Deck 6: Integration
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: Integration
1
Write sigma notation of 4 - 9 + 16 - 25 +... + . 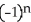
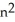
A)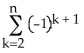
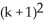
B)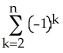
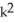
C)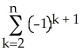
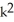
D)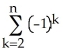
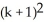
E)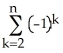
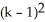
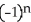
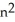
A)
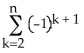
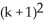
B)
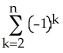
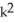
C)
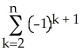
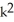
D)
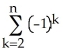
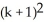
E)
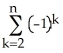
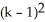
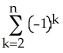
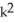
2
Evaluate the sum 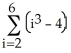 .
.
A) 420
B) 70
C) 67
D) 417
E) 356
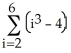 .
.A) 420
B) 70
C) 67
D) 417
E) 356
420
3
Evaluate 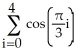 .
.
A) 1 +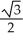
B)
C) -
D) 1 -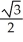
E) -
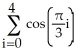 .
.A) 1 +
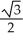
B)

C) -

D) 1 -
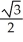
E) -

- 

4
Evaluate the 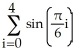 .
.
A) +
+ 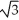
B) -
- 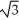
C)
D) 2 -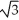
E) 2 +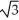
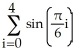 .
.A)
 +
+ 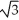
B)
 -
- 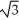
C)

D) 2 -
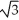
E) 2 +
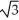

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Find and evaluate the sum 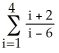 .
.
A)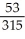
B) -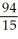
C)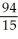
D) -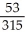
E)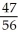
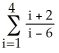 .
.A)
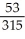
B) -
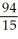
C)
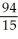
D) -
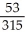
E)
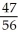

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Evaluate 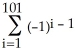 .
.
A) -1
B) 0
C) 51
D) 1
E) 101
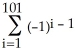 .
.A) -1
B) 0
C) 51
D) 1
E) 101

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Express the sum 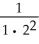 +
+ 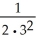 +
+ 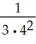 +
+ 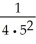 +..... +
+..... + 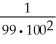 using sigma notation.
using sigma notation.
A)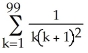
B)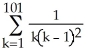
C)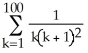
D)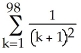
E)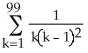
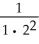 +
+ 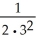 +
+ 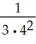 +
+ 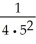 +..... +
+..... + 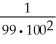 using sigma notation.
using sigma notation.A)
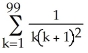
B)
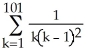
C)
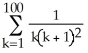
D)
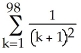
E)
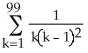

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Simplify the expression 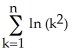 .
.
A) ln((2n)!)
B)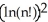
C) (2 ln n)!
D) 2 ln(n!)
E) (ln(n))!
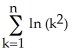 .
.A) ln((2n)!)
B)
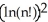
C) (2 ln n)!
D) 2 ln(n!)
E) (ln(n))!

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Express the sum in the series 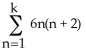 .
.
A) 2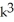 + 9
+ 9  + 7k
+ 7k
B) 2 + 9
+ 9  + 5k
+ 5k
C) 3 + 9
+ 9 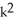 + 7k
+ 7k
D) 3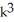 + 9
+ 9 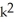 + 5k
+ 5k
E) 2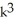 - 9
- 9 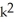 + 7k
+ 7k
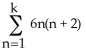 .
.A) 2
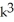 + 9
+ 9 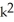 + 7k
+ 7kB) 2
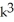 + 9
+ 9 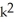 + 5k
+ 5kC) 3
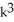 + 9
+ 9 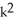 + 7k
+ 7kD) 3
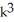 + 9
+ 9 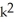 + 5k
+ 5kE) 2
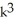 - 9
- 9 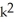 + 7k
+ 7k
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Evaluate the sum 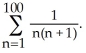 Hint:
Hint: 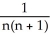 =
=  -
- 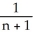 .
.
A) 1
B)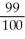
C)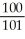
D)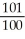
E)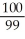
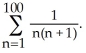 Hint:
Hint: 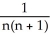 =
=  -
- 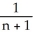 .
.A) 1
B)
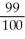
C)
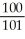
D)
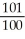
E)
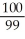

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Evaluate the sum 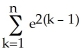 .
.
A)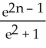
B)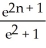
C)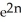
D)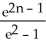
E)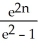
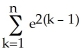 .
.A)
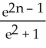
B)
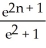
C)
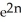
D)
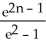
E)
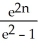

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Express the sum 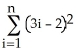 as a polynomial function of n.
as a polynomial function of n.
A) 3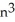 +
+ 
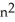 +
+  n
n
B) 3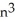 +
+ 
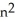 -
-  n
n
C) 3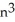 +
+ 
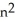 + 4n
+ 4n
D) 3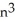 + 3
+ 3 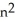 - n
- n
E) 3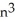 -
- 
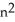 -
-  n
n
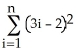 as a polynomial function of n.
as a polynomial function of n.A) 3
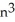 +
+ 
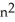 +
+  n
nB) 3
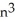 +
+ 
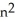 -
-  n
nC) 3
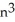 +
+ 
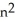 + 4n
+ 4nD) 3
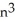 + 3
+ 3 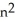 - n
- nE) 3
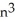 -
- 
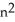 -
-  n
n
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Find an approximation for the area under the curve y = 1 - 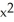 and above the x-axis fromx = 0 to x = 1 using a sum of areas of four rectangles each having width 1/4 and (a) tops lying under the curve, or (b) tops lying above the curve. What does this tell you about the actual area under the curve?
and above the x-axis fromx = 0 to x = 1 using a sum of areas of four rectangles each having width 1/4 and (a) tops lying under the curve, or (b) tops lying above the curve. What does this tell you about the actual area under the curve?
A) (a)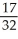 , (b)
, (b) 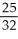 ;
; 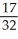 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 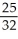
B) (a)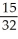 , (b)
, (b) 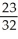 ;
; 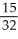 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 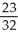
C) (a)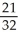 , (b)
, (b) 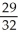 ;
; 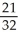 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 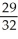
D) (a)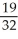 , (b)
, (b) 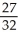 ;
; 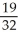 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 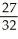
E) (a)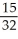 , (b)
, (b) 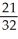 ;
; 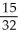 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 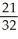
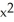 and above the x-axis fromx = 0 to x = 1 using a sum of areas of four rectangles each having width 1/4 and (a) tops lying under the curve, or (b) tops lying above the curve. What does this tell you about the actual area under the curve?
and above the x-axis fromx = 0 to x = 1 using a sum of areas of four rectangles each having width 1/4 and (a) tops lying under the curve, or (b) tops lying above the curve. What does this tell you about the actual area under the curve?A) (a)
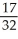 , (b)
, (b) 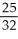 ;
; 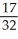 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 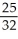
B) (a)
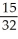 , (b)
, (b) 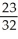 ;
; 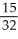 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 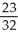
C) (a)
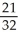 , (b)
, (b) 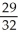 ;
; 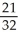 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 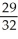
D) (a)
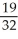 , (b)
, (b) 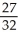 ;
; 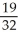 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 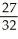
E) (a)
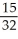 , (b)
, (b) 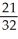 ;
; 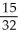 < area under curve <
< area under curve < 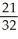

