Deck 8: Effects of Intermolecular Forces
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Effects of Intermolecular Forces
1
Understand the effects of intermolecular forces on condensation, vapourization, and melting and boiling points.
Attractive intermolecular forces are responsible for the condensation of gases and the freezing of liquids.
2
Predict the relative magnitudes of intermolecular forces and their effects on physical properties of substances.
All intermolecular forces are electrostatic and under most conditions are attractive. Intermolecular forces exist among all ions, dipoles, and uncharged non-polar species. A dipole can be induced into a non-polar species by an ion or by a polar species. Hydrogen bonds exist among species having a polar bond between H and O, N, or F.
3
Explain trends in surface tension, capillary action, viscosity, and vapour pressure in terms of intermolecular forces.
Substances with higher intermolecular forces have higher surface tensions, higher viscosities, and lower vapour pressures.
4
Explain the properties of solids in terms of the dominant intermolecular forces present.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Understand amorphous and crystalline solids at the molecular level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Explain enthalpies of phase changes in terms of intermolecular forces and interpret a pressure-temperature phase diagram of a pure substance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following experience the strongest intermolecular forces?
A) F2
B) I2
C) Br2
D) Cl2
A) F2
B) I2
C) Br2
D) Cl2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a liquid under normal atmospheric conditions of temperature and pressure?
A) F2
B) I2
C) Br2
D) Cl2
A) F2
B) I2
C) Br2
D) Cl2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following experience the strongest covalent bond?
A) F2
B) I2
C) Br2
D) Cl2
A) F2
B) I2
C) Br2
D) Cl2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Use the following equation for questions
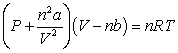
-The relative size of the Van der Waals constant, , correlates well with boiling point; that is, the larger is, the higher the boiling point. The reason for this correlation is
A) the constant is a measure of molecular size.
B) the boiling point is directly proportional to .
C) the constant varies with temperature.
D) the constant is a measure of intermolecular force strength.
E) the constant varies with vapour pressure.
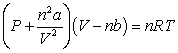
-The relative size of the Van der Waals constant, , correlates well with boiling point; that is, the larger is, the higher the boiling point. The reason for this correlation is
A) the constant is a measure of molecular size.
B) the boiling point is directly proportional to .
C) the constant varies with temperature.
D) the constant is a measure of intermolecular force strength.
E) the constant varies with vapour pressure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Use the following equation for questions
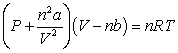
-The value "nb" that is used in the Van der Waals equation accounts for what INCORRECT assumption?
A) that gaseous collisions are not completely elastic
B) that gas molecules do take up space
C) that gas molecules interact with each other
D) that gas molecules do not travel in straight lines
E) that the velocity of gas molecules changes with temperature
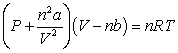
-The value "nb" that is used in the Van der Waals equation accounts for what INCORRECT assumption?
A) that gaseous collisions are not completely elastic
B) that gas molecules do take up space
C) that gas molecules interact with each other
D) that gas molecules do not travel in straight lines
E) that the velocity of gas molecules changes with temperature

