Deck 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
1
Find the domain of the rational function f (x) = ![<strong>Find the domain of the rational function f (x) = .</strong> A) (-?, -2) ? (-2, ?) B) [25, ?) C) (-?, 2] ? [2, ?) D) (-?, 2) ? (2, ?)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696c_1308_8ef4_4d8227d9efd1_TBW1040_11.jpg) .
.
A) (-?, -2) ? (-2, ?)
B) [25, ?)
C) (-?, 2] ? [2, ?)
D) (-?, 2) ? (2, ?)
![<strong>Find the domain of the rational function f (x) = .</strong> A) (-?, -2) ? (-2, ?) B) [25, ?) C) (-?, 2] ? [2, ?) D) (-?, 2) ? (2, ?)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696c_1308_8ef4_4d8227d9efd1_TBW1040_11.jpg) .
.A) (-?, -2) ? (-2, ?)
B) [25, ?)
C) (-?, 2] ? [2, ?)
D) (-?, 2) ? (2, ?)
(-?, 2) ? (2, ?)
2
Find the domain of the rational function.
F (x) =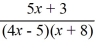
A) (-?, -8) ? (8, ?)
B) (-?, -8) ? (-8, 5/4) ? (5/4, ?)
C) (-8, 5/4)
D) (-?, -3/5) ? (3/5, ?)
F (x) =
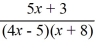
A) (-?, -8) ? (8, ?)
B) (-?, -8) ? (-8, 5/4) ? (5/4, ?)
C) (-8, 5/4)
D) (-?, -3/5) ? (3/5, ?)
(-?, -8) ? (-8, 5/4) ? (5/4, ?)
3
Find the domain of the rational function f (x) = 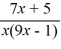 .
.
A) (-?, 1/9) ? (1/9, ?)
B) (-?, 0) ? (0, 1/9) ? (1/9, ?)
C) (1/9, ?)
D) (-?, -5/7) ? (-5/7, ?)
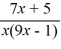 .
.A) (-?, 1/9) ? (1/9, ?)
B) (-?, 0) ? (0, 1/9) ? (1/9, ?)
C) (1/9, ?)
D) (-?, -5/7) ? (-5/7, ?)
(-?, 0) ? (0, 1/9) ? (1/9, ?)
4
Find the domain of the function f (x) = ![<strong>Find the domain of the function f (x) = .</strong> A) (-?, 6) ? (9, ?) B) (-?, -9) ? (-9, -6) ? (-6, ?) C) (-?, 6) ? (6, 9) ? (6, ?) D) (-?, 6] ? [6, 9] ? [6, ?)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696c_130b_8ef4_e1b813d246b1_TBW1040_11.jpg) .
.
A) (-?, 6) ? (9, ?)
B) (-?, -9) ? (-9, -6) ? (-6, ?)
C) (-?, 6) ? (6, 9) ? (6, ?)
D) (-?, 6] ? [6, 9] ? [6, ?)
![<strong>Find the domain of the function f (x) = .</strong> A) (-?, 6) ? (9, ?) B) (-?, -9) ? (-9, -6) ? (-6, ?) C) (-?, 6) ? (6, 9) ? (6, ?) D) (-?, 6] ? [6, 9] ? [6, ?)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696c_130b_8ef4_e1b813d246b1_TBW1040_11.jpg) .
.A) (-?, 6) ? (9, ?)
B) (-?, -9) ? (-9, -6) ? (-6, ?)
C) (-?, 6) ? (6, 9) ? (6, ?)
D) (-?, 6] ? [6, 9] ? [6, ?)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Find the domain of the function f (x) = 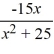 .
.
A) (-5, 5)
B) (-?, -5) ? (-5, 5) ? (5, ?)
C) (-?, -5) ? (5, ?)
D) (-?, ?)
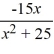 .
.A) (-5, 5)
B) (-?, -5) ? (-5, 5) ? (5, ?)
C) (-?, -5) ? (5, ?)
D) (-?, ?)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
For the rational function f (x) = 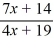 , find all the vertical asymptotes and horizontal asymptotes.
, find all the vertical asymptotes and horizontal asymptotes.
A)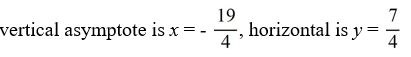
B)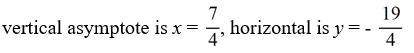
C)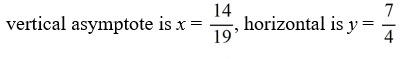
D)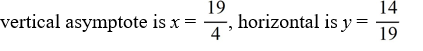
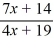 , find all the vertical asymptotes and horizontal asymptotes.
, find all the vertical asymptotes and horizontal asymptotes.A)
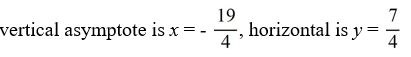
B)
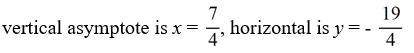
C)
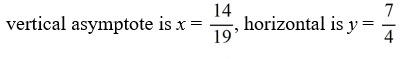
D)
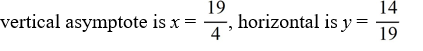