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Given that the area under the curve y = 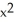 and above the x-axis from x = 0 to x = a > 0 is
and above the x-axis from x = 0 to x = a > 0 is 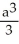 square units, find the area under the same curve from x = -2 to x = 3.
square units, find the area under the same curve from x = -2 to x = 3.
A)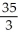 square units
square units
B)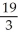 square units
square units
C) 9 square units
D) 6 square units
E)
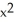 and above the x-axis from x = 0 to x = a > 0 is
and above the x-axis from x = 0 to x = a > 0 is 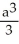 square units, find the area under the same curve from x = -2 to x = 3.
square units, find the area under the same curve from x = -2 to x = 3.A)
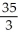 square units
square unitsB)
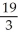 square units
square unitsC) 9 square units
D) 6 square units
E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Construct and simplify a sum approximating the area above the x-axis and under the curve y = 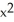 between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying under or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.
between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying under or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.
A)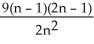 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
B)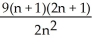 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
C)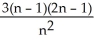 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square units
D)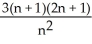 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square units
E)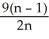 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
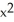 between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying under or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.
between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying under or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.A)
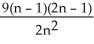 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square unitsB)
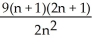 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square unitsC)
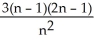 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square unitsD)
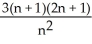 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square unitsE)
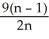 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Construct and simplify a sum approximating the area above the x-axis and under the curvey = 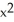 between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying above or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.
between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying above or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.
A)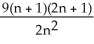 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
B)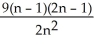 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
C)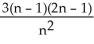 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square units
D)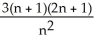 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square units
E)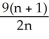 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
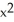 between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying above or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.
between x = 0 and x = 3 by using n rectangles having equal widths and tops lying above or on the curve. Find the actual area as a suitable limit.A)
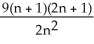 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square unitsB)
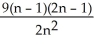 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square unitsC)
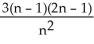 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square unitsD)
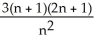 , area = 6 square units
, area = 6 square unitsE)
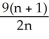 , area = 9 square units
, area = 9 square units
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.
A) Area =![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae51_a0f8_07afbf46ec3c_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae52_a0f8_538d4191884e_TB9661_11.jpg)
B) Area =![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae53_a0f8_71595e2ccafe_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae54_a0f8_39fc107ab655_TB9661_11.jpg)
C) Area =![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae55_a0f8_315be080139d_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae56_a0f8_9d75693ec8ea_TB9661_11.jpg)
D) Area =![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae57_a0f8_6118d21c5f35_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae58_a0f8_0b98319b76ba_TB9661_11.jpg)
E) Area =![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae59_a0f8_018f6baf11f6_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae5a_a0f8_f1e011590917_TB9661_11.jpg)
A) Area =
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae51_a0f8_07afbf46ec3c_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae52_a0f8_538d4191884e_TB9661_11.jpg)
B) Area =
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae53_a0f8_71595e2ccafe_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae54_a0f8_39fc107ab655_TB9661_11.jpg)
C) Area =
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae55_a0f8_315be080139d_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae56_a0f8_9d75693ec8ea_TB9661_11.jpg)
D) Area =
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae57_a0f8_6118d21c5f35_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae58_a0f8_0b98319b76ba_TB9661_11.jpg)
E) Area =
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae59_a0f8_018f6baf11f6_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Write the area under the curve y = cos x and above the interval [0, \pi /2] on the x-axis as the limit of a sum of areas of n rectangles of equal widths. Have the upper-right corners of the rectangles lie on the curve.</strong> A) Area = B) Area = C) Area = D) Area = E) Area =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_ae5a_a0f8_f1e011590917_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Given that ![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56b_a0f8_7fbf7bf4bc0e_TB9661_11.jpg) =
= ![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56c_a0f8_4d782f5f514b_TB9661_11.jpg) , find the area under y =
, find the area under y = ![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56d_a0f8_fdc557a174dc_TB9661_11.jpg) and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.
and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.
A)![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56e_a0f8_d15532da13f6_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
B)![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56f_a0f8_8708fbd3f3b5_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
C)![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d570_a0f8_19a65017618d_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
D)![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d571_a0f8_7bdd7c62d0f0_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
E)![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d572_a0f8_87be8ef3ed5c_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56b_a0f8_7fbf7bf4bc0e_TB9661_11.jpg) =
= ![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56c_a0f8_4d782f5f514b_TB9661_11.jpg) , find the area under y =
, find the area under y = ![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56d_a0f8_fdc557a174dc_TB9661_11.jpg) and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.
and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.A)
![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56e_a0f8_d15532da13f6_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square unitsB)
![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d56f_a0f8_8708fbd3f3b5_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square unitsC)
![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d570_a0f8_19a65017618d_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square unitsD)
![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d571_a0f8_7bdd7c62d0f0_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square unitsE)
![<strong>Given that = , find the area under y = and above the interval [0, a] on the x-axis (where a > 0 ) by interpreting the area as a limit of a suitable sum.</strong> A) square units B) square units C) square units D) square units E) square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7810_d572_a0f8_87be8ef3ed5c_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The limit 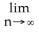
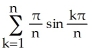 represents the area of a certain region in the xy-plane. Describe the region.
represents the area of a certain region in the xy-plane. Describe the region.
A) region under y = cos x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =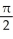
B) region under y = sin x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =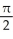
C) region under y = cos x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =
D) region under y = sin x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =
E) region under y = cos x, above y = 0, between x=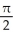 and x =
and x =
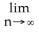
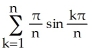 represents the area of a certain region in the xy-plane. Describe the region.
represents the area of a certain region in the xy-plane. Describe the region.A) region under y = cos x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =
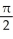
B) region under y = sin x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =
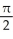
C) region under y = cos x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =
D) region under y = sin x, above y = 0, between x = 0 and x =
E) region under y = cos x, above y = 0, between x=
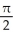 and x =
and x = 
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
By interpreting it as the area of a region in the xy-plane, evaluate the limit 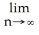 .
. 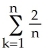
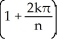
A) 2 + 2 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 1 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 2)
B) 1 + (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 1 + 2 x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 1)
C) 2 + 4 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 1 + 2 x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 2)
D) 4 + 2 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 2 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 2)
E) 2 +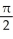 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 2 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 1)
(the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 2 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 1)
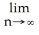 .
. 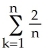
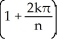
A) 2 + 2 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 1 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 2)
B) 1 + (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 1 + 2 x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 1)
C) 2 + 4 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 1 + 2 x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 2)
D) 4 + 2 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 2 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 2)
E) 2 +
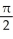 (the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 2 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 1)
(the area of the trapezoidal region under y = 2 + x, above y = 0 from x = 0 to x = 1)
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
By interpreting it as the area of a region in the xy-plane, evaluate the limit 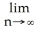 .
. 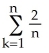
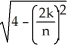
A) (the area of a quarter of a circular disk of radius 2)
B) 2 (the area of half of a circular disk of radius 2)
C) 4 (the area of a circular disk of radius 2)
D) 8 (the area of half of a circular disk of radius 4)
E) 16 (the area of a circular disk of radius 4)
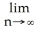 .
. 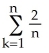
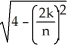
A) (the area of a quarter of a circular disk of radius 2)
B) 2 (the area of half of a circular disk of radius 2)
C) 4 (the area of a circular disk of radius 2)
D) 8 (the area of half of a circular disk of radius 4)
E) 16 (the area of a circular disk of radius 4)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 3] into 4 subintervals of equal length ![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 3] into 4 subintervals of equal length x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f,P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 4x<sup>2</sup>.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 40, L(f,P) = 30 B) U(f,P) = 41, L(f,P) = 29 C) U(f,P) = 42, L(f,P) = 28 D) U(f,P) = 43, L(f,P) = 27 E) U(f,P) = 44, L(f,P) = 26](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee7b0a_b7f1_074c_ae82_c500e20d0813_TB9661_11.jpg) x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f,P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 4x2.
x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f,P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 4x2.
A) U(f,P) = 40, L(f,P) = 30
B) U(f,P) = 41, L(f,P) = 29
C) U(f,P) = 42, L(f,P) = 28
D) U(f,P) = 43, L(f,P) = 27
E) U(f,P) = 44, L(f,P) = 26
![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 3] into 4 subintervals of equal length x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f,P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 4x<sup>2</sup>.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 40, L(f,P) = 30 B) U(f,P) = 41, L(f,P) = 29 C) U(f,P) = 42, L(f,P) = 28 D) U(f,P) = 43, L(f,P) = 27 E) U(f,P) = 44, L(f,P) = 26](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee7b0a_b7f1_074c_ae82_c500e20d0813_TB9661_11.jpg) x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f,P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 4x2.
x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f,P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 4x2.A) U(f,P) = 40, L(f,P) = 30
B) U(f,P) = 41, L(f,P) = 29
C) U(f,P) = 42, L(f,P) = 28
D) U(f,P) = 43, L(f,P) = 27
E) U(f,P) = 44, L(f,P) = 26