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Where would you expect Ne to appear in the following sequence of boiling points?
He < H2 < N2 < F2 < Ar < O2
A) lower than He
B) between He and H2
C) between H2 and N2
D) between F2 and Ar
E) between Ar and O2
He < H2 < N2 < F2 < Ar < O2
A) lower than He
B) between He and H2
C) between H2 and N2
D) between F2 and Ar
E) between Ar and O2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the expected order of boiling points for H2, He, F2 and Ne?
A) H2 < He < F2 < Ne
B) H2 < F2 < Ne < He
C) Ne < H2 < He < F2
D) He < H2 < F2 < Ne
E) He < H2 < Ne < F2
A) H2 < He < F2 < Ne
B) H2 < F2 < Ne < He
C) Ne < H2 < He < F2
D) He < H2 < F2 < Ne
E) He < H2 < Ne < F2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which is the most realistic picture for a container of Ar(l)?
A)
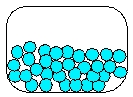
B)
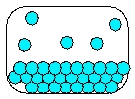
C)
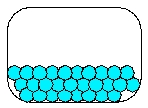
D)
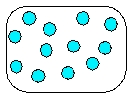
E)
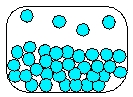
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Consider the following three molecules:  The dominant intermolecular force acting in each is, respectively ,
The dominant intermolecular force acting in each is, respectively ,
A) dipole-dipole; dipole-dipole; hydrogen bonding.
B) hydrogen bonding; dispersion forces; dipole-dipole.
C) hydrogen bonding; ion-ion; dipole-dipole.
D) hydrogen bonding; dipole-dipole; dispersion forces.
E) dipole-dipole; dipole-dipole; dipole-dipole.
 The dominant intermolecular force acting in each is, respectively ,
The dominant intermolecular force acting in each is, respectively ,A) dipole-dipole; dipole-dipole; hydrogen bonding.
B) hydrogen bonding; dispersion forces; dipole-dipole.
C) hydrogen bonding; ion-ion; dipole-dipole.
D) hydrogen bonding; dipole-dipole; dispersion forces.
E) dipole-dipole; dipole-dipole; dipole-dipole.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which is the expected order of increasing boiling point for the following molecules? 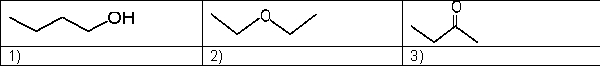
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 3, 2
C) 3, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 3
E) 2, 3, 1

A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 3, 2
C) 3, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 3
E) 2, 3, 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Acetone CH3COCH3 boils at a significantly higher temperature than 2-methylpropane isobutene
A) because dipole-dipole forces are always greater than dispersion forces.
B) because the molecular mass of acetone is slightly less than that of 2-methylpropane.
C) because the density of acetone is greater than that of 2-methylpropane.
D) because the attractive dispersion forces in 2-methylpropane are weaker than those in acetone.
E) because the attractive dispersion forces in 2-methylpropane are weaker than the dipole forces in acetone.
A) because dipole-dipole forces are always greater than dispersion forces.
B) because the molecular mass of acetone is slightly less than that of 2-methylpropane.
C) because the density of acetone is greater than that of 2-methylpropane.
D) because the attractive dispersion forces in 2-methylpropane are weaker than those in acetone.
E) because the attractive dispersion forces in 2-methylpropane are weaker than the dipole forces in acetone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The boiling point of HCl (188 K) is lower than that for HI (238 K) because
A) HI is more polar therefore the intermolecular dipole-dipole forces are stronger in HI.
B) HCl is more polar therefore the intermolecular dipole-dipole forces are stronger in HI.
C) the molecular mass of HI is greater than that of HCl.
D) HI is more polarizable, dispersion forces compensate for the lower dipole forces in HI.
E) HI is capable of hydrogen bonding, HCl is not.
A) HI is more polar therefore the intermolecular dipole-dipole forces are stronger in HI.
B) HCl is more polar therefore the intermolecular dipole-dipole forces are stronger in HI.
C) the molecular mass of HI is greater than that of HCl.
D) HI is more polarizable, dispersion forces compensate for the lower dipole forces in HI.
E) HI is capable of hydrogen bonding, HCl is not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In which of the following pure substances will hydrogen bonding be an important intermolecular force? 1) dichloromethane, CH2Cl2, 2) CH3CH2OH, 3) methylamine, (CH3NH2), 4) trimethylamine, N(CH3)3
A) 2 and 3
B) all
C) none
D) 1 and 2
E) 3 and 4
A) 2 and 3
B) all
C) none
D) 1 and 2
E) 3 and 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
List the following three compounds in order of increasing boiling point: 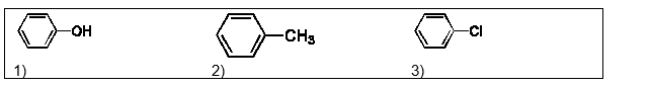
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 3, 2, 1
C) 1, 3, 2
D) 2, 1, 3
E) 2, 3, 1