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
For the rational function f (x) = 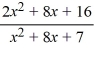 , find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.
, find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.
A) vertical asymptotes x = -1 and x = -7, horizontal asymptote y = 2
B) vertical asymptotes x = -1 and x = -7, horizontal asymptote y =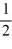
C) no vertical asymptotes, horizontal asymptote y = 2
D) vertical asymptotes x = 1 and x = 7, horizontal asymptote y =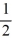
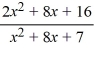 , find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.
, find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.A) vertical asymptotes x = -1 and x = -7, horizontal asymptote y = 2
B) vertical asymptotes x = -1 and x = -7, horizontal asymptote y =
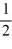
C) no vertical asymptotes, horizontal asymptote y = 2
D) vertical asymptotes x = 1 and x = 7, horizontal asymptote y =
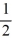

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
For the rational function f (x) = 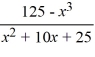 , find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.
, find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.
A) vertical asymptote at 5, there is no horizontal asymptote
B) vertical asymptote at -5, horizontal asymptote at 5
C) vertical asymptote at -5, there is no horizontal asymptote
D) vertical asymptote at 5, horizontal asymptote at -5
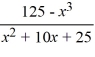 , find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.
, find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes.A) vertical asymptote at 5, there is no horizontal asymptote
B) vertical asymptote at -5, horizontal asymptote at 5
C) vertical asymptote at -5, there is no horizontal asymptote
D) vertical asymptote at 5, horizontal asymptote at -5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Professor Ito is teaching a large lecture course and is trying to learn students' names. The number of names he can remember, N(t), increases with each week in the semester, t, and is given by the rational function:N(t) = 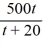 How many students' names does Professor Ito know by the fourth week of the semester? How many students' names should he know by the end of the semester (16 weeks)? Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
How many students' names does Professor Ito know by the fourth week of the semester? How many students' names should he know by the end of the semester (16 weeks)? Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
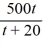 How many students' names does Professor Ito know by the fourth week of the semester? How many students' names should he know by the end of the semester (16 weeks)? Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
How many students' names does Professor Ito know by the fourth week of the semester? How many students' names should he know by the end of the semester (16 weeks)? Round your answer to the nearest whole number.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Use the graphing strategy to graph the rational function.
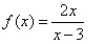
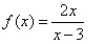

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Match the rational function to the graph.
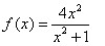
A)
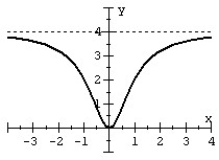
B)
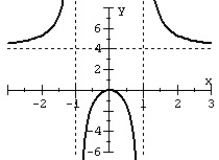
C)
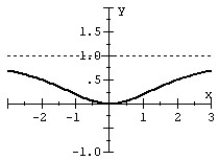
D)
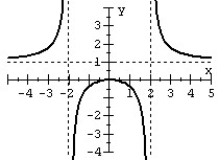
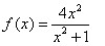
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Match the graph to the rational function.
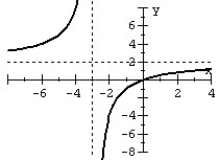
A)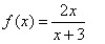
B)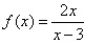
C)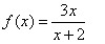
D)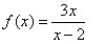

A)
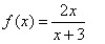
B)
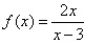
C)
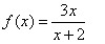
D)
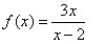

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
For the given graph of the rational function determine: (a) all intercepts, (b) all asymptotes, and (c) equation of the rational function.
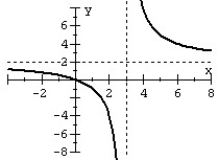


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
For the given graph of the rational function determine: (a) all intercepts, (b) all asymptotes, and (c) equation of the rational function.
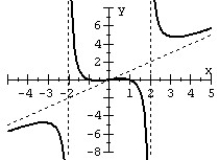
A)

B)
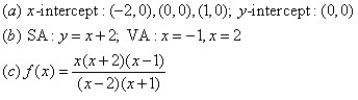
C)
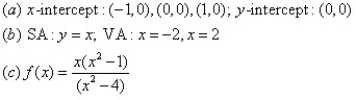
D)
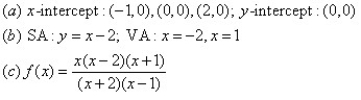

A)

