Deck 8: Conservation of Energy
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Conservation of Energy
1
A 3.2-kg mass is placed at the top of a rough incline( ). The incline makes an angle of 32º with the horizontal, and the height of the incline is 2.5 m. The gravitational potential energy of the mass at the top of the incline is
A) 55 J.
B) 78 J.
C) 46 J.
D) 36 J.
A) 55 J.
B) 78 J.
C) 46 J.
D) 36 J.
78 J.
2
A 3.2-kg mass is placed at the top of a rough incline( ). The incline makes an angle of 32º with the horizontal, and the height of the incline is 2.5 m. The kinetic energy of the mass at the top of the incline is
A) 0 J.
B) 39 J.
C) 78 J.
D) 44 J.
A) 0 J.
B) 39 J.
C) 78 J.
D) 44 J.
0 J.
3
A 3.2-kg mass is placed at the top of a rough incline ( ). The incline makes an angle of 32º with the horizontal, and the height of the incline is 2.5 m. The mass is released and slides down to the bottom. The velocity of the mass at the bottom is
A) 7.0 m/s.
B) 6.8 m/s.
C) 6.6 m/s.
D) 6.4 m/s.
A) 7.0 m/s.
B) 6.8 m/s.
C) 6.6 m/s.
D) 6.4 m/s.
6.4 m/s.
4
A 3.2-kg mass is placed at the top of a rough incline ( ). The incline makes an angle of 32º with the horizontal, and the height of the incline is 2.5 m. The mass is released and slides down to the bottom. The amount of mechanical energy lost is
A) 0 J.
B) 13 J.
C) 4.5 J.
D) 9.8 J.
A) 0 J.
B) 13 J.
C) 4.5 J.
D) 9.8 J.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A 3.2-kg mass is placed at the top of a rough incline ( ). The incline makes an angle of 32º with the horizontal, and the height of the incline is 2.5 m. The mass is released and slides down to the bottom. The kinetic energy of the mass at the bottom is
A) 78 J.
B) 13 J.
C) 66 J.
D) 23 J.
A) 78 J.
B) 13 J.
C) 66 J.
D) 23 J.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A 5.6-kg mass is held 5 cm above the end of a vertically oriented linear spring ( N/m). The mass is released. The maximum distance that the spring is compressed by the mass is
A) 3.6 cm.
B) 7.5 cm.
C) 13 cm.
D) 11 cm.
A) 3.6 cm.
B) 7.5 cm.
C) 13 cm.
D) 11 cm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A 5.6-kg mass is held 5 cm above the end of a vertically oriented linear spring ( N/m). The mass is released; it falls, compressing the spring. The spring then expands and does work on the mass. The velocity of the mass as it leaves the spring (in the upward direction) is
A) 1 m/s.
B) 3 m/s.
C) 4 m/s.
D) 2 m/s.
A) 1 m/s.
B) 3 m/s.
C) 4 m/s.
D) 2 m/s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A nonlinear spring stores potential energy according to , where and are constants and is the distance that the spring is either stretched or compressed. The force that would be required to compress this spring a distance is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The force to compress a nonlinear spring is given by , where . The amount of energy stored in this spring when it is compressed is
A) 450 J.
B) 220 J.
C) 45 J.
D) 15 J.
A) 450 J.
B) 220 J.
C) 45 J.
D) 15 J.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A 1.2-kg mass is attached to the end of a 4.5-m string; the other end of the string is attached to the ceiling (forming a pendulum). The mass is lifted 15 cm (above its lowest point) and then released. The mass freely swings back and forth. The maximum velocity of the mass is
A) 1.7 m/s.
B) 1.2 m/s.
C) 2.2 m/s.
D) 2.6 m/s.
A) 1.7 m/s.
B) 1.2 m/s.
C) 2.2 m/s.
D) 2.6 m/s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A steel spring having spring constant and length is placed in series with a brass spring having spring constant and length . The two springs are then inserted into a vise (in a coaxial arrangement), and the vise squeezes the springs a distance . The entire length of the compressed steel spring is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
A solid ball having a mass of 2.6 kg and a radius of 0.2 m is placed at the top of an incline. The height of the incline is 3.0 m. The ball is then released and rolls without slipping down the incline. The translational velocity of the ball at the bottom of the incline is
A) 7.7 m/s.
B) 6.5 m/s.
C) 8.2 m/s.
D) 6.9 m/s.
A) 7.7 m/s.
B) 6.5 m/s.
C) 8.2 m/s.