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 2] into 8 subintervals of equal length ![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 2] into 8 subintervals of equal length x = 1/8.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 1/x.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 0.7110, L(f,P) = 0.6781 B) U(f,P) = 0.7254, L(f,P) = 0.6629 C) U(f,P) = 0.7302, L(f,P) = 0.6571 D) U(f,P) = 0.7378, L(f,P) = 0.6510 E) U(f,P) = 0.7219, L(f,P) = 0.6683](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee7b0a_b7f1_074c_ae82_c500e20d0813_TB9661_11.jpg) x = 1/8.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 1/x.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.
x = 1/8.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 1/x.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.
A) U(f,P) = 0.7110, L(f,P) = 0.6781
B) U(f,P) = 0.7254, L(f,P) = 0.6629
C) U(f,P) = 0.7302, L(f,P) = 0.6571
D) U(f,P) = 0.7378, L(f,P) = 0.6510
E) U(f,P) = 0.7219, L(f,P) = 0.6683
![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 2] into 8 subintervals of equal length x = 1/8.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 1/x.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 0.7110, L(f,P) = 0.6781 B) U(f,P) = 0.7254, L(f,P) = 0.6629 C) U(f,P) = 0.7302, L(f,P) = 0.6571 D) U(f,P) = 0.7378, L(f,P) = 0.6510 E) U(f,P) = 0.7219, L(f,P) = 0.6683](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee7b0a_b7f1_074c_ae82_c500e20d0813_TB9661_11.jpg) x = 1/8.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 1/x.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.
x = 1/8.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = 1/x.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.A) U(f,P) = 0.7110, L(f,P) = 0.6781
B) U(f,P) = 0.7254, L(f,P) = 0.6629
C) U(f,P) = 0.7302, L(f,P) = 0.6571
D) U(f,P) = 0.7378, L(f,P) = 0.6510
E) U(f,P) = 0.7219, L(f,P) = 0.6683