B)
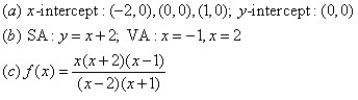
C)
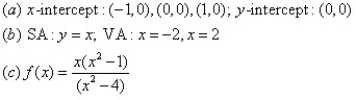
D)
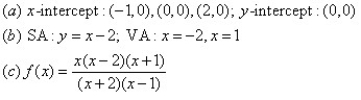

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
For the rational function f (x) = 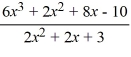 , find the equation of the slant asymptote.
, find the equation of the slant asymptote.
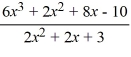 , find the equation of the slant asymptote.
, find the equation of the slant asymptote.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
For the rational function f (x) = 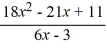 , find the equation of the slant asymptote.
, find the equation of the slant asymptote.
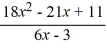 , find the equation of the slant asymptote.
, find the equation of the slant asymptote.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Use the graphing strategy to graph the rational function.
f (x) =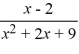
f (x) =
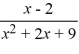


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Use the graphing strategy to graph the rational function.
f (x) =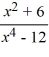
f (x) =
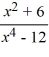


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Use the graphing strategy to graph the rational function.
f (x) =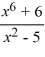
f (x) =
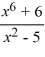


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Find all zeros (real and complex). Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors.
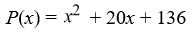
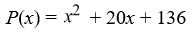

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Find all zeros (real and complex). Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors.
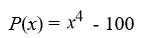
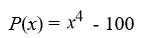

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Find all zeros (real and complex). Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors.
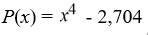
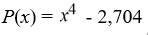

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Given a zero of the polynomial, determine all other zeros (real and complex) and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors.
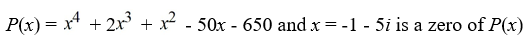
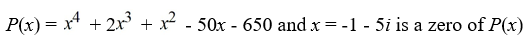

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Given a zero of the polynomial, determine all other zeros (real and complex) and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors. ![<strong>Given a zero of the polynomial, determine all other zeros (real and complex) and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors. </strong> A) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x + 7) B) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x - 7) C) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x - 7) D) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x + 7)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696d_24ad_8ef4_69b5ed0db9bf_TBW1040_00.jpg)
A) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x + 7)
B) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x - 7)
C) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x - 7)
D) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x + 7)
![<strong>Given a zero of the polynomial, determine all other zeros (real and complex) and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors. </strong> A) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x + 7) B) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x - 7) C) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x - 7) D) x = 2 - i, -2, 7; P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x + 7)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696d_24ad_8ef4_69b5ed0db9bf_TBW1040_00.jpg)
A) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x + 7)
B) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x - 7)
C) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x - 2)(x - 7)
D) x = 2 - i, -2, 7;
P(x) = [x - (2 + i)][x - (2 - i)](x + 2)(x + 7)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors.
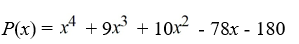
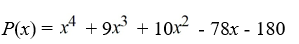

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors. ![<strong>Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors. </strong> A) P(x) = [x + (-5 + 3i)][x + (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4) B) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x + 5)(x + 4) C) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x - 4) D) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696d_4bbf_8ef4_25276e6eccc4_TBW1040_00.jpg)
A) P(x) = [x + (-5 + 3i)][x + (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4)
B) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x + 5)(x + 4)
C) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x - 4)
D) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4)
![<strong>Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors. </strong> A) P(x) = [x + (-5 + 3i)][x + (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4) B) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x + 5)(x + 4) C) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x - 4) D) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696d_4bbf_8ef4_25276e6eccc4_TBW1040_00.jpg)
A) P(x) = [x + (-5 + 3i)][x + (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4)
B) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x + 5)(x + 4)
C) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x - 4)
D) P(x) = [x - (-5 + 3i)][x - (-5 - 3i)](x - 5)(x + 4)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors.
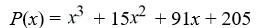
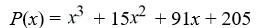

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors. ![<strong>Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors. </strong> A) P(x) = [x + (2 - 3i)][x + (2 + 3i)](x - 1) B) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x + 1) C) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x - 1) D) P(x) = [x - (-2 - 3i)][x + (-2 + 3i)](x + 1)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696d_72d1_8ef4_5dac60e1a057_TBW1040_00.jpg)
A) P(x) = [x + (2 - 3i)][x + (2 + 3i)](x - 1)
B) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x + 1)
C) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x - 1)
D) P(x) = [x - (-2 - 3i)][x + (-2 + 3i)](x + 1)
![<strong>Factor the polynomial as a product of linear factors. </strong> A) P(x) = [x + (2 - 3i)][x + (2 + 3i)](x - 1) B) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x + 1) C) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x - 1) D) P(x) = [x - (-2 - 3i)][x + (-2 + 3i)](x + 1)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBW1040/11ee60ed_696d_72d1_8ef4_5dac60e1a057_TBW1040_00.jpg)
A) P(x) = [x + (2 - 3i)][x + (2 + 3i)](x - 1)
B) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x + 1)
C) P(x) = [x - (2 - 3i)][x - (2 + 3i)](x - 1)
D) P(x) = [x - (-2 - 3i)][x + (-2 + 3i)](x + 1)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has these zeros.
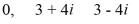
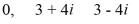