A) 1, 2, 3
B) 3, 2, 1
C) 1, 3, 2
D) 2, 1, 3
E) 2, 3, 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What is the dominant intermolecular force for acetylcetone? 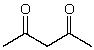
A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole interactions
C) dispersion
D) ionic
E) none of these

A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole interactions
C) dispersion
D) ionic
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What is the dominant intermolecular force for propionic acid? 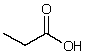
A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole interactions
C) dispersion
D) ionic
E) none of these

A) hydrogen bonding
B) dipole interactions
C) dispersion
D) ionic
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Arrange the following molecules in order of increasing viscosity:
1) CH4,
2) CH3CH2C(H)=CH2,
3) CH3CH2C(CH3)3,
4) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
A) 4 < 3 < 2 < 1
B) 2 < 1 < 4 < 3
C) 1 < 2 < 4 < 3
D) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
E) 3 < 1 < 2 < 4
1) CH4,
2) CH3CH2C(H)=CH2,
3) CH3CH2C(CH3)3,
4) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
A) 4 < 3 < 2 < 1
B) 2 < 1 < 4 < 3
C) 1 < 2 < 4 < 3
D) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
E) 3 < 1 < 2 < 4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following will have the lowest viscosity?
A) nonane
B) octane
C) pentane
D) heptane
E) hexane
A) nonane
B) octane
C) pentane
D) heptane
E) hexane

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Arrange the following in order of increasing vapour pressure at room temperature.
1) CH3OCH3,
2) CH3CH2OCH2CH3,
3) CH3C(O)CH3,
4) CH3CH2OH
A) 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 4 < 3 < 2 < 1
D) 3 < 4 < 1 < 2
E) 4 < 1 < 2 < 3
1) CH3OCH3,
2) CH3CH2OCH2CH3,
3) CH3C(O)CH3,
4) CH3CH2OH
A) 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 4 < 3 < 2 < 1
D) 3 < 4 < 1 < 2
E) 4 < 1 < 2 < 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Arrange the following in order of increasing vapour pressure at room temperature:
1) H2O,
2) Hg,
3) Br2,
4) CH3CH2OH
A) 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 4 < 3 < 2 < 1
D) 4< 3< 1 < 2
E) 2 < 1 < 4 < 3
1) H2O,
2) Hg,
3) Br2,
4) CH3CH2OH
A) 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 4 < 3 < 2 < 1
D) 4< 3< 1 < 2
E) 2 < 1 < 4 < 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Arrange the following in order of decreasing surface tension at room temperature:
1) H2O,
2) Hg,
3) benzene,
4) n-hexane
A) 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 2 < 1 < 3 < 4
D) 4< 3< 1 < 2
E) 2 < 1 < 4 < 3
1) H2O,
2) Hg,
3) benzene,
4) n-hexane
A) 2 < 3 < 1 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 2 < 1 < 3 < 4
D) 4< 3< 1 < 2
E) 2 < 1 < 4 < 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
For the following substances determine which of the selections is arranged in order of increasing expected melting point: 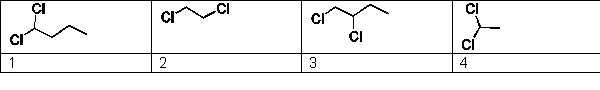
A) 1 < 3 < 2 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 2 < 3 < 4 < 1
D) 3 < 4 < 2 < 1
E) 3 < 2 < 4 < 1