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 4] into 6 subintervals of equal length ![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 4] into 6 subintervals of equal length x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = .Round your answers to 4 decimal places.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 4.9115, L(f,P) = 4.4115 B) U(f,P) = 4.9135, L(f,P) = 4.4109 C) U(f,P) = 4.9180, L(f,P) = 4.4057 D) U(f,P) = 4.9002, L(f,P) = 4.4250 E) U(f,P) = 4.9183, L(f,P) = 4.4093](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee7b0a_b7f1_074c_ae82_c500e20d0813_TB9661_11.jpg) x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) =
x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = ![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 4] into 6 subintervals of equal length x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = .Round your answers to 4 decimal places.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 4.9115, L(f,P) = 4.4115 B) U(f,P) = 4.9135, L(f,P) = 4.4109 C) U(f,P) = 4.9180, L(f,P) = 4.4057 D) U(f,P) = 4.9002, L(f,P) = 4.4250 E) U(f,P) = 4.9183, L(f,P) = 4.4093](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_98cf_a0f8_799da37c05e5_TB9661_11.jpg) .Round your answers to 4 decimal places.
.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.
A) U(f,P) = 4.9115, L(f,P) = 4.4115
B) U(f,P) = 4.9135, L(f,P) = 4.4109
C) U(f,P) = 4.9180, L(f,P) = 4.4057
D) U(f,P) = 4.9002, L(f,P) = 4.4250
E) U(f,P) = 4.9183, L(f,P) = 4.4093
![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 4] into 6 subintervals of equal length x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = .Round your answers to 4 decimal places.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 4.9115, L(f,P) = 4.4115 B) U(f,P) = 4.9135, L(f,P) = 4.4109 C) U(f,P) = 4.9180, L(f,P) = 4.4057 D) U(f,P) = 4.9002, L(f,P) = 4.4250 E) U(f,P) = 4.9183, L(f,P) = 4.4093](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee7b0a_b7f1_074c_ae82_c500e20d0813_TB9661_11.jpg) x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) =
x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = ![<strong>Let P denote the partition of the interval [1, 4] into 6 subintervals of equal length x = 1/2.Evaluate the upper and lower Riemann sums U(f, P) and L(f,P) for the function f(x) = .Round your answers to 4 decimal places.</strong> A) U(f,P) = 4.9115, L(f,P) = 4.4115 B) U(f,P) = 4.9135, L(f,P) = 4.4109 C) U(f,P) = 4.9180, L(f,P) = 4.4057 D) U(f,P) = 4.9002, L(f,P) = 4.4250 E) U(f,P) = 4.9183, L(f,P) = 4.4093](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_98cf_a0f8_799da37c05e5_TB9661_11.jpg) .Round your answers to 4 decimal places.
.Round your answers to 4 decimal places.A) U(f,P) = 4.9115, L(f,P) = 4.4115
B) U(f,P) = 4.9135, L(f,P) = 4.4109
C) U(f,P) = 4.9180, L(f,P) = 4.4057
D) U(f,P) = 4.9002, L(f,P) = 4.4250
E) U(f,P) = 4.9183, L(f,P) = 4.4093

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = ![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe0_a0f8_b73fd8d86e6a_TB9661_11.jpg) + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.
+ 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.
A) U(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe1_a0f8_3be95999351f_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square units
B) U(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe2_a0f8_af33d95c5b47_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square units
C) U(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe3_a0f8_e170d6d079c0_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square units
D) U(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe4_a0f8_1389880269e9_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square units
E) U(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe5_a0f8_9510e548bb52_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square units
![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe0_a0f8_b73fd8d86e6a_TB9661_11.jpg) + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.
+ 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.A) U(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe1_a0f8_3be95999351f_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square unitsB) U(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe2_a0f8_af33d95c5b47_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square unitsC) U(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe3_a0f8_e170d6d079c0_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square unitsD) U(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe4_a0f8_1389880269e9_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square unitsE) U(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the upper Riemann sum for f(x) = + 1 corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 3] into n equal subintervals of length 3/n. Express the sum in closed form and use it to calculate the area under the graph of f, above the x-axis, from x = 0 to x = 3.</strong> A) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units B) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units C) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units D) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units E) U(f,P) = + 3, area = 12 square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_bfe5_a0f8_9510e548bb52_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3, area = 12 square units
+ 3, area = 12 square units
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f6_a0f8_6da4d1f8be41_TB9661_11.jpg) corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that
corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f7_a0f8_a7e882e8dfb4_TB9661_11.jpg) n
n ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f8_a0f8_8be00e934556_TB9661_11.jpg) = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y =
= 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f9_a0f8_3dc16b7beb9d_TB9661_11.jpg) and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.
and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.
A) L(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fa_a0f8_dfe979aa7cc9_TB9661_11.jpg) , area = e square units
, area = e square units
B) L(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fb_a0f8_25198a742b71_TB9661_11.jpg) , area =
, area = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fc_a0f8_7fcef1e9d725_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
C) L(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fd_a0f8_33c39ba0f8e2_TB9661_11.jpg) , area = e - 1 square units
, area = e - 1 square units
D) L(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fe_a0f8_0d19a7f694e4_TB9661_11.jpg) , area =
, area = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6ff_a0f8_01f1f15aebbe_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
E) L(f,P) =![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e700_a0f8_1d7a7e58ebba_TB9661_11.jpg) , area =
, area = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e701_a0f8_ef43bd7e411f_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f6_a0f8_6da4d1f8be41_TB9661_11.jpg) corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that
corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f7_a0f8_a7e882e8dfb4_TB9661_11.jpg) n
n ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f8_a0f8_8be00e934556_TB9661_11.jpg) = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y =
= 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6f9_a0f8_3dc16b7beb9d_TB9661_11.jpg) and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.
and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.A) L(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fa_a0f8_dfe979aa7cc9_TB9661_11.jpg) , area = e square units
, area = e square unitsB) L(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fb_a0f8_25198a742b71_TB9661_11.jpg) , area =
, area = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fc_a0f8_7fcef1e9d725_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square unitsC) L(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fd_a0f8_33c39ba0f8e2_TB9661_11.jpg) , area = e - 1 square units
, area = e - 1 square unitsD) L(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6fe_a0f8_0d19a7f694e4_TB9661_11.jpg) , area =
, area = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e6ff_a0f8_01f1f15aebbe_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square unitsE) L(f,P) =
![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e700_a0f8_1d7a7e58ebba_TB9661_11.jpg) , area =
, area = ![<strong>Calculate the lower Riemann sum for f(x) = corresponding to a partition P of the interval [0, 1] into n equal subintervals of length 1/n. Given that n = 1 (which can be verified by using l'Hopital's Rule), find the area under y = and above the x-axis between x = 0 and x = 1.</strong> A) L(f,P) = , area = e square units B) L(f,P) = , area = square units C) L(f,P) = , area = e - 1 square units D) L(f,P) = , area = square units E) L(f,P) = , area = square units](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e701_a0f8_ef43bd7e411f_TB9661_11.jpg) square units
square units
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Express ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e702_a0f8_818e4e7d2503_TB9661_11.jpg) dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.
dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.
A)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e703_a0f8_65586ad1175f_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e704_a0f8_cd63914af56c_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e705_a0f8_979921677cdc_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e706_a0f8_8b568dfddd49_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e707_a0f8_51555d49ffdf_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3528_a0f8_f7694c3858d8_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3529_a0f8_3f9cdbcb9bb6_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352a_a0f8_83616874c15b_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352b_a0f8_4506dc748086_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352c_a0f8_0d15b6fcc3ad_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352d_a0f8_97ff73a23b6b_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352e_a0f8_8ff6187e5db1_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352f_a0f8_4574c5c0cc70_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3530_a0f8_cb111c9987f9_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3531_a0f8_3179fa6ef898_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3532_a0f8_23d513e87807_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3533_a0f8_c981e3567ccb_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3534_a0f8_5d09f22916ab_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3535_a0f8_639ac6336114_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3536_a0f8_f5e956f8a071_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e702_a0f8_818e4e7d2503_TB9661_11.jpg) dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.
dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.A)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e703_a0f8_65586ad1175f_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e704_a0f8_cd63914af56c_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e705_a0f8_979921677cdc_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e706_a0f8_8b568dfddd49_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7811_e707_a0f8_51555d49ffdf_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3528_a0f8_f7694c3858d8_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3529_a0f8_3f9cdbcb9bb6_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352a_a0f8_83616874c15b_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352b_a0f8_4506dc748086_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352c_a0f8_0d15b6fcc3ad_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352d_a0f8_97ff73a23b6b_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352e_a0f8_8ff6187e5db1_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_352f_a0f8_4574c5c0cc70_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3530_a0f8_cb111c9987f9_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3531_a0f8_3179fa6ef898_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3532_a0f8_23d513e87807_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3533_a0f8_c981e3567ccb_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3534_a0f8_5d09f22916ab_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3535_a0f8_639ac6336114_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of [0, 1] into equal subintervals and using the values of f at the midpoints of the subintervals.</strong> A) dx = B) dx = C) dx = D) dx = E) dx =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_3536_a0f8_f5e956f8a071_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Express ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c47_a0f8_09f9b6861663_TB9661_11.jpg) dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.
dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.
A)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c48_a0f8_fdfbed62a7de_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c49_a0f8_1bde82fb4637_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c4a_a0f8_8dce853af70e_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
B)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835b_a0f8_f9173a26d0c3_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835c_a0f8_a9b9fa114758_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835d_a0f8_272c6a314f49_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
C)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835e_a0f8_a5745c1e9ba4_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835f_a0f8_79d8783331d8_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8360_a0f8_4f30e134221b_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
D)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8361_a0f8_ff248ba5429f_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8362_a0f8_ffa16f0e2c1f_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8363_a0f8_695c56e29cb5_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
E)![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8364_a0f8_8583b07c1267_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8365_a0f8_091a1fa3f10a_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8366_a0f8_41ab7ba05fe8_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c47_a0f8_09f9b6861663_TB9661_11.jpg) dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.
dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.A)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c48_a0f8_fdfbed62a7de_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c49_a0f8_1bde82fb4637_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_5c4a_a0f8_8dce853af70e_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.B)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835b_a0f8_f9173a26d0c3_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835c_a0f8_a9b9fa114758_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835d_a0f8_272c6a314f49_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.C)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835e_a0f8_a5745c1e9ba4_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_835f_a0f8_79d8783331d8_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8360_a0f8_4f30e134221b_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.D)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8361_a0f8_ff248ba5429f_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8362_a0f8_ffa16f0e2c1f_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8363_a0f8_695c56e29cb5_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.E)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8364_a0f8_8583b07c1267_TB9661_11.jpg) dx =
dx = ![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8365_a0f8_091a1fa3f10a_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Express dx as a limit of lower Riemann sums corresponding to partitions of[0, 2] into equal subintervals.</strong> A) dx = . B) dx = . C) dx = . D) dx = . E) dx = .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7812_8366_a0f8_41ab7ba05fe8_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Write the following limit as a definite integral: . 
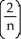
A)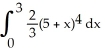
B)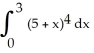
C)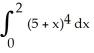
D)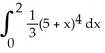
E)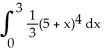
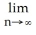
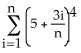
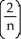
A)
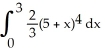
B)
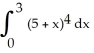
C)
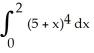
D)
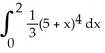
E)
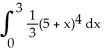