D) 6.9 m/s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A solid ball having a mass of 2.6 kg and a radius of 0.2 m is placed at the top of an incline. The height of the incline is 3.0 m. The ball is then released and rolls without slipping down the incline. The rotational velocity of the ball at the bottom of the incline is
A) 32 rad/s.
B) 26 rad/s.
C) 19 rad/s.
D) 12 rad/s.
A) 32 rad/s.
B) 26 rad/s.
C) 19 rad/s.
D) 12 rad/s.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A solid ball having a mass of 2.6 kg and a radius of 0.2 m is placed at the top of an incline. The incline makes an angle of = 51º with the horizontal. The ball is then released and rolls without slipping down the incline. The acceleration of the ball's center of mass along the incline is
A) 6.9 m/s
B) 6.3 m/s
C) 4.5 m/s
D) 5.4 m/s
A) 6.9 m/s
B) 6.3 m/s
C) 4.5 m/s
D) 5.4 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A solid ball having a mass of 2.6 kg and a radius of 0.2 m is placed at the top of an incline. The incline makes an angle of = 51º with the horizontal. The ball is then released and rolls without slipping down the incline. The frictional force that the incline exerts on the (rolling) ball is
A) 20 N.
B) 5.7 N.
C) 7.9 N.
D) 0.0 N.
A) 20 N.
B) 5.7 N.
C) 7.9 N.
D) 0.0 N.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Two objects of differing masses are released from the top of two frictionless inclines having the same height. Mass is on an incline that makes an angle of with the horizontal; mass is on an incline that makes an angle of with the horizontal. At the bottom, the mass that has the greater speed is
A)
B)
C) Both masses have the same speed.
D) This cannot be determined unless both masses ( ) are known.
A)
B)
C) Both masses have the same speed.
D) This cannot be determined unless both masses ( ) are known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Two objects of differing masses are placed at the top of two frictionless inclines having the same height. Mass is on an incline that makes an angle of with the horizontal; mass is on an incline that makes an angle of with the horizontal. The masses are released at the same time. The mass that has the greater acceleration along the incline is:
A)
B)
C) Both masses have the same acceleration.
D) This cannot be determined unless both masses ( ) are known.
A)
B)
C) Both masses have the same acceleration.
D) This cannot be determined unless both masses ( ) are known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Two objects of differing masses are placed at the top of two frictionless inclines having the same height. Mass is on an incline that makes an angle of with the horizontal; mass is on an incline that makes an angle of with the horizontal. The masses are released at the same time. The mass that reaches the bottom first is
A)
B)
C) Both masses reach the bottom at the same time.
D) This cannot be determined unless both the masses ( ) are known.
A)
B)
C) Both masses reach the bottom at the same time.
D) This cannot be determined unless both the masses ( ) are known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A solid ball of mass and radius is placed at the top of a smooth, frictionless incline. Another solid ball of equal mass and equal radius is placed at the top of a rough incline. Both inclines have the same height and the same angle. The balls are released. At the bottom, the ball that has the greater total kinetic energy is
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both have the same.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both have the same.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
A solid ball of mass and radius is placed at the top of a smooth, frictionless incline. Another solid ball of equal mass and equal radius is placed at the top of a rough incline. Both inclines have the same height and the same angle. The balls are released. At the bottom, the ball that has the greater translational kinetic energy is
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both have the same.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both have the same.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A solid ball of mass and radius is placed at the top of a smooth, frictionless incline. Another solid ball of equal mass and equal radius is placed at the top of a rough incline. Both inclines have the same height and the same angle. The balls are released. At the bottom, the ball that has the greater rotational kinetic energy is
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both have the same.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both have the same.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A solid ball of mass and radius is placed at the top of a smooth, frictionless incline. Another solid ball of equal mass and equal radius is placed at the top of a rough incline. Both inclines have the same height and the same angle. The balls are released at the same time. The ball that reaches the bottom first is
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both reach the bottom at the same time.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.
A) ball A.
B) ball B.
C) Both reach the bottom at the same time.
D) This cannot be determined unless of the rough incline is known.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
An object of mass initially at rest is acted upon by a single force over a distance of . The final velocity of the mass is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
An object of mass initially at rest is acted upon by a single force over a distance of . The final kinetic energy of the object is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
An object of mass initially at rest is acted upon by a single force over a distance of . If the single force is the weight of the object, and the distance that the object moved was its original height , the final kinetic energy of the object is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A conservative force
A) may do net work on a body that moves no net distance during the application of the force.
B) may change the speed of a body that moves no net distance during the application of the force.
C) may do net work on a body undergoing motion confined to a direction perpendicular to the direction of the force.
