Deck 24: Gauss Law
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 24: Gauss Law
1
A solid sphere with a radius of one unit has a uniform charge distribution. The graph of the electric field as a function of radius has the form of
A)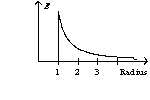
B)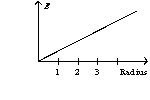
C)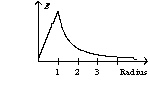
D)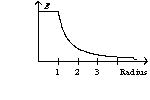
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
A cubic box with sides of length a is located with its center at the origin. A constant electric field is in the + x direction. The side of the cube, which has a zero flux is
A) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = -a/2.
B) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = a/2.
C) parallel to the x-z plane located at y = a/2.
D) Hold on. All of the above have a nonzero flux.
A) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = -a/2.
B) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = a/2.
C) parallel to the x-z plane located at y = a/2.
D) Hold on. All of the above have a nonzero flux.
parallel to the x-z plane located at y = a/2.
3
Charge is placed on a conductor and allowed to reach an equilibrium state. The following statements are correct except
A) the electric field lines are normal to the surface.
B) the charge resides on the surface of the conductor.
C) the net electric field in the conductor is zero.
D) Hold on. All of the above statements are correct.
A) the electric field lines are normal to the surface.
B) the charge resides on the surface of the conductor.
C) the net electric field in the conductor is zero.
D) Hold on. All of the above statements are correct.
Hold on. All of the above statements are correct.
4
A solid sphere with a radius of one unit has a charge on its surface. The graph of the electric field as a function of the sphere's radius has the form of
A)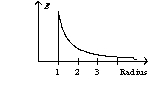
B)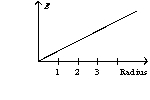
C)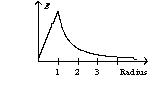
D)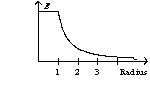
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Six equal charges, Q, are represented by circles and are arranged as illustrated here. The contributions to the net flux through the rectangle boundary include
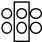
A) none of the charges.
B) all six charges.
C) the two charges enclosed by the boundary.
D) the four charges outside the boundary.

A) none of the charges.
B) all six charges.
C) the two charges enclosed by the boundary.
D) the four charges outside the boundary.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
An infinitely long wire with a radius of one unit has a charge on its surface. The graph of the electric field as a function of the radius has the form of
A)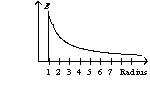
B)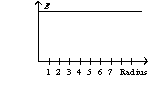
C)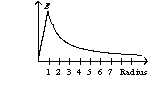
D)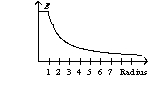
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
An electron and a proton are enclosed inside a Gaussian surface. The net flux produced by the pair is
A) zero.
B) positive.
C) negative.
D) none of the above.
A) zero.
B) positive.
C) negative.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Two oppositely charged conducting plates have surface charge densities of + and - respectively. If the two plates are located at x = +1 and -1 unit, the graph of the resulting electric field is best represented by
A)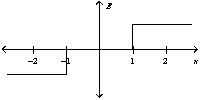
B)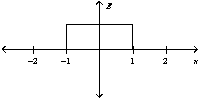
C)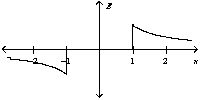
D)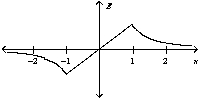
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The electric flux due to a constant electric field is
A) a vector.
B) a scalar.
C) always zero.
D) none of the above.
A) a vector.
B) a scalar.
C) always zero.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The electric flux in metric units is
A) [newton]/[meter]2/[coulomb].
B) [newton]·[meter]/[coulomb]2.
C) [newton]·[meter]/[coulomb].
D) [newton]·[meter]2/[coulomb].
A) [newton]/[meter]2/[coulomb].
B) [newton]·[meter]/[coulomb]2.
C) [newton]·[meter]/[coulomb].
D) [newton]·[meter]2/[coulomb].

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The units [coulomb]/[meter] are associated with the
A) linear charge density.
B) surface charge density.
C) volume charge density.
D) none of the above.
A) linear charge density.
B) surface charge density.
C) volume charge density.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The units [coulomb]/[meter]2 are associated with the
A) linear charge density.
B) surface charge density.
C) volume charge density.
D) none of the above.
A) linear charge density.
B) surface charge density.