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has these zeros.
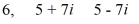
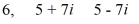

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has these zeros.
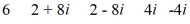
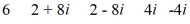

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
For the polynomial f (x) = 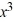 + 3
+ 3 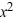 - 5x + 3, use synthetic division to find f (-3).
- 5x + 3, use synthetic division to find f (-3).
A) -18
B) -12
C) 18
D) 12
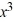 + 3
+ 3 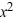 - 5x + 3, use synthetic division to find f (-3).
- 5x + 3, use synthetic division to find f (-3).A) -18
B) -12
C) 18
D) 12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
For the polynomial function f (x) = 5 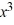 +3x - 7, use synthetic division to find f (6).
+3x - 7, use synthetic division to find f (6).
A) 1091
B) 1104
C) 1182
D) 6
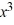 +3x - 7, use synthetic division to find f (6).
+3x - 7, use synthetic division to find f (6).A) 1091
B) 1104
C) 1182
D) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Determine whether the number 2 is a zero of f (x) = 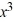 + 5
+ 5 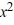 - 22x + 16. If it is, find the other real zeros.
- 22x + 16. If it is, find the other real zeros.
A) 2 is not a zero.
B) 2 is a zero and the others are 1 and -8.
C) 2 is a zero and the others are -1 and 8.
D) 2 is a zero and there are no other real zeros.
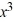 + 5
+ 5 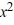 - 22x + 16. If it is, find the other real zeros.
- 22x + 16. If it is, find the other real zeros.A) 2 is not a zero.
B) 2 is a zero and the others are 1 and -8.
C) 2 is a zero and the others are -1 and 8.
D) 2 is a zero and there are no other real zeros.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Determine whether the number -7 is a zero of f (x) = 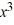 + 3
+ 3 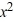 - 36x + 32. If it is, find the other real zeros.
- 36x + 32. If it is, find the other real zeros.
A) -7 is not a zero.
B) -7 is a zero and the others are 3 and -36.
C) -7 is a zero and the other is 32.
D) -7 is a zero and there are no other real zeros.
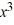 + 3
+ 3 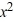 - 36x + 32. If it is, find the other real zeros.
- 36x + 32. If it is, find the other real zeros.A) -7 is not a zero.
B) -7 is a zero and the others are 3 and -36.
C) -7 is a zero and the other is 32.
D) -7 is a zero and there are no other real zeros.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Determine whether -5 is a zero of the polynomial. If it is, then find the other real zeros.P(x) = 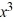 + 4
+ 4 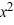 - 4x + 5
- 4x + 5
A) -5 is not a zero.
B) -5 is a zero and the other zeros are 4 and -4.
C) -5 is a zero and the other is 5.
D) -5 is a zero and there are no other real zeros.
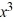 + 4
+ 4 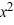 - 4x + 5
- 4x + 5A) -5 is not a zero.
B) -5 is a zero and the other zeros are 4 and -4.
C) -5 is a zero and the other is 5.
D) -5 is a zero and there are no other real zeros.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Given that 4 is a zero of the polynomial P(x) = 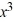 - 11
- 11 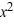 + 34x - 24, determine all other zeros.
+ 34x - 24, determine all other zeros.
A) -6 and 1
B) 6 and 1
C) -6 and -1
D) 6 and -1
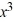 - 11
- 11 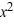 + 34x - 24, determine all other zeros.
+ 34x - 24, determine all other zeros.A) -6 and 1
B) 6 and 1
C) -6 and -1
D) 6 and -1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Use Descartes' rule of signs to determine the possible number of positive real zeros and negative real zeros. 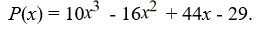
A)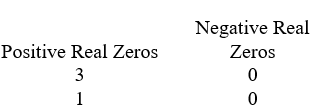
B)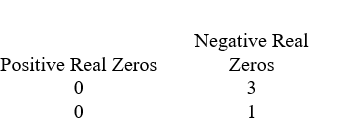
C)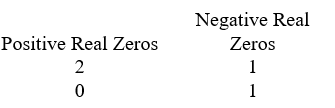
D)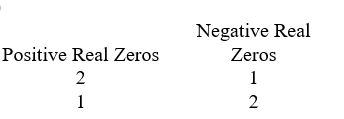
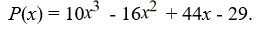
A)
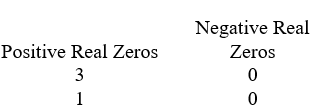
B)
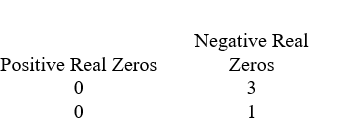
C)
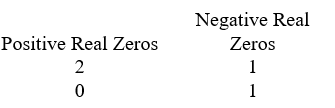
D)
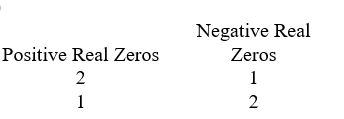