D) may change the direction of motion of a body that moves no net distance during the application of the force.
A) may do net work on a body that moves no net distance during the application of the force.
B) may change the speed of a body that moves no net distance during the application of the force.
C) may do net work on a body undergoing motion confined to a direction perpendicular to the direction of the force.
D) may change the direction of motion of a body that moves no net distance during the application of the force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
For a conservative force F, all of the following are correct except
A) the line integral of F around a closed path is zero.
B) the line integral of F between points A and B by way of point C is independent of point C.
C) the line integral of F with limits A and B is independent of the order of the limits.
D) there exists an associated potential energy function.
A) the line integral of F around a closed path is zero.
B) the line integral of F between points A and B by way of point C is independent of point C.
C) the line integral of F with limits A and B is independent of the order of the limits.
D) there exists an associated potential energy function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A) gravitational.
B) kinetic.
C) normal.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
All of the following are acceptable dimensions for energy except
A) kilowatt-hours.
B) kilocalories.
C) kilograms.
D) electron-volts.
A) kilowatt-hours.
B) kilocalories.
C) kilograms.
D) electron-volts.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Power has the same dimensions as all of the following except
A) [force] x [speed].
B) [work] x [acceleration].
C) [energy] / [time].
D) none of the above.
A) [force] x [speed].
B) [work] x [acceleration].
C) [energy] / [time].
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Force has the same dimensions as all of the following except
A) BTUs/foot.
B) kilograms-meters/second2.
C) watt-feet.
D) horsepower/(feet/second).
A) BTUs/foot.
B) kilograms-meters/second2.
C) watt-feet.
D) horsepower/(feet/second).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
For a small body in contact with and sliding down a frictionless surface of a large stationary sphere, all of the following are dependent on the location of the body on the sphere except
A) the radius of the path.
B) the angle the surface of contact makes with horizontal.
C) the height above the bottom point of the sphere.
D) none of the above.
A) the radius of the path.
B) the angle the surface of contact makes with horizontal.
C) the height above the bottom point of the sphere.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
For a small body in contact with and sliding down a frictionless surface of a large stationary sphere, all of the following depend on the location of the body on the sphere except
A) the gravitational potential energy of the small body.
B) the speed of the body.
C) the velocity of the body.
D) none of the above.
A) the gravitational potential energy of the small body.
B) the speed of the body.
C) the velocity of the body.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
For a small body in contact with and sliding down the surface of a large stationary sphere, if friction is introduced , the distance along the sphere before the small body loses contact is
A) greater than the distance for the frictionless case.
B) equal to the distance for the frictionless case.
C) less than the distance for the frictionless case.
D) unknown; insufficient information is given to determine the answer.
A) greater than the distance for the frictionless case.
B) equal to the distance for the frictionless case.
C) less than the distance for the frictionless case.
D) unknown; insufficient information is given to determine the answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The potential energy U is related to the (conservative) force F by an equation of the form
A) U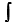 F · dr.
F · dr.
B) U 11ef2d7c_8600_0f4c_a6da_1197495b9a7b_TBN1003_11 Fr dt.
C) U dFr/dr.
D) U dFr/dt.
A) U
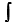 F · dr.
F · dr.B) U 11ef2d7c_8600_0f4c_a6da_1197495b9a7b_TBN1003_11 Fr dt.
C) U dFr/dr.
D) U dFr/dt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The (conservative) force FY is related to the potential energy U by an equation of the form
A) FY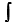 U dy.
U dy.
B) FY 11ef2d7c_8600_0f4c_a6da_1197495b9a7b_TBN1003_11U dt.
C) FY dU/dy.
D) FY dU/dt.
A) FY
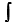 U dy.
U dy.B) FY 11ef2d7c_8600_0f4c_a6da_1197495b9a7b_TBN1003_11U dt.
C) FY dU/dy.
D) FY dU/dt.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If the force exerted by a spring is given by Fz = -kz, then the potential energy associated with the spring is given by U
A) kz2.
B) k + a constant.
C) -kz + a constant.
D) kz3.
A) kz2.
B) k + a constant.
C) -kz + a constant.
D) kz3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
If a force of 1 newton is required to compress a spring 1 meter, the potential energy stored in a spring compressed 2 meters from its uncompressed length is (in joules)
A) 0.5.
B) 1.0.
C) 2.0.
D) 4.0.
A) 0.5.
B) 1.0.
C) 2.0.
D) 4.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If the total potential energy stored in a spring compressed 2 centimeters from its uncompressed length is 20.0 joules, the total potential energy stored in a spring compressed an additional 1 centimeter is (in joules)
A) 10.0.
