
B) 150 V/m.
C) 190 V/m.
D) 250 V/m.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