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Use Descartes' rule of signs to determine the possible number of positive real zeros and negative real zeros. 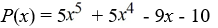
A)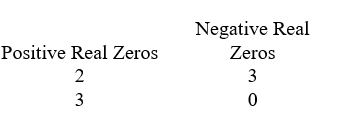
B)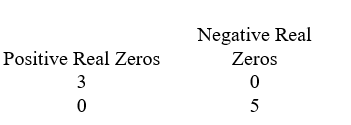
C)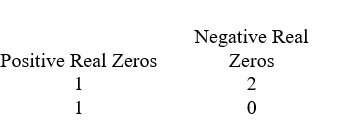
D)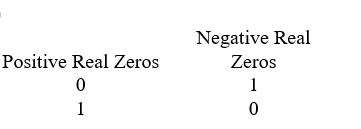
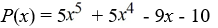
A)
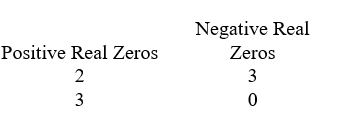
B)
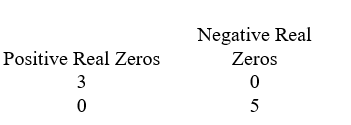
C)
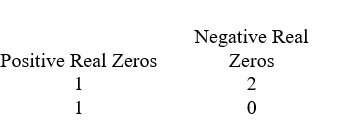
D)
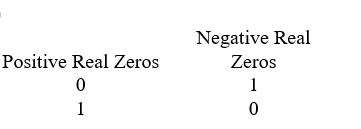

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Use Descartes' rule of signs to determine the possible number of positive real zeros and negative real zeros. 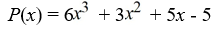
A)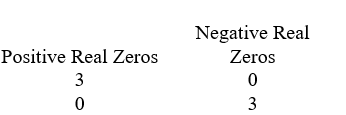
B)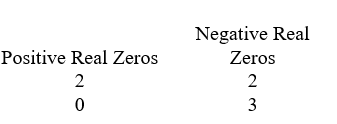
C)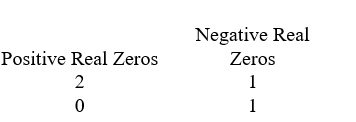
D)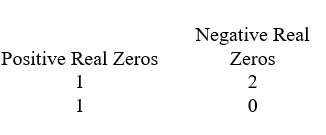
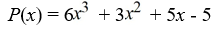
A)
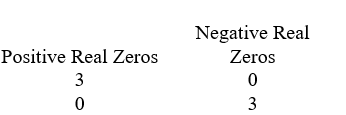
B)
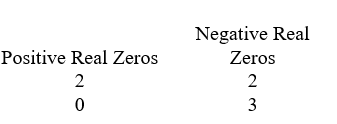
C)
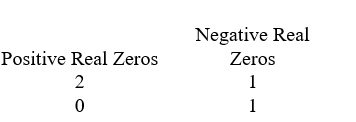
D)
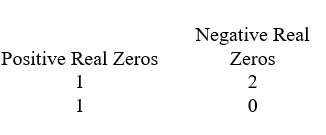

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Use Descartes' rule of signs to determine the possible number of positive real zeros, negative real zeros, and imaginary zeros. 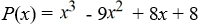
A)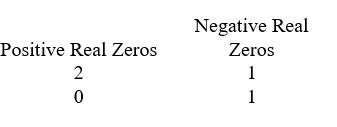
B)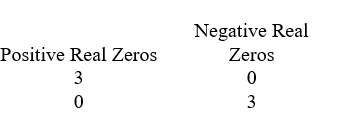
C)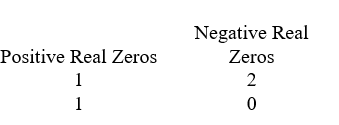
D)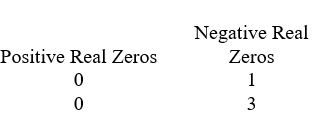
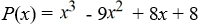
A)
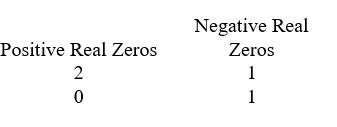
B)
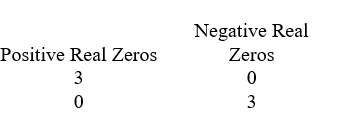
C)
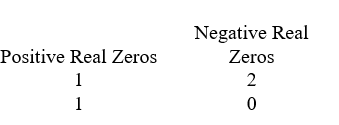
D)
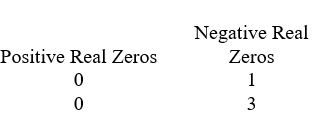