B) 22.5.
C) 45.0.
D) 67.5.
A) 10.0.
B) 22.5.
C) 45.0.
D) 67.5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The magnitude of the additional potential energy stored in a spring stretched an additional 2 centimeters from some designated reference length
A) increases as that reference length increases beyond the unstretched length.
B) increases as that reference length increases beyond any length.
C) remains unchanged as that reference length increases beyond the unstretched length.
D) remains unchanged as that reference length increases beyond any length.
A) increases as that reference length increases beyond the unstretched length.
B) increases as that reference length increases beyond any length.
C) remains unchanged as that reference length increases beyond the unstretched length.
D) remains unchanged as that reference length increases beyond any length.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The justification for your previous response depends on the fact that
A) the force required to stretch a spring increases as the length of stretching increases.
B) the force required to stretch a spring increases as the absolute length of the spring increases.
C) the force required to stretch a spring remains unchanged as the length of stretching increases.
D) the force required to stretch a spring remains unchanged as the absolute length of the spring increases.
A) the force required to stretch a spring increases as the length of stretching increases.
B) the force required to stretch a spring increases as the absolute length of the spring increases.
C) the force required to stretch a spring remains unchanged as the length of stretching increases.
D) the force required to stretch a spring remains unchanged as the absolute length of the spring increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
When a mass hanging vertically from a spring attached to the ceiling is in stable equilibrium, the two forms of energy for the system that are at a minimum are
A) the total energy and the kinetic energy.
B) the kinetic energy and the gravitational potential energy.
C) the gravitational potential energy and the spring potential energy.
D) none of the above.
A) the total energy and the kinetic energy.
B) the kinetic energy and the gravitational potential energy.
C) the gravitational potential energy and the spring potential energy.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
When a mass hanging vertically from a spring attached to the ceiling is in stable equilibrium, the two forms of energy for the system that are at a minimum are
A) the total energy and the gravitational potential energy.
B) the kinetic energy and the spring potential energy.
C) the spring potential energy and the total energy.
D) none of the above.
A) the total energy and the gravitational potential energy.
B) the kinetic energy and the spring potential energy.
C) the spring potential energy and the total energy.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
When nonconservative forces are included in a system, energy conservation equations
A) hold just as before.
B) hold, with modification by including thermal energy changes.
C) no longer hold, no matter how modified.
D) Hold it! Nonconservative forces cannot (by definition) be included in the analysis of a system.
A) hold just as before.
B) hold, with modification by including thermal energy changes.
C) no longer hold, no matter how modified.
D) Hold it! Nonconservative forces cannot (by definition) be included in the analysis of a system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Two common forms of energy that cannot be negative are
A) total energy and kinetic energy.
B) kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy.
C) gravitational potential energy and spring potential energy.
D) none of the above.
A) total energy and kinetic energy.
B) kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy.
C) gravitational potential energy and spring potential energy.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Two common forms of energy that cannot be negative are
A) total energy and gravitational potential energy.
B) kinetic energy and spring potential energy.
C) spring potential energy and total energy.
D) none of the above.
A) total energy and gravitational potential energy.
B) kinetic energy and spring potential energy.
C) spring potential energy and total energy.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The mechanical power delivered by a force F that moves a body at a velocity v is given by
A) F v.
B) F · v.
C) F/v.
D) v/F.
A) F v.
B) F · v.
C) F/v.
D) v/F.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The proper relationship between power P and work W is
A) P = dW/dt.
B) W = dP/dt.
C) Either of the first two responses is valid, depending on the circumstances.
D) Neither of the first two responses is valid.
A) P = dW/dt.
B) W = dP/dt.
C) Either of the first two responses is valid, depending on the circumstances.
D) Neither of the first two responses is valid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The relationship between kilowatt-hours and joules is
A) 3.6 x 106 kilowatt-hours = 1 joule.
B) 3.6 x 106 joules = 1 kilowatt-hour.
C) 1/3600 kilowatt-hours = 1 joule.
D) 1/3600 joules = 1 kilowatt-hour.
A) 3.6 x 106 kilowatt-hours = 1 joule.
B) 3.6 x 106 joules = 1 kilowatt-hour.
C) 1/3600 kilowatt-hours = 1 joule.
D) 1/3600 joules = 1 kilowatt-hour.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The equation E = mc2 implies all of the following except that
A) energy must travel at the speed of light.
B) any mass has energy.
C) any energy has mass.
D) none of the above.
A) energy must travel at the speed of light.
B) any mass has energy.
C) any energy has mass.
D) none of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