C) volume charge density.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
An infinite, insulating slab of thickness d = 1 unit has a uniform volume charge density with x = 0 at the center of the slab. The graph of the electric field as a function of distance from the origin can be best represented by
A)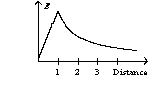
B)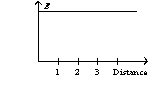
C)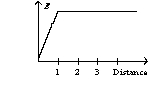
D)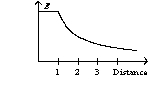
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A single electron enclosed inside a Gaussian surface produces
A) no net flux.
B) a net positive flux.
C) a net negative flux.
D) none of the above.
A) no net flux.
B) a net positive flux.
C) a net negative flux.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A single electron located outside a Gaussian surface produces
A) no net flux.
B) a net positive flux.
C) a net negative flux.
D) none of the above.
A) no net flux.
B) a net positive flux.
C) a net negative flux.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A charge is initially surrounded by a cubic Gaussian surface whose volume is d3. The cubic surface is replaced by a spherical surface of radius d/2. The net flux of the spherical surface is
A) greater than the net flux through the cube.
B) less than the net flux through the cube.
C) equal to the net flux through the cube.
D) none of the above.
A) greater than the net flux through the cube.
B) less than the net flux through the cube.
C) equal to the net flux through the cube.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A uniform electric field is directed along the positive y axis. A net flux of 5.00 104 N.m2/C passes through a surface whose area is 400.0 cm2 and is aligned along the x-z plane. The magnitude of the electric field is
A) zero.
B) 1.25 106 N/C.
C) 2.50 105 N/C.
D) 1.25 102 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 1.25 106 N/C.
C) 2.50 105 N/C.
D) 1.25 102 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A uniform electric field is directed along the positive y axis. If the magnitude of the electric field is 5.00 106 N/C, the electric flux through a 400.0-cm2 surface aligned along the x-z plane is
A) zero.
B) 2.00 105 N.m2/C.
C) 2.00 104 N.m2/C.
D) 1.20 105 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 2.00 105 N.m2/C.
C) 2.00 104 N.m2/C.
D) 1.20 105 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A uniform electric field is directed along the positive y axis. If the magnitude of the electric field is 5.00 106 N/C, the electric flux through a 400.0 cm2 surface aligned along the y-z plane is
A) zero.
B) 2.00 105 N.m2/C.
C) 2.00 104 N.m2/C.
D) 1.20 105 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 2.00 105 N.m2/C.
C) 2.00 104 N.m2/C.
D) 1.20 105 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A uniform electric field is directed along the positive y axis. The magnitude of the electric field is 5.0 106 N/C. The electric flux through a surface whose area is 400.0 cm2 and intersects the x-z plane at a 60° angle is
A) zero.
B) 1.0 105 N.m2/C.
C) 1.7 105 N.m2/C.
D) 1.7 106 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 1.0 105 N.m2/C.
C) 1.7 105 N.m2/C.
D) 1.7 106 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Two point charges, +12 C and -6.0 C, are placed inside a cube whose volume is 2.0 cm3. The net electric flux through the surface of the cube due to these charges is
A) 6.8 * 105 N·m2/C.
B) 6.8 *106 N·m2/C.
C) 6.8 * 107 N·m2/C.
D) zero.
A) 6.8 * 105 N·m2/C.
B) 6.8 *106 N·m2/C.
C) 6.8 * 107 N·m2/C.
D) zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A net flux of 1.7 *106 N.m2/C is produced by a set of point charges inside a cube whose side length is 0.10 m. The set of charges that can produce this flux is .
A) -20 C, +8 C, -3 C.
B) 20 C, -8 C, +3 C.
C) 10 C, -5 C, -4 C.
D) -10 C, -8 C, -3 C.
A) -20 C, +8 C, -3 C.
B) 20 C, -8 C, +3 C.
C) 10 C, -5 C, -4 C.
D) -10 C, -8 C, -3 C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A solid metal cylinder is placed in a uniform electric field that is directed along the axis of the cylinder. The electric field in the cylinder
A) is directed parallel to the axis of the cylinder.
B) is directed along the radius of the cylinder.
C) will vary along the length of the cylinder.
D) is zero.
A) is directed parallel to the axis of the cylinder.
B) is directed along the radius of the cylinder.
C) will vary along the length of the cylinder.
D) is zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A +10.0- C charge is placed on the surface of a metal shell whose radius is 5.0 cm. The electric field at the center of the shell is
A) zero.
B) 9.0 106 N/C.
C) -9.0 106 N/C.
D) 1.4 105 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 9.0 106 N/C.
C) -9.0 106 N/C.