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Use the rational zero theorem to list the possible rational zeros of the polynomial 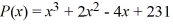
A) {±1/3, ±1/11, ±1/7, ±1/33, ±1/77, ±1/21, ±1/231}
B) {±1, ±3, ±11, ±7}
C) {±1, ±3, ±11, ±7, ±33, ±77, ±21, ±231}
D) {±1/3, ±1/11, ±1/7}
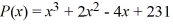
A) {±1/3, ±1/11, ±1/7, ±1/33, ±1/77, ±1/21, ±1/231}
B) {±1, ±3, ±11, ±7}
C) {±1, ±3, ±11, ±7, ±33, ±77, ±21, ±231}
D) {±1/3, ±1/11, ±1/7}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Use the rational zero theorem to list the possible rational zeros. 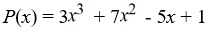
A) {±1, ±3}
B) {±1}
C) {±1, ±1/7}
D) {±1, ±1/3}
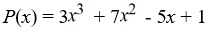
A) {±1, ±3}
B) {±1}
C) {±1, ±1/7}
D) {±1, ±1/3}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Use the rational zero theorem to list the possible rational zeros. 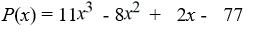
A) {±1, ±1/11, ±7/11}
B) {±1, ±11, ±7, ±77}
C) {±1, ±11, ±7, ±77, ±1/11, ±7/11}
D) {±1, ±11, ±7}
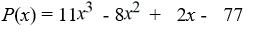
A) {±1, ±1/11, ±7/11}
B) {±1, ±11, ±7, ±77}
C) {±1, ±11, ±7, ±77, ±1/11, ±7/11}
D) {±1, ±11, ±7}

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Given that -4 is a zero of the polynomial P(x) = 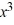 + 7
+ 7 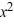 + 14x + 8, determine all other zeros and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors.
+ 14x + 8, determine all other zeros and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors.
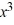 + 7
+ 7 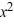 + 14x + 8, determine all other zeros and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors.
+ 14x + 8, determine all other zeros and write the polynomial in terms of a product of linear factors.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Use the rational zero theorem to list the possible rational zeros. 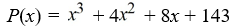

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Use the intermediate value theorem to approximate the real zero in the indicated interval. Approximate to two decimal places if necessary.r 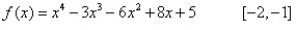

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Use the rational zero theorem to list the possible rational zeros.P(x) = 4 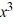 - 8
- 8 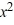 + 11x - 55
+ 11x - 55
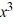 - 8
- 8 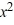 + 11x - 55
+ 11x - 55
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Use Descartes' rule of signs to determine the possible number of positive real zeros, negative real zeros, and imaginary zeros.P(x) = 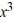 - 3
- 3 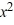 + 3x + 6
+ 3x + 6
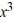 - 3
- 3 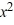 + 3x + 6
+ 3x + 6
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Use Descartes' rule of signs along with the rational root theorem to sketch a graph of the polynomial. 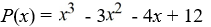

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Use long division to divide the polynomials. Express the answers in the form of 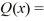 and
and 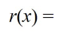
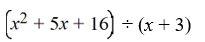
A) Q(x) = x + 2; r(x) = 10
B) Q(x) = x + 2; r(x) = 0
C) Q(x) =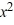 + 4x + 13; r(x) = 10
+ 4x + 13; r(x) = 10
D) Q(x) = x + 2; r(x) = -10
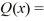 and
and 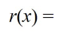
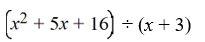
A) Q(x) = x + 2; r(x) = 10
B) Q(x) = x + 2; r(x) = 0
C) Q(x) =
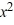 + 4x + 13; r(x) = 10
+ 4x + 13; r(x) = 10D) Q(x) = x + 2; r(x) = -10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Use long division to divide 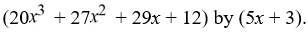
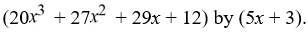

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Use long division to divide 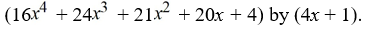
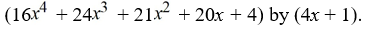

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Compute the following using synthetic division. 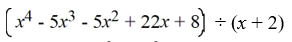
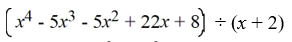

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Divide the polynomials by either long division or synthetic division. 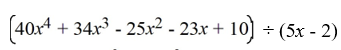
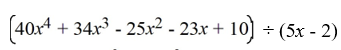

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Divide the polynomials. 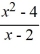
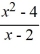