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Write the following limit as a definite integral: 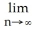
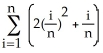
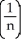
A)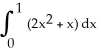
B)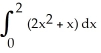
C)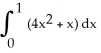
D)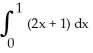
E)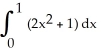
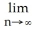
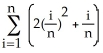
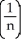
A)
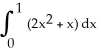
B)
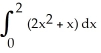
C)
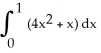
D)
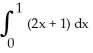
E)
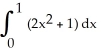

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Use the limit definition of definite integral to evaluate 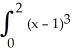 dx.
dx.
A) 0
B) -
C)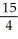
D) 1
E) -1
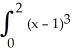 dx.
dx.A) 0
B) -

C)
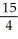
D) 1
E) -1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Use the limit definition of the definite integral to evaluate 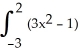 dx.
dx.
A) 10
B) 18
C) 6
D) 30
E) 9
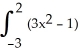 dx.
dx.A) 10
B) 18
C) 6
D) 30
E) 9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Write the following limit as a definite integral: 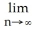
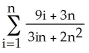
A)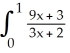 dx
dx
B)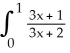 dx
dx
C)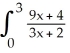 dx
dx
D)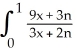 dx
dx
E)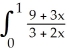 dx
dx
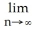
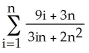
A)
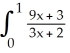 dx
dxB)
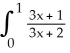 dx
dxC)
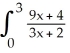 dx
dxD)
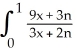 dx
dxE)
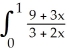 dx
dx
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Given that 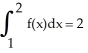 and
and 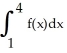 = -1, find
= -1, find 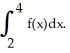
A) -3
B) -1
C) 3
D) 1
E) -2
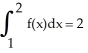 and
and 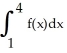 = -1, find
= -1, find 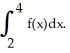
A) -3
B) -1
C) 3
D) 1
E) -2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Suppose that 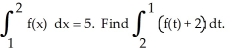
A) -5
B) -3
C) -7
D) -1
E) 7
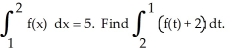
A) -5
B) -3
C) -7
D) -1
E) 7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Evaluate  dx.
dx.
A) 42
B) 0
C) 21
D) 51
E) 16
 dx.
dx.A) 42
B) 0
C) 21
D) 51
E) 16