D) 1.4 105 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A +10.0- C charge is placed on the surface of a metal shell whose radius is 5.0 cm. The electric field at a point 5.0 cm from the surface of the shell is
A) zero.
B) 9.0 106 N/C.
C) -9.0 106 N/C.
D) 1.4 105 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 9.0 106 N/C.
C) -9.0 106 N/C.
D) 1.4 105 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The vector normal to the plane defined by the points (1, 0, 0), (0, 2, 0) and parallel to the z axis is
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) k.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) k.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The vector that is normal to the plane defined by the points (3, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0), and (0, 0, 4) is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The unit-normal vector to the plane defined by the points (0, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0), and (1, 3, 1) is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The unit-normal vector to the plane defined by the points (-2, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0), and (0, 0, 3) is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A surface, whose area is 0.10 m2 and normal, is given by ; it intersects with an electric field given by E= N/C. The electric flux through this surface is
A) zero.
B) 0.50 105 N.m2/C.
C) 1.0 105 N.m2/C.
D) 2.0 105 N.m2/C.
E) 4.0 105 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 0.50 105 N.m2/C.
C) 1.0 105 N.m2/C.
D) 2.0 105 N.m2/C.
E) 4.0 105 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A surface, whose area is 0.10 m2 and normal, is given by ; it intersects an electric field given by E = N/C. The electric flux through this surface is
A) zero.
B) 0.50 N·m2/C.
C) 1.0 N·m2/C.
D) 2.0 N·m2/C.
E) 4.0 N·m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 0.50 N·m2/C.
C) 1.0 N·m2/C.
D) 2.0 N·m2/C.
E) 4.0 N·m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A surface, whose area is 0.10 m2 and normal, is given by ; it intersects an electric field given by E = N/C. The electric flux through this surface is
A) zero.
B) 0.50 N.m2/C.
C) 1.0 N.m2/C.
D) 2.0 N.m2/C.
E) 4.0 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 0.50 N.m2/C.
C) 1.0 N.m2/C.
D) 2.0 N.m2/C.
E) 4.0 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A charge of 10.0 C is placed on a corner of a cube. The flux through one of the sides opposite to the corner where the charge is placed is
A) 1.0 104 N.m2/C.
B) 2.3 104 N.m2/C.
C) 4.7 104 N.m2/C.
D) 5.5 104 N.m2/C.
A) 1.0 104 N.m2/C.
B) 2.3 104 N.m2/C.
C) 4.7 104 N.m2/C.
D) 5.5 104 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A surface that has an area of 0.20 m2 lies on a plane whose normal is perpendicular to the plane defined by the points (3, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0), and (0, 0, 3). The surface intersects with an electric field given by 8.5 105 N/C. The magnitude of the electric flux through the surface is
A) zero.
B) 9.0 105 N.m2/C.
C) 1.9 106 N.m2/C.
D) 4.0 106 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 9.0 105 N.m2/C.
C) 1.9 106 N.m2/C.
D) 4.0 106 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A surface that has an area of 0.20 m2 lies on a plane whose normal is perpendicular to the plane defined by the points (2, 1, 0), (0, 1, -1), and (1, 0, 2). The surface intersects with an electric field given by 4.5 * 105 N/C. The electric flux through the surface is
A) zero.
B) 1.0 * 106 N.m2/C.
C) 2.0* 106 N.m2/C.
D) 4.0 *106 N.m2/C.
A) zero.
B) 1.0 * 106 N.m2/C.
C) 2.0* 106 N.m2/C.
D) 4.0 *106 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The magnitude of the electric field 10.0 cm from an infinitely long charged wire that has a linear charge density of 1.1 C/m is
A) 1.0 105 N/C.
B) 2.0 105 N/C.
C) 3.0 105 N/C.
D) 4.0 105 N/C.
A) 1.0 105 N/C.
B) 2.0 105 N/C.
C) 3.0 105 N/C.
D) 4.0 105 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A cylindrical wire of radius 1.0 cm has charge distributed throughout its volume with a uniform charge density of 10 C/m3. The electric field at a point 0.50 cm from the central axis of the wire is
A) zero.
B) 2.8 103 N/C.
C) 5.6 103 N/C.
D) 8.4 103 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 2.8 103 N/C.
C) 5.6 103 N/C.
D) 8.4 103 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A cylindrical wire of radius 1.0 cm has charge distributed throughout its volume with a uniform charge density of 10.0 C/m3. The electric field at a point 0.50 cm from the surface of the wire is
A) zero.
B) 3.8 103 N/C.
C) 7.6 103 N/C.
D) 11 103 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 3.8 103 N/C.