A) 1 < 3 < 2 < 4
B) 1 < 4 < 3 < 2
C) 2 < 3 < 4 < 1
D) 3 < 4 < 2 < 1
E) 3 < 2 < 4 < 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
For the following substances, choose the answer which best describes what type of solid will form, respectively, upon solidification: 
A) ionic, network, ionic, metallic
B) ionic, molecular, molecular, metallic
C) network, molecular, ionic, network
D) network, molecular, ionic, metallic
E) network, ionic, ionic, metallic

A) ionic, network, ionic, metallic
B) ionic, molecular, molecular, metallic
C) network, molecular, ionic, network
D) network, molecular, ionic, metallic
E) network, ionic, ionic, metallic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
For the following substances, choose the answer which best describes what type of solid will form respectively, upon solidification: 
A) ionic, metallic, ionic, network
B) ionic, molecular, molecular, metallic
C) network, metallic, molecular, ionic
D) molecular, metallic, ionic, molecular
E) ionic, metallic, molecular, ionic

A) ionic, metallic, ionic, network
B) ionic, molecular, molecular, metallic
C) network, metallic, molecular, ionic
D) molecular, metallic, ionic, molecular
E) ionic, metallic, molecular, ionic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
For the following substances, choose the answer which best describes what type of solid will form respectively, upon solidification: 
A) molecular, ionic, molecular, ionic
B) metallic, molecular, molecular, ionic
C) network, metallic, molecular, ionic
D) molecular, network, ionic, ionic
E) molecular, ionic, network, ionic

A) molecular, ionic, molecular, ionic
B) metallic, molecular, molecular, ionic
C) network, metallic, molecular, ionic
D) molecular, network, ionic, ionic
E) molecular, ionic, network, ionic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Your solid is non-conductive and melts at relatively low temperature. Based on this information, one can conclude that bonding in the solid is most likely
A) metallic.
B) covalent.
C) molecular covalent.
D) ionic.
E) polar covalent.
A) metallic.
B) covalent.
C) molecular covalent.
D) ionic.
E) polar covalent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
You have a non-conductive solid. On melting at 30oC, it forms a conductive liquid. It is soluble in water, and when dissolved, the aqueous solution is conductive. Based on this information one can conclude that bonding in the solid is most likely
A) metallic.
B) covalent.
C) molecular covalent.
D) ionic.
E) polar covalent.
A) metallic.
B) covalent.
C) molecular covalent.
D) ionic.
E) polar covalent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
You have a solid that it characterized by high melting and boiling points, is NOT conductive, and does NOT dissolve in water. Bonding is most likely
A) metallic.
B) covalent.
C) molecular covalent.
D) ionic.
E) polar covalent.
A) metallic.
B) covalent.
C) molecular covalent.
D) ionic.
E) polar covalent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Metals are ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (forced into thin sheets by hammering) because
A) bonding is omnidirectional.
B) bonding is by directed covalent bonds.
C) they are good electrical conductors.
D) they have partially filled bonding bands.
E) they have a range of melting points.
A) bonding is omnidirectional.
B) bonding is by directed covalent bonds.
C) they are good electrical conductors.
D) they have partially filled bonding bands.
E) they have a range of melting points.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
30 In the simple cubic crystal structure at right, the unit cell is outlined in heavy lines which intersect to form the corners at the center of the spheres. If the corners of the unit cells are at the center of the spheres, how many atoms are in one unit cell? 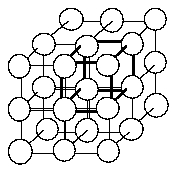
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The face-centered cubic unit cell to the right has been shaded to add clarity; the balls in the corners are black: those in the faces are gray. If the corners of the unit cells are at the center of the corner spheres, how many atoms are in one unit cell? 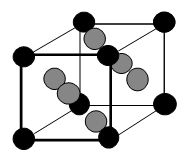
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Ruby is a crystalline compound that contains aluminum, oxygen and chromium. The structure of ruby is best described as having
A) amorphous structure.
B) interstitial defects.
C) substitutional defects.
D) a and c
E) a and b
A) amorphous structure.
B) interstitial defects.
C) substitutional defects.
D) a and c
E) a and b