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then ![If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then = . dx.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_46d7_a0f8_7bef248ebb78_TB9661_11.jpg) =
= ![If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then = . dx.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_46d8_a0f8_7316423072f8_TB9661_11.jpg) .
. ![If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then = . dx.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_46d9_a0f8_3f1a89228eb2_TB9661_11.jpg) dx.
dx.
![If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then = . dx.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_46d7_a0f8_7bef248ebb78_TB9661_11.jpg) =
= ![If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then = . dx.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_46d8_a0f8_7316423072f8_TB9661_11.jpg) .
. ![If f and g are integrable functions on the interval [a, b], then = . dx.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_46d9_a0f8_3f1a89228eb2_TB9661_11.jpg) dx.
dx.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If f(x) is an even function and g(x) is an odd function ,both of which are integrable over the interval [-a, a], then ![If f(x) is an even function and g(x) is an odd function ,both of which are integrable over the interval [-a, a], then](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_6dec_a0f8_890b30bfaf34_TB9661_11.jpg)
![If f(x) is an even function and g(x) is an odd function ,both of which are integrable over the interval [-a, a], then](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_6dec_a0f8_890b30bfaf34_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Evaluate 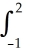 (2 -
(2 -  ) dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.
) dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.
A)
B) 4
C) 2
D)
E) -
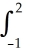 (2 -
(2 -  ) dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.
) dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.A)

B) 4
C) 2
D)

E) -


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Evaluate 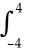
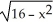 dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.
dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.
A) 8
B) 4
C) 16
D) 8
E) 16
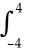
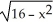 dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.
dx by interpreting the integral as representing an area.A) 8
B) 4
C) 16
D) 8
E) 16

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Given that 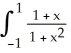 dx =
dx = 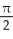 , evaluate
, evaluate 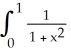 dx.
dx.
A) /4
B) /2
C)
D) 1/2
E)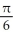
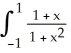 dx =
dx = 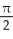 , evaluate
, evaluate 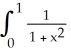 dx.
dx.A) /4
B) /2
C)
D) 1/2
E)
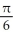

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Given the piecewise continuous function f(x) = 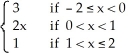 evaluate
evaluate 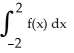 by using the properties of definite integrals and interpreting integrals as areas.
by using the properties of definite integrals and interpreting integrals as areas.
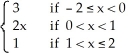 evaluate
evaluate 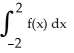 by using the properties of definite integrals and interpreting integrals as areas.
by using the properties of definite integrals and interpreting integrals as areas.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
If f(x) is an even function integrable on the closed interval [0 , 2a] , a > 0 , then ![If f(x) is an even function integrable on the closed interval [0 , 2a] , a > 0 , then =2 .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_bb1a_a0f8_dfc64fac00be_TB9661_11.jpg) =2
=2 ![If f(x) is an even function integrable on the closed interval [0 , 2a] , a > 0 , then =2 .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_bb1b_a0f8_ade562813f1e_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
![If f(x) is an even function integrable on the closed interval [0 , 2a] , a > 0 , then =2 .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_bb1a_a0f8_dfc64fac00be_TB9661_11.jpg) =2
=2 ![If f(x) is an even function integrable on the closed interval [0 , 2a] , a > 0 , then =2 .](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_bb1b_a0f8_ade562813f1e_TB9661_11.jpg) .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + on [- , ].
A)
B)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + \pi on [- \pi , \pi ].</strong> A) \pi B) C) 2 \pi D) E) 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_e22c_a0f8_bf4af6a19026_TB9661_11.jpg)
C) 2
D)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + \pi on [- \pi , \pi ].</strong> A) \pi B) C) 2 \pi D) E) 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_e22d_a0f8_dd4a1d8ed468_TB9661_11.jpg)
E) 2![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + \pi on [- \pi , \pi ].</strong> A) \pi B) C) 2 \pi D) E) 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_e22e_a0f8_7975f2707772_TB9661_11.jpg)
A)
B)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + \pi on [- \pi , \pi ].</strong> A) \pi B) C) 2 \pi D) E) 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_e22c_a0f8_bf4af6a19026_TB9661_11.jpg)
C) 2
D)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + \pi on [- \pi , \pi ].</strong> A) \pi B) C) 2 \pi D) E) 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_e22d_a0f8_dd4a1d8ed468_TB9661_11.jpg)
E) 2
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin (x/2) + \pi on [- \pi , \pi ].</strong> A) \pi B) C) 2 \pi D) E) 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7813_e22e_a0f8_7975f2707772_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The velocity of a particle moving along a straight line at time t is given by v(t) = t2 - 6t + 8 m/s.Find the distance travelled by the particle from t = 0 to t = 3.
A)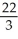 m
m
B) 21 m
C) 6 m
D) 4 m
E) 33 m
A)
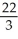 m
mB) 21 m
C) 6 m
D) 4 m
E) 33 m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What values of a and b, satisfying a < b, maximize the value of 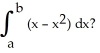
A) a = 0, b = 1
B) a = -1, b = 1
C) a = 0, b = 2
D) a = - , b =
E) a = -1, b = 0
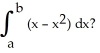
A) a = 0, b = 1
B) a = -1, b = 1
C) a = 0, b = 2
D) a = - , b =
E) a = -1, b = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What values of a and b, satisfying a < b, maximize the value of 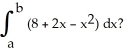
A) a = -2, b = 4
B) a = 0, b = 4
C) a = - , b =
D) a = -2, b = 0
E) a = 1, b = 3
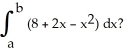
A) a = -2, b = 4
B) a = 0, b = 4
C) a = - , b =
D) a = -2, b = 0
E) a = 1, b = 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Evaluate the definite integral 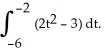
A) -
B)
C)
D) -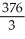
E) -12
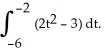
A) -
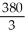
B)
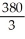
C)
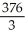
D) -
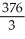
E) -12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Compute the definite integral 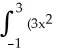 - 2x + 1)dx.
- 2x + 1)dx.
A) 14
B) 22
C) 21
D) 24
E) 20
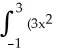 - 2x + 1)dx.
- 2x + 1)dx.A) 14
B) 22
C) 21
D) 24
E) 20

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Compute the integral 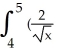 - x)dx.
- x)dx.
A) 4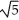 -
- 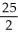
B) 4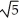 +
+ 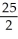
C) 4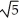 -
- 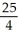
D) 4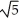 +
+ 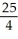
E) 2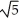 -
- 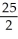
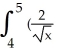 - x)dx.
- x)dx.A) 4
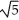 -
- 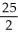
B) 4
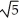 +
+ 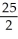
C) 4
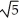 -
- 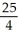
D) 4
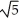 +
+ 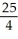
E) 2
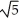 -
- 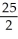