C) 7.6 103 N/C.
D) 11 103 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An infinitely long cylinder with a radius of 1.0 cm has a charge density that is proportional to the distance from the axis of symmetry, = ar, where a = 10.0 C/m4. The charge per unit length within the cylinder is
A) 12 C/m.
B) 21 C/m.
C) 35 C/m.
D) 5.0 C/m.
A) 12 C/m.
B) 21 C/m.
C) 35 C/m.
D) 5.0 C/m.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
An infinitely long cylinder with a radius of 1.0 cm has a charge density that is proportional to the distance from the axis of symmetry, = ar, where a = 10.0 C/m4. The electric field 1.0 cm from the surface of the cylinder is
A) 1.5 106 N/C.
B) 1.0 107 N/C.
C) 1.5 107 N/C.
D) 1.9 107 N/C.
A) 1.5 106 N/C.
B) 1.0 107 N/C.
C) 1.5 107 N/C.
D) 1.9 107 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
An infinitely long cylinder with a radius of 1.0 cm has a charge density that is proportional to the distance from the axis of symmetry, = ar, where a = 10.0 C/m4. The electric field 0.50 cm from the central axis of the cylinder is
A) 1.4 106 N/C.
B) 5.4 106 N/C.
C) 9.4 106 N/C.
D) 1.4 107 N/C.
A) 1.4 106 N/C.
B) 5.4 106 N/C.
C) 9.4 106 N/C.
D) 1.4 107 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A solid sphere of radius 10.0 cm has a total charge of 10.0 C on its surface. The electric field 10.0 cm from the surface of the sphere is
A) 9.00 106 N/C.
B) 2.25 106 N/C.
C) 4.50 106 N/C.
D) 4.50 105 N/C.
A) 9.00 106 N/C.
B) 2.25 106 N/C.
C) 4.50 106 N/C.
D) 4.50 105 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The net electrical flux through a spherical Gaussian surface of radius 1.0 cm is 24 N.m2/C. If the radius of the surface is doubled to 2.0 cm, the electric flux will become
A) 24 N.m2/C.
B) 12 N.m2/C.
C) 6.0 N.m2/C.
D) 3.0 N.m2/C.
A) 24 N.m2/C.
B) 12 N.m2/C.
C) 6.0 N.m2/C.
D) 3.0 N.m2/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The electric field produced by a sheet of charge varies according to the distance d from the surface by the relationship
A) E proportional to d.
B) E proportional to 1/d.
C) E proportional to 1/d2.
D) Hold on! E is a constant.
A) E proportional to d.
B) E proportional to 1/d.
C) E proportional to 1/d2.
D) Hold on! E is a constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A flat conducting surface with a charge density of 10.0 C/m2 produces an electric field. The magnitude of the electric field 15 cm from the surface is
A) zero.
B) 0.55 * 106 N/C.
C) 1.1 * 106 N/C.
D) 2.2 *106 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 0.55 * 106 N/C.
C) 1.1 * 106 N/C.
D) 2.2 *106 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A flat conducting slab with a charge density of 10.0 C/m2 produces an electric field. The magnitude of the electric field 15 cm from the surface is
A) zero.
B) 0.55 * 106 N/C.
C) 1.1 * 106 N/C.
D) 2.2 * 106 N/C.
A) zero.
B) 0.55 * 106 N/C.
C) 1.1 * 106 N/C.
D) 2.2 * 106 N/C.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The electric field at the surface of a charged conductor
A) is parallel to the surface.
B) is perpendicular to the surface.
C) is parallel and perpendicular to the surface.
D) depends on the curvature of the surface.
A) is parallel to the surface.
B) is perpendicular to the surface.
C) is parallel and perpendicular to the surface.
D) depends on the curvature of the surface.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The charge on a conductor
A) is distributed throughout the material.
B) produces a nonzero electric field in the conductor.
C) is on the surface of the conductor.
D) is not in an equilibrium state.
A) is distributed throughout the material.
B) produces a nonzero electric field in the conductor.
C) is on the surface of the conductor.
D) is not in an equilibrium state.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A cubic box with sides of length a is located with its center at the origin. A constant electric field is in the + x direction. The side of the cube that has a negative flux is
A) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = -a/2.
B) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = a/2.
C) parallel to the x-z plane located at y = a/2.
D) parallel to the x-z plane located at y = -a/2.
A) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = -a/2.
B) parallel to the y-z plane located at x = a/2.
C) parallel to the x-z plane located at y = a/2.
D) parallel to the x-z plane located at y = -a/2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 49 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