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which type of solid is the most densely packed?
A) simple cubic
B) face-centered cubic
C) body-centered cubic
D) amorphous solid
E) density is the same for all
A) simple cubic
B) face-centered cubic
C) body-centered cubic
D) amorphous solid
E) density is the same for all

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Below is the structure for zinc sulphide. If the zinc atoms (zinc) are contained within the unit cell and the sulphur atoms (clear) form a face-centered cubic structure, how many sulphur atoms must be contained within the unit cell to balance the charge? 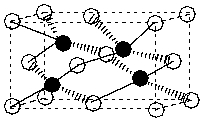
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Polonium metal crystallizes in a simple cubic structure. If the atomic radius of polonium is 160 pm, what is the volume of a unit cell?
A) 3.28x10-23 cm3
B) 4.10 x 10-29 m3
C) 4.10 x106 pm3
D) 3.28 x 10-6 m3
E) 3.28 x 10-23 m3
A) 3.28x10-23 cm3
B) 4.10 x 10-29 m3
C) 4.10 x106 pm3
D) 3.28 x 10-6 m3
E) 3.28 x 10-23 m3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Na+ has an ionic radius of 116 pm and Cl- an ionic radius of 167 pm. Estimate the volume of a NaCl unit cell.
A) 1.81 x 10-4 m3
B) 2.27 x 10-29 m3
C) 1.81x10?28 m3
D) 3.73 x10-29 m3
E) 2.27 x 107 pm3
A) 1.81 x 10-4 m3
B) 2.27 x 10-29 m3
C) 1.81x10?28 m3
D) 3.73 x10-29 m3
E) 2.27 x 107 pm3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Use the phase diagram of oxygen to determine the phases oxygen passes through starting at 0.001 atm and 100oK, cooling and increasing the pressure steadily to 25 K at 1 atm. 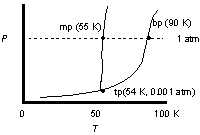
A) gas, liquid
B) liquid, solid
C) gas, liquid, solid
D) liquid, solid, gas
E) gas, solid