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Compute the integral 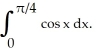
A)
B)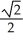
C) -
D) -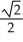
E)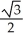
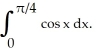
A)

B)
C) -

D) -
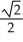
E)
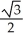

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Evaluate the integral 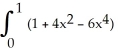 dx.
dx.
A)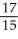
B) 1
C)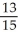
D)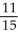
E)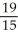
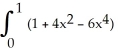 dx.
dx.A)
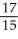
B) 1
C)
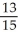
D)
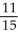
E)
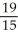

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Find 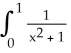 dx.
dx.
A)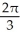
B)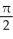
C)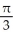
D)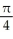
E)
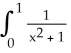 dx.
dx.A)
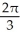
B)
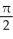
C)
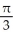
D)
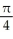
E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Evaluate the integral 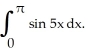
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) -
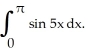
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) -


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Find the average value of the function f(x) = ![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccba_a0f8_157b05721be5_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3
+ 3 ![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbb_a0f8_51b559352ea1_TB9661_11.jpg) - 2
- 2 ![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbc_a0f8_8976d290e643_TB9661_11.jpg) - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].
- 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].
A)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbd_a0f8_793c3cf0c343_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbe_a0f8_2baadf88eeef_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbf_a0f8_8f17c9814236_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccc0_a0f8_cd85493bf67c_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d1_a0f8_a18ab4d84552_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccba_a0f8_157b05721be5_TB9661_11.jpg) + 3
+ 3 ![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbb_a0f8_51b559352ea1_TB9661_11.jpg) - 2
- 2 ![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbc_a0f8_8976d290e643_TB9661_11.jpg) - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].
- 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].A)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbd_a0f8_793c3cf0c343_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbe_a0f8_2baadf88eeef_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccbf_a0f8_8f17c9814236_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_ccc0_a0f8_cd85493bf67c_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = + 3 - 2 - 3x + 1 on the interval [0, 2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d1_a0f8_a18ab4d84552_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 /2].
A)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d2_a0f8_1fb6a0232526_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d3_a0f8_47fc7629aaf9_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d4_a0f8_a16c2f325970_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d5_a0f8_d503bb500458_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d6_a0f8_77a47e0d9eb6_TB9661_11.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d2_a0f8_1fb6a0232526_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d3_a0f8_47fc7629aaf9_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d4_a0f8_a16c2f325970_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d5_a0f8_d503bb500458_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = sin x on [0, 3 \pi /2].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7814_f3d6_a0f8_77a47e0d9eb6_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Evaluate the definite integral 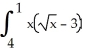 dx.
dx.
A) 11.1
B) 9.9
C) 10.1
D) 15
E) -10.1
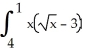 dx.
dx.A) 11.1
B) 9.9
C) 10.1
D) 15
E) -10.1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Evaluate the integral 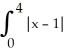 dx.
dx.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 7
D) 5
E) 3
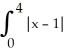 dx.
dx.A) 4
B) 6
C) 7
D) 5
E) 3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
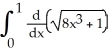 dx = 4
dx = 4
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Find the average value of the function f(x) = ![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aea_a0f8_2f5d68493925_TB9661_11.jpg) 3x, over the interval [- /12, /12].
3x, over the interval [- /12, /12].
A)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aeb_a0f8_ef64a91079bf_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aec_a0f8_d189ee916014_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aed_a0f8_93f5e6e6bd6c_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aee_a0f8_0bdb15ee3503_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aef_a0f8_fbc56efdd5b8_TB9661_11.jpg)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aea_a0f8_2f5d68493925_TB9661_11.jpg) 3x, over the interval [- /12, /12].
3x, over the interval [- /12, /12].A)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aeb_a0f8_ef64a91079bf_TB9661_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aec_a0f8_d189ee916014_TB9661_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aed_a0f8_93f5e6e6bd6c_TB9661_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aee_a0f8_0bdb15ee3503_TB9661_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>Find the average value of the function f(x) = 3x, over the interval [- \pi /12, \pi /12].</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9661/11ee77e1_7815_1aef_a0f8_fbc56efdd5b8_TB9661_11.jpg)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Let f(t) = 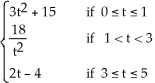 Evaluate
Evaluate 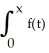 dt.
dt.
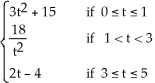 Evaluate
Evaluate 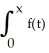 dt.
dt.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Evaluate the definite integral 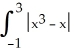 dx.
dx.
A) -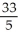
B)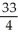
C)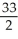
D) -33
E)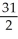
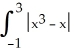 dx.
dx.A) -
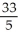
B)
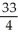
C)
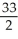
D) -33
E)
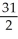

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Find the derivative of F(x) = 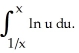
A) 2 ln x
B) 0
C)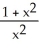 ln(u)
ln(u)
D)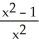 ln x
ln x
E)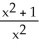 ln x
ln x
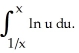
A) 2 ln x
B) 0
C)
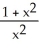 ln(u)
ln(u)D)
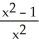 ln x
ln xE)
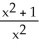 ln x
ln x
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Find the derivative of F(x) = 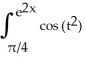 dt.
dt.
A) 2 cos (
cos (  )
)
B) 2 sin (
sin (  )
)
C) 2 cos (
cos (  )
)
D) cos (
cos (  )
)
E)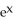 cos (
cos ( 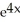 )
)
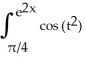 dt.
dt.A) 2
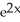 cos (
cos ( 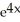 )
)B) 2
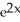 sin (
sin ( 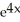 )
)C) 2
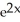 cos (
cos ( 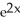 )
)D)
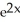 cos (
cos ( 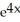 )
)E)
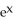 cos (
cos ( 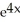 )
)
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Given that the relation 3 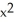 +
+ 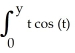 dt = 3 defines y implicitly as a differentiable function of x, find
dt = 3 defines y implicitly as a differentiable function of x, find 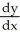 .
.
A)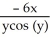
B)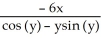
C) 6x + cos (t) - t sin (t)
D) 6x +cos(y) - ysin (y)
E) 6x + ycos (y)
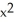 +
+ 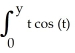 dt = 3 defines y implicitly as a differentiable function of x, find
dt = 3 defines y implicitly as a differentiable function of x, find 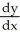 .
.A)
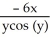
B)
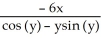
C) 6x + cos (t) - t sin (t)
D) 6x +cos(y) - ysin (y)
E) 6x + ycos (y)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Evaluate 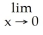
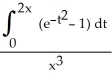
A) -
B) -
C)
D) 1
E)
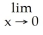
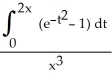
A) -