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Divide the polynomials. 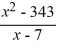
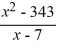

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Divide the polynomials by either long division or synthetic division. 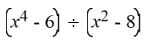
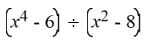

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The area of a rectangle is 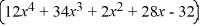 . If the width of the rectangle is
. If the width of the rectangle is 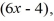 find the length.
find the length.
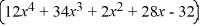 . If the width of the rectangle is
. If the width of the rectangle is 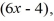 find the length.
find the length.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Determine if the function is a polynomial. 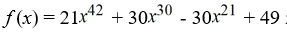 If it is, state the degree.
If it is, state the degree.
A) Not a polynomial
B) a polynomial of degree 21
C) a polynomial of degree 42
D) a polynomial of degree 4
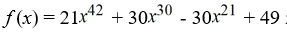 If it is, state the degree.
If it is, state the degree.A) Not a polynomial
B) a polynomial of degree 21
C) a polynomial of degree 42
D) a polynomial of degree 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Determine if the function f 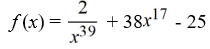 is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
A) Not a polynomial
B) a polynomial of degree 17
C) a polynomial of degree 39
D) a polynomial of degree -39
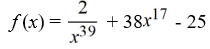 is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.A) Not a polynomial
B) a polynomial of degree 17
C) a polynomial of degree 39
D) a polynomial of degree -39

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Determine if the function 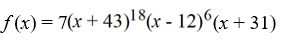 is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree
is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree
A) Not a polynomial
B) a polynomial of degree 18
C) a polynomial of degree 7
D) a polynomial of degree 25
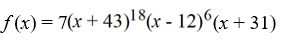 is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree
is a polynomial. If it is, state the degreeA) Not a polynomial
B) a polynomial of degree 18
C) a polynomial of degree 7
D) a polynomial of degree 25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Find all the real zeros (and state their multiplicity) of the polynomial function. 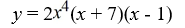
A) 0, -7, 1
B) -7, 1
C) 0 (multiplicity 4), -7, and 1
D) 0 (multiplicity 4), 7, and -1
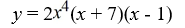
A) 0, -7, 1
B) -7, 1
C) 0 (multiplicity 4), -7, and 1
D) 0 (multiplicity 4), 7, and -1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Find all the real zeros (and state their multiplicity) of the polynomial function. 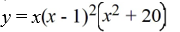
A) 0, 1 (multiplicity 2)
B) 0, -1, (multiplicity 2)
C) 1, 1, (multiplicity 2), 20 (multiplicity 2)
D) 0, 1 (multiplicity 2),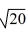
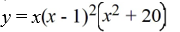
A) 0, 1 (multiplicity 2)
B) 0, -1, (multiplicity 2)
C) 1, 1, (multiplicity 2), 20 (multiplicity 2)
D) 0, 1 (multiplicity 2),
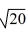

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Find all the real zeros (and state their multiplicity) of the polynomial function. 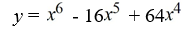
A) 0, 8
B) 0 (multiplicity 4), 8 (multiplicity 2)
C) 8 (multiplicity 2)
D) 0 (multiplicity 6), 8 (multiplicity 2)
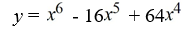
A) 0, 8
B) 0 (multiplicity 4), 8 (multiplicity 2)
C) 8 (multiplicity 2)
D) 0 (multiplicity 6), 8 (multiplicity 2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Find a polynomial of minimum degree with zeros 4, -3 and 5 (of multiplicity 2).
A)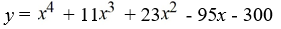
B)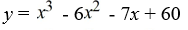
C)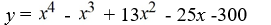
D)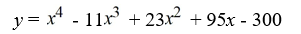
A)
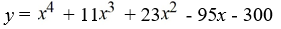
B)
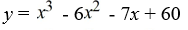
C)
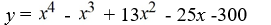
D)
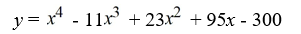

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has zeros -9, 0 (multiplicity 2) and 7.
A)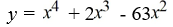
B)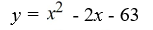
C)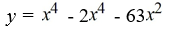
D)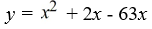
A)
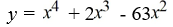
B)
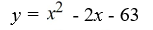
C)
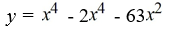
D)
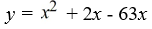

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Find a polynomial of minimum degree with zeros 0, 10 + 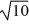 , and 10 -
, and 10 - 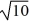 .
.
A)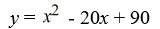
B)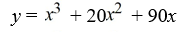
C)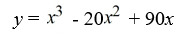
D)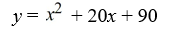
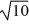 , and 10 -
, and 10 - 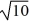 .
.A)
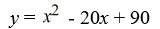
B)
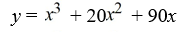
C)
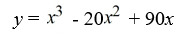
D)
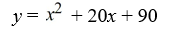