A) gas, liquid
B) liquid, solid
C) gas, liquid, solid
D) liquid, solid, gas
E) gas, solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
What feature makes the phase diagram of water unusual?
A) The boiling point is high.
B) The positive slope of the liquid-gas equilibrium line.
C) The positive slope of the solid-liquid equilibrium line.
D) The negative slope of the liquid-gas equilibrium line.
E) The negative slope of the solid-liquid equilibrium line.
A) The boiling point is high.
B) The positive slope of the liquid-gas equilibrium line.
C) The positive slope of the solid-liquid equilibrium line.
D) The negative slope of the liquid-gas equilibrium line.
E) The negative slope of the solid-liquid equilibrium line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The order of increasing melting point for several simple molecular compounds is: H2, F2, O2, N2, Ar, while for these same compounds boiling point increases as H2, N2, F2, Ar, O2. Explain why the trends for boiling point and melting point are different.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A sample of 1.5 moles of CO2 (a = 3.59 atm•L2/mol2; b = 0.0427 L/mol) is contained in a cylinder of 100 mL volume at a temperature of 350oK. What is the percent deviation from ideal behaviour?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A tank of nitrogen in a lab contains about 125 moles of N2 (a = 1.39 atm•L2/mol2; b = 0.0391 L/mol) in a volume of 20 L. Calculate the percent deviation from ideal behaviour at 298oK.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Some believe that differences between boiling points are truer indicators of relative intermolecular forces than melting points. Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Draw molecular pictures that illustrate and explain the different polarizabilities of CH2Cl2 and CHCl3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Of the following pairs, select the pair that undergoes hydrogen bonding and draw a molecular picture of the hydrogen bond interaction.
1. NaCl and acetone, (CH3)2CO
2. CH3OCH3 and CF3Cl
3. NH3 and CCl4
4. NF3 and CF4
5. CH3NH2 and CH3OCH3
1. NaCl and acetone, (CH3)2CO
2. CH3OCH3 and CF3Cl
3. NH3 and CCl4
4. NF3 and CF4
5. CH3NH2 and CH3OCH3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Draw how water can hydrogen bond with itself.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
For the three molecules whose structures and boiling points are shown below, explain the trend in boiling points in terms of the strength and types of intermolecular forces acting between the molecules in the pure liquids. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of the following molecules will have the greatest surface tension and why?
1) methanol, CH3OH
2) gasoline, ~C8H18
3) diethyl ether, CH3CH2OCH2CH3.
1) methanol, CH3OH
2) gasoline, ~C8H18
3) diethyl ether, CH3CH2OCH2CH3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Describe how trees are able to transport water from their roots to the leaves on their branches high in the air.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The leaves of the lotus plant are extremely hydrophobic. That is, water does not stick to the leaves. In 2004, scientists were able to replicate this phenomenon on a film. Sketch what you think the meniscus of water would look like in a tube made of this material? What would the meniscus look like for oil?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Explain why water "beads" up on waxed surfaces, but oil spreads out on the same surface?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which will have the highest vapour pressure at standard condition and explain why.
1. 1-hexanol, C6H13OH
2. benzene, C6H6
3. hexane, C6H14
1. 1-hexanol, C6H13OH
2. benzene, C6H6
3. hexane, C6H14

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
What are the differences in interparticle forces for network and metallic solids?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
List at least two different physical properties between network and molecular solids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
What are the differences in interparticle forces for metallic and ionic?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The figure shows the unit cell of a compound containing A (open spheres) and X (shaded spheres). What is the empirical formula of this compound if the shaded spheres form a face-centered cubic arrangement and the open spheres are contained within the unit cell?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What is the main difference between an amorphous solid and a crystalline solid?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Cesium chloride forms a body-centered cubic solid. One of the elements is in the middle; the other is on each corner of the cube. Which element is in each location and why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Oxygen is an important component of the atmosphere. Draw the phase diagram for O2 given the normal melting point (-218°C), the normal boiling point (-183°C) and the triple point (-219°C and 1.10 mm Hg.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Use the phase diagram of oxygen to estimate the temperature at which liquid oxygen will boil under 0.5 atm external pressure and compare that to the normal boiling point. 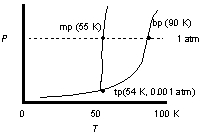


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Sketch a phase diagram for hydrazine locating all points given: normal melting point (1.4˚C), normal boiling point (113.5˚C), critical point (380˚C, 145 atm), triple point (2.0˚C, 3.4 mm Hg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Sketch the phase diagram for benzene identifying the solid, liquid, and gas phases given the following: normal boiling point (80.1˚C), triple point (5.5˚C, 35.8 mm Hg), critical point (288.5˚C and 47.7 atm)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Define supercritical fluid and how to make such a fluid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
To melt or vapourize a substance, a certain amount of energy needs to be supplied. These are referred to as the heat of fusion and heat of vapourization. Which is typically a lot larger and why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
How much energy is required when 23 grams of ethanol at 30˚C are vapourized from a "flaming" desert? ΔH˚vap = 39.3 kJ/mol, Tvap = 351 K, ΔH˚fus = 7.61 kJ/mol, Tfus = 156 K, Cethanol = 112 J/mol˚C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
How much energy is required when 23 grams of ice at -4?C are melted in a 240 ml glass of pop? ?H?vap = 40.7 kJ/mol, ?H?fus = 6.0 kJ/mol, Cice = 37.8 J/mol?C, Cwater = 75.3 J/mol?C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