B) -

C)

D) 1
E)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Find the point on the graph of the function f(x) = 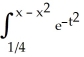 dt where the graph has a horizontal tangent line.
dt where the graph has a horizontal tangent line.
A)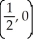
B)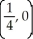
C)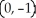
D) (1, 0)
E)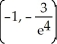
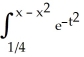 dt where the graph has a horizontal tangent line.
dt where the graph has a horizontal tangent line.A)
B)
C)
D) (1, 0)
E)
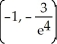

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
: 
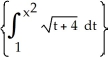 is equal to
is equal to
A) 2x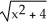
B)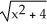 -
- 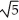
C) 2x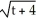
D) 2x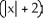
E) 2x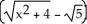
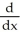
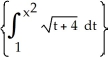 is equal to
is equal toA) 2x
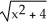
B)
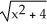 -
- 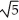
C) 2x
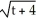
D) 2x
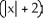
E) 2x
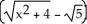

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Evaluate the integral 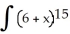 dx.
dx.
A)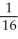
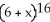 + C
+ C
B)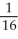
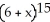 + C
+ C
C)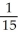
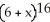 + C
+ C
D) -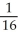
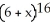 + C
+ C
E) -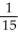
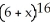 + C
+ C
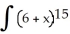 dx.
dx.A)
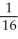
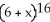 + C
+ CB)
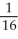
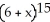 + C
+ CC)
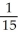
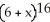 + C
+ CD) -
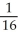
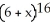 + C
+ CE) -
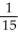
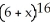 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Find the inflection point of the function f(x) = 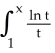 dt, where x > 0.
dt, where x > 0.
A) (1, 0)
B) (e, )
)
C) (e, 1)
D) (e, )
)
E)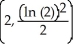
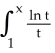 dt, where x > 0.
dt, where x > 0.A) (1, 0)
B) (e,
 )
)C) (e, 1)
D) (e,
 )
)E)
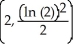

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Evaluate the integral 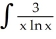 dx.
dx.
A) ln(3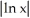 ) + C
) + C
B) ln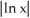 + C
+ C
C) 3ln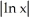 + C
+ C
D)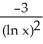 + C
+ C
E)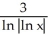 + C
+ C
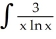 dx.
dx.A) ln(3
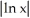 ) + C
) + CB) ln
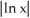 + C
+ CC) 3ln
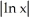 + C
+ CD)
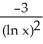 + C
+ CE)
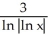 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Evaluate the integral 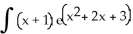 dx.
dx.
A)
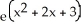 + C
+ C
B)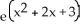 + C
+ C
C) -
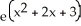 + C
+ C
D) -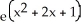 + C
+ C
E)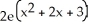 + C
+ C
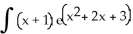 dx.
dx.A)

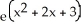 + C
+ CB)
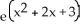 + C
+ CC) -

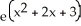 + C
+ CD) -
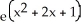 + C
+ CE)
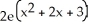 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Evaluate the integral 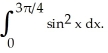
A)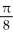 -
- 
B)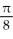 +
+ 
C)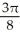 -
- 
D)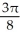 +
+ 
E)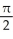
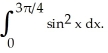
A)
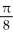 -
- 
B)
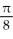 +
+ 
C)
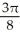 -
- 
D)
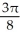 +
+ 
E)
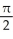

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Evaluate the integral dx. 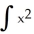
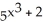
A)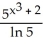 + C
+ C
B)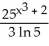 + C
+ C
C)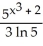 + C
+ C
D)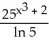 + C
+ C
E)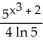 + C
+ C
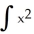
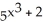
A)
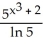 + C
+ CB)
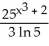 + C
+ CC)
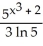 + C
+ CD)
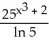 + C
+ CE)
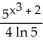 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Evaluate the integral 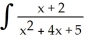 dx.
dx.
A) ln(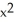 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + C
B) 2 ln(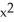 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + C
C) ln(
ln( 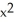 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + C
D) -2 ln(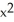 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + C
E) - ln(
ln( 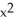 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + C
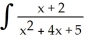 dx.
dx.A) ln(
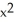 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + CB) 2 ln(
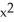 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + CC)
 ln(
ln( 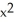 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + CD) -2 ln(
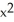 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + CE) -
 ln(
ln( 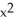 + 4x + 5) + C
+ 4x + 5) + C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Evaluate the integral 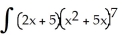 dx.
dx.
A)
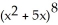 + C
+ C
B)
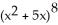 + C
+ C
C)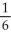
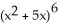 + C
+ C
D)
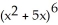 + C
+ C
E)
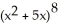 + C
+ C
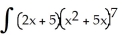 dx.
dx.A)

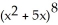 + C
+ CB)

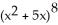 + C
+ CC)
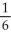
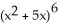 + C
+ CD)

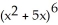 + C
+ CE)

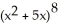 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Evaluate 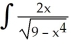 dx.
dx.
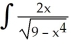 dx.
dx.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Evaluate the integral 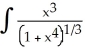 dx.
dx.
A)
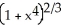 + C
+ C
B) -3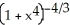 + C
+ C
C)
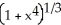 + C
+ C
D) -
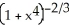 + C
+ C
E) -
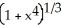 + C
+ C
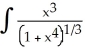 dx.
dx.A)

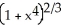 + C
+ CB) -3
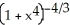 + C
+ CC)

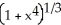 + C
+ CD) -

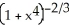 + C
+ CE) -

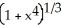 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Evaluate the integral 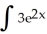 cos (
cos ( 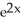 ) dx.
) dx.
A)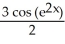 + C
+ C
B)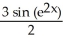 + C
+ C
C) -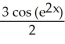 + C
+ C
D) -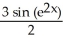 + C
+ C
E)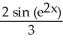 + C
+ C
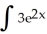 cos (
cos ( 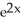 ) dx.
) dx.A)
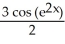 + C
+ CB)
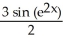 + C
+ CC) -
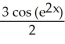 + C
+ CD) -
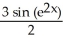 + C
+ CE)
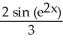 + C
+ C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 117 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