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has the zeros 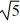 (with multiplicity 2) and -
(with multiplicity 2) and - 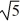 (with multiplicity 2).
(with multiplicity 2).
A)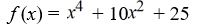
B)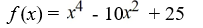
C)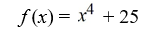
D)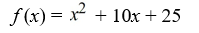
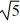 (with multiplicity 2) and -
(with multiplicity 2) and - 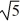 (with multiplicity 2).
(with multiplicity 2).A)
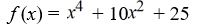
B)
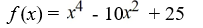
C)
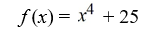
D)
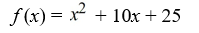

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
For the polynomial function 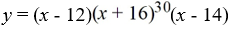 , determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x - intercept (-16, 0).
, determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x - intercept (-16, 0).
A) crosses the y - axis at (-16, 0)
B) touches the y - axis at (-16, 0)
C) crosses the x - axis at (-16, 0)
D) touches the x - axis at (-16, 0)
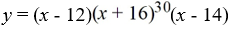 , determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x - intercept (-16, 0).
, determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x - intercept (-16, 0).A) crosses the y - axis at (-16, 0)
B) touches the y - axis at (-16, 0)
C) crosses the x - axis at (-16, 0)
D) touches the x - axis at (-16, 0)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
For the polynomial function 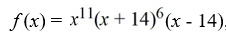 , determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x-intercept (0, 0).
, determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x-intercept (0, 0).
A) touches the x-axis at (0, 0)
B) crosses the x-axis at (0, 0)
C) touches the x-axis at (14, 0)
D) neither
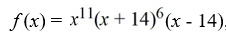 , determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x-intercept (0, 0).
, determine whether the graph touches or crosses at the x-intercept (0, 0).A) touches the x-axis at (0, 0)
B) crosses the x-axis at (0, 0)
C) touches the x-axis at (14, 0)
D) neither

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
For the polynomial function 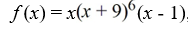 , find the y-intercept.
, find the y-intercept.
A) (1, 0)
B) (-1, 0)
C) (0, 0)
D) (0, 1)
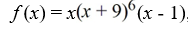 , find the y-intercept.
, find the y-intercept.A) (1, 0)
B) (-1, 0)
C) (0, 0)
D) (0, 1)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
For the polynomial function 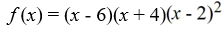 , find the y-intercept.
, find the y-intercept.
A) (0, -48)
B) (0, -96)
C) (0, 48)
D) (0, 2)
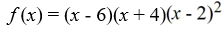 , find the y-intercept.
, find the y-intercept.A) (0, -48)
B) (0, -96)
C) (0, 48)
D) (0, 2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Determine if the function 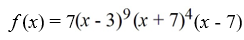 is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
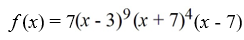 is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
is a polynomial. If it is, state the degree.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Find all the real zeros (and state their multiplicity) of the polynomial function. 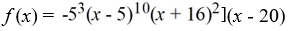
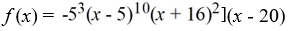

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Find a polynomial of minimum degree that has the zeros 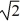 (with multiplicity 2) and -
(with multiplicity 2) and - 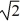 (with multiplicity 2).
(with multiplicity 2).
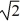 (with multiplicity 2) and -
(with multiplicity 2) and - 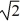 (with multiplicity 2).
(with multiplicity 2).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Sketch the graph of the polynomial function.
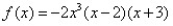
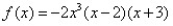

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Sketch the graph of the polynomial function.
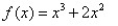
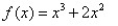

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Match the polynomial function with its graph.
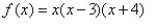
A)
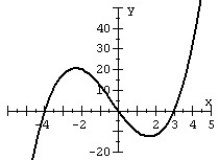
B)
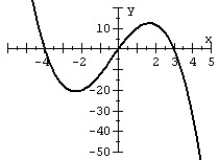
C)
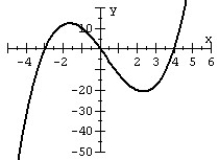
D)
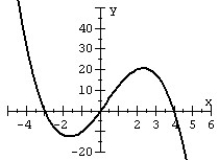
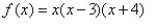
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Match the polynomial function with its graph.
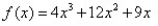
A)
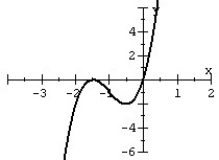
B)
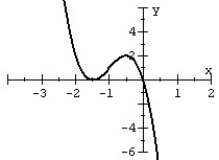
C)
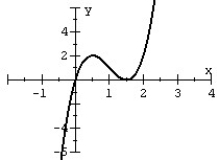
D)
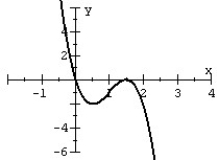
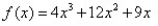
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 115 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








